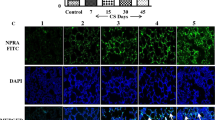
We studied the effect of cigarette smoke extract (CSE), LPS, or their combination on the activity and pyroptosis of pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells (PMVEC) in rats. PMVEC were cultured without treatment, with CSE in different concentrations (1-25%), with 20 ng/ml LPS, or with 20% CSE+20 ng/ml LPS. Cell viability was determined using the CCK8 kit, apoptosis was evaluated by flow cytometry, and cell morphology was evaluated using light microscopy. The content of IL-1β and IL-18 was measured by ELISA. CSE decreased cell viability in a dose-dependent manner. The morphology of cells in the CSE+LPS group showed the most significant cytomorphological changes and the highest pyroptosis rate. Flow cytometry showed that the apoptosis rates in the CSE and LPS groups were higher than in the control group, but the highest rate of apoptosis was revealed in the CSE+LPS group (p<0.01). The levels of IL-18 and IL-1β in the cell supernatant of the CSE, LPS, and CSE+LPS groups were significantly (p<0.01) increased in comparison with the control. These levels in the CSE+LPS group were higher (p<0.01) than in other groups. There were no differences between the CSE and LPS groups. Thus, the effect of CSE on cell viability is dose-dependent. Combined treatment with CSE+LPS can induce cell pyroptosis and increase the levels of inflammatory cytokines in PMVEC. These observations demonstrated that pyroptosis caused by CSE and LPS can play an important role in pulmonary vascular remodeling.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Galiè N, Humbert M, Vachiery JL, Gibbs S, Lang I, Torbicki A, Simonneau G, Peacock A, Vonk Noordegraaf A, Beghetti M, Ghofrani A, Gomez Sanchez MA, Hansmann G, Klepetko W, Lancellotti P, Matucci M, McDonagh T, Pierard LA, Trindade PT, Zompatori M, Hoeper M. 2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: The Joint Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS): Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT). Eur. Respir. J. 2015;46(4):903-975. https://doi.org/10.1183/13993003.01032-2015
Prins KW, Thenappan T. World Health Organization Group I Pulmonary Hypertension: Epidemiology and Pathophysiology. Cardiol. Clin. 2016;34(3):363-374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccl.2016.04.001
Elias AS, Oliveira GP, Ornellas DS, Morales MM, Capelozzi VL, Haddad R, Pelosi P, Rocco PR, Garcia CS. Effects of early and late pneumothorax drainage on the development of pulmonary oedema. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2014;195:27-36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resp.2014.02.004
Vande Walle L, Lamkanfi M. Pyroptosis. Curr. Biol. 2016;26(13):R568-R572. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2016.02.019
Li D, Ren W, Jiang Z, Zhu L. Regulation of the NLRP3 inflammasome and macrophage pyroptosis by the p38 MAPK signaling pathway in a mouse model of acute lung injury. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018;18(5):4399-4409. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2018.9427
Zhang MY, Jiang YX, Yang YC, Liu JY, Huo C, Ji XL, Qu YQ. Cigarette smoke extract induces pyroptosis in human bronchial epithelial cells through the ROS/NLRP3/caspase-1 pathway. Life Sci. 2021;269:119090. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119090
Tuder RM. Pulmonary vascular remodeling in pulmonary hypertension. Cell Tissue Res. 2017;367(3):643-649. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-016-2539-y
Solodushko V, Fouty B. Proproliferative phenotype of pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2007;292(3):L671-L677. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajplung.00304.2006
Synn AJ, Zhang C, Washko GR, Estépar RSJ, O’Connor GT, Li W, Mittleman MA, Rice MB. Cigarette Smoke Exposure and Radiographic Pulmonary Vascular Morphology in the Framingham Heart Study. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2019;16(6):698-706. https://doi.org/10.1513/AnnalsATS.201811-795OC
Colarusso C, Terlizzi M, Molino A, Pinto A, Sorrentino R. Role of the inflammasome in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Oncotarget. 2017;8(47):81813-81824. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.17850
Zhang H, Sun GY. LPS induces permeability injury in lung microvascular endothelium via AT(1) receptor. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2005;441(1):75-83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2005.06.022
Kratzer E, Tian Y, Sarich N, Wu T, Meliton A, Leff A, Birukova AA. Oxidative stress contributes to lung injury and barrier dysfunction via microtubule destabilization. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2012;47(5):688-697. https://doi.org/10.1165/rcmb.2012-0161OC
Rathinam VAK, Zhao Y, Shao F. Innate immunity to intracellular LPS. Nat. Immunol. 2019;20(5):527-533. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41590-019-0368-3
Liu B, He R, Zhang L, Hao B, Jiang W, Wang W, Geng Q. Inflammatory Caspases Drive Pyroptosis in Acute Lung Injury. Front. Pharmacol. 2021;12:631256. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.631256
Shi J, Gao W, Shao F. Pyroptosis: Gasdermin-Mediated Programmed Necrotic Cell Death. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2017;42(4):245-254. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2016.10.004
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 174, No. 12, pp. 698-704, December, 2022
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Liu, M., Liu, Y. et al. Cigarette Smoke Extract and Lipopolysaccharide Induce Pyroptosis in Pulmonary Microvascular Endothelial Cells of Rats. Bull Exp Biol Med 174, 728–733 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-023-05780-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-023-05780-8