Abstract
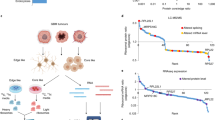
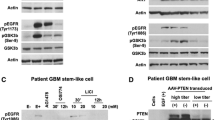
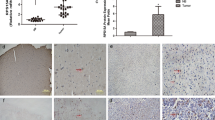
The characteristic features of plasticity and heterogeneity in glioblastoma (GB) cells cause therapeutic difficulties. GB cells are exposed to various stimuli from the tumor microenvironment and acquire the potential to resist chemoradiotherapy. To investigate how GB cells acquire stem cell-like phenotypes, we focused on ribosomal proteins, because ribosome incorporation has been reported to induce stem cell-like phenotypes in somatic cells. Furthermore, dysregulation of ribosome biogenesis has been reported in several types of cancer. We focused on ribosomal protein S6, which promotes sphere-forming ability and stem cell marker expression in GB cells. We expect that investigation of dysregulation of ribosome biogenesis and extra-ribosomal function in GB will provide new insights about the plasticity, heterogeneity, and therapeutic resistance of GB cells, which can potentially lead to revolutionary therapeutic strategies.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP et al (2009) Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol 10:459–466
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ et al (2005) Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 352:987–996
Singh SK, Clarke ID, Hide T et al (2004) Cancer stem cells in nervous system tumors. Oncogene 23:7267–7273
Singh SK, Hawkins C, Clarke ID et al (2004) Identification of human brain tumour initiating cells. Nature 432:396–401
Andersen BM, Faust Akl C, Wheeler MA et al (2021) Glial and myeloid heterogeneity in the brain tumour microenvironment. Nat Rev Cancer 21:786–802
Hernandez A, Domenech M, Munoz-Marmol AM et al (2021) Glioblastoma: relationship between metabolism and immunosuppressive microenvironment. Cells 10(12):3529
Neftel C, Laffy J, Filbin MG et al (2019) An integrative model of cellular states, plasticity, and genetics for glioblastoma. Cell 178(835–849):e821
Yang K, Wu Z, Zhang H et al (2022) Glioma targeted therapy: insight into future of molecular approaches. Mol Cancer 21:39
Hide T, Komohara Y, Miyasato Y et al (2018) Oligodendrocyte progenitor cells and macrophages/microglia produce glioma stem cell niches at the tumor border. EBioMedicine 30:94–104
Hide T, Shibahara I, Kumabe T (2019) Novel concept of the border niche: glioblastoma cells use oligodendrocytes progenitor cells (GAOs) and microglia to acquire stem cell-like features. Brain Tumor Pathol 36:63–73
Ito N, Katoh K, Kushige H et al (2018) Ribosome incorporation into somatic cells promotes lineage transdifferentiation towards multipotency. Sci Rep 8:1634
Shirakawa Y, Hide T, Yamaoka M et al (2020) Ribosomal protein S6 promotes stem-like characters in glioma cells. Cancer Sci 111:2041–2051
Domenech M, Hernandez A, Plaja A et al (2021) Hypoxia: the cornerstone of glioblastoma. Int J Mol Sci 22(22):12608
Vartanian A, Singh SK, Agnihotri S et al (2014) GBM’s multifaceted landscape: highlighting regional and microenvironmental heterogeneity. Neuro Oncol 16:1167–1175
Basheer AS, Abas F, Othman I et al (2021) Role of inflammatory mediators, macrophages, and neutrophils in glioma maintenance and progression: mechanistic understanding and potential therapeutic applications. Cancers (Basel) 13(16):4226
Simon T, Jackson E, Giamas G (2020) Breaking through the glioblastoma micro-environment via extracellular vesicles. Oncogene 39:4477–4490
Mohiuddin E, Wakimoto H (2021) Extracellular matrix in glioblastoma: opportunities for emerging therapeutic approaches. Am J Cancer Res 11:3742–3754
Broekman ML, Maas SLN, Abels ER et al (2018) Multidimensional communication in the microenvirons of glioblastoma. Nat Rev Neurol 14:482–495
Kressler D, Hurt E, Bassler J (2010) Driving ribosome assembly. Biochim Biophys Acta 1803:673–683
Zhou X, Liao WJ, Liao JM et al (2015) Ribosomal proteins: functions beyond the ribosome. J Mol Cell Biol 7:92–104
Zhang D, Chen HP, Duan HF et al (2016) Aggregation of ribosomal protein S6 at nucleolus is cell cycle-controlled and its function in Pre-rRNA processing is phosphorylation dependent. J Cell Biochem 117:1649–1657
Biever A, Valjent E, Puighermanal E (2015) Ribosomal protein S6 phosphorylation in the nervous system: from regulation to function. Front Mol Neurosci 8:75
Chow S, Minden MD, Hedley DW (2006) Constitutive phosphorylation of the S6 ribosomal protein via mTOR and ERK signaling in the peripheral blasts of acute leukemia patients. Exp Hematol 34:1183–1191
Chen B, Tan Z, Gao J et al (2015) Hyperphosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 predicts unfavorable clinical survival in non-small cell lung cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 34:126
Khalaileh A, Dreazen A, Khatib A et al (2013) Phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 attenuates DNA damage and tumor suppression during development of pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res 73:1811–1820
Puchalski RB, Shah N, Miller J et al (2018) An anatomic transcriptional atlas of human glioblastoma. Science 360:660–663
Shirakawa Y, Ohta K, Miyake S et al (2021) Glioma cells acquire stem-like characters by extrinsic ribosome stimuli. Cells 10(11):2970
Court FA, Hendriks WT, MacGillavry HD et al (2008) Schwann cell to axon transfer of ribosomes: toward a novel understanding of the role of glia in the nervous system. J Neurosci 28:11024–11029
Lopez-Leal R, Alvarez J, Court FA (2016) Origin of axonal proteins: Is the axon-schwann cell unit a functional syncytium? Cytoskeleton (Hoboken) 73:629–639
Pinto G, Saenz-de-Santa-Maria I, Chastagner P et al (2021) Patient-derived glioblastoma stem cells transfer mitochondria through tunneling nanotubes in tumor organoids. Biochem J 478:21–39
Yi YW, You KS, Park JS et al (2021) Ribosomal protein S6: a potential therapeutic target against cancer? Int J Mol Sci 23(1):48
Pecoraro A, Pagano M, Russo G et al (2021) Ribosome biogenesis and cancer: overview on ribosomal proteins. Int J Mol Sci 22(11):5496
Orgebin E, Lamoureux F, Isidor B et al (2020) Ribosomopathies: new therapeutic perspectives. Cells 9(9):2080
Norris K, Hopes T, Aspden JL (2021) Ribosome heterogeneity and specialization in development. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA 12:e1644
Warner JR, McIntosh KB (2009) How common are extraribosomal functions of ribosomal proteins? Mol Cell 34:3–11
Narla A, Ebert BL (2010) Ribosomopathies: human disorders of ribosome dysfunction. Blood 115:3196–3205
Barna M, Pusic A, Zollo O et al (2008) Suppression of Myc oncogenic activity by ribosomal protein haploinsufficiency. Nature 456:971–975
Bursac S, Prodan Y, Pullen N et al (2021) Dysregulated ribosome biogenesis reveals therapeutic liabilities in cancer. Trends Cancer 7:57–76
El Khoury W, Nasr Z (2021) Deregulation of ribosomal proteins in human cancers. Biosci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20211577
Jeon YJ, Kim IK, Hong SH et al (2008) Ribosomal protein S6 is a selective mediator of TRAIL-apoptotic signaling. Oncogene 27:4344–4352
Yanai A, Inoue N, Yagi T et al (2015) Activation of mTOR/S6K but not MAPK pathways might be associated with high Ki-67, ER(+), and HER2(-) breast cancer. Clin Breast Cancer 15:197–203
Grundy M, Jones T, Elmi L et al (2018) Early changes in rpS6 phosphorylation and BH3 profiling predict response to chemotherapy in AML cells. PLoS ONE 13:e0196805
Hagner PR, Mazan-Mamczarz K, Dai B et al (2011) Ribosomal protein S6 is highly expressed in non-Hodgkin lymphoma and associates with mRNA containing a 5’ terminal oligopyrimidine tract. Oncogene 30:1531–1541
Liu Z, Yun R, Yu X et al (2016) Overexpression of Notch3 and pS6 is associated with poor prognosis in human ovarian epithelial cancer. Mediators Inflamm 2016:5953498
Pinto AP, Degen M, Barron P et al (2013) Phosphorylated S6 as an immunohistochemical biomarker of vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia. Mod Pathol 26:1498–1507
Molinolo AA, Hewitt SM, Amornphimoltham P et al (2007) Dissecting the Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin signaling network: emerging results from the head and neck cancer tissue array initiative. Clin Cancer Res 13:4964–4973
Zheng Z, Zheng Y, Zhang M et al (2016) Reciprocal expression of p-AMPKa and p-S6 is strongly associated with the prognosis of gastric cancer. Tumour Biol 37:4803–4811
Knoll M, Macher-Goeppinger S, Kopitz J et al (2016) The ribosomal protein S6 in renal cell carcinoma: functional relevance and potential as biomarker. Oncotarget 7:418–432
Corcoran RB, Rothenberg SM, Hata AN et al (2013) TORC1 suppression predicts responsiveness to RAF and MEK inhibition in BRAF-mutant melanoma. Sci Transl Med 5:196ra198
Li YJ, Wang Y, Wang YY (2019) MicroRNA-99b suppresses human cervical cancer cell activity by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol 234:9577–9591
Ganger DR, Hamilton PD, Fletcher JW et al (1997) Metallopanstimulin is overexpressed in a patient with colonic carcinoma. Anticancer Res 17:1993–1999
Fernandez-Pol JA, Fletcher JW, Hamilton PD et al (1997) Expression of metallopanstimulin and oncogenesis in human prostatic carcinoma. Anticancer Res 17:1519–1530
Atsuta Y, Aoki N, Sato K et al (2002) Identification of metallopanstimulin-1 as a member of a tumor associated antigen in patients with breast cancer. Cancer Lett 182:101–107
Wang YW, Qu Y, Li JF et al (2006) In vitro and in vivo evidence of metallopanstimulin-1 in gastric cancer progression and tumorigenicity. Clin Cancer Res 12:4965–4973
Fernandez-Pol JA (2012) Increased serum level of RPMPS-1/S27 protein in patients with various types of cancer is useful for the early detection, prevention and therapy. Cancer Genomics Proteomics 9:203–256
Xiong X, Zhao Y, He H et al (2011) Ribosomal protein S27-like and S27 interplay with p53-MDM2 axis as a target, a substrate and a regulator. Oncogene 30:1798–1811
Liu Y, Ma J, Zhang L et al (2021) Overexpressed MPS-1 contributes to endometrioma development through the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 19:111
Feldheim J, Kessler AF, Schmitt D et al (2020) Ribosomal protein S27/Metallopanstimulin-1 (RPS27) in Glioma-a new disease biomarker? Cancers (Basel) 12(5):1085
Anam MB, Istiaq A, Kariya R et al (2021) Ribosome induces transdifferentiation of A549 and H-111-TC cancer cell lines. Biochem Biophys Rep 26:100946
Kudo M, Anam MB, Istiaq A et al (2021) Ribosome incorporation induces EMT-like phenomenon with cell cycle arrest in human breast cancer cell. Cells Tissues Organs. https://doi.org/10.1159/000513908:1-10
Setayesh-Mehr Z, Poorsargol M (2021) Toxic proteins application in cancer therapy. Mol Biol Rep 48:3827–3840
Rotondo R, Ragucci S, Castaldo S et al (2021) Cytotoxicity effect of quinoin, type 1 ribosome-inactivating protein from quinoa seeds, on glioblastoma cells. Toxins (Basel) 13(10):684
Lapik YR, Fernandes CJ, Lau LF et al (2004) Physical and functional interaction between Pes1 and Bop1 in mammalian ribosome biogenesis. Mol Cell 15:17–29
Holzel M, Rohrmoser M, Schlee M et al (2005) Mammalian WDR12 is a novel member of the Pes1-Bop1 complex and is required for ribosome biogenesis and cell proliferation. J Cell Biol 170:367–378
Li YZ, Zhang C, Pei JP et al (2022) The functional role of Pescadillo ribosomal biogenesis factor 1 in cancer. J Cancer 13:268–277
Mi L, Qi Q, Ran H et al (2021) Suppression of ribosome biogenesis by targeting WD repeat domain 12 (WDR12) inhibits glioma stem-like cell growth. Front Oncol 11:751792
Li JL, Chen C, Chen W et al (2020) Integrative genomic analyses identify WDR12 as a novel oncogene involved in glioblastoma. J Cell Physiol 235:7344–7355
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) Grant Number JP20K09374 (to Takuichiro Hide) from Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hide, T., Shibahara, I., Inukai, M. et al. Ribosomal proteins induce stem cell-like characteristics in glioma cells as an “extra-ribosomal function”. Brain Tumor Pathol 39, 51–56 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10014-022-00434-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10014-022-00434-5