Abstract
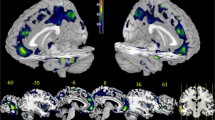
We applied diffusion-tensor imaging (DTI) including measurements of fractional anisotropy (FA), a parameter of neuronal fiber integrity, mean diffusivity (MD), a parameter of brain tissue integrity, as well as voxel-based morphometry (VBM), a measure of gray and white matter volume, to provide a basis to improve our understanding of the neurobiological basis of dependent personality disorder (DPD). DTI was performed on young girls with DPD (N = 17) and young female healthy controls (N = 17). Tract-based spatial statistics (TBSS) were used to examine microstructural characteristics. Gray matter volume differences between the two groups were investigated using voxel-based morphometry (VBM). The Pearson correlation analysis was utilized to examine the relationship between distinct brain areas of white matter and gray matter and the Dy score on the MMPI. The DPD had significantly higher fractional anisotropy (FA) values than the HC group in the right retrolenticular part of the internal capsule, right external capsule, the corpus callosum, right posterior thalamic radiation (include optic radiation), right cerebral peduncle (p < 0.05), which was strongly positively correlated with the Dy score of MMPI. The volume of gray matter in the right postcentral gyrus and left cuneus in DPD was significantly increased (p < 0.05), which was strongly positively correlated with the Dy score of MMPI (r1,2= 0.467,0.353; p1,2 = 0.005,0.04). Our results provide new insights into the changes in the brain structure in DPD, which suggests that alterations in the brain structure might implicate the pathophysiology of DPD. Possible visual and somatosensory association with motor nerve circuits in DPD.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available but are available from the corresponding author at reasonable request.
References
Agoalikum E, Klugah-Brown B, Wu H, Hu P, Jing J, Biswal B (2023) Structural differences among children, adolescents, and adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and abnormal granger causality of the right pallidum and whole-brain. Front Hum Neurosci 17:1076873. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2023.1076873
Aguilar-Ortiz S, Salgado-Pineda P, Marco-Pallarés J, Pascual JC, Vega D, Soler J, Brunel C, Martin-Blanco A, Soto A, Ribas J, Maristany T, Sarró S, Salvador R, Rodríguez-Fornells A, Pomarol-Clotet E, McKenna PJ (2018) Abnormalities in gray matter volume in patients with borderline personality disorder and their relation to lifetime depression: a VBM study. PLoS ONE 13(2):e0191946. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0191946
Alves GS, Knochel C, Paulitsch MA, Reinke B, Carvalho AF, Feddern R, Prvulovic D, Sudo FK, Pantel J, Reif A, Oertel V (2018) White matter microstructural changes and episodic memory disturbances in late-onset bipolar disorder. Front Psychiatry 9:480. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00480
American Psychiatric Association (2013) American Psychiatric Association: diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 5th edn. American Psychiatric Association, Arlington
Ampollini P, Marchesi C, Signifredi R, Ghinaglia E, Scardovi F, Codeluppi S, Maggini C (1999) Temperament and personality features in patients with major depression, panic disorder and mixed conditions. J Affect Disord 52(1–3):203–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/s01650327(98)00048-2
Ashburner J, Friston KJ (2005) Unified segmentation. NeuroImage 26(3):839–851
Bachrach N, Croon MA, Bekker MH (2012) Factor structure of self-reported clinical disorders and personality disorders: a review of the existing literature and a factor analytical study. J Clin Psychol 68(6):645–660. https://doi.org/10.1002/jclp.21841
Benotsch EG, Sawyer AN, Martin AM, Allen ES, Nettles CD, Richardson D, Rietmeijer CA (2017) Dependency traits, relationship power, and health risks in women receiving sexually-transmitted infection clinic services. Behav Med 43(3):176–183. https://doi.org/10.1080/08964289.2017.1297291
Bergouignan L, Chupin M, Czechowska Y, Kinkingnéhun S, Lemogne C, Le Bastard G, Lepage M, Garnero L, Colliot O, Fossati P (2009) Can voxel based morphometry, manual segmentation and automated segmentation equally detect hippocampal volume differences in acute depression? Neuroimage 45(1):29–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.11.006
Bhalsing KS, Kumar KJ, Saini J, Yadav R, Gupta AK, Pal PK (2015) White matter correlates of cognitive impairment in essential tremor. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 36(3):448–453. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A4138
Blasi F, Whalen MJ, Ayata C (2015) Lasting pure-motor deficits after focal posterior internal capsule white-matter infarcts in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 35(6):977–984. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2015.7
Bornstein RF (2012) From dysfunction to adaptation: an interactionist model of dependency. Annu Rev Clin Psychol 8:291–316. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-032511-143058
Bornstein RF, Riggs JM, Hill EL, Calabrese C (1996) Activity, passivity, self-denigration, and self-promotion: toward an interactionist model of interpersonal dependency. J Pers 64(3):637. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-6494.1996.tb00525.x
Cai S, Jiang Y, Wang Y, Wu X, Ren J, Lee MS, Lee S, Huang L (2017) Modulation on brain gray matter activity and white matter integrity by APOE ε4 risk gene in cognitively intact elderly: a multimodal neuroimaging study. Behav Brain Res 322(Pt A):100–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2017.01.027
Canal-Rivero M, Tordesillas-Gutierrez D, Ruiz-Veguilla M, de la Ortiz-Garcia VF, Cuevas-Esteban J, de Marco EL, Vazquez-Bourgon J, Ayesa-Arriola R, Crespo-Facorro B (2020) Brain grey matter abnormalities in first episode non-affective psychosis patients with suicidal behaviours: the role of neurocognitive functioning. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 102:109948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2020.109948
Chen Z, Peng W, Sun H, Kuang W, Li W, Jia Z, Gong Q (2016) High-field magnetic resonance imaging of structural alterations in first-episode, drug-naive patients with major depressive disorder. Transl Psychiatry 6(11):e942. https://doi.org/10.1038/tp.2016.209
Cho H, Yang DW, Shon YM, Kim BS, Kim YI, Choi YB, Lee KS, Shim YS, Yoon B, Kim W, Ahn KJ (2008) Abnormal integrity of corticocortical tracts in mild cognitive impairment: a diffusion tensor imaging study. J Korean Med Sci 23(3):477–483. https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2008.23.3.477
Dazzan P, Soulsby B, Mechelli A, Wood SJ, Velakoulis D, Phillips LJ, Yung AR, Chitnis X, Lin A, Murray RM, McGorry PD, McGuire PK, Pantelis C (2012) Volumetric abnormalities predating the onset of schizophrenia and affective psychoses: an MRI study in subjects at ultrahigh risk of psychosis. Schizophr Bull 38(5):1083–1091. https://doi.org/10.1093/schbul/sbr035
De Francisco Carvalho L, Pianowski G, Gonçalves AP (2019) Dimensional clinical personality inventory-2: investigating key factors on the assessment of dependent personality disorder. Psychol Health Med 24(6):732–738. https://doi.org/10.1080/13548506.2018.1554254
Deo AA, Grill RJ, Hasan KM, Narayana PA (2006) In vivo serial diffusion tensor imaging of experimental spinal cord injury. J Neurosci Res 83(5):801–810. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.20783
Di X, Azeez A, Li X, Haque E, Biswal BB (2018) Disrupted focal white matter integrity in autism spectrum disorder: a voxel-based meta-analysis of diffusion tensor imaging studies. Prog Neuro-psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 82:242–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2017.11.007
Domen PA, Michielse S, Gronenschild E, Habets P, Roebroeck A, Schruers K, van Os J, Marcelis M (2013) Microstructural white matter alterations in psychotic disorder: a family-based diffusion tensor imaging study. Schizophr Res 146(1–3):291–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2013.03.002
Escoffier N, Zhong J, Schirmer A, Qiu A (2013) Emotional expressions in voice and music: same code, same effect? Hum Brain Mapp 34(8):1796–1810. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.22029
Fitzgerald PB, Srithiran A, Benitez J, Daskalakis ZZ, Oxley TJ, Kulkarni J, Egan GF (2008) An fMRI study of prefrontal brain activation during multiple tasks in patients with major depressive disorder. Hum Brain Mapp 29(4):490–501. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.20414
Flandin G, Friston KJ (2019) Analysis of family-wise error rates in statistical parametric mapping using random field theory. Hum Brain Mapp 40(7):2052–2054. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.23839
Furnham A (2018) A big five facet analysis of sub-clinical dependent personality disorder (dutifulness). Psychiatry Res 270:622–626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2018.10.052
Göbel A, Göttlich M, Heldmann M, Georges R, Nieberding R, Rogge B, Sartorius A, Brabant G, Münte TF (2019) Experimentally induced subclinical hypothyroidism causes decreased functional connectivity of the cuneus: a resting state fMRI study. Psychoneuroendocrinology 102:158–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2018.12.012
Good CD, Johnsrude IS, Ashburner J, Henson RN, Friston KJ, Frackowiak RS (2001) A voxel-based morphometric study of ageing in 465 normal adult human brains. Neuroimage 14(1 Pt 1):21–36. https://doi.org/10.1006/nimg.2001.0786
Gude T, Karterud S, Pedersen G, Falkum E (2006) The quality of the diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, fourth edition dependent personality disorder prototype. Compr Psychiatry 47(6):456–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comppsych.2006.02.007
Haber SN, Behrens TE (2014) The neural network underlying incentive-based learning: implications for interpreting circuit disruptions. Neuron 83(5):1019–1039. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2014.08.031
Hamlat EJ, Young JF, Hankin BL (2020) Developmental course of personality disorder traits in childhood and adolescence. J Pers Disord. https://doi.org/10.1521/pedi_2019_33_433
Heesink L, Edward Gladwin T, Terburg D, van Honk J, Kleber R, Geuze E (2017) Proximity alert! Distance related cuneus activation in military veterans with anger and aggression problems. Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging 266:114–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pscychresns.2017.06.012
Henderson SE, Johnson AR, Vallejo AI, Katz L, Wong E, Gabbay V (2013) A preliminary study of white matter in adolescent depression: relationships with illness severity, anhedonia, and irritability. Front Psychiatry 4:152. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2013.00152
Holleran L, Ahmed M, Anderson-Schmidt H, McFarland J, Emsell L, Leemans A, Scanlon C, Dockery P, McCarthy P, Barker GJ, McDonald C, Cannon DM (2014) Altered interhemispheric and temporal lobe white matter microstructural organization in severe chronic schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 39(4):944–954. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2013.294
Hulkower MB, Poliak DB, Rosenbaum SB, Zimmerman ME, Lipton ML (2013) A decade of DTI in traumatic brain injury: 10 years and 100 articles later. Am J Neuroradiol 34(11):2064–2074. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A3395
Hyett MP, Perry A, Breakspear M, Wen W, Parker GB (2018) White matter alterations in the internal capsule and psychomotor impairment in melancholic depression. PLoS ONE 13(4):e0195672. https://doi.org/10.1371/journalpone0195672
Jiang J, Borowiak K, Tudge L, Otto C, von Kriegstein K (2016) Neural mechanisms of eye contact when listening to another person talking. Soc Cognit Affect Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.1093/scan/nsw127
Kang H, Zhang M, Ouyang M, Guo R, Yu Q, Peng Q, Zhang N, Zhang Y, Duan Y, Tang X, Mishra V, Fang F, Li W, Huang H, Peng Y (2018) Brain white matter microstructural alterations in children of type I gaucher disease characterized with diffusion tensor MR imaging. Eur J Radiol 102:22–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2018.02.014
Karababa IF, Bayazıt H, Kılıçaslan N, Celik M, Cece H, Karakas E, Selek S (2015) Microstructural changes of anterior corona radiata in bipolar depression. Psychiatry Investig 12(3):367–371. https://doi.org/10.4306/pi.2015.12.3.367
Kerestes R, Ladouceur CD, Meda S, Nathan PJ, Blumberg HP, Maloney K, Ruf B, Saricicek A, Pearlson GD, Bhagwagar Z, Phillips ML (2012) Abnormal prefrontal activity subserving attentional control of emotion in remitted depressed patients during a working memory task with emotional distracters. Psychol Med 42(1):29–40. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291711001097
Korgaonkar MS, Grieve SM, Etkin A, Koslow SH, Williams LM (2013) Using standardized fMRI protocols to identify patterns of prefrontal circuit dysregulation that are common and specific to cognitive and emotional tasks in major depressive disorder: first wave results from the iSPOT-D study. Neuropsychopharmacology 38(5):863–871. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2012.252
Kosaka H, Omori M, Munesue T, Ishitobi M, Matsumura Y, Takahashi T, Narita K, Murata T, Saito DN, Uchiyama H, Morita T, Kikuchi M, Mizukami K, Okazawa H, Sadato N, Wada Y (2010) Smaller insula and inferior frontal volumes in young adults with pervasive developmental disorders. Neuroimage 50(4):1357–1363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.01.085
Kropf E, Syan SK, Minuzzi L, Frey BN (2019) From anatomy to function: the role of the somatosensory cortex in emotional regulation. Braz J Psychiatry 41(3):261–269. https://doi.org/10.1590/1516-4446-2018-0183
Lee SJ, Kim B, Oh D, Kim MK, Kim KH, Bang SY, Choi TK, Lee SH (2016) White matter alterations associated with suicide in patients with schizophrenia or schizophreniform disorder. Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging 248:23–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pscychresns.2016.01.011
Lee WT, Lin JH, Weng WC, Peng SS (2017) Microstructural changes of brain in patients with aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase deficiency. Hum Brain Mapp 38(3):1532–1540. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.23470
Lener MS, Wong E, Tang CY, Byne W, Goldstein KE, Blair NJ, Haznedar MM, New AS, Chemerinski E, Chu KW, Rimsky LS, Siever LJ, Koenigsberg HW, Hazlett EA (2015) White matter abnormalities in schizophrenia and schizotypal personality disorder. Schizophr Bull 41(1):300–310. https://doi.org/10.1093/schbul/sbu093
Li W, Zhu J, Li Q, Ye J, Chen J, Liu J, Li Z, Li Y, Yan X, Wang Y, Wang W (2016) Brain white matter integrity in heroin addicts during methadone maintenance treatment is related to relapse propensity. Brain Behav 6(2):e00436. https://doi.org/10.1002/brb3.436
Liu J, Yin C, Xia S, Jia L, Guo Y, Zhao Z, Li X, Han Y, Jia J (2013) White matter changes in patients with amnestic mild cognitive impairment detected by diffusion tensor imaging. PLoS ONE 8(3):e59440. https://doi.org/10.1371/journalpone0059440
Liu K, Zhang T, Zhang Q, Sun Y, Wu J, Lei Y, Chu WC, Mok VC, Wang D, Shi L (2016) Characterization of the fiber connectivity profile of the cerebral cortex in schizotypal personality disorder: a pilot study. Front Psychol 7:809. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2016.00809
Lloyd DM, McGlone FP, Yosipovitch G (2015) Somatosensory pleasure circuit: from skin to brain and back. Exp Dermatol 24(5):321–324. https://doi.org/10.1111/exd.12639
Lou J, Sun Y, Cui Z, Gong L (2021) Common and distinct patterns of gray matter alterations in borderline personality disorder and posttraumatic stress disorder: A dual meta-analysis. Neurosci Lett 741:135376. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33221476/
Lou J, Sun Y, Cui Z, Gong L (2023) Structural brain alterations in young adult males with narcissistic personality disorder: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Int J Neurosci 133(2):133–140. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207454.2021.1896504
Lövblad KO, Schaller K, Vargas MI (2014) The fornix and limbic system. Semin Ultrasound CT MR 35(5):459–473. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.sult.2014.06.005
Maccaferri GE, Dunker-Scheuner D, De Roten Y, Despland JN, Sachse R, Kramer U (2020) Psychotherapy of dependent personality disorder: the relationship of patient-therapist interactions to outcome. Psychiatry 83(2):179–194. https://doi.org/10.1080/00332747.2019.1675376
Mastropietro A, Rizzo G, Fontana L, Figini M, Bernardini B, Straffi L, Marcheselli S, Ghirmai S, Nuzzi NP, Malosio ML, Grimaldi M (2019) Microstructural characterization of corticospinal tract in subacute and chronic stroke patients with distal lesions by means of advanced diffusion MRI. Neuroradiology 61(9):1033–1045. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-01902249-2
Matsubara T, Suzuki K, Okamura M, Shiina T, Miyamoto M, Nakamura T, Hirata K (2017) A 70-year-old woman presenting with restless shoulder following posterior internal capsule infarction. Rinsho Shinkeigaku 57(11):711–715. https://doi.org/10.5692/clinicalneurol.cn-001048
Matsukawa H, Shinoda M, Fujii M, Takahashi O, Yamamoto D, Murakata A, Ishikawa R (2011) Genu of corpus callosum in diffuse axonal injury induces a worse 1-year outcome in patients with traumatic brain injury. Acta Neurochir 153(8):1687–1693. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-011-1002-9
Matsuo K, Glahn DC, Peluso MA, Hatch JP, Monkul ES, Najt P, Sanches M, Zamarripa F, Li J, Lancaster JL, Fox PT, Gao JH, Soares JC (2007) Prefrontal hyperactivation during working memory task in untreated individuals with major depressive disorder. Mol Psychiatry 12(2):158–166. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001894
Mcclintock AS, Mccarrick SM (2017) An examination of dependent personality disorder in the alternative DSM-5 model for personality disorders. J Psychopathol Behav Assess. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10862-017-9621-y
Meng X, Jiang R, Lin D, Bustillo J, Jones T, Chen J, Yu Q, Du Y, Zhang Y, Jiang T, Sui J, Calhoun VD (2017) Predicting individualized clinical measures by a generalized prediction framework and multimodal fusion of MRI data. Neuroimage 145:218–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.05.026
Min Y, Yuan-Meng H, Wen-Yu L (2013) A cross-sectional study of xiangxi minority senior middle school students' personality dysfunction. Chin J Clin Psychol 21(4):620–619.
Mirowitz S, Sartor K, Gado M, Torack R (1989) Focal signal-intensity variations in the posterior internal capsule: normal MR findings and distinction from pathologic findings. Radiology 172(2):535–539. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiology.172.2.2748836
Mulder R, Singh AB, Hamilton A, Das P, Outhred T, Morris G, Bassett D, Baune BT, Berk M, Boyce P, Lyndon B, Parker G, Malhi GS (2018) The limitations of using randomised controlled trials as a basis for developing treatment guidelines. Evid Based Ment Health 21(1):4–6. https://doi.org/10.1136/eb-2017-102701
Murata Y, Higo N (2016) Development and characterization of a macaque model of focal internal capsular infarcts. PLoS ONE 11(5):e0154752. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.015475241
Navran L (1954) A rationally derived MMPI Scale to measure dependence. J Consult Psychol 18(3):192. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0056592
Nierenberg J, Salisbury DF, Levitt JJ, David EA, McCarley RW, Shenton ME (2005) Reduced left angular gyrus volume in first-episode schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 162(8):1539–1541. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.162.8.1539
Niznikiewicz M et al (2000) Abnormal angular gyrus asymmetry in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 157(3):428–437. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.157.3.428
Nobre AC, Sebestyen GN, Gitelman DR, Mesulam MM, Frackowiak RS, Frith CD (1997) Functional localization of the system for visuospatial attention using positron emission tomography. Brain 120(3):515–533. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/120.3.515
Olson EA, Collins PF, Hooper CJ, Muetzel R, Lim KO, Luciana M (2009) White matter integrity predicts delay discounting behavior in 9- to 23-year-olds: a diffusion tensor imaging study. J Cogn Neurosci 21(7):1406–1421. https://doi.org/10.1162/jocn.2009.21107
Parise M, Kubo TT, Doring TM, Tukamoto G, Vincent M, Gasparetto EL (2014) Cuneus and fusiform cortices thickness is reduced in trigeminal neuralgia. J Headache Pain 15(1):17. https://doi.org/10.1186/1129-2377-15-17
Park KM, Shin KJ, Ha SY, Park J, Kim SE (2014) Isolated rotational vertigo due to internal capsular infarction. J Neuroophthalmol 34(1):61–63. https://doi.org/10.1097/WNO.0000000000000088
Pickut BA, Van Hecke W, Kerckhofs E, Mariën P, Vanneste S, Cras P, Parizel PM (2013) Mindfulness based intervention in Parkinson’s disease leads to structural brain changes on MRI: a randomized controlled longitudinal trial. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 115(12):2419–2425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2013.10.002
Planetta PJ, Servos P (2012) The postcentral gyrus shows sustained fMRI activation during the tactile motion aftereffect. Exp Brain Res 216(4):535–544. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-011-2957-8
Polosan M, Baciu M, Cousin E, Perrone M, Pichat C, Bougerol T (2011) An fMRI study of the social competition in healthy subjects. Brain Cogn 77(3):401–411. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bandc.2011.08.018
Qin Y, Gu J-w, Li G-l, Xu X-h, Yu K, Gao F-b (2015) Cerebral vasospasm and corticospinal tract injury induced by a modified rat model of subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurol Sci 358(1–2):193–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2015.08.1536
Ranzenberger LR, Snyder T (2022) Diffusion tensor imaging. StatPearls Publishing, Treasure Island
Riegel M, Wierzba M, Grabowska A, Jednorog K, Marchewka A (2016) Effect of emotion on memory for words and their context. J Comp Neurol 524(8):1636–1645. https://doi.org/10.1002/cne.23928
Rushworth MF, Noonan MP, Boorman ED, Walton ME, Behrens TE (2011) Frontal cortex and reward-guided learning and decision-making. Neuron 70(6):1054–1069. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2011.05.014
Sachse R, Kramer U (2018) Clarification-oriented psychotherapy of dependent personality disorder. J Contemp Psychother. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10879-018-9397-8
Saeedeh M, Arash K, Chunyan C, Parastu K, Jan PJ, Krishnakant GS, Azita K, Iqbal SH (2018) Quantitative assessment of changes in diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) metrics along the courses of the cortico-ponto‐cerebellar tracts secondary to supratentorial human brain glial tumors. Cancer Rep 1:e1108. https://doi.org/10.1002/cnr2.1108
Safadi Z, Grisot G, Jbabdi S, Behrens TE, Heilbronner SR, McLaughlin NCR, Mandeville J, Versace A, Phillips ML, Lehman JF, Yendiki A, Haber SN (2018) Functional segmentation of the anterior limb of the internal capsule: linking white matter abnormalities to specific connections. J Neurosci 38(8):2106–2117. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2335-17.2017
Saitoh O, Karns CM, Courchesne E (2001) Development of the hippocampal formation from 2 to 42 years: MRI evidence of smaller area dentata in autism. Brain: J Neurol 124(Pt 7):1317–1324. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/124.7.1317
Sampedro F, Farrés CCI, Soler J, Elices M, Schmidt C, Corripio I, Domínguez-Clavé E, Pomarol-Clotet E, Salvador R, Pascual JC (2021) Structural brain abnormalities in borderline personality disorder correlate with clinical severity and predict psychotherapy response. Brain Imaging Behav 15(5):2502–2512. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-021-00451-6
Scheffers F, van Vugt E, Lanctôt N, Lemieux A (2019) Experiences of (young) women after out of home placement: an examination of personality disorder symptoms through the lens of child maltreatment. Child Abuse Negl 92:116–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chiabu.2019.03.022
Seok JH, Choi S, Lim HK, Lee SH, Kim I, Ham BJ (2013) Effect of the COMT val158met polymorphism on white matter connectivity in patients with major depressive disorder. Neurosci Lett 545:35–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2013.04.012
Silver M, Moore CM, Villamarin V, Jaitly N, Hall JE, Rothschild AJ, Deligiannidis KM (2018) White matter integrity in medication-free women with peripartum depression: a tract-based spatial statistics study. Neuropsychopharmacol: Off Publ Am Coll Neuropsychopharmacol 43(7):1573–1580. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-018-0023-y
Sinanaj I, Cojan Y, Vuilleumier P (2015) Inter-individual variability in metacognitive ability for visuomotor performance and underlying brain structures. Conscious Cogn 36:327–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.concog.2015.07.012
Sivagnanasundaram S, Crossett B, Dedova I, Cordwell S, Matsumoto I (2007) Abnormal pathways in the genu of the corpus callosum in schizophrenia pathogenesis: a proteome study. Proteomics Clin Appl 1(10):1291–1305. https://doi.org/10.1002/prca.200700230
Solso S, Xu R, Proudfoot J, Hagler DJ Jr, Campbell K, Venkatraman V, Carter Barnes C, Ahrens-Barbeau C, Pierce K, Dale A, Eyler L, Courchesne E (2016) Diffusion tensor imaging provides evidence of possible axonal overconnectivity in frontal lobes in autism spectrum disorder toddlers. Biol Psychiatry 79(8):676–684. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2015.06.029
Starrs CJ, Abela JRZ, Zuroff DC, Amsel R, Shih JH, Yao S, Zhu XZ, Hong W (2017) Predictors of stress generation in adolescents in Mainland China. J Abnorm Child Psychol 45(6):1207–1219. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-016-0239-4
Takeuchi H, Taki Y, Nouchi R, Yokoyama R, Kotozaki Y, Nakagawa S, Sekiguchi A, Iizuka K, Yamamoto Y, Hanawa S, Araki T, Miyauchi CM, Sakaki K, Nozawa T, Ikeda S, Yokota S, Magistro D, Sassa Y, Kawashima R (2018) The effects of family socioeconomic status on psychological and neural mechanisms as well as their sex differences. Front Hum Neurosci 12:543. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2018.00543
Tan AS, Chew QH, Sim K (2020) Cerebral white matter changes in deficit and non-deficit subtypes of schizophrenia. J Neural Transm 127(7):1073–1079. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-020-02207-w
Tyrer H, Tyrer P, Barrett B (2013) Influence of dependent personality status on the outcome and health service costs of health anxiety. Int J Soc Psychiatry 59(3):274–280. https://doi.org/10.1177/0020764012438483
van den Heuvel MP, Mandl RC, Kahn RS, Hulshoff Pol HE (2009) Functionally linked resting-state networks reflect the underlying structural connectivity architecture of the human brain. Hum Brain Mapp 30(10):3127–3141. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.20737
Vanni S, Tanskanen T, Seppa M (2001) Coinciding early activation of the human primary visual cortex and anteromedial cuneus. Proc Natl Acad Sci 98(5):2776–2780. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.041600898
Vasic N, Walter H, Sambataro F, Wolf RC (2009) Aberrant functional connectivity of dorsolateral prefrontal and cingulate networks in patients with major depression during working memory processing. Psychol Med 39(6):977–987. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291708004443
Versaevel C, Martin JB, Lajugie C (2017) Links between depressive disorders and dependent personality disorders: the important effect of locus of control. L’Encephale 43(3):217–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.encep.2015.12.014
Vollm BA, Taylor AN, Richardson P, Corcoran R, Stirling J, McKie S, Deakin JF, Elliott R (2006) Neuronal correlates of theory of mind and empathy: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study in a nonverbal task. Neuroimage 29(1):90–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2005.07.022
Wang J, Fan Y, Dong Y, Ma M, Dong Y, Niu Y, Jiang Y, Wang H, Wang Z, Wu L, Sun H, Cui C (2018) Combining gray matter volume in the cuneus and the cuneus-prefrontal connectivity may predict early relapse in abstinent alcohol-dependent patients. PLoS ONE 13(5):e0196860. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0196860
Welander-Vatn A, Ystrom E, Tambs K, Neale MC, Kendler KS, Reichborn-Kjennerud T, Knudsen GP (2016) The relationship between anxiety disorders and dimensional representations of DSM-IV personality disorders: a co-twin control study. J Affect Disord 190:349–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2015.09.038
Weyandt L, Swentosky A, Gudmundsdottir BG (2013) Neuroimaging and ADHD: fMRI, PET, DTI findings, and methodological limitations. Dev Neuropsychol 38(4):211–225. https://doi.org/10.1080/87565641.2013.783833
Wolff JJ, Gu H, Gerig G, Elison JT, Styner M, Gouttard S, Botteron KN, Dager SR, Dawson G, Estes AM, Evans AC, Hazlett HC, Kostopoulos P, McKinstry RC, Paterson SJ, Schultz RT, Zwaigenbaum L, Piven J (2012) Differences in white matter fiber tract development present from 6 to 24 months in infants with autism. Am J Psychiatry 169(6):589–600. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.2011.11091447
Xu J, Rasmussen IA, Lagopoulos J, Haberg A (2007) Diffuse axonal injury in severe traumatic brain injury visualized using high-resolution diffusion tensor imaging. J Neurotrauma 24(5):753–765. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2006.0208
Xu Y, Zheng R, Guo H, Wei Y, Wen B, Dai S, Han S, Cheng J, Zhang Y (2023) Structural and functional deficits and couplings in severe and moderate OCD. J Psychiatr Res 160:240–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2023.02.022
Yang YP, Shen DY, Wang JY (2002) The reliability and validity of PDQ-4 + in China. Chin J Clin Psychol 03:165–168.
Yin B, Li DD, Huang H, Gu CH, Bai GH, Hu LX, Zhuang JF, Zhang M (2019) Longitudinal changes in diffusion tensor imaging following mild traumatic brain Injury and correlation with outcome. Front Neural Circuits 13:28. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncir.2019.00028
Yoshimura S, Sato W, Kochiyama T, Uono S, Sawada R, Kubota Y, Toichi M (2017) Gray matter volumes of early sensory regions are associated with individual differences in sensory processing. Hum Brain Mapp 38(12):6206–6217. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.23822
Yoshino A, Okamoto Y, Doi M, Okada G, Takamura M, Ichikawa N, Yamawaki S (2017) Functional alterations of Postcentral gyrus modulated by angry facial expressions during intraoral tactile stimuli in patients with burning mouth syndrome: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Front Psychiatry 8:224. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2017.00224
Zarnowski O, Ziton S, Holmberg R, Musto S, Riegle S, Van Antwerp E, Santos-Nunez G (2021) Functional MRI findings in personality disorders: a review. J Neuroimaging 31(6):1049–1066. https://doi.org/10.1111/jon.12924
Zhou SY, Suzuki M, Takahashi T, Hagino H, Kawasaki Y, Matsui M, Seto H, Kurachi M (2007) Parietal lobe volume deficits in schizophrenia spectrum disorders. Schizophr Res 89(1–3):35–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2006.08.032
Zhou L, Zhao Y, Liu X, Kuang W, Zhu H, Dai J, He M, Lui S, Kemp GJ, Gong Q (2018) Brain gray and white matter abnormalities in preterm-born adolescents: a meta-analysis of voxel-based morphometry studies. PLoS ONE 13(10):e0203498. https://doi.org/10.1371/journalpone0203498
Zhuo C, Lin X, Wang C, Song X, Xu X, Li G, Xu Y, Tian H, Zhang Y, Wang W, Zhou C (2020) Unified and disease specific alterations to brain structure in patients across six categories of mental disorders who experience own-thought auditory verbal hallucinations: a pilot study. Brain Res Bull 160:33–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2020.04.001
Acknowledgements
We thank Professor Sun for revising the previous manuscript.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YS contributed to the study’s conception and design. Material preparation was performed by LM. QZ was responsible for data collection. JL and YL went through the data analysis. The first draft of the manuscript was written by ZC and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose. The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics Approval
Ethics approval was received for this study from the institutional ethical committee of Dalian Medical University. The study`s methods were carried out in compliance with the Declaration of the Helsinki-World Health Organization`s standard ethical guidelines.
Consent to Participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Armida Mucci.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, Z., Meng, L., Zhang, Q. et al. White and Gray Matter Abnormalities in Young Adult Females with Dependent Personality Disorder: A Diffusion-Tensor Imaging and Voxel-Based Morphometry Study. Brain Topogr 37, 102–115 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-023-01013-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-023-01013-3