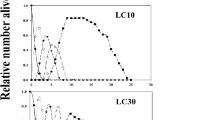
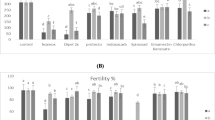
Abstract
The use of pesticides for greenbug, Schizaphis graminum in wheat not only can manage the pest population but also can influence its predator, Coccinella septempunctata. Acute and chronic effects of imidacloprid, clothianidin and sulfoxaflor on S. graminum and its predator, C. septempunctata were investigated. The results showed that LC50 of imidacloprid, clothianidin and sulfoxaflor to S. graminum at 48 h was 9.80, 34.29 and 4.40 ml a.i. L−1, respectively, while LC50 of imidacloprid, clothianidin and sulfoxaflor to C. septempunctata at 48 h was 107.80, 49.52 and 379.26 ml a.i. L−1. Sulfoxaflor and clothianidin were found the most toxic to S. graminum and C. septempunctata, respectively. Tested sublethal doses (LC10 and LC30) of all insecticides had significant effects on percent repellency of both S. graminum and C. septempunctata. Sulfoxaflor and clothianidin proved the most repellent to S. graminum (67.00 ± 2.03% at LC10 and 86.20 ± 1.62% at LC30) and C. septempunctata (50.60 ± 2.81% at LC10 and 60.00 ± 3.26% at LC30), respectively. Sublethal doses also demonstrated significant and the lowest percentage reduction in feeding by C. septempunctata on S. graminum in sulfoxaflor treatment (LC10: 4.13 ± 0.61%; LC30: 5.26 ± 0.69%). Additionally, sublethal doses reduced body-weight of C. septempunctata adults emerged from its treated grubs. These results revealed that sublethal doses of sulfoxaflor, imidacloprid and clothianidin negatively affected the biological activities of S. graminum and C. septempunctata as compared to control. Hence it can be concluded that more attention should be paid towards strategic application of these chemicals as a part of an integrated pest management program for an agro-ecosystem exhibiting maximum activity of coccinelid-predators. Overall, sulfoxaflor proved more appropriate for use against S. graminum in C. septempunctata manipulated agro-ecosystem. However, C. septempunctata compatible integration-strategy for field-application of sulfoxaflor should be devised to enhance its effectiveness against S. graminum and selectivity against C. septempunctata.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SAR:
-
Structure activity relationship
- SP3 :
-
Mixing character of one 2 s-orbital and three 2p-orbitals to create four hybrid orbitals with similar characteristics
- CF3 :
-
Trifluoromethyl
- nAChR:
-
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors
- L:D:
-
Light:Dark
- SL:
-
Soluble liquid
- SC:
-
Suspension concentrate
- C1 :
-
Highest concentration of stock solution
- C2 :
-
Serial dilution from stock solution
- sec:
-
Second(s)
- min:
-
Minute(s)
- d:
-
Day(s)
- h:
-
Hour(s)
- LC:
-
Lethal concentration
- LC10 :
-
Lethal concentration required to kill 10% of insects
- LC30 :
-
Lethal concentration required to kill 30% of insects
- LC50 :
-
Lethal concentration required to kill 50% of insects
- Nc :
-
Number of insects on the control half
- Nt :
-
Number of insects on the treated half
- Fc :
-
Number of prey consumed in control unit
- Ft :
-
Number of prey consumed in treated unit
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- Tukey’s HSD test:
-
Tukey’s Honestly Significant Difference test
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- IPM:
-
Integrated pest management
- FDR:
-
Field Recommended Dose
- ml/a:
-
milliliter per acre
- a.i.:
-
Active ingredients; CL, Confidence interval; SE, Standard error; χ2, Chi-square; df, Degree of freedom
References
Akhtar MS, Parveen S (2002) Studies on population of wheat aphids on wheat crop in new campus area, Lahore. Punjab Univ J Zool 17:14–22
Akhtar N, Ashfaque M, Gillani WA, Ata-ul-Mohsin TA, Begum I (2010) Antibiosis resistance in national uniform wheat yield trials against Rhopalosiphum padi (L.). Pak J Agric Res 23(1–2):59–63
Alavanja MCR, Hoppin JA, Kamel F (2004) Health effects of chronic pesticide exposure: Cancer and neurotoxicity. Annu Rev Public Health 25:155–197
Ali A, Memon SA, Mastoi AH, Narejo MN, Azizullah AM, Ahmed S (2017) Biology and feeding potential of ladybird beetle (Coccinella septempunctata) against different species of aphids. Sci Int (Lahore) 29(6):1261–1263
Atta B, Gogi MD, Arif MJ, Mustafa F, Raza MF, Hussain MJ, Farooq MA, Nisar MJ, Iqbal M (2015) Toxicity of some insect growth regulators (IGRs) against different life stages of dusky cotton bugs Oxycarenus hyalinipennis Costa (Hemiptera: Lygaeidae: Oxycareninae). Bulg J Agric Sci 21(2):367–371
Atta B, Rizwan M, Sabir AM, Gogi MD, Sabar M, Bakhtawar AF, Sarwar M (2020) Toxic and repellent characteristics of some plant extracts used against Tribolium castaneum (Herbst) (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) improve the grain quality of stored wheat. J Innov Sci 6(1):1–11
Ayyanath MM, Cutler GC, Scott-Dupree CD, Prithiviraj B, Kandasamy S, Prithiviraj K (2014) Gene expression during imidacloprid-induced hormesis in green peach aphid. Dose-Response 12(3):480–497
Babcock JM, Gerwick CB, Huang JX, Loso MR, Nakamura G, Nolting SP, Rogers RB, Sparks TC, Thomas J, Watson GB, Zhu Y (2011) Biological characterization of sulfoxaflor, a novel insecticide. Pest Manag Sci 67:328–334
Bacci L, Convertini S, Rossaro B (2018) A review of sulfoxaflor, a derivative of biological acting substances as a class of insecticides with a broad range of action against many insect pests. J Entomol Acarolog Res 50(3):51–71
Bao HB, Liu SH, Gu JH, Wang XZ, Liang XL, Liu ZW (2009) Sublethal effects of four insecticides on the reproduction and wing formation of brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens. Pest Manag Sci 65:170–174
Chagnon M, Kreutzweiser D, Mitchell EAD, Morrissey CA, Noome DA, Van der Sluijs JP (2015) Risks of large-scale use of systemic insecticides to ecosystem functioning and services. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(1):119–134
Charpentier G, Louat F, Bonmatin JM, Marchand PA, Vanier F, Locker D, Decoville M (2014) Lethal and sublethal effects of imidacloprid, after chronic exposure, on the insect model Drosophila melanogaster. Environ Sci Technol 48(7):4096–4102
Chen X, Ma K, Li F, Liang P, Liu Y, Guo T, Song D, Desneux N, Gao X (2016) Sublethal and transgenerational effects of sulfoxaflor on the biological traits of the cotton aphid, Aphis gossypii glover (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Ecotoxicology 25:1841–1848
Costa V, Moradas-Ferreira P (2001) Oxidative stress and signal transduction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: insights into ageing, apoptosis and diseases. Mol Asp Med 22:217–246
Cui L, Sun L, Yang D, Yan X, Yuan H (2012) Effects of cycloxaprid, a novel cis-nitromethylene neonicotinoid insecticide, on the feeding behaviour of Sitobion avenae. Pest Manag Sci 68(11):1484–1491
Cutler GC (2013) Insect, insecticide and Hormesis: evidence and considerations for study. Dose-Response 11:154–177
Danho M, Gaspar C, Haubruge E (2002) The impact of grain quantity on the biology of Sitophilus zeamais Motschulsky (Coleoptera: Curculionidae): oviposition, distribution of eggs, adult emergence, body weight, and sex ratio. J Stored Prod Res 38:259–266
Daniels M, Bale JS, Newbury HJ, Lind RJ, Pritchard J (2009) A sublethal dose of thiamethoxam causes a reduction in xylem feeding by the bird cherry-oat aphid (Rhopalosiphum padi), which is associated with dehydration and reduced performance. J Insect Physiol 55:758–765
de Castro AA, Corrêa AS, Legaspi JC, Guedes RNC, Serrã JE, Zanuncio JC (2012) Survival and behavior of the insecticide-exposed predators Podisus nigrispinus and Supputius cincticeps (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae). Chemosphere 93(6):1043–1050
de França SM, Breda MO, Barbosa DR, Araujo AM, Guedes CA (2017) The sublethal effects of insecticides in insects. Biological control of pest and vector insects. intechopen. p.23
Deng ZZ, Zhang F, Wu ZL, Yu ZY (2016) Chlorpyrifos-induced hormesis in insecticide-resistant and -susceptible Plutella xylostella under normal and high temperatures. Bull Entomol Res 106(3):378–386
Desneux N, Fauvergue X, Dechaume-Moncharmont FX, Kerhoas L, Ballanger Y, Kaiser L (2005) Diaeretiella rapae limits Myzus persicae populations after applications of deltamethrin in oilseed rape. J Econ Entomol 98:9–17
Desneux N, Decourtye A, Delpuech JM (2007) The sublethal effects of pesticides on beneficial arthropods. Annu Rev Entomol 52:81–106
Devine GJ, Harling ZK, Scarr AW, Devonshire AL (1996) Lethal and sublethal effects of imidacloprid on nicotine-tolerant Myzus nicotianae and Myzus persicae. Pestic Sci 48:57–62
Ding J, Zhao Y, Zhang Z, Xu C, Mu W (2018) Sublethal and Hormesis effects of Clothianidin on the black cutworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J Econ Entomol 111(6):2809–2816
El-Wakeil N, Gaafar N, Sallam A, Volkmar C (2013) Side effects of insecticides on natural enemies and possibility of their integration in plant protection strategies. Insecticides-Development of safer and more effective technologies. In: Insecticides: development of safer and more effective technologies (ISBN 978–953–51-0958-7). Intech Open Access Publisher 3–56 pp.
Fang Y, Wang J, Luo C, Wang R (2018) Lethal and sublethal effects of Clothianidin on the development and reproduction of Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) MED and MEAM1. J Insect Sci 18(2):37
Fernandes MES, Alves FM, Pereira RC, Aquino LA, Fernandes FL, Zanuncio JC (2016) Lethal and sublethal effects of seven insecticides on three beneficial insects in laboratory assays and field trials. Chemosphere 156:45–55
Finney DJ (1971) Probit Analysis, 3rd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Gerami S, Jahromi KT, Ashouri A, Rasoulian G, Heidari A (2005) Sublethal effects of imidacloprid and pymetrozine on the life table parameters of Aphis gossypii glover (Homoptera: Aphididae). Commun Appl Biol Sci 70:779–785
Gogi MD, Sarfraz RM, Dosdall LM, Arif MJ, Keddie AB, Ashfaq M (2006) Effectiveness of two insect growth regulators against Bemisia tabaci (Gennadius) (Homoptera: Aleyrodidae) and Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) and their impact on population densities of arthropod predators in cotton in Pakistan. Pest Manag Sci 62:982990
Gonalons C, Farina WM (2015) Effects of sublethal doses of imidacloprid on young adult honeybee behaviour. PLoS One 10(10):e0140814
Guedes RNC, Cutler GC (2014) Insecticide-induced hormesis and arthropod pest management. Pest Manag Sci 70:690–697
Guedes NMP, Tolledo J, Corrêa AS, Guedes RNC (2010) Insecticide-induced hormesis in an insecticide-resistant strain of the maize weevil, Sitophilus zeamais. J Appl Entomol 134(2):142–148
Guedes R, Smagghe G, Stark J, Desneux N (2016) Pesticide-induced stress in arthropod pests for optimized integrated pest management programs. Annu Rev Entomol 61:43–62
Guo L, Desneux N, Sonoda S, Liang P, Han P, Gao XW (2013) Sublethal and transgenerational effects of chlorantraniliprole on bilological traits of the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella L. Crop Prot 48:29–34
Guoyong L, Yan W, Yangyang L, Xiangsheng C (2018) Insecticides resistance and detoxification enzymes activity changes in brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens in Guizhou Province. Acta Ecol Sin 39(3):234–241
Hadi BAR, Garcia CPF, Heong KL (2015) Susceptibility of Nilaparvata lugens (Hemipteran: Delphacidae) populations in the Philippines to insecticides. Crop Prot 76:100–102
Han W, Zhang S, Shen F, Liu M, Ren C, Gao X (2012) Residual toxicity and sublethal effects of chlorantraniliprole on Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). Pest Manag Sci 68(8):1184–1190
He Y, Zhao J, Zheng Y, Desneux N, Wu KG (2012) Lethal effect of imidacloprid on the coccinellid predator Serangium japonicum and sublethal effects on predator voracity and on functional response to the whitefly Bemisia tabaci. Ecotoxicology 21:1291–1300
Hirata K (2016) Studies on the mode of action of neurotoxic insecticides. J Pestic Sci 41(3):87–94
Inayat TP, Rana SA, Rana N, Ruby T, Sadiqui MJI, Abbas MN (2011) Predation rate in selected coccinellid (coleoptera) predators on some major aphidid and cicadellid (hemipteran) pests. Int J Agric Biol 13:427–430
Inayatullah C (1985) Greenbug biotypes in relation to host plant resistance. USDA & Oklahoma State University, Stillwater
Jam NA, Kocheyli F, Mossadegh MS, Rasekh A, Saber M (2014) Lethal and sublethal effects of imidacloprid and pirimicarb on the melon aphid, Aphis gossypii glover (Hemiptera: Aphididae) under laboratory conditions. J Crop Prot 3(1):89–98
Jiang J, Zhang Z, Yu X, Ma D, Yu C, Liu F, Mu W (2018) Influence of lethal and sublethal exposure to clothianidin on the seven-spotted lady beetle, Coccinella septempunctata L. (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 161:208–213
Juan-juan X, Wen-xin YU, Xiao-qing YI, Jun-ping GAO, Xi-wu GAO, Xiao-peng ZENG (2019) Sublethal effects of sulfoxaflor on the fitness of two species of wheat aphids, Sitobion avenae (F.) and Rhopalosiphum padi (L.). J Integr Agric 18(7):1613–1623
Kajita H (1979) Effects of temperature and humidity on fecundity and longevity of Encarsia formosa Gahan, an introduced parasite of the greenhouse whitefly, Trialeurodes vaporariorum (Westwood). Proc Assoc Plant Prot Kyushu 25:112–114
Komblas KN, Long WH (1972) Field studies of aphid vectors of sugarcane mosaic. J Econ Entomol 65(2):439–445
Koo HN, Lee SW, Yun SH, Kim HK, Kim GH (2015) Feeding response of the cotton aphid, Aphis gossypii, to sublethal rates of flonicamid and imidacloprid. Entomol Exp Appl 154:110–119
Lashkari MR, Sahragard A, Ghadamyari M (2007) Sublethal effects of imidacloprid and pymetrozine on population growth parameters of cabbage aphid, Brevicoryne brassicae on rapeseed, Brassica napus L. Insect Sci 14(3):207–212
Laurent FM, Rathahao E (2003) Distribution of [14C]- imidacloprid in sunflowers (Helianthus annuus L.) following seed treatment. J Agric Food Chem 51:8005–8010
Lee CY (2000) Sublethal effects of insecticide on longevity, fecundity, and behaviour of insect pests: a review. Biosci J 11:107–112
Li W, Lu Z, Li L, Yu Y, Dong S, Men X, Ye B (2018) Sublethal effects of imidacloprid on the performance of the bird cherry-oat aphid Rhopalosiphum padi. PLoS One 13(9):e0204097
Liang P, Tian YA, Biondi A, Desneux N, Gao XW (2012) Short-term and transgenerational effects of the neonicotinoid nitenpyram on susceptibility to insecticides in two whitefly species. Ecotoxicology 21:1889–1898
Lu YH, Gao XW (2009) Multiple mechanisms responsible for differential susceptibilities of Sitobion avenae (Fabricius) and Rhopalosiphum padi (Linnaeus) to pirimicarb. Bull Entomol Res 99:611–617
Lucas E, Gagné I, Coderre D (2002) Impact of the arrival of Harmonía axyridis on adults of Coccinella septempunctata and Coleomegilla maculata (Coleóptera: Coccinellidae). Eur J Entomol 99:457–463
Meikle WG, Adamczyk JJ, Weiss M, Gregorc A, Johnson DR, Stewart SD, Zawislak J, Carroll MJ, Lorenz GM (2016) Sublethal effects of imidacloprid on honey bee colony growth and activity at three sites in the U.S. PLoS One 11(12):e0168603
Mensah RK, Madden JL (1993) Life history and biology of Ctenarytania thysanura Ferris (Hemiptera, Psyllidae) on Boronia megastigma Nees ex Bartl. (Rutaceae) in Tasmania. J Aust Entomol Soc 32:327–337
Morse JG (1998) Agricultural implications of pesticide-induced hormesis of insects and mites. Hum Exp Toxicol 17:266–269
Morse JG, Zareh N (1991) Pesticide-induced hormoligosis of citrus thrips (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) fecundity. J Econ Entomol 84:1169–1174
Mozaddedul HNM, Hasan HMM, Rezaul KANM (2002) Insecticide Hormoligosis on Brown Planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) in resistant and susceptible Rice varieties of Bangladesh. Pak J Biol Sci 5:915–918
Nauen R, Koob B, Elbert A (1998) Antifeedant effects of sublethal dosages of imidacloprid on Bemisia tabaci. Entomol Exp Appl 88:287–293
Ngwej LM, Hattingh I, Mlambo G, Mashat EM, Kashala JCK, Malonga FK, Bangs MJ (2019) Indoor residual spray bio-efficacy and residual activity of a clothianidin-based formulation (SumiShield® 50WG) provides long persistence on various wall surfaces for malaria control in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Malar J 18:72
Pettersson J (1971) An aphid sex attractant. Insect Syst Evol 2(2):6–93
Piiroinen S, Lindström L, Lyytinen A, Mappes J, Chen YH, Izzo V, Grapputo A (2013) Pre-invasion history and demography shape the genetic variation in the insecticide resistance-related acetylcholinesterase 2 gene in the invasive Colorado potato beetle. BMC Evol Biol 13:1–13
Piiroinen S, Boman S, Lyytinen A, Mappes J, Lindström L (2014) Sublethal effects of deltamethrin exposure of parental generations on physiological traits and overwintering in Leptinotarsa decemlineata. J Appl Entomol 138:149–158
Plumb RT (1983) Barley yellow dwarf virus: a global problem. In: Plumb RT, Thresh JM (eds) Plant virus epidemiology, The spread and control of insect-borne viruses. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford, pp 185–198
Qu YY, Xiao D, Li JY, Chen Z, Biondi A, Desneux N, Gao X, Song D (2015) Sublethal and hormesis effects of imidacloprid on the soybean aphid Aphis glycines. Ecotoxicol 24:479–487
Rizvi NH, Hussain T, Ali SS, Rajput MR, Ahmed M, Shakoori AR (1994) Comparative predatory behaviour of larvae and adults of Coccinella septempunctata L. Proc Pak Congr Zool 12:285–289
Sadeghi A, Van Damme EJM, Smagghe G (2009) Evaluation of the susceptibility of the pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum, to a selection of novel biorational insecticides using an artificial diet. J Insect Sci 9(1):65
Saleem MS, Akbar MF, Sultan A, Ali S (2018) An environment friendly pest management strategy through biorational insecticides against Amrasca Devastans Dist. On Brinjal crop. Sarhad J Agric 34(3):583–588
Saran RK, Ziegler M, Kudlie S, Harrison D, Leva DM, Scherer C, Coffelt MA (2014) Behavioral effects and tunneling responses of eastern subterranean termites (Isoptera: rhinotermitidae) exposed to chlorantraniliprole-treated soils. J Econ Entomol 107:1878–1889
Sarmad SA, Afzal M, Raza ABM, Khalil MS, Khalil H, Aqueel MA, Mansoor MM (2015) Feeding efficacy of Coccinella septempunctata and Propylea quatuordecimpunctata against Macrosiphum rosae. Sci Agric 12(2):105–108
Schwarz T, Frank T (2019) Aphid feeding by lady beetles: higher consumption at higher temperature. BioControl 64(3):323–332
Sial MU, Zhao Z, Zhang L, Zhang Y, Mao L, Jiang H (2018) Evaluation of insecticides induced hormesis on the demographic parameters of Myzus persicae and expression changes of metabolic resistance detoxification genes. Sci Rep 8:16601
Simon-Delso N, Amaral-Rogers V, Belzunces LP, Bonmatin JM, Chagnon M, Downs C, Furlan L, Gibbons DW, Giorio C, Girolami V, Goulson D, Kreutzweiser DP, Krupke CH, Liess M, Long E, McField M, Mineau P, Mitchell EAD, Morrissey CA, Noome DA, Pisa L, Settele J, Stark JD, Tapparo A, Van Dyck H, Van Praagh J, Van der Sluijs JP, Whitehorn PR, Wiemers M (2015) Systemic insecticides (neonicotinoids and fipronil): trends, uses, mode of action and metabolites. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(1):5–34
Singh JP, Marwaha KK (2000) Effects of sublethal concentrations of some insecticides on growth and development of maize stalk borer, Chilo partellus (Swinhoe) larvae. Shashpa 7:181–186
Sohn L, Brodie RJ, Couldwell G, Demmons E, Sturve J (2018) Exposure to a nicotinoid pesticide reduces defensive behaviors in a non-target organism, the rusty crayfish Orconectes rusticus. Ecotoxicology 27:900–907
Sohrabi F, Shishehbor P, Saber M, Mosaddegh MS (2013) Lethal and sublethal effects of imidacloprid and buprofezin on the sweetpotato whitefly parasitoid Eretmocerus mundus (Hymenoptera: Aphelinidae). Crop Prot 45:98–103
Sparks TC, DeBoer GJ, Wang NX, Hasler JM, Loso MR, Watson GB (2012) Differential metabolism of sulfoximine and neonicotinoid insecticides by Drosophila melanogaster monooxygenase CYP6G1. Pestic Biochem Physiol 103:159–165
Sparks TC, Watson GB, Loso MR, Geng C, Babcock JM, Thomas JD (2013) Sulfoxaflor and the sulfoximine insecticides: chemistry, mode of action and basis for efficacy on resistant insects. Pestic Biochem Physiol 107:1–7
Tan Y, Biondi A, Desneux N, Gao XW (2012) Assessment of physiological sublethal effects of imidacloprid on the mirid bug Apolygus lucorum (Meyer-dür). Ecotoxicology 21:1989–1997
Tang Q, Xiang M, Hu H, An C, Gao X (2015) Evaluation of sublethal effects of sulfoxaflor on the green peach aphid (Hemiptera: Aphididae) using life table parameters. J Econ Entomol 108(6):2720–2728
Tang Q, Ma K, Chi H, Hou Y, Gao X (2019) Transgenerational hormetic effects of sublethal dose of flupyradifurone on the green peach aphid, Myzus persicae (Sulzer) (Hemiptera: Aphididae). PLoS One 14(1):e0208058
Tengfei L, Yao W, Lixia Z, Yongyu X, Zhengqun Z, Wei M (2019) Sublethal effects of four insecticides on the seven spotted lady beetle (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). J Econ Entomol 112(5):2177–2185
Unal S, Er A, Akkuzu E, Šálek L (2017) Predation efficacy of the predator Coccinella septempunctata L. on the aphid species Macrosiphum rosae (L.) in Kastamonu Province, Turkey. Pak J Zool 49(1):345–349
Wang NX, Watson GB, Loso MR, Sparks TC (2016) Molecular modeling of sulfoxaflor and neonicotinoid binding in insect nicotinic acetylcholine receptors: impact of the Myzus β1 R81T mutation. Pest Manag Sci 72(8):1467–1474
Watson GB, Olson MB, Beavers KW, Loso MR, Sparks TC (2017) Characterization of a nicotinic acetylcholine receptor binding site for sulfoxaflor, a new sulfoximine insecticide for the control of sap-feeding insect pests. Pestic Biochem Physiol 143:90–94
Xiao D, Yang T, Desneux N, Han P, Gao X (2015) Assessment of sublethal and transgenerational effects of pirimicarb on the wheat aphids Rhopalosiphum padi and Sitobion avenae. PLoS One 10(6):e0128936
Xiao D, Zhao J, Guo X, Chen H, Qu M, Zhai W, Desneux N, Biondi A, Zhang F, Wang S (2016) Sublethal effects of imidacloprid on the predatory seven-spot ladybird beetle Coccinella septempunctata. Ecotoxicology 25(10):1782–1793
Xu L, Zhao C, Zhang YN, Gu ZY (2016) Lethal and sublethal effects of sulfoxaflor on the small brown planthopper Laodelphax striatellus. J Asia Pac Entomol 19(3):683–689
Yu C, Lin R, Fu M, Zhou Y, Zong F, Jiang H, Lv N, Piao X, Zhang J, Liu Y, Brock TC (2014) Impact of imidacloprid on life-cycle development of Coccinella septempunctata in laboratory microcosms. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 110:168–173
Zeng XY, He YQ, Wu JX, Tang YM, Gu J, Ding W, Zhang Y (2016) Sublethal effects of cyantraniliprole and imidacloprid on feeding behavior and life table parameters of Myzus persicae (Hemiptera: Aphididae). J Econ Entomol 109:1595–1602
Zhu Y, Loso MR, Watson GB, Sparks TC, Rogers RB, Huang JX, Gerwick BC, Babcock JM, Kelley D, Hegde VB, Nugent BM, Renga JM, Denholm I, Gorman K, DeBoer GJ, Hasler J, Meade T, Thomas JD (2011) Discovery and characterization of sulfoxaflor, a novel insecticide targeting sap-feeding pests. J Agric Food Chem 59(7):2950–2957
Availability of data and material
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BA, MR and AMS designed the experiment. BA, MR and AJ conducted the experiment, collected and analyzed the data and wrote manuscript. MDG and MAF helped in apprehending the idea of this research, designing the layout of experiment and improving the write-up, format and language of this manuscript. BA and AJ contributed in data setting for analysis, reviewed the final manuscript and made the format of this manuscript according to the format of this journal. This final manuscript was ultimately perused, scrutinized and approved for final submission by all the authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The authors agree to all the concerned regulations.
Consent for publication
The authors agree to publish this scientific paper in the International Journal of Tropical Insect Science.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Atta, B., Rizwan, M., Sabir, A.M. et al. Lethal and sublethal effects of clothianidin, imidacloprid and sulfoxaflor on the wheat aphid, Schizaphis graminum (Hemiptera: Aphididae) and its coccinellid predator, Coccinella septempunctata. Int J Trop Insect Sci 41, 345–358 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42690-020-00212-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42690-020-00212-w