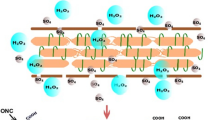
Abstract
Reacting with reductive phenolic hydroxyls (–OH) and methoxy groups (–OCH3) on lignin, silver ions (Ag+) were reduced to metallic silver nanoparticles (NPs) with sizes smaller than 40 nm. The resulting Ag/lignin NPs were then physically crosslinked in the cellulose hydrogel, followed by freeze-drying to obtain the final Ag/lignin NP-loaded cellulose aerogel. Loaded with Ag/lignin NPs, the aerogel exhibited strengthened mechanical property (387 ± 11 kPa) against the external deformation at a compressive strain of 65% due to the nano-reinforcement by the loaded Ag/lignin NPs when compared with pure cellulose aerogel (246 ± 32 kPa). The Ag/lignin NP-loaded aerogel also showed robust killing efficiency against different pathogenic bacteria in aqueous solution (Escherichia coli: > 99.99%, Pseudomonas aeruginosa: > 99.9%, Vibrio cholera: > 99.99%, Staphylococcus aureus: > 99.99%, Bacillus subtilis: > 97.4%). Moreover, the loaded Ag/lignin NPs provided the aerogel with excellent catalytic degradation ability toward various organic compounds, including dyes, pollutants, and antibiotics, evidenced by the degradation of methylene blue (99.8% in 30 min) and methyl orange (99.9% in 180 min) in the presence of NaBH4 and natural sunlight radiation, and degradation of rhodamine B (99.9% in 35 min), 4-nitrophenol (99.5% in 180 min) and doxycycline hyclate (99.8% in 30 min) in the presence of NaBH4 without natural sunlight. In addition, the Ag/lignin NP-loaded aerogel could be reused after facile regeneration washing with water while retaining excellent performance on efficiently degrading (~ 100%) the organic dyes for at least three cycles. The roles of loaded Ag/lignin NPs as photoelectron generators and relay centers for transferring electrons from the reductant to the targeted organic compounds during the degradation process were comprehensively investigated and explained.












Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Research data and materials are not shared.
References
Ardakani LS, Alimardani V, Tamaddon AM, Amani AM, Taghizadeh S (2021) Green synthesis of iron-based nanoparticles using Chlorophytum comosum leaf extract: methyl orange dye degradation and antimicrobial properties. Heliyon 7:e06159
Barros A, Pizzolato T, Carissimi E, Schneider I (2006) Decolorizing dye wastewater from the agate industry with Fenton oxidation process. Miner Eng 19:87–90
Benincá C, Peralta-Zamora P, Tavares CRG, Igarashi-Mafra L (2013) Degradation of an azo dye (Ponceau 4R) and treatment of wastewater from a food industry by ozonation. Ozone Sci Eng 35:295–301
Cai J, Kimura S, Wada M, Kuga S (2009) Nanoporous cellulose as metal nanoparticles support. Biomacromol 10:87–94
Cao HL, Huang HB, Chen Z, Karadeniz B, Lü J, Cao R. (2017) Ultrafine silver nanoparticles supported on a conjugated microporous polymer as high-performance nanocatalysts for nitrophenol reduction. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:5231–5236
Chen H, Sharma SK, Sharma PR, Yeh H, Johnson K, Hsiao BS (2019) Arsenic (iii) removal by nanostructured dialdehyde cellulose–cysteine microscale and nanoscale fibers. ACS Omega 4:22008–22020
Chook SW, Chia CH, Chan CH, Chin SX, Zakaria S, Sajab MS, Huang NM (2015) A porous aerogel nanocomposite of silver nanoparticles-functionalized cellulose nanofibrils for SERS detection and catalytic degradation of rhodamine B. RSC Adv 5:88915–88920
Cisneros RL, Espinoza AG, Litter MI (2002) Photodegradation of an azo dye of the textile industry. Chemosphere 48:393–399
Das R, Lindstrom T, Sharma PR, Chi K, Hsiao BS (2022) Nanocellulose for sustainable water purification. Chem Rev 122:8936–9031
Davies J, Davies D (2010) Origins and evolution of antibiotic resistance. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 74:417–433
Dizaj SM, Lotfipour F, Barzegar-Jalali M, Zarrintan MH, Adibkia K (2014) Antimicrobial activity of the metals and metal oxide nanoparticles. Mater Sci Eng C 44:278–284
Dong H, Snyder JF, Tran DT, Leadore JL (2013) Hydrogel, aerogel and film of cellulose nanofibrils functionalized with silver nanoparticles. Carbohydr Polym 95:760–767
Dubey SP, Dwivedi AD, Kim IC, Sillanpaa M, Kwon YN, Lee C (2014) Synthesis of graphene–carbon sphere hybrid aerogel with silver nanoparticles and its catalytic and adsorption applications. Chem Eng J 244:160–167
Essner JB, Laber CH, Baker GA (2015) Carbon dot reduced bimetallic nanoparticles: size and surface plasmon resonance tunability for enhanced catalytic applications. J Mater Chem A 3:16354–16360
Feng XJ, He X, Lai L, Lu Q, Cheng L, Wu J (2021) Polydopamine-anchored polyether on Fe3O4 as magnetic recyclable nanoparticle-demulsifiers. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 617:126142
Figueiredo P, Santos HA (2021) Lignin-based materials for biomedical applications: preparation, characterization, and implementation. Elsevier
Garcia AM, Martins TS, Camilo FF (2021) Free facile preparation of Ag-nanoparticles on cellulose membrane for catalysis. Cellulose 28:4899–4911
Gupta N, Singh HP, Sharma RK (2011) Metal nanoparticles with high catalytic activity in degradation of methyl orange: an electron relay effect. J Mol Catal A Chem 335:248–252
He X, Liang C, Liu Q, Xu Z (2019) Magnetically responsive Janus nanoparticles synthesized using cellulosic materials for enhanced phase separation in oily wastewaters and water-in-crude oil emulsions. Chem Eng J 378:122045
He X, Liu Q, Xu Z (2020) Treatment of oily wastewaters using magnetic Janus nanoparticles of asymmetric surface wettability. J Colloid Interface Sci 568:207–220
He X, Li Z, Li J, Mishra D, Ren Y, Gates I, Hu J, Lu Q (2021) Ultrastretchable, adhesive, and antibacterial hydrogel with robust spinnability for manufacturing strong hydrogel micro/nanofibers. Small 17:2103521
Hosseini H, Zirakjou A, Goodarzi V, Mousavi SM, Khonakdar HA, Zamanlui S (2020) Lightweight aerogels based on bacterial cellulose/silver nanoparticles/polyaniline with tuning morphology of polyaniline and application in soft tissue engineering. Int J Biol Macromol 152:57–67
Javaid R, Qazi UY (2019) Catalytic oxidation process for the degradation of synthetic dyes: an overview. Int J Environ Res Public Health 16:2066
Jiang ZJ, Liu CY, Sun LW (2005) Catalytic properties of silver nanoparticles supported on silica spheres. J Phys Chem B 109:1730–1735
Joseph S, Mathew B (2015) Facile synthesis of silver nanoparticles and their application in dye degradation. Mater Sci Eng B Solid State Mater Adv Technol 195:90–97
Kaushik P, Malik A (2009) Fungal dye decolourization: recent advances and future potential. Environ Int 35:127–141
Liao G, Chen J, Zeng W, Yu C, Yi C, Xu Z (2016) Facile preparation of uniform nanocomposite spheres with loading silver nanoparticles on polystyrene-methyl acrylic acid spheres for catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. J Phys Chem C 120:25935–25944
Liebner F, Aigner N, Schimper C, Potthast A, Rosenau T (2012) Bacterial cellulose aerogels: from lightweight dietary food to functional materials. In: Liebner F, Rosenau T (eds) Functional materials from renewable sources. American Chemical Society, Washington, DC, pp 57–74. https://doi.org/10.1021/bk-2012-1107.ch004
Liu Q, Yu H, Zeng F, Li X, Sun J, Hu X, Pan Q, Li C, Lin H, Su Min Z (2020) Polyaniline as interface layers promoting the in-situ growth of zeolite imidazole skeleton on regenerated cellulose aerogel for efficient removal of tetracycline. J Colloid Interface Sci 579:119–127
Ma J, Guo X, Zhang Y, Ge H (2014) Catalytic performance of TiO2@ Ag composites prepared by modified photodeposition method. Chem Eng J 258:247–253
Mallick K, Witcomb M, Scurrell M (2006) Silver nanoparticle catalysed redox reaction: an electron relay effect. Mater Chem Phys 97:283–287
Manivel A, Lee GJ, Chen CY, Chen JH, Ma SH, Horng TL, Wu JJ (2015) Synthesis of MoO3 nanoparticles for azo dye degradation by catalytic ozonation. Mater Res Bull 62:184–191
Milczarek G, Rebis T, Fabianska J (2013) One-step synthesis of lignosulfonate-stabilized silver nanoparticles. Colloids Surf B 105:335–341
Mollahosseini A, Rahimpour A, Jahamshahi M, Peyravi M, Khavarpour M (2012) The effect of silver nanoparticle size on performance and antibacteriality of polysulfone ultrafiltration membrane. Desalination 306:41–50
Murugadoss A, Chattopadhyay A (2007) A ‘green’chitosan–silver nanoparticle composite as a heterogeneous as well as micro-heterogeneous catalyst. Nanotechnology 19:015603
Patel DK, Dutta SD, Lim KT (2019) Nanocellulose-based polymer hybrids and their emerging applications in biomedical engineering and water purification. RSC Adv 9:19143–19162
Peker H, Atilgan A, Ulusoy H, Goktas O (2013) Usage opportunities of the natural dye extracted from acorn (Quercus ithaburensis Decaisne) in the furniture industry upper surface treatment. Int J Phy Sci 7:5552–5558
Qi J, He X, Lu Q (2022) Novel chelating polyacrylonitrile membrane for efficient capture of Cu2+, Pb2+ and Fe3+. Chem Eng J 450:138203
Rajan PI, Vijaya JJ, Jesudoss S, Kaviyarasu K, Kennedy LJ, Jothiramalingam R, Al-Lohedan HA, Vaali-Mohammed M-A (2017) Green-fuel-mediated synthesis of self-assembled NiO nano-sticks for dual applications—photocatalytic activity on Rose Bengal dye and antimicrobial action on bacterial strains. Mater Res Express 4:085030
Ren Y, Hersch SJ, He X, Zhou R, Dong TG, Lu Q (2022) A lightweight, mechanically strong, and shapeable copper-benzenedicarboxylate/cellulose aerogel for dye degradation and antibacterial applications. Sep Purif Technol 283:120229
Saad A, Snoussi Y, Abderrabba M, Chehimi MM (2016) Ligand-modified mesoporous silica SBA-15/silver hybrids for the catalyzed reduction of methylene blue. RSC Adv 6:57672–57682
Sakthivel S, Neppolian B, Shankar M, Arabindoo B, Palanichamy M, Murugesan V (2003) Solar photocatalytic degradation of azo dye: comparison of photocatalytic efficiency of ZnO and TiO2. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 77:65–82
Sathishkumar M, Sneha K, Yun Y-S (2010) Immobilization of silver nanoparticles synthesized using Curcuma longa tuber powder and extract on cotton cloth for bactericidal activity. Bioresour Technol 101:7958–7965
Sathiyan K, Bar-Ziv R, Mendelson O, Zidki T (2020) Controllable synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles and their photocatalytic activity in dye degradation. Mater Res Bull 126:110842
Schlatter H, Long T, Gray J (2007) An overview of hair dye safety. J Cosmet Dermatol 6:32–36
Sharma PR, Chattopadhyay A, Sharma SK, Hsiao BS (2017) Efficient removal of UO22+ from water using carboxycellulose nanofibers prepared by the nitro-oxidation method. Ind Eng Chem Res 56:13885–13893
Sharma PR, Chattopadhyay A, Sharma SK, Geng L, Amiralian N, Martin D, Hsiao BS (2018a) Nanocellulose from spinifex as an effective adsorbent to remove cadmium (II) from water. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:3279–3290
Sharma PR, Chattopadhyay A, Zhan C, Sharma SK, Geng L, Hsiao BS (2018b) Lead removal from water using carboxycellulose nanofibers prepared by nitro-oxidation method. Cellulose 25:1961–1973
Sharma PR, Sharma SK, Lindström T, Hsiao BS (2020) Nanocellulose-enabled membranes for water purification: perspectives. Adv Sustain Syst 4:1900114
Sharma SK, Sharma PR, Johnson KI, Madan Y, Li S, Cai G, Brahmbhatt I, Borges W, Hsiao BS (2022) Plant-derived carboxycellulose: highly efficient bionanomaterials for removal of toxic lead from contaminated water. In: Satinder A (ed) Separation Science and Technology, vol 15, 1st edn. Elsevier, London, pp 87–95
Shi B, Li G, Wang D, Feng C, Tang H (2007) Removal of direct dyes by coagulation: the performance of preformed polymeric aluminum species. J Hazard Mater 143:567–574
Singh RK, Behera SS, Singh KR, Mishra S, Panigrahi B, Sahoo TR, Parhi PK, Mandal D (2020) Biosynthesized gold nanoparticles as photocatalysts for selective degradation of cationic dye and their antimicrobial activity. J Photochem Photobiol A 400:112704
Sjahro N, Yunus R, Abdullah LC, Rashid SA, Asis AJ, Akhlisah Z (2021) Recent advances in the application of cellulose derivatives for removal of contaminants from aquatic environments. Cellulose 28:7521–7557
Smitha S, Nissamudeen K, Philip D, Gopchandran K (2008) Studies on surface plasmon resonance and photoluminescence of silver nanoparticles. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 71:186–190
Suresh K, Islam MA, Rastgar M, Mohammadnezhad A, Fleck BA, Sadrzadeh M (2022) Poly (methyl methacrylate) grafted wheat straw for economical and eco-friendly treatment of oily wastewater. Cellulose 29:3351–3374
Tang J, Shi Z, Berry RM, Tam KC (2015) Mussel-inspired green metallization of silver nanoparticles on cellulose nanocrystals and their enhanced catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol in the presence of β-cyclodextrin. Ind Eng Chem Res 54:3299–3308
Thakur M, Sharma G, Ahamad T, Ghfar AA, Pathania D, Naushad M (2017) Efficient photocatalytic degradation of toxic dyes from aqueous environment using gelatin-Zr (IV) phosphate nanocomposite and its antimicrobial activity. Colloid Surf B 157:456–463
Tian Y, Cao Y-y, Pang F, Chen G-q, Zhang X (2014) Ag nanoparticles supported on N-doped graphene hybrids for catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. RSC Adv 4:43204–43211
Uddin F (2021) Environmental hazard in textile dyeing wastewater from local textile industry. Cellulose 28:10715–10739
Wan C, Li J (2016) Cellulose aerogels functionalized with polypyrrole and silver nanoparticles: in-situ synthesis, characterization and antibacterial activity. Carbohydr Polym 146:362–367
Wan C, Jiao Y, Sun Q, Li J (2016) Preparation, characterization, and antibacterial properties of silver nanoparticles embedded into cellulose aerogels. Polym Compos 37:1137–1142
Wang Z, Bo N, Liu Y, Yang G, Liu Y, Zhao Y (2013) Preparation of lignin-based anion exchangers and their utilization for nitrate removal. BioResources 8:3505–3517
Wang X, Sui Y, Jian J, Yuan Z, Zeng J, Zhang L, Wang T, Zhou H (2020) Ag@ AgCl nanoparticles in-situ deposited cellulose acetate/silk fibroin composite film for photocatalytic and antibacterial applications. Cellulose 27:7721–7737
Winiarz JG, Zhang L, Lal M, Friend CS, Prasad PN (1999) Observation of the photorefractive effect in a hybrid organic− inorganic nanocomposite. J Am Chem Soc 121:5287–5295
Wu J, Zhao N, Zhang X, Xu J (2012) Cellulose/silver nanoparticles composite microspheres: eco-friendly synthesis and catalytic application. Cellulose 19:1239–1249
Xia J, Liu Z, Chen Y, Cao Y, Wang Z (2020) Effect of lignin on the performance of biodegradable cellulose aerogels made from wheat straw pulp-LiCl/DMSO solution. Cellulose 27:879–894
Xiao W-D, Xiao L-P, Xiao W-Z, Wang Q, Zhai S-R, Sun R-C (2022) The new identity of cellulose pulp: A green silver nanoparticles support for highly efficient catalytic hydrogenation of 4-nitrophenol. J Clean Prod 355:131833
Xie Y, He Y, Irwin PL, Jin T, Shi X (2011) Antibacterial activity and mechanism of action of zinc oxide nanoparticles against Campylobacter jejuni. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:2325–2331
Xiong Y, Xu L, Jin C, Sun Q (2020) Cellulose hydrogel functionalized titanate microspheres with self-cleaning for efficient purification of heavy metals in oily wastewater. Cellulose 27:7751–7763
Xiu ZM, Zhang QB, Puppala HL, Colvin VL, Alvarez PJ (2012) Negligible particle-specific antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles. Nano Lett 12:4271–4275
Xu M, Bao W, Xu S, Wang X, Sun R (2016) Porous cellulose aerogels with high mechanical performance and their absorption behaviors. BioResources 11:8–20
Yagub MT, Sen TK, Afroze S, Ang HM (2014) Dye and its removal from aqueous solution by adsorption: a review. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 209:172–184
Yang X, Zhang L, Jin X, Liu L, Zhang Y, Ni Q, Yao J (2017) Synthesis of hydrophobically modified cellulose-based flocculant and its application in treatments of kaolin suspension and machining wastewater. Cellulose 24:5639–5647
Yang F, He X, Tan W, Liu G, Yi T, Lu Q, Wei X, Xie H, Long Q, Wang G (2022) Adhesion-Shielding based synthesis of interfacially active magnetic Janus nanoparticles. J Colloid Interface Sci 607:1741–1753
Yao C, Wang F, Cai Z, Wang X (2016) Aldehyde-functionalized porous nanocellulose for effective removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions. RSC Adv 6:92648–92654
Ye X, Shang S, Zhao Y, Cui S, Zhong Y, Huang L (2021) Ultra-efficient adsorption of copper ions in chitosan–montmorillonite composite aerogel at wastewater treatment. Cellulose 28:7201–7212
Yin IX, Zhang J, Zhao IS, Mei ML, Li Q, Chu CH (2020) The antibacterial mechanism of silver nanoparticles and its application in dentistry. Int J Nanomed 15:2555
Zhan C, Sharma PR, He H, Sharma SK, McCauley-Pearl A, Wang R, Hsiao BS (2020) Rice husk based nanocellulose scaffolds for highly efficient removal of heavy metal ions from contaminated water. Environ Sci Water Res Technol 6:3080–3090
Zhang W, Sun Y, Zhang L (2015) In situ synthesis of monodisperse silver nanoparticles on sulfhydryl-functionalized poly (glycidyl methacrylate) microspheres for catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Ind Eng Chem Res 54:6480–6488
Zhang W, Sun Y, Zhang L (2016) Fabrication of high efficient silver nanoparticle catalyst supported on poly (glycidyl methacrylate)–polyacrylamide. Ind Eng Chem Res 55:12398–12406
Zhang T, Zhao Y, Muhetaer M, Wang K (2020) Silver nanoparticles cross-linked polyimide aerogels with improved high temperature microstructure stabilities and high mechanical performances. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 297:110035
Zhou Q, Qian G, Li Y, Zhao G, Chao Y, Zheng J (2008) Two-dimensional assembly of silver nanoparticles for catalytic reduction of 4-nitroaniline. Thin Solid Films 516:953–956
Zhou S, Wang M, Chen X, Xu F (2015) Facile template synthesis of microfibrillated cellulose/polypyrrole/silver nanoparticles hybrid aerogels with electrical conductive and pressure responsive properties. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 3:3346–3354
Zhu J, Xiong R, Zhao F, Peng T, Hu J, Xie L, Xie H, Wang K, Jiang C (2019) Lightweight, high-strength, and anisotropic structure composite aerogel based on hydroxyapatite nanocrystal and chitosan with thermal insulation and flame retardant properties. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 8:71–83
Acknowledgment
The authors acknowledge the support from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) discovery grant and alliance grant (Q. Lu), Canada Foundation of Innovation (CFI) (Q. Lu), the Canadian Institute of Health Research (T. Dong, Q. Lu) and the University of Calgary’s Canada First Research Excellence Fund (CFREF) program, the Global Research Initiative (GRI) in Sustainable Low Carbon Unconventional Resources and GRI-University of Alberta’s Future Energy Systems Joint Research Fund. The authors would also like to thank Drs. Jeroen de Buck, Gisele Peirano and Johann Pitout for helping provide bacterial strains P. aeruginosa, B. subtilis, and S. aureus, respectively.
Funding
The authors acknowledge the support from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) discovery grant and alliance grant (Q. Lu), Canada Foundation of Innovation (CFI) (Q. Lu), the Canadian Institute of Health Research (T. Dong, Q. Lu) and the University of Calgary’s Canada First Research Excellence Fund (CFREF) program, the Global Research Initiative (GRI) in Sustainable Low Carbon Unconventional Resources and GRI-University of Alberta’s Future Energy Systems Joint Research Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, validation, formal analysis, investigation, visualization were performed by XH. Experiments regarding the antibacterial activity were performed by HK. Conceptualization, supervision and funding acquisition were performed by QL. The first draft of the manuscript was written by XH and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interest.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
The authors give the publisher permission to publish the work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
He, X., Kim, H., Dong, T.G. et al. Green synthesis of Ag/lignin nanoparticle-loaded cellulose aerogel for catalytic degradation and antimicrobial applications. Cellulose 29, 9341–9360 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04848-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04848-4