Abstract
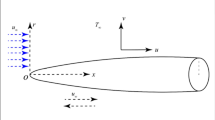
The melting phenomenon in two-dimensional (2D) flow of fourth-grade material over a stretching surface is explored. The flow is created via a stretching surface. A Darcy-Forchheimer (D-F) porous medium is considered in the flow field. The heat transport is examined with the existence of the Cattaneo-Christov (C-C) heat flux. The fourth-grade material is electrically conducting subject to an applied magnetic field. The governing partial differential equations (PDEs) are reduced into ordinary differential equations (ODEs) by appropriate transformations. The solutions are constructed analytically through the optimal homotopy analysis method (OHAM). The fluid velocity, temperature, and skin friction are examined under the effects of various involved parameters. The fluid velocity increases with higher material parameters and velocity ratio parameter while decreases with higher magnetic parameter, porosity parameter, and Forchheimer number. The fluid temperature is reduced with higher melting parameter while boosts against higher Prandtl number, magnetic parameter, and thermal relaxation parameter. Furthermore, the skin friction coefficient decreases against higher melting and velocity ratio parameters while increases against higher material parameters, thermal relaxation parameter, and Forchheimer number.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- u, v :
-
components of velocity
- v f :
-
kinematic fluid viscosity
- Pr :
-
Prandtl number
- x, y :
-
Cartesian coordinates
- k f :
-
fluid thermal conductivity
- τ w :
-
wall shear stress
- c pf :
-
fluid specific heat
- μ f :
-
fluid dynamic viscosity
- U 0, U ∞ :
-
stretching and free stream velocities
- f′, θ, φ :
-
dimensionless velocity, temperature, and concentration
- α f :
-
thermal diffusivity of the fluid
- α 11 :
-
viscoelastic parameter
- α 22 :
-
cross viscous parameter
- γ 11, γ 22, γ 33 :
-
fourth-grade fluid parameters
- M :
-
melting parameter
- Me :
-
magnetic parameter
- σ f :
-
electrical conductivity
- B 0 :
-
magnetic field strength
- c b :
-
drag coefficient
- φ1 :
-
porosity of the porous medium
- λ f :
-
fluid latent heat
- Fr :
-
Forchheimer number
- k 1 :
-
permeability of the porous medium
- λ :
-
porosity parameter
- T ∞ :
-
ambient temperature
- β :
-
third-grade fluid parameter
- ρ f :
-
fluid density
- τ*:
-
heat flux relaxation time
- β 11 :
-
Biot number for temperature
- Re x :
-
local Reynolds number
- ħ f, ħ θ, ħ φ :
-
convergence control variables
- β 22 :
-
Biot number for concentration
- f 0, θ 0, φ 0 :
-
initial guesses
- τ :
-
Cauchy stress tensor
- γ :
-
thermal relaxation parameter
- α i, β i, γ i :
-
material constants
- C s :
-
surface heat capacity
- T w :
-
wall temperature
- ψ :
-
stream function
- T 0 :
-
ambient temperature
- U e(x):
-
free-stream velocity
- ε f, ε θ :
-
average square residual errors at the mth-order approximation.
References
SALAWU, S. O., KAREEM, R. A., SHAMSHUDDIN, M. D., and KHAN, S. U. Double exothermic reaction of viscous dissipative Oldroyd 8-constant fluid and thermal ignition in a channel. Chemical Physics Letters, 760, 138011 (2020)
KHAN, S. U., AL-KHALED, K., and BHATTI, M. M. Bioconvection analysis for flow of Oldroyd-B nanofluid configured by a convectively heated surface with partial slip effects. Surfaces and Interface, 23, 100982 (2021)
WAQAS, M., HAYAT, T., ALSAEDI, A., and KHAN, W. A. Analytical evaluation of Oldroyd-B nanoliquid under thermo-solutal Robin conditions and stratifications. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 19, 105474 (2020)
AWAN, A. U., ABID, S., ULLAH, N., and NADEEM, S. Magnetohydrodynamic oblique stagnation point flow of second grade fluid over an oscillatory stretching surface. Results in Physics, 18, 103233 (2020)
KRISHNA, M. V., AHAMAD, N. A., and CHAMKHA, A. J. Hall and ion slip impacts on unsteady MHD convective rotating flow of heat generating/absorbing second grade fluid. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 60, 845–858 (2021)
HAYAT, T., SHAH, F., and ALSEADI, A. Cattaneo-Christov double diffusions and entropy generation in MHD second grade nanofluid flow by a Riga wall. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 119, 104824 (2020)
ARIFUZZAMAN, S. M., KHAN, M. S., AL-MAMUN, A., REZA-E-RABBI, S., BISWAS, P., and KARIM, I. Hydrodynamic stability and heat and mass transfer flow analysis of MHD radiative fourth-grade fluid through porous plate with chemical reaction. Journal of King Saud University—Science, 31, 1388–1398 (2019)
SOBAMOWO, M. G., YINUSA, A. A., and ALADENUSI, S. T. Impacts of magnetic field and thermal radiation on squeezing flow and heat transfer of third grade nanofluid between two disks embedded in a porous medium. Heliyon, 6, e03621 (2020)
HAYAT, T., MUHAMMAD, K., ALSAEDI, A., and AHMAD, B. Melting effect in squeezing flow of third-garde fluid with non-Fourier heat flux model. Physica Scripta, 94, 105705 (2019)
NANDEPPANAVAR, M. M., VAISHALI, S., KEMPARAJU, M. C., and RAVEENDRA, N. Theoretical analysis of thermal characteristics of Casson nano fluid flow past an exponential stretching sheet in Darcy porous media. Case Studies in Thermal Engineering, 21, 100717 (2020)
TURKYILMAZOGLU, M. Single phase nanofluids in fluid mechanics and their hydrodynamic linear stability analysis. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 187, 105171 (2020)
HAYAT, T., MUHAMMAD, K., and MOMANI, S. Melting heat and viscous dissipation in flow of hybrid nanomaterial: a numerical study via finite difference method. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry (2021) https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-021-10944-7
RASHIDI, M. M., GHAHREMANIAN, S., TOGHRAIE, D., and ROY, P. Effect of solid surface structure on the condensation flow of argon in rough nanochannels with different roughness geometries using molecular dynamics simulation. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer, 117, 104741 (2020)
RASOOL, G., CHAMKHA, A. J., MUHAMMAD, T., SHAFIQ, A., and KHAN, I. Darcy-Forchheimer relation in Casson type MHD nanofluid flow over non-linear stretching surface. Propulsion and Power Research, 9, 159–168 (2020)
SEIKH, A., AKINSHILO, A., TAHERI, M. H., GORJI, M. R., ALHARTHI, N. H., KHAN, I., and KHAN, A. R. Influence of the nanoparticles and uniform magnetic field on the slip blood flows in arterial vessels. Physica Scripta, 49, 125218 (2019)
IBRAHIM, W. Magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) boundary layer stagnation point flow and heat transfer of a nanofluid past a stretching sheet with melting. Propulsion and Power Research, 6, 214–222 (2017)
GOUD, B. S. Heat generation/absorption influence on steady stretched permeable surface on MHD flow of a micropolar fluid through a porous medium in the presence of variable suction/injection. International Journal of Thermofluids, 7–8, 100044 (2020)
HAYAT, T., MUHAMMAD, K., and ALSAEDI, A. Melting effect in MHD stagnation point flow of Jeffrey nanomaterial. Physica Scripta, 94, 115702 (2019)
PATIL, V. S., PATIL, A. B., GANESH, S., HUMANE, P. P., and PATIL, N. S. Unsteady MHD flow of a nano Powell-Eyring fluid near stagnation point past a convectively heated stretching sheet in the existence of chemical reaction with thermal radiation. Materials Today: Proceedings, 44, 3767–3776 (2021)
SABU, A. S., MATHEW, A., NEETHU, T. S., and GEORGE, K. A. Statistical analysis of MHD convective ferro-nanofluid flow through an inclined channel with hall current, heat source and soret effect. Thermal Science and Engineering Progress, 22, 100816 (2021)
HAYAT, T., MUHAMMAD, K., FAROOQ, M., and ALSAEDI, A. Unsteady squeezing flow of carbon nanotubes with convective boundary conditions. PLoS One, 11, 0152923 (2016)
NAZEER, M., ALI, N., AHMAD, F., and LATIF, M. Numerical and perturbation solutions of third-grade fluid in a porous channel: boundary and thermal slip effects. Pramana: Journal of Physics, 94, 44 (2020)
KAZEMI, M. A., JAVANMARD, M., TAHERI, M. H., and ASKARI, N. Heat transfer investigation of the fourth-grade non-Newtonian MHD fluid flow in a plane duct considering the viscous dissipation, joule heating and forced convection on the walls. SN Applied Sciences, 2, 1752 (2020)
OKECHI, N. F. and ASGHAR, S. MHD Stokes flow in a corrugated curved channel. Chinese Journal of Physics, 71, 38–53 (2021)
MUHAMMAD, K., HAYAT, T., and ALSAEDI, A. Numerical study of Newtonian heating in flow of hybrid nanofluid (SWCNTs+CuO+ethylene glycol) past a curved surface with viscous dissipation. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetery, 143, 1291–1302 (2021)
DERO, S., ROHNI, A. M., and SAABAN, A. Stability analysis of Cu-C6H9NaO7 and Ag-C6H9NaO7 nanofluids with effect of viscous dissipation over stretching and shrinking surfaces using a single phase model. Heliyon, 6, e03510 (2020)
BHATTI, M. M. and RASHIDI, M. M. Effects of thermo-diffusion and thermal radiation on Williamson nanofluid over a porous shrinking/stretching sheet. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 221, 567–573 (2016)
SHAW, S., MABOOD, F., MUHAMMAD, T., NAYAK, M. K., and ALGHAMDI, M. Numerical simulation for entropy optimized nonlinear radiative flow of GO-Al2O3 magneto nanomaterials with auto catalysis chemical reaction. Numerical Methods for Partial Differential Equations, 10, 22623 (2020)
BILAL, M., SAGHEER, M., and HUSSAIN, S. Numerical study of magnetohydrodynamics and thermal radiation on Williamson nanofluid flow over a stretching cylinder with variable thermal conductivity. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 57, 3281–3289 (2018)
EID, M. R. and MABOOD, F. Entropy analysis of a hydromagnetic micropolar dusty carbon NTs-kerosene nanofluid with heat generation: Darcy-Forchheimer scheme. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 143, 2419–2436 (2021)
AHMED, F. and KHAN, W. A. Efficiency enhancement of an air-conditioner utilizing nanofluids: an experimental study. Energy Reports, 7, 575–583 (2021)
SOUAYEH, B., KUMAR, K. G., REDDY, M. G., RANI, S., HDHIRI, N., ALFANNAKH, H., and GORJI, M. R. Slip flow and radiative heat transfer behavior of titanium alloy and ferromagnetic nanoparticles along with suspension of dusty fluid. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 290, 111223 (2019)
AL-HOSSAINY, A. F. and EID, M. R. Combined experimental thin films, TDDFT-DFT theoretical method, and spin effect on [PEG-H2O/ZrO2+MgO]h hybrid nanofluid flow with higher chemical rate. Surfaces and Interfaces, 23, 100971 (2021)
KHAN, N. A., SAEED, U. B., SULTAN, F., and ULLAH, S. Study of velocity and temperature distributions in boudary layer flow of fourth grade fluid over an exponential stretching sheet. AIP Advances, 8, 025011 (2018)
MUHAMMAD, K., HAYAT, T., and ALSAEDI, A. OHAM analysis of fourth grade nanomaterial in presence of stagnation point and convective heat-mass conditions. Waves in Random and Complex Media, 1, 1–17 (2021)
FAROOQ, U., ZHAO, Y. L., HAYAT, T., and LIAO, S. J. Application of the HAM-based mathematica package BVPh 2.0 on MHD Falkner-Skan flow of nanofluid. Computers and Fluids, 111, 64–75 (2015)
ZHENG, L. and ZHANG, X. Homotopy analytical method. Modeling and Analysis of Modern Fluid Problems, 1, 115–178 (2017)
SINGH, K. and KUMAR, M. Melting and heat absorption effects in boundary layer stagnation-point flow towards a stretching sheet in a micropolar fluid. Ain Shams Engineering Journal, 9, 861–868 (2018)
AZEANY, N. A., NASIR, M., ISHAK, A., and POP, I. Stagnation-point flow and heat transfer past a permeable quadratically stretching/shrinking sheet. Chinese Journal of Physics, 55, 2081–2091 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Citation: HAYAT, T., MUHAMMAD, K., and ALSAEDI, A. Melting effect and Cattaneo-Christov heat flux in fourth-grade material flow through a Darcy-Forchheimer porous medium. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 42(12), 1787–1798 (2021) https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-021-2798-6
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hayat, T., Muhammad, K. & Alsaedi, A. Melting effect and Cattaneo-Christov heat flux in fourth-grade material flow through a Darcy-Forchheimer porous medium. Appl. Math. Mech.-Engl. Ed. 42, 1787–1798 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-021-2798-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-021-2798-6
Key words
- melting heat
- Darcy-Forchheimer (D-F) porous medium
- magnetohydrodynamics (MHD)
- Cattaneo-Christov (C-C) heat flux
- fourth-grade fluid
- optimal homotopy analysis method (OHAM)