Abstract
The survival of farmed fish can be threatened by incidence of Aeromonas hydrophila infection. In addition, gut infection may promote dysbiosis of gut flora and dysregulate immune response in gut-liver axis in teleost fish. The current study aimed to evaluate the pathogenesis of A. hydrophila on gut barrier breach and synchronized immune response in gut-liver axis of RCCs. RCCs were subjected to continuous anal-intubation with A. hydrophila. Midgut sections were stained with periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) and immune-related gene expressions and biochemical indices in gut-liver axis were investigated. The severe midgut injury was detected in RCC anal-intubated with A. hydrophila, along with atrophy of the midgut villi, and the expression levels of tight junction (TJ) genes were consistently lower than those of the control (P < 0.05). Moreover, RCC receiving anal intubation with A. hydrophila showed the upregulation of pathological indices and immure genes in the midgut and liver. These findings demonstrated that gut infection with A. hydrophila can significantly disrupt epithelial permeability to exacerbate gut barrier breach and increase bacterial burdens in tissues as well as dysregulate immune response in gut-liver axis of RCC.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article [and/or] its supplementary materials.
References
Abd-El-Malek AM (2017) Incidence and virulence characteristics of Aeromonas spp. in fish. Veterinary world 10:34
Albillos A, De Gottardi A, Rescigno M (2020) The gut-liver axis in liver disease: pathophysiological basis for therapy. Journal of hepatology 72:558–577
Anturaniemi J, Zaldívar-López S, Savelkoul HF, Elo K, Hielm-Björkman A (2020) The effect of atopic dermatitis and diet on the skin transcriptome in Staffordshire Bull Terriers. Frontiers in Veterinary Science:763
Atli G, Ariyurek SY, Kanak EG, Canli M (2015) Alterations in the serum biomarkers belonging to different metabolic systems of fish (Oreochromis niloticus) after Cd and Pb exposures. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology 40:508–515
Austin B (1998) The effects of pollution on fish health. Journal of applied microbiology 85:234S–242S
Awan F, Dong Y, Wang N, Liu J, Ma K, Liu Y (2018) The fight for invincibility: environmental stress response mechanisms and Aeromonas hydrophila. Microbial pathogenesis 116:135–145
Barrera-Chimal J, Pérez-Villalva R, Ortega JA, Uribe N, Gamba G, Cortés-González C et al (2014) Intra-renal transfection of heat shock protein 90 alpha or beta (Hsp90α or Hsp90β) protects against ischemia/reperfusion injury. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 29:301–312
Dee CT, Nagaraju RT, Athanasiadis EI, Gray C, Fernandez del Ama L, Johnston SA et al (2016) CD4-transgenic zebrafish reveal tissue-resident Th2-and regulatory T cell–like populations and diverse mononuclear phagocytes. The Journal of Immunology 197:3520–3530
Deng Y, Zhang Y, Chen H, Xu L, Wang Q, Feng J (2020) Gut–liver immune response and gut microbiota profiling reveal the pathogenic mechanisms of Vibrio harveyi in pearl gentian grouper (Epinephelus lanceolatus♂× E. fuscoguttatus♀). Frontiers in immunology 11:607754
Dong K, Chen W, Pan X, Wang H, Sun Y, Qian C et al (2022) FCER1G positively relates to macrophage infiltration in clear cell renal cell carcinoma and contributes to unfavorable prognosis by regulating tumor immunity. BMC cancer 22:1–20
Gao B, Jeong WI, Tian Z (2008) Liver: an organ with predominant innate immunity. Hepatology 47:729–736
Gray S, Stickler D, Bryant T (1990) The incidence of virulence factors in mesophilic Aeromonas species isolated from farm animals and their environment. Epidemiology & Infection 105:277–294
Holland MCH, Lambris JD (2002) The complement system in teleosts. Fish & Shellfish Immunology 12:399–420
Jeong MK, Kim B-H (2022) Grading criteria of histopathological evaluation in BCOP assay by various staining methods. Toxicological Research 38:9–17
Kagnoff MF, Eckmann L (1997) Epithelial cells as sensors for microbial infection. The Journal of clinical investigation 100:6–10
Kim YS, Ho SB (2010) Intestinal goblet cells and mucins in health and disease: recent insights and progress. Current gastroenterology reports 12:319–330
Kümmerer K (2004) Resistance in the environment. Journal of antimicrobial chemotherapy 54:311–320
Li Z, Wang ZW, Wang Y, Gui JF (2018) Crucian carp and gibel carp culture. Aquaculture in China: success stories and modern 25:149–157
Luo S-W, Wei W, Yang P, Lai C-M, Liang QJ, Liu Y et al (2019) Characterization of a CD59 in orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides). Fish & shellfish immunology 89:486–497
Ma X, Wang Y, Yin H, Hua L, Zhang X, Xiao J et al (2021) Down-regulated long non-coding RNA RMST ameliorates dopaminergic neuron damage in Parkinson’s disease rats via regulation of TLR/NF-κB signaling pathway. Brain research bulletin 174:22–30
Morrish E, Ruland J (2022) Cytotoxic FCER1G+ innate-like T cells: new potential for tumour immunotherapy. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy 7:204
Nielsen ME, Høi L, Schmidt A, Qian D, Shimada T, Shen J, Larsen J (2001) Is Aeromonas hydrophila the dominant motile Aeromonas species that causes disease outbreaks in aquaculture production in the Zhejiang Province of China? Diseases of aquatic organisms 46:23–29
Oliveira ST, Veneroni-Gouveia G, Costa MM (2012) Molecular characterization of virulence factors in Aeromonas hydrophila obtained from fish. Pesquisa Veterinária Brasileira 32:701–706
Portoles P, Rojo J, Golby A, Bonneville M, Gromkowski S, Greenbaum L et al (1989) Monoclonal antibodies to murine CD3 epsilon define distinct epitopes, one of which may interact with CD4 during T cell activation. Journal of immunology 142:4169–4175
Qi Z-H, Liu Y-F, Luo S-W, Chen C-X, Liu Y, Wang W-N (2013) Molecular cloning, characterization and expression analysis of tumor suppressor protein p53 from orange-spotted grouper, Epinephelus coioides in response to temperature stress. Fish & shellfish immunology 35:1466–1476
Rizwan S, ReddySekhar P, MalikAsrar B (2014) Reactive oxygen species in inflammation and tissue injury. Antioxidants & redox signaling
Rodger HD (2016) Fish disease causing economic impact in global aquaculture. Fish vaccines:1–34
Schäfer H, Mathey D, Hugo F, Bhakdi S (1986) Deposition of the terminal C5b-9 complement complex in infarcted areas of human myocardium. The Journal of Immunology 137:1945–1949
Schneeberger EE, Lynch RD (2004) The tight junction: a multifunctional complex. American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology 286:C1213–C1228
Shan Y, Zhang Y, Zhuo X, Li X, Peng J, Fang W (2016) Matrix metalloproteinase-9 plays a role in protecting zebrafish from lethal infection with Listeria monocytogenes by enhancing macrophage migration. Fish & shellfish immunology 54:179–187
Song X, Zhao J, Bo Y, Liu Z, Wu K, Gong C (2014) Aeromonas hydrophila induces intestinal inflammation in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella): an experimental model. Aquaculture 434:171–178
Tlaskalová-Hogenová H, Štěpánková R, Kozáková H, Hudcovic T, Vannucci L, Tučková L et al (2011) The role of gut microbiota (commensal bacteria) and the mucosal barrier in the pathogenesis of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases and cancer: contribution of germ-free and gnotobiotic animal models of human diseases. Cellular & molecular immunology 8:110–120
Uribe C, Folch H, Enríquez R, Moran G (2011) Innate and adaptive immunity in teleost fish: a review. Veterinarni Medicina 56:486
Wang L, Fan C, Xu W, Zhang Y, Dong Z, Xiang J et al (2017) Characterization and functional analysis of a novel C1q-domain-containing protein in Japanese flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Developmental & Comparative Immunology 67:322–332
Warner K, Hamza M, Oliver-Smith A, Renaud F, Julca A (2010) Climate change, environmental degradation and migration. Natural Hazards 55:689–715
Wischhusen P, Larroquet L, Durand T, Oger C, Galano J-M, Rocher A et al (2020) Oxidative stress and antioxidant response in rainbow trout fry exposed to acute hypoxia is affected by selenium nutrition of parents and during first exogenous feeding. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 155:99–113
Wu N, Song Y-L, Wang B, Zhang X-Y, Zhang X-J, Wang Y-L et al (2016) Fish gut-liver immunity during homeostasis or inflammation revealed by integrative transcriptome and proteome studies. Scientific reports 6:1–17
Xiong N-X, Fang Z-X, Kuang X-Y, Ou J, Luo S-W, Liu S-J (2023) Integrated analysis of gene expressions and metabolite features unravel immunometabolic interplay in hybrid fish (Carassius cuvieri♀× Carassius auratus red var♂) infected with Aeromonas hydrophila. Aquaculture 563:738981
Xiong N-X, Luo S-W, Fan L-F, Mao Z-W, Luo K-K, Liu S-J et al (2021) Comparative analysis of erythrocyte hemolysis, plasma parameters and metabolic features in red crucian carp (Carassius auratus red var) and triploid hybrid fish following Aeromonas hydrophila challenge. Fish & Shellfish Immunology 118:369–384
Xiong N-X, Mao Z-W, Ou J, Fan L-F, Chen Y, Luo S-W et al (2022a) Metabolite features and oxidative response in kidney of red crucian carp (Carassius auratus red var) after Aeromonas hydrophila challenge. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part C: Toxicology & Pharmacology 255:109293
Xiong N-X, Ou J, Fan L-F, Kuang X-Y, Fang Z-X, Luo S-W et al (2022b) Blood cell characterization and transcriptome analysis reveal distinct immune response and host resistance of different ploidy cyprinid fish following Aeromonas hydrophila infection. Fish & Shellfish Immunology 120:547–559
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, China (grant no. 31902363), Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China, China (grant no.2021JJ40340).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Fei Wang performed methodology and formal analysis. Zi-Le Qin and Wei-Sheng Luo performed methodology. Ning-Xia Xiong performed formal analysis and verification. Sheng-Wei Luo performed Conceptualization, supervision, project management and article writing.
The authors of this manuscript are all aware of the journal to which the manuscript was submitted, and all agree to continue to support the follow-up work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the case and use of animals were followed. Chinese animal welfare laws, guidelines and policies (GB/T 35892-2018).
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing of interests.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Patrice Forget
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
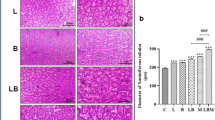
1. Severe tissue injury and GC hyperplasia was monitored in the midgut of A. hydrophila-perfused RCC.
2. RCC receiving gut infection with A. hydrophila showed a sharp decreased level of tight junction genes.
3. Increased bacterial burdens in tissues and altered immune response were monitored in gut-liver axis of RCC after continuous gut infection.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, F., Qin, ZL., Luo, WS. et al. Aeromonas hydrophila can modulate synchronization of immune response in gut-liver axis of red crucian carp via the breach of gut barrier. Aquacult Int 32, 871–885 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-023-01185-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-023-01185-6