Abstract
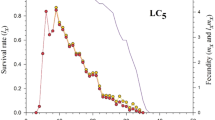
Flonicamid is a novel systemic insecticide that efficiently controls sap-sucking insect pests. However, the impact of sublethal concentrations of flonicamid on key demographic parameters and the feeding behavior of greenbug, Schizaphis graminum has not yet been studied. In this study, we used the age stage, two-sex life table approach, and electrical penetration graphs (EPGs) to investigate the sublethal effects of flonicamid on the biological traits and feeding behavior of S. graminum. Bioassays showed that flonicamid possesses high toxicity to adult S. graminum with LC50 of 5.111 mg L−1 following 48 h exposure. Sublethal concentrations of flonicamid (LC5 and LC10) significantly decreased the longevity and fecundity of directly exposed parental aphids (F0), while the reproductive days were reduced only at LC10. The pre-adult stage and total pre-reproductive period (TPRP) increased in F1 individuals after exposure of F0 aphids to the sublethal concentrations of flonicamid. Furthermore, the adult longevity, fecundity and key demographic parameters (R0, r, and λ) were significantly reduced in progeny generation (F1). EPG recordings showed that the total duration of phloem sap ingestion and concurrent salivation (E2) decreased substantially in F0 and F1 aphids after exposure to LC5 and LC10 of flonicamid. Taken together, our results showed that the sublethal concentrations of flonicamid affect the demographic parameters and feeding behavior that ultimately suppress the population growth of S. graminum. This study provides in-depth information about the overall effects of flonicamid on S. graminum that might help to manage this key pest.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aeinehchi P, Naseri B, Rafiee Dastjerdi H, Nouri-Ganbalani G, Golizadeh A (2021) Lethal and sublethal effects of thiacloprid on Schizaphis graminum (Rondani)(Hemiptera: Aphididae) and its predator Hippodamia variegata (Goeze)(Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Toxin Rev 40(4):1261–1271
Ali E, Liao X, Yang P, Mao K, Zhang X, Shakeel M, Salim AM, Wan H, Li J (2017) Sublethal effects of buprofezin on development and reproduction in the white-backed planthopper, Sogatella furcifera (Hemiptera: Delphacidae). Scientific Rep 7(1):16913
Atta B, Rizwan M, Sabir AM, Gogi MD, Farooq MA, Jamal A (2021) Lethal and sublethal effects of clothianidin, imidacloprid and sulfoxaflor on the wheat aphid, Schizaphis graminum (Hemiptera: Aphididae) and its coccinellid predator, Coccinella septempunctata. Int J Trop Insect Sci 41(1):345–358
Cameron R, Lang EB, Annan IB, Portillo HE, Alvarez JM (2013) Use of fluorescence, a novel technique to determine reduction in Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) nymph feeding when exposed to Benevia and other insecticides. J Econ Entomol 106(2):597–603
Chen X, Ma K, Li F, Liang P, Liu Y, Guo T, Song D, Desneux N, Gao X (2016) Sublethal and transgenerational effects of sulfoxaflor on the biological traits of the cotton aphid, Aphis gossypii Glover (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Ecotoxicology 25(10):1841–1848
Chi H (2022) TIMING-MSChart: a computer program for the population projection based on age-stage, two-sex life table. National Chung Hsing University, Taichung, Taiwan, http://140.120.197.173/Ecology/Download/TIMING-MSChart-exe.rar
Chi H, Güncan A, Kavousi A, Gharakhani G, Atlihan R, Özgökçe MS, Shirazi J, Amir-Maafi M, Maroufpoor M, Taghizadeh R (2022a) TWOSEX-MSChart: the key tool for life table research and education. Entomol Gen 42(6):845–849
Chi H, You M, Atlıhan R, Smith CL, Kavousi A, Özgökçe MS, Güncan A, Tuan S-J, Fu J-W, Xu Y-Y, Zheng F-Q, Ye B-H, Chu D, Yu Y, Gharekhani G, Saska P, Gotoh T, Schneider MI, Bussaman P, Gökçe A, Liu T-X (2020) Age-Stage, two-sex life table: an introduction to theory, data analysis, and application. Entomol Gen 40(2):102–123.
Chi H, Kara H, Özgökçe MS, Atlihan R, Güncan A, Rişvanlı MR (2022b) Innovative application of set theory, cartesian product, and multinomial theorem in demographic research. Entomol Gen 42:863–874
Cho S-R, Koo H-N, Yoon C, Kim G-H (2011) Sublethal effects of flonicamid and thiamethoxam on green peach aphid, Myzus persicae and feeding behavior analysis. J Korean Soc Appl Biol Chem 54(6):889–898
Civolani S, Cassanelli S, Chicca M, Rison JL, Bassi A, Alvarez JM, Billy Annan I, Parrella G, Giorgini M, Fano EA (2014) An EPG study of the probing behavior of adult Bemisia tabaci biotype Q (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) following exposure to cyantraniliprole. J Econ Entomol 107(3):910–919
Cui L, Sun L, Yang D, Yan X, Yuan H (2012) Effects of cycloxaprid, a novel cis‐nitromethylene neonicotinoid insecticide, on the feeding behaviour of Sitobion avenae. Pest Manag Sci 68(11):1484–1491
Cui L, Yuan H, Wang Q, Wang Q, Rui C (2018) Sublethal effects of the novel cis-nitromethylene neonicotinoid cycloxaprid on the cotton aphid Aphis gossypii Glover (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Scientific Rep 8(1):8915
Desneux N, Decourtye A, Delpuech J-M (2007) The sublethal effects of pesticides on beneficial arthropods. Annu Rev Entomol 52:81–106
Desneux N, Fauvergue X, Dechaume-Moncharmont F-X, Kerhoas L, Ballanger Y, Kaiser L (2005) Diaeretiella rapae limits Myzus persicae populations after applications of deltamethrin in oilseed rape. J Econ Entomol 98(1):9–17
Gong Y, Shi X, Desneux N, Gao X (2016) Effects of spirotetramat treatments on fecundity and carboxylesterase expression of Aphis gossypii Glover. Ecotoxicology 25(4):655–663
Gul H, Ullah F, Hafeez M, Tariq K, Desneux N, Gao X, Song D (2021) Sublethal concentrations of clothianidin affect fecundity and key demographic parameters of the chive maggot, Bradysia odoriphaga. Ecotoxicology 30:1150–1160
Guo R, Ren X, Ren H (2012) Effects of dimethoate on rotifer Brachionus calyciflorus using multigeneration toxicity tests. J Environ Sci Health Part B 47(9):883–890
Hafeez M, Ullah F, Khan MM, Wang Z, Gul H, Li X, Huang J, Siddiqui JA, Qasim M, Wang R-L (2022) Comparative low lethal effects of three insecticides on demographical traits and enzyme activity of the Spodoptera exigua (Hübner). Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:60198–60211
Hannig GT, Ziegler M, Marçon PG (2009) Feeding cessation effects of chlorantraniliprole, a new anthranilic diamide insecticide, in comparison with several insecticides in distinct chemical classes and mode‐of‐action groups. Pest Manag Sci 65(9):969–974
He Y, Zhang J, Chen J, Wu Q, Chen L, Chen L, Xiao P, Cheng Zhu Y (2011) Influence of pymetrozine on feeding behaviors of three rice planthoppers and a rice leafhopper using electrical penetration graphs. J Econ Entomol 104(6):1877–1884
Huang H-W, Chi H, Smith CL (2017) Linking demography and consumption of Henosepilachna vigintioctopunctata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) fed on Solanum photeinocarpum (Solanales: Solanaceae): with a new method to project the uncertainty of population growth and consumption. J Econ Entomol 111(1):1–9
Hullé M, Chaubet B, Turpeau E, Simon JC (2020) Encyclop’Aphid: A website on aphids and their natural enemies. Entomologia Generalis 40(1):97–101
Jacobson AL, Kennedy GG (2013) Effect of cyantraniliprole on feeding behavior and virus transmission of Frankliniella fusca and Frankliniella occidentalis (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) on Capsicum annuum. Crop Prot 54:251–258
Jactel H, Verheggen F, Thiéry D, Escobar-Gutiérrez AJ, Gachet E, Desneux N (2019) Alternatives to neonicotinoids. Environ Int 129:423–429
Jager T, Barsi A, Ducrot V (2013) Hormesis on life-history traits: is there such thing as a free lunch? Ecotoxicology 22(2):263–270
Jie M, Gao Y, Kuang D, Shi Y, Wang H, Jing W (2021) Relationship between imidacloprid residues and control effect on cotton aphids in arid region. Environ Geochem Health 43(5):1941–1952
Kodandaram M, Rai A, Halder J (2010) Novel insecticides for management of insect pests in vegetable crops: a review. Veg Sci 37(2):109–123
Koo HN, Lee SW, Yun SH, Kim HK, Kim GH (2015) Feeding response of the cotton aphid, Aphis gossypii, to sublethal rates of flonicamid and imidacloprid. Entomol Exp Appl 154(2):110–119
Liang P-Z, Ma K-S, Chen X-W, Tang C-Y, Xia J, Chi H, Gao X-W (2019) Toxicity and sublethal effects of flupyradifurone, a novel butenolide insecticide, on the development and fecundity of Aphis gossypii (Hemiptera: Aphididae) J Econ Entomol 112(2):852–858
Liang HY, Yang XM, Sun LJ, Zhao CD, Chi H, Zheng CY (2021) Sublethal effect of spirotetramat on the life table and population growth of Frankliniella occidentalis (Thysanoptera: Thripidae). Entomol Gen 41:219–231
Ma K-S, Tang Q-L, Liang P-Z, Li J-H, Gao X-W (2022) A sublethal concentration of afidopyropen suppresses the population growth of the cotton aphid, Aphis gossypii Glover (Hemiptera: Aphididae). J Integr Agric 21(7):2055–2064
Damalas CA, Eleftherohorinos IG (2011) Pesticide exposure, safety issues, and risk assessment indicators. Int J Environ Res Public Health 8:1402–1419
Mallqui KV, Vieira J, Guedes R, Gontijo L (2014) Azadirachtin-induced hormesis mediating shift in fecundity-longevity trade-off in the Mexican bean weevil (Chrysomelidae: Bruchinae). J Econ Entomol 107(2):860–866
Miao J, Du ZB, Wu YQ, Gong ZJ, Jiang YL, Duan Y, Li T, Lei CL (2014) Sub‐lethal effects of four neonicotinoid seed treatments on the demography and feeding behaviour of the wheat aphid Sitobion avenae. Pest Manag Sci 70(1):55–59
Milenovic M, Wosula EN, Rapisarda C, Legg JP (2019) Impact of host plant species and whitefly species on feeding behavior of Bemisia tabaci. Front Plant Sci. 10:1
Mostafiz MM, Alam MB, Chi H, Hassan E, Shim J-K, Lee K-Y (2020) Effects of sublethal doses of methyl benzoate on the life history traits and acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity of Aphis gossypii. Agronomy 10(9):1313
Nieri R, Anfora G, Mazzoni V, Stacconi R (2022) Semiochemicals, semiophysicals and their integration for the development of innovative multi-modal systems for agricultural pests’ monitoring and control. Entomol Gen 41(2):167–183
Pakyari H, Enkegaard A (2015) Sublethal and transgenerational effects of abamectin on the biological performance of the predatory thrips Scolothrips longicornis (Thysanoptera: Thripidae). J Econ Entomol 108(2):559–565
Palma-Onetto V, Oliva D, Gonzalez-Teuber M (2021) Lethal and oxidative stress side effects of organic and synthetic pesticides on the insect scale predator Rhyzobius lophanthae. Entomol Gen 41:345–355
Pan H, Liu Y, Liu B, Lu Y, Xu X, Qian X, Wu K, Desneux N (2014) Lethal and sublethal effects of cycloxaprid, a novel cis-nitromethylene neonicotinoid insecticide, on the mirid bug Apolygus lucorum. J Pest Sci 87(4):731–738
Ren M, Niu J, Hu B, Wei Q, Zheng C, Tian X, Gao C, He B, Dong K, Su J (2018) Block of Kir channels by flonicamid disrupts salivary and renal excretion of insect pests. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 99:17–26
Roditakis E, Fytrou N, Staurakaki M, Vontas J, Tsagkarakou A (2014) Activity of flonicamid on the sweet potato whitely Bemisia tabaci (Homoptera: Aleyrodidae) and its natural enemies. Pest Managt Sci 70(10):1460–1467
Sauge MH, Lacroze JP, Poëssel JL, Pascal T, Kervella J (2002) Induced resistance by Myzus persicae in the peach cultivar ‘Rubira’. Entomol Exp Appl 102(1):29–37
Shi D, Luo C, Lv H, Zhang L, Desneux N, You H, Li J, Ullah F, Ma K (2022) Impact of sublethal and low lethal concentrations of flonicamid on key biological traits and population growth associated genes in melon aphid, Aphis gossypii Glover. Crop Prot 152:105863
Stark JD, Banks JE (2003) Population-level effects of pesticides and other toxicants on arthropods. Annu Rev Entomol 48(1):505–519
Tang Q, Ma K, Chi H, Hou Y, Gao X (2019) Transgenerational hormetic effects of sublethal dose of flupyradifurone on the green peach aphid, Myzus persicae (Sulzer)(Hemiptera: Aphididae). PLoS One 14(1):e0208058
Tariq K, Noor M, Backus EA, Hussain A, Ali A, Peng W, Zhang H (2017) The toxicity of flonicamid to cotton leafhopper, Amrasca biguttula (Ishida), is by disruption of ingestion: an electropenetrography study. Pest Manag Sci 73(8):1661–1669
Thomine E, Mumford J, Rusch A, Desneux N (2022) Using crop diversity to lower pesticide use: socio-ecological approaches. Sci Total Environ 804:150156
Ullah F, Gul H, Desneux N, Gao X, Song D (2019a) Imidacloprid-induced hormesis effects on demographic traits of the melon aphid, Aphis gossypii. Entomol Gen 39(3-4):325–337
Ullah F, Gul H, Desneux N, Qu Y, Xiao X, Khattak AM, Gao X, Song D (2019b) Acetamiprid-induced hormetic effects and vitellogenin gene (Vg) expression in the melon aphid, Aphis gossypii. Entomol Gen 39(3-4):259–270
Ullah F, Gul H, Desneux N, Tariq K, Ali A, Gao X, Song D (2019c) Clothianidin-induced sublethal effects and expression changes of vitellogenin and ecdysone receptors genes in the melon aphid, Aphis gossypii. Entomol Gen 39(2):137–149
Ullah F, Gul H, Tariq K, Desneux N, Gao X, Song D (2020) Thiamethoxam induces transgenerational hormesis effects and alteration of genes expression in Aphis gossypii. Pestic Biochem Physiol 165:104557
Ullah F, Gul H, Yousaf HK, Xiu W, Qian D, Gao X, Tariq K, Han P, Desneux N, Song D (2019d) Impact of low lethal concentrations of buprofezin on biological traits and expression profile of chitin synthase 1 gene (CHS1) in melon aphid, Aphis gossypii. Scientific Rep 9(1):12291
Vakhide N, Safavi SA (2014) Lethal and sublethal effects of direct exposure to acetamiprid on reproduction and survival of the greenbug, Schizaphis graminum (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Arch Phytopathol Plant Prot 47(3):339–348
Verheggen F, Barrès B, Bonafos R, Desneux N, Escobar-Gutiérrez AJ, Gachet E, Laville J, Siegwart M, Thiéry D, Jactel H (2022) Producing sugar beets without neonicotinoids: an evaluation of alternatives for the management of viruses-transmitting aphids. Entomol Gen 42(4):491–498
Wei M, Chi H, Guo Y, Li X, Zhao L, Ma R (2020) Demography of Cacopsylla chinensis (Hemiptera: Psyllidae) reared on four cultivars of Pyrus bretschneideri (Rosales: Rosaceae) and P. communis pears with estimations of confidence intervals of specific life table statistics. J Econ Entomol 113(5):2343–2353
Weisenburger DD (1993) Human health-effects of agrichemicals use. Human Pathol 24:571–576
Yao F-L, Zheng Y, Zhao J-W et al. (2015) Lethal and sublethal effects of thiamethoxam on the whitefly predator Serangium japonicum (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) through different exposure routes. Chemosphere 128:49–55
Yuan HB, Li JH, Liu YQ, Cui L, Lu YH, Xu XY, Li Z, Wu KM, Desneux N (2017) Lethal, sublethal and transgenerational effects of the novel chiral neonicotinoid pesticide cycloxaprid on demographic and behavioral traits of Aphis gossypii (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Insect Sci 24(5):743–752
Zang L-S, Wang S, Zhang F, Desneux N (2021) Biological control with Trichogramma in China: history, present status and perspectives. Annu Rev Entomol 66(1):463–484
Zeng X, He Y, Wu J, Tang Y, Gu J, Ding W, Zhang Y (2016) Sublethal effects of cyantraniliprole and imidacloprid on feeding behavior and life table parameters of Myzus persicae (Hemiptera: Aphididae). J Econ Entomol 109(4):1595–1602
Zhang Q, Liu Y, Wyckhuys KA, Liang H, Desneux N, Lu YH (2021a) Lethal and sublethal effects of chlorantraniliprole on Helicoverpa armigera adults enhance the potential for use in ‘attract-and-kill’control strategies. Entomol Gen 41(1):111–120
Zhang X, Wang H-C, Du W-M, Zang L-S, Ruan C-C, Zhang J-J, Zou Z, Monticelli LS, Harwood JD, Desneux N (2021b) Multi-parasitism: a promising approach to simultaneously produce Trichogramma chilonis and T. dendrolimi on eggs of Antheraea pernyi. Entomol Gen 41(6):627–636
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2022YFD1400300).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XL, ND, IH, FU, and HG designed the experiment. HG performed the experiments and wrote the manuscript. SK, AY, and SKS helped in experiments. AG helped in analysis and critically reviewed the manuscript. HG, FU, KT, and AG revised the manuscript. XL and IH contributed to the reagents/materials. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical Approval
This article does not describe any studies involving human participants performed by the authors. All applicable international, national and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gul, H., ul Haq, I., Ullah, F. et al. Impact of sublethal concentrations of flonicamid on key demographic parameters and feeding behavior of Schizaphis graminum. Ecotoxicology 32, 756–767 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-023-02682-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-023-02682-3