Abstract
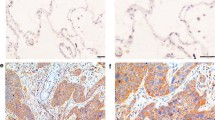
Background: Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer death worldwide, and EGFR mutation is the most common genetic alteration among Asian patients with lung adenocarcinoma. While osimertinib has been shown to be effective in lung cancer patients with EGFR mutation, the majority of patients eventually develop acquired resistance to treatment. We explored the significance of the cyclin D1 expression in patients with EGFR mutation and the potential efficacy of adding abemaciclib, a cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 4/6 inhibitor, simultaneously with osimertinib in vitro. Materials and methods: Immunohistochemical staining, using an anti-cyclin D1 antibody, of specimens from 83 patients with EGFR mutation (male, n = 27; pStage 0-I, n = 71) who were treated by surgical resection between 2017 and 2020, and the relationship between the cyclin D1 expression and clinicopathological factors was analyzed. Additionally, the combined effect of osimertinib and abemaciclib in lung cancer cell lines were analyzed using a growth inhibition test, and the signaling pathway underlying the combined effect was investigated. Results: Cyclin D1 was negative in 18.1% of patients with EGFR mutation, and cyclin D1 negativity was associated with pStage ≥ II (p = 0.02), lymph node metastasis (p = 0.001), and lymphatic invasion (p = 0.01). The cyclin D1-negative group had significantly shorter recurrence-free survival (p = 0.02), although this difference disappeared when limited to pN0 patients. In EGFR mutated cell lines, the combination of osimertinib and abemaciclib demonstrated synergistic effects, which were thought to be mediated by the inhibition of AKT phosphorylation. Conclusion: Combination therapy with CDK4/6 inhibitors and EGFR-TKIs may be a promising approach.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- EGFR:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor
- TKI:
-
Tyrosine kinase inhibitor
- CDK:
-
Cyclin- dependent kinase
- CI:
-
Combination index
- Fa:
-
Fraction affected
- EdU:
-
5-ethynyl-2’-deoxyuridine
- HER2:
-
Human epidermal growth factor 2
- MST:
-
Median survival time
References
Ferlay J, Colombet M, Soerjomataram I, Mathers C, Parkin DM, Pineros M, Znaor A, Bray F (2019) Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods. Int J Cancer 144:1941–1953. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.31937
Kohno T, Nakaoku T, Tsuta K, Tsuchihara K, Matsumoto S, Yoh K, Goto K (2015) Beyond ALK-RET, ROS1 and other oncogene fusions in lung cancer. Transl Lung Cancer Res 4:156–164. https://doi.org/10.3978/j.issn.2218-6751.2014.11.11
Soria JC, Ohe Y, Vansteenkiste J, Reungwetwattana T, Chewaskulyong B, Lee KH, Dechaphunkul A, Imamura F, Nogami N, Kurata T, Okamoto I, Zhou C, Cho BC, Cheng Y, Cho EK, Voon PJ, Planchard D, Su WC, Gray JE, Lee SM, Hodge R, Marotti M, Rukazenkov Y, Ramalingam SS, Investigators F (2018) Osimertinib in untreated EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N Engl J Med 378:113–125. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1713137
Finn RS, Martin M, Rugo HS, Jones S, Im SA, Gelmon K, Harbeck N, Lipatov ON, Walshe JM, Moulder S, Gauthier E, Lu DR, Randolph S, Dieras V, Slamon DJ (2016) Palbociclib and Letrozole in Advanced breast Cancer. N Engl J Med 375:1925–1936. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1607303
Goetz MP, Toi M, Campone M, Sohn J, Paluch-Shimon S, Huober J, Park IH, Tredan O, Chen SC, Manso L, Freedman OC, Garnica Jaliffe G, Forrester T, Frenzel M, Barriga S, Smith IC, Bourayou N, Di Leo A (2017) MONARCH 3: Abemaciclib as initial therapy for advanced breast Cancer. J Clin Oncol 35:3638–3646. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2017.75.6155
Mishina T, Dosaka-Akita H, Kinoshita I, Hommura F, Morikawa T, Katoh H, Kawakami Y (1999) Cyclin D1 expression in non-small-cell lung cancers: its association with altered p53 expression, cell proliferation and clinical outcome. Br J Cancer 80:1289–1295. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6990500
Osoegawa A, Gills JJ, Kawabata S, Dennis PA (2017) Rapamycin sensitizes cancer cells to growth inhibition by the PARP inhibitor olaparib. Oncotarget 8:87044–87053. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.19667
Chou TC (2006) Theoretical basis, experimental design, and computerized simulation of synergism and antagonism in drug combination studies. Pharmacol Rev 58:621–681 58/3/621 [pii]. https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.58.3.10
Brand TM, Iida M, Li C, Wheeler DL (2011) The nuclear epidermal growth factor receptor signaling network and its role in cancer. Discov Med 12:419–432
Lin SY, Makino K, Xia W, Matin A, Wen Y, Kwong KY, Bourguignon L, Hung MC (2001) Nuclear localization of EGF receptor and its potential new role as a transcription factor. Nat Cell Biol 3:802–808. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb0901-802
Leonetti A, Sharma S, Minari R, Perego P, Giovannetti E, Tiseo M (2019) Resistance mechanisms to osimertinib in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer 121:725–737. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-019-0573-8
Gautschi O, Ratschiller D, Gugger M, Betticher DC, Heighway J (2007) Cyclin D1 in non-small cell lung cancer: a key driver of malignant transformation. Lung Cancer 55:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2006.09.024
Wang J, Miao LJ, Wu YM, Wu YJ, Wang XC (2006) [Expression of AKT2, cyclin D1, and MMP-9 and their correlations to clinicopathologic features of non-small cell lung cancer]. Ai Zheng 25:69–72
Osoegawa A, Yoshino I, Tanaka S, Sugio K, Kameyama T, Yamaguchi M, Maehara Y (2004) Regulation of p27 by S-phase kinase-associated protein 2 is associated with aggressiveness in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 22:4165–4173. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2004.01.035
Fry DW, Harvey PJ, Keller PR, Elliott WL, Meade M, Trachet E, Albassam M, Zheng X, Leopold WR, Pryer NK, Toogood PL (2004) Specific inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 by PD 0332991 and associated antitumor activity in human tumor xenografts. Mol Cancer Ther 3:1427–1438
Puyol M, Martin A, Dubus P, Mulero F, Pizcueta P, Khan G, Guerra C, Santamaria D, Barbacid M (2010) A synthetic lethal interaction between K-Ras oncogenes and Cdk4 unveils a therapeutic strategy for non-small cell lung carcinoma. Cancer Cell 18:63–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2010.05.025
Yu HA, Goldberg SB, Le X, Piotrowska Z, Goldman JW, De Langen AJ, Okamoto I, Cho BC, Smith P, Mensi I, Ambrose H, Kraljevic S, Maidment J, Chmielecki J, Li-Sucholeiki X, Doughton G, Patel G, Jewsbury P, Szekeres P, Riess JW (2021) Biomarker-Directed phase II platform study in patients with EGFR sensitizing mutation-positive Advanced/Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer whose disease has progressed on first-line osimertinib therapy (ORCHARD). Clin Lung Cancer 22:601–606. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cllc.2021.06.006
Osoegawa A, Yamaguchi M, Nakamura T, Morinaga R, Tanaka K, Kashiwabara K, Miura T, Suetsugu T, Harada T, Asoh T, Taguchi K, Nabeshima K, Kishimoto J, Sakai K, Nishio K, Sugio K (2021) High incidence of C797S mutation in patients with Long Treatment History of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors including Osimertinib. JTO Clin Res Rep 2:100191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtocrr.2021.100191
Cabanos HF, Hata AN (2021) Emerging insights into targeted therapy-tolerant Persister cells in Cancer. Cancers (Basel) 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13112666
Moore G, Annett S, McClements L, Robson T (2020) Top notch targeting strategies in Cancer: a detailed overview of recent insights and current perspectives. Cells 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9061503
Nakagawa K, Garon EB, Seto T, Nishio M, Ponce Aix S, Paz-Ares L, Chiu CH, Park K, Novello S, Nadal E, Imamura F, Yoh K, Shih JY, Au KH, Moro-Sibilot D, Enatsu S, Zimmermann A, Frimodt-Moller B, Visseren-Grul C, Reck M, Investigators RS (2019) Ramucirumab plus erlotinib in patients with untreated, EGFR-mutated, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (RELAY): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 20:1655–1669. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30634-5
Saito H, Fukuhara T, Furuya N, Watanabe K, Sugawara S, Iwasawa S, Tsunezuka Y, Yamaguchi O, Okada M, Yoshimori K, Nakachi I, Gemma A, Azuma K, Kurimoto F, Tsubata Y, Fujita Y, Nagashima H, Asai G, Watanabe S, Miyazaki M, Hagiwara K, Nukiwa T, Morita S, Kobayashi K, Maemondo M (2019) Erlotinib plus bevacizumab versus erlotinib alone in patients with EGFR-positive advanced non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer (NEJ026): interim analysis of an open-label, randomised, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 20:625–635. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30035-X
Seto T, Kato T, Nishio M, Goto K, Atagi S, Hosomi Y, Yamamoto N, Hida T, Maemondo M, Nakagawa K, Nagase S, Okamoto I, Yamanaka T, Tajima K, Harada R, Fukuoka M, Yamamoto N (2014) Erlotinib alone or with bevacizumab as first-line therapy in patients with advanced non-squamous non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring EGFR mutations (JO25567): an open-label, randomised, multicentre, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol 15:1236–1244. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70381-X
Cho BC, Felip E, Hayashi H, Thomas M, Lu S, Besse B, Sun T, Martinez M, Sethi SN, Shreeve SM, Spira AI (2022) MARIPOSA: phase 3 study of first-line amivantamab + lazertinib versus osimertinib in EGFR-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer. Future Oncol 18:639–647. https://doi.org/10.2217/fon-2021-0923
Janjigian YY, Smit EF, Groen HJ, Horn L, Gettinger S, Camidge DR, Riely GJ, Wang B, Fu Y, Chand VK, Miller VA, Pao W (2014) Dual inhibition of EGFR with afatinib and cetuximab in kinase inhibitor-resistant EGFR-mutant lung cancer with and without T790M mutations. Cancer Discov 4:1036–1045. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-14-0326
Wu Q, Luo W, Li W, Wang T, Huang L, Xu F (2021) First-Generation EGFR-TKI Plus Chemotherapy Versus EGFR-TKI alone as first-line treatment in Advanced NSCLC with EGFR activating mutation: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of Randomized controlled trials. Front Oncol 11:598265. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.598265
Soria JC, Wu YL, Nakagawa K, Kim SW, Yang JJ, Ahn MJ, Wang J, Yang JC, Lu Y, Atagi S, Ponce S, Lee DH, Liu Y, Yoh K, Zhou JY, Shi X, Webster A, Jiang H, Mok TS (2015) Gefitinib plus chemotherapy versus placebo plus chemotherapy in EGFR-mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer after progression on first-line gefitinib (IMPRESS): a phase 3 randomised trial. Lancet Oncol 16:990–998. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00121-7
Asahina H, Tanaka K, Morita S, Maemondo M, Seike M, Okamoto I, Oizumi S, Kagamu H, Takahashi K, Kikuchi T, Isobe T, Sugio K, Kobayashi K (2021) A phase II study of Osimertinib Combined with Platinum Plus Pemetrexed in patients with EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non-Small-cell Lung Cancer: the OPAL Study (NEJ032C/LOGIK1801). Clin Lung Cancer 22:147–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cllc.2020.09.023
Planchard D, Feng PH, Karaseva N, Kim SW, Kim TM, Lee CK, Poltoratskiy A, Yanagitani N, Marshall R, Huang X, Howarth P, Janne PA, Kobayashi K (2021) Osimertinib plus platinum-pemetrexed in newly diagnosed epidermal growth factor receptor mutation-positive advanced/metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: safety run-in results from the FLAURA2 study. ESMO Open 6:100271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esmoop.2021.100271
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr. Brian Quinn for his critical comments on the manuscript and Ms. Kaori Ogata for her technical support for the experiments. This work was supported by KAKENHI (Grant Number JP 21K08889 and 20K09168), Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, Tokyo, Japan.
Funding
This work was supported by KAKENHI (Grant Number JP 21K08889 and 20K09168), Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, Tokyo, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Atsushi Osoegawa, Yohei Takumi, Takafumi Hashimoto, Shotaro Nakatsuji, Mayu Hori, Mayu Sakai, Takashi Karashima, Miyuki Abe, Michiyo Miyawaki, and Kenji Sugio. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Atsushi Osoegawa and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the internal review board of Oita University Faculty of Medicine (IRB No. 698).
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Financial interests
Yohei Takumi, Takafumi Hashimoto, Shotaro Nakatsuji, Mayu Hori, Mayu Sakai, Takashi Karashima, Miyuki Abe, and Michiyo Miyawaki declare they have no financial interests. Atsushi Osoegawa and Kenji Sugio have received speaker and consultant honoraria from AstraZeneca (Cambridge, UK).
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Osoegawa, A., Takumi, Y., Hashimoto, T. et al. Cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 4/6 inhibition in non-small cell lung cancer with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations. Invest New Drugs 41, 183–192 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-023-01337-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-023-01337-8