Abstract
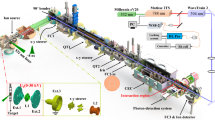
We have developed the KEK Isotope Separation System (KISS) at RIKEN to study the nuclear structure of the nuclei in the vicinity of neutron magic number \(N=\) 126 from the astrophysical perspective. These neutron-rich nuclei have been produced by using multinucleon transfer (MNT) reactions with combinations of the low-energy \(^{136}\)Xe beam and the production targets of W, Ir, and Pt. At the KISS facility, radioisotopes are ionized by applying in-gas-cell laser ionization technique. In this process, we can perform laser ionization spectroscopy of the refractory elements with the atomic number \(Z=\) 70–78 such as Hf, Ta, W, Re, Os, Ir, and Pt, which cannot be performed in other facilities. Laser spectroscopy can effectively investigate nuclear structure through the measured magnetic moments, isotope shifts (IS) \(\Delta \nu \), changes in the mean-square charge radii \(\delta <r^2>\), and quadrupole deformation parameters \(|<\beta ^2_2>|^{1/2}\). We have studied the ionization schemes of these elements through offline tests and performed in-gas-cell laser ionization spectroscopy of these refractory neutron-rich nuclei produced at KISS.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Campbell, P., Moore, I.D., Pearson, M.R.: Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 86, 127 (2016)
Yang, X.F., Wang, S.J., S.G., W., Garcia Ruiz, R.F.: Laser spectroscopy for the study of exotic nuclei. Prog. Part. Nucl. Phys. 129, 104005 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ppnp.2022.104005
Jeong, S.C., Imai, N., Ishiyama, H., Hirayama, Y., Miyatake, H., Watanabe, Y.X.: KISS: KEK isotope separation system for \({\beta }\)-decay spectroscopy : toward the full understanding of r-process nucleosynthesis (R &D program for upgrade of the TRIAC research capabilities). KEK report, 2010-2, (2010)
Aoki, T., Hirayama, Y., Ishiyama, H., Jeong, S.C., Kimura, S., Makida, Y., Miyatake, H., Mukai, M., Nishimura, S., Nishio, K., Niwase, T., Ogawa, T., Okuno, H., Rosenbusch, M., Schury, P., Watanabe, Y.X., Wada, M.: Design report of the KISS-II facility for exploring the origin of uranium. KEK report, 2022-2. arXiv:2209.12649 (2022)
Hirayama, Y., Watanabe, Y.X., Imai, N., Ishiyama, H., Jeong, S.C., Miyatake, H., Oyaizu, M., Kimura, S., Mukai, M., Kim, Y.H., Sonoda, T., Wada, M., Huyse, M., Kudryavtsev, Y., Van Duppen, P.: Laser ion source for multi-nucleon transfer reaction products. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 353, 4 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nimb.2015.04.001
Hirayama, Y., Watanabe, Y.X., Mukai, M., Oyaizu, M., Ahmed, M., Ishiyama, H., Jeong, S.C., Kakiguchi, Y., Kimura, S., Moon, J.Y., Park, J.H., Schury, P., Wada, M., Miyatake, H.: Doughnut-shaped gas cell for KEK isotope separation system. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 412, 11 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nimb.2017.08.037
Hirayama, Y., Watanabe, Y.X., Mukai, M., Schury, P., Ahmed, M., Ishiyama, H., Jeong, S.C., Kakiguchi, Y., Kimura, S., Moon, J.Y., Oyaizu, M., Park, J.H., Wada, M., Miyatake, H.: Nuclear spectroscopy of r-process nuclei using KEK isotope separation system. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 463, 425 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nimb.2019.04.035
Dasso, C.H., Pollarolo, G., Winther, A.: Systematics of isotope production with radioactive beams. Phys. Rev. Lett. 73, 1907 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.73.1907
Watanabe, Y.X., Kim, Y.H., Jeong, S.C., Hirayama, Y., et al.: Pathway for the production of neutron-rich isotopes around \({N}=\) 126 shell closure. Phys. Rev. Lett. 115, 172503 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.115.172503
Hirayama, Y., Mukai, M., Watanabe, Y.X., et al.: In-gas-cell laser spectroscopy of the magnetic dipole moment of the \({N} \approx \) 126 isotope \(^{199}\)Pt. Phys. Rev. C 96, 014307 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevC.96.014307
Hirayama, Y., Mukai, M., Watanabe, Y.X., et al.: In-gas-cell laser resonance ionization spectroscopy of \(^{200,201}\)Pt. Phys. Rev. C 106, 034326 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevC.106.034326
Mukai, M., Hirayama, Y., Watanabe, Y.X., et al.: In-gas-cell laser resonance ionization spectroscopy of \(^{196,197,198}\)Ir. Phys. Rev. C 102, 054307 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevC.102.054307
Choi, H., Hirayama, Y., Choi, S., et al.: In-gas-cell laser ionization spectroscopy of \(^{194,196}\)Os isotopes by using a multireflection time-of-flight mass spectrograph. Phys. Rev. C 102, 034309 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevC.102.034309
Hirayama, Y., et al.: Efficient two-color two-step laser ionization schemes of \({\lambda }_1 \sim \) 250 nm and \({\lambda }_2 =\) 307.9 nm for heavy refractory elements –Measurements of ionization cross-sections and hyperfine spectra of tantalum and tungsten. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 90, 115104 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5124444
Mukai, M., Hirayama, Y., Watanabe, Y.X., Schury, P., et al.: High-efficiency and low-background multi-segmented proportional gas counter for \({\beta }\)-decay spectroscopy. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 884, 1 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2017.12.013
Hirayama, Y., Schury, P., Mukai, M., et al.: Three-dimensional tracking multi-segmented proportional gas counter for \({\beta }\)-decay spectroscopy of unstable nuclei. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. A 997, 165152 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2021.165152
Moon, J.Y., Hashimoto, T., Jeong, S.C., Wada, M., Schury, P., Watanabe, Y.X., Hirayama, Y., Ito, Y., Rosenbusch, M., Niwase, T., Wollnik, H., Miyatake, H.: RIKEN Accel. Prog. Rep. 53, 128 (2019)
Moon, J.Y., Jeong, S.C., Wada, M., Schury, P., Watanabe, Y.X., Hirayama, Y., Ito, Y., Rosenbusch, M., Kimura, S., Ishizawa, S., Niwase, T., Wollnik, H., Miyatake, H.: Development of multiple reflection time of flight mass spectrograph at KISS. RIKEN Accel. Prog. Rep. 52, 138 (2018)
Schury, P., Hashimoto, T., Ito, Y., Miyatake, H., Moon, J.Y., T., N., Hirayama, Y., Rosenbusch, M., Wada, M., Watanabe, Y.X., Wollnik, H. RIKEN Accel. Prog. Rep. 53, 115 (2019)
Tajima, N., Suzuki, N.: Prolate dominance of nuclear shape caused by a strong interference between the effects of spin-orbit and \(l^2\) terms of the nilsson potential. Phys. Rev. C 64, 037301 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevC.64.037301
Takahara, S., Onishi, N., Shimizu, Y., Tajima, N.: The role of spin-orbit potential in nuclear prolate-shape dominance. Phys. Lett. B 702, 429 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physletb.2011.07.030
Sugawara, M.: Prolate-shape dominance and dual-shell mechanism. Phys. Rev. C 106, 024301 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevC.106.024301
Sarriguren, P., Rodríguez-Guzmán, R., Robledo, L.M.: Shape transitions in neutron-rich Yb, Hf, W, Os, and Pt isotopes within a Skyrme Hartree-Fock + BCS approach. Phys. Rev. C 77, 064322 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevC.77.064322
Robledo, L.M., Rodríguez-Guzmán, R., Sarriguren, P.: Role of triaxiality in the ground-state shape of neutron-rich Yb, Hf, W, Os and Pt isotopes. J. Phys. G 36, 115104 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1088/0954-3899/36/11/115104
Nomura, K., et al.: Spectroscopic calculations of the low-lying structure in exotic Os and W isotopes. Phys. Rev. C 83, 054303 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevC.83.054303
Nomura, K., Rodríguez-Guzmán, R., Robledo, L.M.: Prolate-to-oblate shape phase transitions in neutron-rich odd-mass nuclei. Phys. Rev. C 97, 064314 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevC.97.064314
Yang, X.Q., Wang, L.J., Xiang, J., Wu, X.Y., Li, Z.P.: Microscopic analysis of prolate-oblate shape phase transition and shape coexistence in the Er-Pt region. Phys. Rev. C 103, 054321 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevC.103.054321
Ulm, G., Bhattacherjee, S.K., Dabkiewicz, P., Huber, G., Kluge, H.-J., Kühl, T., Lochmann, H., Otten, E.-W., Wendt, K.: Isotope shift of \(^{182}\)Hg and an update of nuclear moments and charge radii in the isotope range \(^{181}\)Hg-\(^{206}\)Hg. Z. Phys. A 325, 247 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01294605
Rodriguez, J., Bonn, J., Huber, G., Kluge, H.-J., Otten, E.W.: Determination of spin, magnetic moment and isotopic shift of neutron rich \(^{205}\)Hg by optical pumping. Z. Phys. A 272, 369 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01440863
Delaroche, J.-P., Girod, M., Libert, J., Goutte, H., Hilaire, S., Péru, S., Pillet, N., Bertsch, G.F.: Structure of even-even nuclei using a mapped collective Hamiltonian and the D1S Gogny interaction. Phys. Rev. C 81, 014303 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevC.81.014303
Möller, P., Sierk, A.J., Bengtsson, R., Sagawa, H., Ichikawa, T.: Nuclear shape isomers. At. Data and Nucl. Data Table 98, 149 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adt.2010.09.002
Watanabe, H., Watanabe, Y.X., Hirayama, Y., et al.: Beta decay of the axially asymmetric ground state of \(^{192}\)Re. Phys. Lett. B 814, 136088 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physletb.2021.136088
Bütttgenbach, S., Dicke, R., Gölz, G., Träber, F.: High precision hyperfine structure measurements in \(^{185}\)Re and \(^{187}\)Re. Z. Phys. A 302, 281 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01414258
Stone, N.J.: Table of nuclear magnetic dipole and electric quadrupole moments. At. Data and Nucl. Data Table 90, 75 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adt.2005.04.001
Niwase, T., Watanabe, Y.X., Hirayama, Y., et al.: Discovery of new isotope \(^{241}\)U and systematic high-precision atomic mass measurements of neutron-rich Pa-Pu nuclei produced via multinucleon transfer reactions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 130, 132502 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.130.132502
Acknowledgements
This experiment was performed at the RI Beam Factory operated by RIKEN Nishina Center and CNS, University of Tokyo. The authors wish to acknowledge the staff of the accelerator for their support. This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grants No. JP23244060, No. JP24740180, No. JP26247044, No. JP15H02096, No. JP17H01132, No. JP17H06090, No. JP18H03711, No. JP20H00169, No. JP21H04479, and No. JP22H00136.
Funding
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grants No. JP23244060, No. JP24740180, No. JP26247044, No. JP15H02096, No. JP17H01132, No. JP17H06090, No. JP18H03711, No. JP20H00169, No. JP21H04479, and No. JP22H00136.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.H. wrote the main manuscript text and prepared all figures. Y.H., M.M, Y.W, P.S., T.N., H.C., T.H., S.I., S.J., H.M., J.M., M.O., M.R., A.T., M.T., A.T., and M.W : data acquisition. Y.H., M.M., and H.C. : data analysis. H.N. : interpretation of data.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Ethical approval was not required for this study.
Competing of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hirayama, Y., Mukai, M., Watanabe, Y. et al. In-gas-cell laser ionization spectroscopy at KISS. Hyperfine Interact 245, 41 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-024-01886-1
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-024-01886-1