Abstract
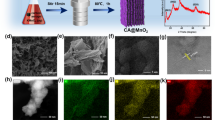
Lithium sulfur (Li–S) batteries show great prospect as a next generation high energy density rechargeable battery systems. However, the practical utilization of Li–S batteries is still obstructed by the shuttle effects which inducing the fast capacity fading and the loss of active sulfur. Herein, a special graphene @ nitrogen and phosphorous dual-doped porous carbon (N–P–PC/G) is presented to modify a commercial separator for an advanced Li–S battery. The N–P–PC/G nanosheet employs graphene layer as an excellent conductive framework covered with uniform layers of N, P dual-doped porous carbon on both sides which possessing massive interconnected meso-/micropores. It is demonstrated that the N–P–PC/G-modified separator can suppress the shuttle effects by coupling interactions including physical absorption, chemical adsorption and interfacial interaction. With the aid of the N–P–PC/G-modified separator, the pure sulfur cathode with high-sulfur loading of 3 mg cm−2 offers a high initial discharge capacity of 1207 mA h g−1 at 0.5 C (1 C = 1675 mA h g−1), and a maintained capacity of 635 mA h g−1 (fading rate of only 0.095% per cycle), after 500 cycles. This work suggests that combining hybrid nanocarbon with multi-heteroatom doping to modify the commercial separator is an effective approach to obtain high electrochemical performance Li–S batteries.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li Z, Huang Y, Yuan L, Hao Z, Huang Y (2015) Status and prospects in sulfur–carbon composites as cathode materials for rechargeable lithium–sulfur batteries. Carbon 92:41–63
Pope MA, Aksay IA (2015) Structural design of cathodes for Li–S batteries. Adv Energy Mater 5(16):1500124
Yang Y, Zheng G, Cui Y (2013) Nanostructured sulfur cathodes. Chem Soc Rev 42(7):3018–3032
Fang R, Zhao S, Hou P et al (2016) 3D interconnected electrode materials with ultrahigh areal sulfur loading for Li–S batteries. Adv Mater 28(17):3374–3382
Hwang J-Y, Kim HM, Lee S-K et al (2016) High-energy, high-rate, lithium–sulfur batteries: synergetic effect of hollow TiO2-webbed carbon nanotubes and a dual functional carbon-paper interlayer. Adv Energy Mater 6(1):1501480
Wang Q, Wen Z, Yang J et al (2016) Electronic and ionic co-conductive coating on the separator towards high-performance lithium–sulfur batteries. J Power Sour 306:347–353
Barchasz C, Leprêtre J-C, Alloin F, Patoux S (2012) New insights into the limiting parameters of the Li/S rechargeable cell. J Power Sour 199:322–330
Manthiram A, Fu Y, Chung SH, Zu C, Su YS (2014) Rechargeable lithium–sulfur batteries. Chem Rev 114(23):11751–11787
Sahore R, Levin BDA, Pan M, Muller DA, DiSalvo FJ, Giannelis EP (2016) Design principles for optimum performance of porous carbons in lithium–sulfur batteries. Adv Energy Mater 6(14):1600134
Ji X, Lee KT, Nazar LF (2009) A highly ordered nanostructured carbon–sulphur cathode for lithium–sulphur batteries. Nat Mater 8(6):500–506
Sohn H, Gordin ML, Regula M et al (2016) Porous spherical polyacrylonitrile-carbon nanocomposite with high loading of sulfur for lithium–sulfur batteries. J Power Sour 302:70–78
Yan J, Li B, Liu X (2015) Nano-porous sulfur–polyaniline electrodes for lithium–sulfur batteries. Nano Energy 18:245–252
Li Z, Zhang J, Lou XW (2015) Hollow carbon nanofibers filled with MnO2 nanosheets as efficient sulfur hosts for lithium–sulfur batteries. Angew Chem Int Ed 54(44):12886–12890
Liang X, Nazar LF (2016) In situ reactive assembly of scalable core–shell sulfur–MnO2 composite cathodes. ACS Nano 10(4):4192–4198
Wu F, Lee JT, Nitta N, Kim H, Borodin O, Yushin G (2015) Lithium iodide as a promising electrolyte additive for lithium–sulfur batteries: mechanisms of performance enhancement. Adv Mater 27(1):101–108
Azimi N, Weng W, Takoudis C, Zhang Z (2013) Improved performance of lithium–sulfur battery with fluorinated electrolyte. Electrochem Commun 37:96–99
Yao H, Yan K, Li W et al (2014) Improved lithium–sulfur batteries with a conductive coating on the separator to prevent the accumulation of inactive S-related species at the cathode–separator interface. Energy Environ Sci 7(10):3381–3390
Pang Q, Liang X, Kwok CY, Nazar LF (2016) Advances in lithium–sulfur batteries based on multifunctional cathodes and electrolytes. Nat Energy. doi:10.1038/nenergy.2016.132
Su YS, Manthiram A (2012) Lithium–sulphur batteries with a microporous carbon paper as a bifunctional interlayer. Nat Commun. doi:10.1038/ncomms2163
Deng N, Kang W, Liu Y, Ju J, Wu D, Li L et al (2016) A review on separators for lithium sulfur battery: progress and prospects. J Power Sour 331:132–155
Xiang Y, Li J, Lei J, Liu D, Xie Z, Qu D et al (2016) Advanced separators for lithium–ion and lithium–sulfur batteries: a review of recent progress. ChemSusChem 9:3023–3039
Chung S-H, Manthiram A (2014) Bifunctional separator with a light-weight carbon-coating for dynamically and statically stable lithium–sulfur batteries. Adv Funct Mater 24(33):5299–5306
Chung SH, Manthiram A (2014) A polyethylene glycol-supported microporous carbon coating as a polysulfide trap for utilizing pure sulfur cathodes in lithium–sulfur batteries. Adv Mater 26(43):7352–7357
Balach J, Jaumann T, Klose M, Oswald S, Eckert J, Giebeler L (2015) A polyethylene glycol-supported microporous carbon coating as a polysulfide trap for utilizing pure sulfur cathodes in lithium–sulfur batteries. Adv Mater 26(43):7352–7357
Ma G, Wen Z, Wang Q et al (2015) Enhanced performance of lithium sulfur battery with self-assembly polypyrrole nanotube film as the functional interlayer. J Power Sour 273:511–516
Zhou X, Liao Q, Tang J, Bai T, Chen F, Yang J (2016) A high-level N-doped porous carbon nanowire modified separator for long-life lithium–sulfur batteries. J Electroanal Chem 768:55–61
Zu C, Manthiram A (2014) High-Performance Li/dissolved polysulfide batteries with an advanced cathode structure and high sulfur content. Adv Energy Mater 4(18):1400897
Su YS, Manthiram A (2012) A new approach to improve cycle performance of rechargeable lithium–sulfur batteries by inserting a free-standing MWCNT interlayer. Chem Commun 48(70):8817–8819
Zhou G, Li L, Wang DW et al (2015) A flexible sulfur-graphene-polypropylene separator integrated electrode for advanced Li–S batteries. Adv Mater 27(4):641–647
Zhao Y, Liu M, Lv W et al (2016) Dense coating of Li4Ti5O12 and graphene mixture on the separator to produce long cycle life of lithium–sulfur battery. Nano Energy 30:1–8
Yang J, Liao Q, Zhou X, Liu X, Tang J (2013) Efficient synthesis of graphene-based powder via in situ spray pyrolysis and its application in lithium ion batteries. RSC Adv 3(37):16449–16455
Niu S, Lv W, Zhang C et al (2015) A carbon sandwich electrode with graphene filling coated by N-doped porous carbon layers for lithium–sulfur batteries. J Mater Chem A 3(40):20218–20224
Bai H, Sheng K, Zhang P, Li C, Shi G (2011) Graphene oxide/conducting polymer composite hydrogels. J Mater Chem 21(46):18653–18658
Pan L, Yu G, Zhai D et al (2012) Hierarchical nanostructured conducting polymer hydrogel with high electrochemical activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci 109(24):9287–9292
Yang J, Chen F, Li C, Bai T, Long B, Zhou X (2016) A free-standing sulfur-doped microporous carbon interlayer derived from luffa sponge for high performance lithium–sulfur batteries. J Mater Chem A 4(37):14324–14333
Gu X, Tong C-J, Lai C et al (2015) A porous nitrogen and phosphorous dual doped graphene blocking layer for high performance Li–S batteries. J Mater Chem A 3(32):16670–16678
Zhou G, Paek E, Hwang GS, Manthiram A (2015) Long-life Li/polysulphide batteries with high sulphur loading enabled by lightweight three-dimensional nitrogen/sulphur-codoped graphene sponge. Nat Commun 6:7760
Zeng Q, Li F, Gentle IR, Cheng H-M, Wang D-W (2015) Dispersible percolating carbon nano-electrodes for improvement of polysulfide utilization in Li–S batteries. Carbon 93:161–168
Xiao Z, Yang Z, Wang L et al (2015) A lightweight TiO2/graphene interlayer, applied as a highly effective polysulfide absorbent for fast, long-life lithium–sulfur batteries. Adv Mater 27(18):2891–2898
Wang G, Lai Y, Zhang Z, Li J, Zhang Z (2015) Enhanced rate capability and cycle stability of lithium–sulfur batteries with a bifunctional MCNT@PEG-modified separator. J Mater Chem A 3:7139–7144
Yang J, Xie J, Zhou X et al (2014) Functionalized N-doped porous carbon nanofiber webs for a lithium–sulfur battery with high capacity and rate performance. J Phys Chem C 118(4):1800–1807
Zhou X, Xie J, Yang J et al (2013) Improving the performance of lithium–sulfur batteries by graphene coating. J Power Sour 243:993–1000
Acknowledgements
Funding for this work was provided by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51204209 and 51274240) and Grants from the Project of Innovation-driven Plan in Central South University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, X., Liao, Q., Bai, T. et al. Rational design of graphene @ nitrogen and phosphorous dual-doped porous carbon sandwich-type layer for advanced lithium–sulfur batteries. J Mater Sci 52, 7719–7732 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1029-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-1029-2