Abstract
Purpose
Erythritol is a valuable compound as sweetener and chemical material however cannot be fermented from the abundant substrate xylose.
Methods
The strain Trichosporonoides oedocephalis ATCC 16958 was employed to produce polyols including xylitol and erythritol by metabolic engineering approaches.
Results
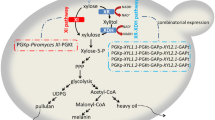
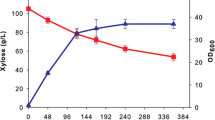
The introduction of a substrate-specific ribose-5-phosphate isomerase endowed T. oedocephalis with xylose-assimilation activity to produce xylitol, and eliminated glycerol production simultaneously. A more value-added product, erythritol was produced by further introducing a homologous xylulose kinase. The carbon flux was redirected from xylitol to erythritol by adding high osmotic pressure. The production of erythritol was improved to 46.5 g/L in flasks by fermentation adjustment, and the process was scaled up in a 5-L fermentor, with a 40 g/L erythritol production after 120 h, and a time–space yield of 0.56 g/L/h.
Conclusion
This study demonstrated the potential of T. oedocephalis in the synthesis of multiple useful products from xylose.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amada Y, Watanabe H, Hirai Y et al (2012) Production of biobutanediols by the hydrogenolysis of erythritol. ChemSusChem 5:1991–1999. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.201200121
Burschäpers J, Schustolla D, Schügerl K et al (2002) Engineering aspects of the production of sugar alcohols with the osmophilic yeast Moniliella tomentosa var pollinis: Part 2. Batch and fed-batch operation in bubble column and airlift tower loop if reactors. Process Biochem 38:559–570. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(02)00179-6
Carly F, Gamboa-Melendez H, Vandermies M et al (2017) Identification and characterization of EYK1, a key gene for erythritol catabolism in Yarrowia lipolytica. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101:6587–6596. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8361-y
Chi P, Wang S, Ge X et al (2019) Efficient D-threitol production by an engineered strain of Yarrowia lipolytica overexpressing xylitol dehydrogenase gene from Scheffersomyces stipitis. Biochem Eng J 149:107259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2019.107259
den Hartog GJM, Boots AW, Adam-Perrot A et al (2010) Erythritol is a sweet antioxidant. Nutrition 26:449–458. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2009.05.004
Erian AM, Sauer M (2022) Utilizing yeasts for the conversion of renewable feedstocks to sugar alcohols—a review. Bioresour Technol 346:126296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2021.126296
Fox KJ, Prather KLJ (2020) Carbon catabolite repression relaxation in Escherichia coli: global and sugar-specific methods for glucose and secondary sugar co-utilization. Curr Opin Chem Eng 30:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coche.2020.05.005
Guo J, Li J, Chen Y et al (2016) Improving erythritol production of Aureobasidium pullulans from xylose by mutagenesis and medium optimization. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 180:717–727. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-016-2127-3
Guo Q, Ullah I, Zheng L-J et al (2022) Intelligent self-control of carbon metabolic flux in SecY-engineered Escherichia coli for xylitol biosynthesis from xylose-glucose mixtures. Biotechnol Bioeng 119:388–398. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.28002
Hentenaar DFM, De Waal YCM, Stewart RE et al (2021) Erythritol airpolishing in the non-surgical treatment of peri-implantitis: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Oral Implants Res 32:840–852. https://doi.org/10.1111/clr.13757
Hollinshead W, He L, Tang YJ (2014) Biofuel production: an odyssey from metabolic engineering to fermentation scale-up. Front Microbiol 5:344. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2014.00344
Jagtap SS, Rao CV (2018) Production of D-arabitol from D-xylose by the oleaginous yeast Rhodosporidium toruloides IFO0880. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102:143–151. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-017-8581-1
Jo S, Yoon J, Lee S-M et al (2017) Modular pathway engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum to improve xylose utilization and succinate production. J Biotechnol 258:69–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2017.01.015
Kang P, Li L, Yan L et al (2019) Enhancement of erythritol production in Trichosporonoides oedocephalis by regulating cellular morphology with betaine. Chem Pap 73:2065–2072. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-019-00766-1
Kayingo G, Kilian SG, Prior BA (2001) Conservation and release of osmolytes by yeasts during hypo-osmotic stress. Arch Microbiol 177:29–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-001-0358-2
Khatape AB, Dastager SG, Rangaswamy V (2022) An overview of erythritol production by yeast strains. FEMS Microbiol Lett 369:fnac107. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsle/fnac107
Kim SR, Park Y-C, Jin Y-S, Seo J-H (2013) Strain engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for enhanced xylose metabolism. Biotechnol Adv 31:851–861. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2013.03.004
Kim J, Hwang S, Lee S-M (2022) Metabolic engineering for the utilization of carbohydrate portions of lignocellulosic biomass. Metab Eng 71:2–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2021.10.002
Kobayashi Y, Iwata H, Mizushima D et al (2015a) Erythritol production by Moniliella megachiliensis using nonrefined glycerol waste as carbon source. Lett Appl Microbiol 60:475–480. https://doi.org/10.1111/lam.12391
Kobayashi Y, Iwata H, Yoshida J et al (2015b) Metabolic correlation between polyol and energy-storing carbohydrate under osmotic and oxidative stress condition in Moniliella megachiliensis. J Biosci Bioeng 120:405–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2015.02.014
Lee S-M, Jellison T, Alper HS (2014) Systematic and evolutionary engineering of a xylose isomerase-based pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae for efficient conversion yields. Biotechnol Biofuels 7:122. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-014-0122-x
Li L, Yang T, Guo W et al (2016a) Construction of an efficient mutant strain of trichosporonoides oedocephalis with HOG1 gene deletion for production of erythritol. J Microbiol Biotechnol 26:700–709. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1510.10049
Li L, Yang T, Hu C et al (2016b) Transformation of the yeast Trichosporonoides oedocephalis. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 109:305–309. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-015-0633-x
Li L, Gu L, Ju X et al (2017) Osmotic pressure regulation using KCl for enhanced erythritol production using trichosporonoides oedocephalis ATCC 16958. Food Sci Technol Res 23:793–800. https://doi.org/10.3136/fstr.23.793
Li L, Kang P, Ju X et al (2018) Enhancement of erythritol production by Trichosporonoides oedocephalis ATCC 16958 through regulating key enzyme activity and the NADPH/NADP ratio with metal ion supplementation. Prep Biochem Biotechnol 48:257–263. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826068.2018.1425712
Liang P, Cao M, Li J et al (2023) Expanding sugar alcohol industry: microbial production of sugar alcohols and associated chemocatalytic derivatives. Biotechnol Adv 64:108105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2023.108105
Martău GA, Coman V, Vodnar DC (2020) Recent advances in the biotechnological production of erythritol and mannitol. Crit Rev Biotechnol 40:608–622. https://doi.org/10.1080/07388551.2020.1751057
Palladino F, Rodrigues RCLB, da Silva SP, Rosa CA (2023) Strategy to reduce acetic acid in sugarcane bagasse hemicellulose hydrolysate concomitantly with xylitol production by the promising yeast Cyberlindnera xylosilytica in a bioreactor. Biotechnol Lett 45:263–272. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-022-03337-9
Rice T, Zannini E, Arendt KE, Coffey A (2020) A review of polyols—biotechnological production, food applications, regulation, labeling and health effects. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 60:2034–2051. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2019.1625859
Rosa CA, Jindamorakot S, Limtong S et al (2009) Synonymy of the yeast genera Moniliella and Trichosporonoides and proposal of Moniliella fonsecae sp. nov. and five new species combinations. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:425–429. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.65117-0
Tang H, Ju X, Zhao J, Li L (2021) Engineering ribose-5-phosphate isomerase B from a central carbon metabolic enzyme to a promising sugar biocatalyst. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 105:509–523. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-11075-z
Tang H, Zhou Z, Chen Z et al (2022) Development of a sugar isomerase cascade to convert D-xylose to rare sugars. Mol Catal 531:112672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcat.2022.112672
Tang H, Chen Z, Shao Y et al (2023) Development of an enzymatic cascade to systematically utilize lignocellulosic monosaccharide. J Sci Food Agric 103:1974–1980. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.12364
Wang B, Xu X, Fang Y et al (2022) Effect of different ratios of glycerol and erythritol on properties of corn starch-based films. Front Nutr 9:882682
Wasylenko TM, Stephanopoulos G (2015) Metabolomic and 13C-metabolic flux analysis of a xylose-consuming Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain expressing xylose isomerase. Biotechnol Bioeng 112:470–483. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.25447
Yang L-B, Zhan X-B, Zheng Z-Y et al (2014) A novel osmotic pressure control fed-batch fermentation strategy for improvement of erythritol production by Yarrowia lipolytica from glycerol. Bioresour Technol 151:120–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.10.031
Yuhe L, Steven-Friso K, den Gil VB et al (2020) A sustainable wood biorefinery for low–carbon footprint chemicals production. Science 367:1385–1390. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aau1567
Zhang L, Chen Z, Wang J et al (2021a) Stepwise metabolic engineering of Candida tropicalis for efficient xylitol production from xylose mother liquor. Microb Cell Fact 20:105. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12934-021-01596-1
Zhang L, Nie M-Y, Liu F et al (2021b) Multiple gene integration to promote erythritol production on glycerol in Yarrowia lipolytica. Biotechnol Lett 43:1277–1287. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-021-03113-1
Zhou H, Cheng J, Wang BL et al (2012) Xylose isomerase overexpression along with engineering of the pentose phosphate pathway and evolutionary engineering enable rapid xylose utilization and ethanol production by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Metab Eng 14:611–622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2012.07.011
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant no. 21676173), the Agricultural Infrastructure Project of Suzhou Science and Technology Development Plan (Grant no. SNG2022057) and the Graduate Research and Innovation Projects of Jiangsu Province (Grant no. KYCX21_3042).
Supplementary data
Table S1—Strains and plasmids used in this study.
Table S2—Primers and sequences used in this study.
Table S3—Comparison of erythritol production by strains with different carbon sources.
Table S4—Comparison of xylitol production by strains with different carbon sources.
Table S5—Summary of fermentation with xylose and glucose.
Figure S1—Construction of expression vectors. A) agarose gel analysis of GAL1, B) OsRpiB, C) xylulose kinase, and D) xylitol dehydrogenase genes; E) plasmid diagram of three vectors that contain OsRpiB, OsRpiB+ xylulose kinase, and OsRpiB+ xylulose kinase+ xylitol dehydrogenase genes respectively.
Figure S2—HPLC diagram of product analysis. A) TOR (OsRpiB containing strain) fermentation with xylose; B) TORKD fermentation with xylose; C) TORKD xylose-glucose cofermentation; the retention time of glucose, xylose, erythritol and xylitol is 15.7 min, 17.5 min, 23.3 min and 26.9 min.
Figure S3—HPLC diagram of product purity under different fermentation conditions.
Figure S4—Time courses of parameters in xylose concentration comparison. A) erythritol production, B) xylitol production, and C) variation of pH.
Funding
National Natural Science Foundation (Grant no. 21676173).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZD and YM: Investigation, Writing—original draft. ZC and LY: Writing—review & editing. XJ: Methodology, Supervision. LL: Funding acquisition, Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing—review & editing, Supervision.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals.
Consent to participations
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, Z., Mu, Y., Chen, Z. et al. Construction of a xylose metabolic pathway in Trichosporonoides oedocephalis ATCC 16958 for the production of erythritol and xylitol. Biotechnol Lett 45, 1529–1539 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-023-03428-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-023-03428-1