Abstract
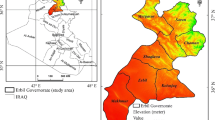
Land use/land cover (LULC) change is an important indicator used for assessing the function and health of ecosystems. Understanding the patterns of LULC change assists in managing natural resources effectively, especially for regions where there are minimal or no reported data on the status of LULC. In this study, remotely sensed Landsat satellite imagery from 5 years (i.e., 1988, 1996, 2002, 2008, and 2017), geographic information systems (GIS), and the hybrid cellular automata (CA)-Markov model were used to (i) quantify the past and present LULC changes and (ii) model the future changes in Sulaimani Province in the Kurdistan region of Iraq (KRI). To accomplish these objectives, five LULC maps with various class categories were generated using the maximum likelihood classifier (MCL). The classified maps for 1996, 2002, 2008, and 2017 were used in the hybrid model to simulate LULC maps for 2017 and 2037. The map simulated for 2017 was validated with the classified 2017 LULC map. The change analysis demonstrated that between 1988 and 2017, the built-up areas and agricultural fallow land increased by 419% and 226%, respectively. In the future predictions for 2037, built-up areas and agricultural fallow land showed increasing trends of 5.5% and 26.5%, respectively. In contrast, agricultural land, plantation land, and sparse vegetation areas were predicted to decrease by 29.4%, 65.8%, and 36.9%, respectively. In addition, in 2008, waterbodies shrank by 43.36% in comparison with their status in 1988, suggesting that 2008 was a severe drought year. These findings provide invaluable baseline information with which conservation biologists, agricultural engineers, urban planners, and decision makers can better manage natural resources and monitor environmental changes. Based on these results, sustainable development actions and an early warning system can be established.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Available on request.
References
Aburas, M. M., Ho, Y. M., Pradhan, B., Salleh, A. H., & Alazaiza, M. Y. (2021). Spatio-temporal simulation of future urban growth trends using an integrated CA-Markov model. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 14(2), 1–12.
Aburas, M. M., Ho, Y. M., & RamliAsh’aari, Z. H., M. F. (2017). Improving the capability of an integrated CA-Markov model to simulate spatio-temporal urban growth trends using an analytical hierarchy process and frequency ratio. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 59, 65–78.
Al-Quraishi, A. M. F., Qader, S. H., & Wu, W. (2020). Drought monitoring using spectral and meteorological based indices combination: a case study in Sulaimaniyah, Kurdistan region of Iraq. In Environmental Remote Sensing and GIS in Iraq(pp. 377-393). Springer.
Al-Sharif, A. A., & Pradhan, B. (2014). Monitoring and predicting land use change in Tripoli Metropolitan City using an integrated Markov chain and cellular automata models in GIS. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 7(10), 4291–4301.
Alnasrawi, A. (2001). Iraq: economic sanctions and consequences, 1990–2000. Third World Quarterly, 22(2), 205–218.
Amici, V., Marcantonio, M., La Porta, N., & Rocchini, D. (2017). A multi-temporal approach in MaxEnt modelling: A new frontier for land use/land cover change detection. Ecological informatics, 40, 40–49.
Anderson, J. R. (1976). A land use and land cover classification system for use with remote sensor data (Vol. 964): US Government Printing Office.
Awchi, T. A., & Kalyana, M. M. (2017). Meteorological drought analysis in northern Iraq using SPI and GIS. Sustainable Water Resources Management, 3(4), 451–463.
Baumann, M., Radeloff, V. C., Avedian, V., & Kuemmerle, T. (2015). Land-use change in the Caucasus during and after the Nagorno-Karabakh conflict. Regional Environmental Change, 15(8), 1703–1716.
Bolstad, P., & Lillesand, T. (1991). Rapid maximum likelihood classification. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 57(1), 67–74.
Butt, A., Shabbir, R., Ahmad, S. S., & Aziz, N. (2015). Land use change mapping and analysis using Remote Sensing and GIS: A case study of Simly watershed, Islamabad, Pakistan. The Egyptian Journal of Remote Sensing and Space Science, 18(2), 251–259.
Chamling, M., & Bera, B. (2020). Spatio-temporal patterns of land use/land cover change in the Bhutan–Bengal foothill region between 1987 and 2019: study towards geospatial applications and policy making. Earth Systems and Environment, 1–14.
Congalton, R., & Green, C. (1999). Assessing the accuracy of remotely sensed data: Principles and practices. Boca Raton, Florida: CRC/Lewis Press.
da Cunha, E. R., Santos, C. A. G., da Silva, R. M., Bacani, V. M., & Pott, A. (2021). Future scenarios based on a CA-Markov land use and land cover simulation model for a tropical humid basin in the Cerrado/Atlantic forest ecotone of Brazil. Land Use Policy, 101, 105141.
Eklund, L., Persson, A., & Pilesjö, P. (2016). Cropland changes in times of conflict, reconstruction, and economic development in Iraqi Kurdistan. Ambio, 45(1), 78–88.
Eklund, L., & Seaquist, J. (2015). Meteorological, agricultural and socioeconomic drought in the Duhok Governorate Iraqi Kurdistan. Natural Hazards, 76(1), 421–441.
Fichera, C. R., Modica, G., & Pollino, M. (2012). Land Cover classification and change-detection analysis using multi-temporal remote sensed imagery and landscape metrics. European Journal of Remote Sensing, 45(1), 1–18.
Firozjaei, M. K., Sedighi, A., Argany, M., Jelokhani-Niaraki, M., & Arsanjani, J. J. (2019). A geographical direction-based approach for capturing the local variation of urban expansion in the application of CA-Markov model. Cities, 93, 120–135.
Foley, J. A., DeFries, R., Asner, G. P., Barford, C., Bonan, G., Carpenter, S. R., et al. (2005). Global consequences of land use. Science, 309(5734), 570–574.
Gorsevski, V., Kasischke, E., Dempewolf, J., Loboda, T., & Grossmann, F. (2012). Analysis of the Impacts of armed conflict on the Eastern Afromontane forest region on the South Sudan—Uganda border using multitemporal Landsat imagery. Remote Sensing of Environment, 118, 10–20.
Guan, D., Zhao, Z., & Tan, J. (2019). Dynamic simulation of land use change based on logistic-CA-Markov and WLC-CA-Markov models: a case study in three gorges reservoir area of Chongqing, China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 1–20.
Hadeel, A., Jabbar, M. T., & Chen, X. (2010). Environmental change monitoring in the arid and semi-arid regions: a case study Al-Basrah Province Iraq. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 167(1–4), 371–385.
Hadi, S. J., Shafri, H. Z., & Mahir, M. D. (2014). Factors affecting the eco-environment identification through change detection analysis by using remote sensing and GIS: a case study of Tikrit, Iraq. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 39(1), 395–405.
Hamad, R., Balzter, H., & Kolo, K. (2017). Multi-criteria assessment of land cover dynamic changes in halgurd sakran national park (HSNP), kurdistan region of Iraq, using remote sensing and GIS. Land, 6(1), 18.
Hao, X., Zhang, H., Xu, X., Wang, L., & Cui, Y. (2020). Evolution and simulation of land use/land cover pattern in northern Shanxi Province. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 40(1), 257–265.
He, C., Liu, Z., Gou, S., Zhang, Q., Zhang, J., & Xu, L. (2019). Detecting global urban expansion over the last three decades using a fully convolutional network. Environmental Research Letters, 14(3), 034008.
Hietel, E., Waldhardt, R., & Otte, A. (2004). Analysing land-cover changes in relation to environmental variables in Hesse Germany. Landscape Ecology, 19(5), 473–489.
Hishe, S., Bewket, W., Nyssen, J., & Lyimo, J. (2020). Analysing past land use land cover change and CA-Markov-based future modelling in the Middle Suluh Valley Northern Ethiopia. Geocarto International, 35(3), 225–255.
Houghton, R. A. (1994). The worldwide extent of land-use change. BioScience, 44(5), 305–313.
Hyandye, C., & Martz, L. W. (2017). A Markovian and cellular automata land-use change predictive model of the Usangu Catchment. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 38(1), 64–81.
Jensen, J. R. (2015). Introductory digital image processing: a remote sensing perspective: Prentice Hall Press.
Joorabian, S., Silva, S., Raheli Namin, T., & Shayesteh, K. (2019). Land Use and Cover Change Assessment and Dynamic Spatial Modeling in the Ghara-su Basin, Northeastern Iran. J Indian Soc Remote Sens. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-019-01054-x
Khawaldah, H., Farhan, I., & Alzboun, N. (2020). Simulation and prediction of land use and land cover change using GIS, remote sensing and CA-Markov model. Global Journal of Environmental Science and Management, 6(2), 215–232.
Khwarahm, N. R. (2020). Mapping current and potential future distributions of the oak tree (Quercus aegilops) in the Kurdistan Region Iraq. Ecological Processes, 9(1), 1–16.
Khwarahm, N. R., Qader, S., Ararat, K., & Al-Quraishi, A. M. F. (2020). Predicting and mapping land cover/land use changes in Erbil/Iraq using CA-Markov synergy model. Earth Science Informatics, 1–14.
Kumar, P., Singh, B. K., & Rani, M. (2013). An efficient hybrid classification approach for land use/land cover analysis in a semi-desert area using ETM+ and LISS-III sensor. IEEE Sensors Journal, 13(6), 2161–2165.
Kurdistan Region Statistics Office (KRSO) (2020). Agriculture: Livestock and Domestic Animals Production, KRSO, Erbil, Iraq (2020) http://www.krso.net/default.aspx?page=article&id=899&l=1 Accessed December 2020
Liping, C., Yujun, S., & Saeed, S. (2018). Monitoring and predicting land use and land cover changes using remote sensing and GIS techniques—A case study of a hilly area, Jiangle China. PLoS One, 13(7), e0200493.
Mansour, S., Al-Belushi, M., & Al-Awadhi, T. (2020). Monitoring land use and land cover changes in the mountainous cities of Oman using GIS and CA-Markov modelling techniques. Land Use Policy, 91, 104414.
Matthew, M. W., Adler-Golden, S. M., Berk, A., Richtsmeier, S. C., Levine, R. Y., Bernstein, L. S., et al. Status of atmospheric correction using a MODTRAN4-based algorithm. In Algorithms for multispectral, hyperspectral, and ultraspectral imagery VI, 2000 (Vol. 4049, pp. 199–207): International Society for Optics and Photonics
Memarian, H., Balasundram, S. K., Talib, J. B., Sung, C. T. B., Sood, A. M., & Abbaspour, K. (2012). Validation of CA-Markov for simulation of land use and cover change in the Langat Basin, Malaysia.
Meyer, J., & Califano, M. (2006). Good intentions corrupted: The oil-for-food program and the threat to the UN New York: Public Affairs.
Mondal, M. S., Sharma, N., Garg, P., & Kappas, M. (2016). Statistical independence test and validation of CA Markov land use land cover (LULC) prediction results. The Egyptian Journal of Remote Sensing and Space Science, 19(2), 259–272.
Mubareka, S., & Ehrlich, D. (2010). Identifying and modelling environmental indicators for assessing population vulnerability to conflict using ground and satellite data. Ecological indicators, 10(2), 493–503.
Munthali, K. G., & Murayama, Y. (2015). Modeling deforestation in Dzalanyama Forest Reserve, Lilongwe, Malawi: a multi-agent simulation approach. GeoJournal, 80(5), 743–757.
Munthali, M., Mustak, S., Adeola, A., Botai, J., Singh, S., & Davis, N. (2020). Modelling land use and land cover dynamics of Dedza district of Malawi using hybrid Cellular Automata and Markov model. Remote Sensing Applications: Society and Environment, 17, 100276.
Mustafa, Y. T., Ali, R. T., & Saleh, R. M. (2012). Monitoring and evaluating land cover change in the Duhok city, Kurdistan region-Iraq, by using remote sensing and GIS. International Journal of Engineering Inventions, 1(11), 28–33.
Notaro, M., Yu, Y., & Kalashnikova, O. V. (2015). Regime shift in Arabian dust activity, triggered by persistent Fertile Crescent drought. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 120(19), 10,229–210,249.
Parker, D. C., Manson, S. M., Janssen, M. A., Hoffmann, M. J., & Deadman, P. (2003). Multi-agent systems for the simulation of land-use and land-cover change: a review. Annals of the Association of American Geographers, 93(2), 314–337.
Pontius, R. G., Jr. (2002). Statistical methods to partition effects of quantity and location during comparison of categorical maps at multiple resolutions. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 68(10), 1041–1050.
Ralha, C. G., Abreu, C. G., Coelho, C. G., Zaghetto, A., Macchiavello, B., & Machado, R. B. (2013). A multi-agent model system for land-use change simulation. Environmental Modelling & Software, 42, 30–46.
Regmi, R., Saha, S., & Subedi, D. (2017). Geospatial analysis of land use land cover change modeling in Phewa Lake watershed of Nepal by using GEOMOD model. Himalayan Physics, 65–72.
Richards, J. A., & Richards, J. (1999). Remote sensing digital image analysis (Vol. 3): Springer.
Rimal, B., Keshtkar, H., Sharma, R., Stork, N., Rijal, S., & Kunwar, R. (2019). Simulating urban expansion in a rapidly changing landscape in eastern Tarai Nepal. Environmental monitoring and assessment, 191(4), 255.
Ruben, G. B., Zhang, K., Dong, Z., & Xia, J. (2020). Analysis and projection of land-use/land-cover dynamics through scenario-based simulations using the CA-Markov model: a case study in Guanting Reservoir Basin China. Sustainability, 12(9), 3747.
Salem, M., Tsurusaki, N., & Divigalpitiya, P. (2020). Land use/land cover change detection and urban sprawl in the peri-urban area of greater Cairo since the Egyptian revolution of 2011. Journal of Land Use Science, 15(5), 592–606.
Schneider, L. C., & Pontius, R. G., Jr. (2001). Modeling land-use change in the Ipswich watershed, Massachusetts, USA. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 85(1–3), 83–94.
Schulp, C. J., Levers, C., Kuemmerle, T., Tieskens, K. F., & Verburg, P. H. (2019). Mapping and modelling past and future land use change in Europe’s cultural landscapes. Land Use Policy, 80, 332–344.
Shalaby, A., & Tateishi, R. (2007). Remote sensing and GIS for mapping and monitoring land cover and land-use changes in the Northwestern coastal zone of Egypt. Applied Geography, 27(1), 28–41.
Shelestov, A., Lavreniuk, M., Kussul, N., Novikov, A., & Skakun, S. (2017). Exploring Google Earth Engine Platform for Big Data Processing: Classification of Multi-Temporal Satellite Imagery for Crop Mapping. [Original Research]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 5(17). https://doi.org/10.3389/feart.2017.000172017.00017
Shen, S., Chen, L., Fan, C., & Gao, Y. (2019). Dynamic simulation of urban green space evolution based on Ca-Markov model-a case study of Hexi new town of Nanjing city China. Applied Ecology and Environmental Research, 17(4), 8569–8581.
Singh, S. K., Mustak, S., Srivastava, P. K., Szabó, S., & Islam, T. (2015). Predicting spatial and decadal LULC changes through cellular automata Markov chain models using earth observation datasets and geo-information. Environmental Processes, 2(1), 61–78.
Somvanshi, S. S., Bhalla, O., Kunwar, P., Singh, M., & Singh, P. (2020). Monitoring spatial LULC changes and its growth prediction based on statistical models and earth observation datasets of Gautam Budh Nagar, Uttar Pradesh, India. Environment, Development and Sustainability, 22(2), 1073–1091.
Stevens, K., Campbell, L., Urquhart, G., Kramer, D., & Qi, J. (2011). Examining complexities of forest cover change during armed conflict on Nicaragua’s Atlantic Coast. Biodiversity and Conservation, 20(12), 2597–2613.
Turner, B., Meyer, W. B., & Skole, D. L. (1994). Global land-use/land-cover change: towards an integrated study. Ambio Stockholm, 23(1), 91–95.
Verburg, P. H., Alexander, P., Evans, T., Magliocca, N. R., Malek, Z., Rounsevell, M. D., et al. (2019). Beyond land cover change: towards a new generation of land use models. Current Opinion in Environmental Sustainability, 38, 77–85.
Verburg, P. H., Kok, K., Pontius, R. G., & Veldkamp, A. (2006). Modeling land-use and land-cover change. In Land-use and land-cover change (pp. 117–135): Springer.
Viera, A. J., & Garrett, J. M. (2005). Understanding interobserver agreement: the kappa statistic. Family Medicine, 37(5), 360–363.
Wang, S., Zheng, X., & Zang, X. (2012). Accuracy assessments of land use change simulation based on Markov-cellular automata model. Procedia Environmental Sciences, 13, 1238–1245.
Xie, Y., Batty, M., & Zhao, K. (2007). Simulating emergent urban form using agent-based modeling: Desakota in the Suzhou-Wuxian region in China. Annals of the association of American Geographers, 97(3), 477–495.
Yang, X., Zheng, X.-Q., & Lv, L.-N. (2012). A spatiotemporal model of land use change based on ant colony optimization, Markov chain and cellular automata. Ecological Modelling, 233, 11–19.
Yenigun, K., & Ibrahim, W. A. (2019). Investigation of drought in the northern Iraq region. Meteorological Applications, 26(3), 490–499.
Yin, H., Pflugmacher, D., Li, A., Li, Z., & Hostert, P. (2018). Land use and land cover change in Inner Mongolia-understanding the effects of China’s re-vegetation programs. Remote Sensing of Environment, 204, 918–930.
Acknowledgements
I would like to thank Dr. Sara Othman for providing useful feedback on the manuscript. I also would like to express sincere thanks to the USGS for making the Landsat data available for public use through (https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/) portal.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khwarahm, N.R. Spatial modeling of land use and land cover change in Sulaimani, Iraq, using multitemporal satellite data. Environ Monit Assess 193, 148 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-08959-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-021-08959-6