Abstract
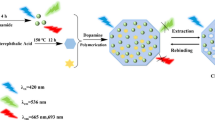
Fluorescein-functionalized fluorescent polymer dots (F-PDs) were prepared by a facile one-pot method by magnetic stirring under mild conditions based on carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) and fluorescein as the precursors. The obtained F-PDs exhibited a nanoscale size of 3.2 ± 1.1 nm, excellent water solubility, and bright yellow fluorescence emission with a fluorescence quantum yield of 12.0%. The fluorescent probe displays rapid and sensitive chiral discrimination for lysine focused on different complexation abilities between lysine enantiomers and Cu2+. The concentration of L-lysine in the range 4 to 14 mM (R2 = 0.997) was measured by the fluorescence intensity ratio (I513/I429); the exitation wavelength was set to λex = 365 nm. The detection limit was 0.28 mM (3σ/slope). Importantly, this sensor accurately predicted the enantiomeric excess (ee) of lysine enantiomers at the designed concentration (lysine: 20 mM; Cu2+: 10 mM) ranges. The proposed sensor was successfully applied to determine L-lys (recovery: 95.8–101%; RSD: 0.465–3.34%) and ee values (recovery: 98.5–102%; RSD: 2.61–3.21%) in human urine samples using the standard addition method.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this work are available from the corresponding author, [Guang Yang], upon reasonable request.
References
Xue YP, Cao CH, Zheng YG (2018) Enzymatic asymmetric synthesis of chiral amino acids. Chem Soc Rev 47(4):1516–1561. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7cs00253j
Zhao Y, Askarpour AN, Sun L, Shi J, Li X, Alu A (2017) Chirality detection of enantiomers using twisted optical metamaterials. Nat Commun 8:14180. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms14180
Yan J, Yao Y, Yan S, Gao R, Lu W, He W (2020) Chiral protein supraparticles for tumor suppression and synergistic immunotherapy: an enabling strategy for bioactive supramolecular chirality construction. Nano Lett 20(8):5844–5852. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.0c01757
Zor E, Bekar N (2017) Lab-in-a-syringe using gold nanoparticles for rapid colorimetric chiral discrimination of enantiomers. Biosens Bioelectron 91:211–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.12.031
Gao P, Xie Z, Zheng M (2020) Chiral carbon dots-based nanosensors for Sn(II) detection and lysine enantiomers recognition. Sens Actuators B Chem 319:128265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.128265
Li G, Feng L, Zhao P, Xu W, Wang Y, Song A, Hao J (2014) Lysine-based chiral vesicles. J Colloid Interface Sci 431:233–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2014.05.069
Zhang M, Qiao J, Zhang S, Qi L (2018) Copper nanoclusters as probes for turn-on fluorescence sensing of L-lysine. Talanta 182:595–599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.02.035
Ji J, Qu L, Wang Z, Li G, Feng W, Yang G (2022) A facile electrochemical chiral sensor for tryptophan enantiomers based on multiwalled carbon nanotube/hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin functionalized carboxymethyl cellulose. Microchem J 175:107133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2021.107133
Zhang X, Yin J, Yoon J (2014) Recent advances in development of chiral fluorescent and colorimetric sensors. Chem Rev 114(9):4918–4959. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr400568b
Hou X, Song J, Wu Q, Lv H (2021) Chiral carbon quantum dots as fluorescent probe for rapid chiral recognition of isoleucine enantiomers. Anal Chim Acta 1184:339012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2021.339012
Da Silva MS, Vao ER, Temtem M, Mafra L, Caldeira J, Aguiar-Ricardo A, Casimiro T (2010) Clean synthesis of molecular recognition polymeric materials with chiral sensing capability using supercritical fluid technology. Biosens Bioelectron 25(7):1742–1747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2009.12.023
Namera A, Yashiki M, Nishida M, Kojima T (2012) Direct extract derivatization for determination of amino acids in human urine by gas chromatography and mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 41(1):448–479. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1570-0232(02)00075-2
Wang Y, Liu J, Zhao X, Yang C, Ozaki Y, Xu Z, Zhao B, Yu Z (2019) A chiral signal-amplified sensor for enantioselective discrimination of amino acids based on charge transfer-induced SERS. Chem Commun 55(65):9697–9700. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9cc04665h
Li C, Zeng J, Guo D, Liu L, Xiong L, Luo X, Hu Z, Wu F (2021) Cobalt-doped carbon quantum dots with peroxidase-mimetic activity for ascorbic acid detection through both fluorometric and colorimetric methods. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 13(41):49453–49461. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c13198
Yang G, Hu W, Xia H, Zou G, Zhang Q (2014) Highly selective and reproducible detection of picric acid in aqueous media, based on a polydiacetylene microtube optical waveguide. J Mater Chem A 2(37):15660–15665. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ta03667k
Consoli GML, Giuffrida ML, Satriano C, Musumeci T, Forte G, Petralia S (2022) A novel facile one-pot synthesis of photothermally responsive carbon polymer dots as promising drug nanocarriers. Chem Commun 58(19):3126–3129. https://doi.org/10.1039/d1cc06530k
Liu Y, Huangfu M, Wu P, Jiang M, Zhao X, Liang L, Xie L, Bai J, Wang J (2019) Post-imparting bronsted acidity into an amino-functionalized MOF as a bifunctional luminescent turn-ON sensor for the detection of aluminum ions and lysine. Dalton Trans 48(36):13834–13840. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9dt02962a
Copur F, Bekar N, Zor E, Alpaydin S, Bingol H (2019) Nanopaper-based photoluminescent enantioselective sensing of L-lysine by L-cysteine modified carbon quantum dots. Sens Actuators B Chem 279:305–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.10.026
Seo SH, Kim S, Han MS (2014) Gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric chiral discrimination of histidine: application to determining the enantiomeric excess of histidine. Anal Methods 6(1):73–76. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ay41735b
Pan D, Zhang J, Li Z, Wu M (2010) Hydrothermal route for cutting graphene sheets into blue-luminescent graphene quantum dots. Adv Mater 22(6):734–738. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200902825
Chen Y, Zhang Y, Lyu T, Wang Y, Yang X, Wu X (2019) A facile strategy for the synthesis of water-soluble fluorescent nonconjugated polymer dots and their application in tetracycline detection. J Mater Chem C 7(30):9241–9247. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9tc02738f
Zhang S, Wang Y, Yang G (2021) A facile strategy for the preparation of carboxymethylcellulose-derived polymer dots and their application to detect tetracyclines. Macromol Chem Phys 222(22):2100267. https://doi.org/10.1002/macp.202100267
Zhong D, Cao Z, Wu B, Zhang Q, Wang G (2018) Polymer dots of DASA-functionalized polyethyleneimine: synthesis, visible light/pH responsiveness, and their applications as chemosensors. Sens Actuators B Chem 254:385–392. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.07.107
Zhang H, Dong X, Wang J, Guan R, Cao D, Chen Q (2019) Fluorescence emission of polyethylenimine-derived polymer dots and its application to detect copper and hypochlorite ions. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11(35):32489–32499. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b09545
Chabok A, Shamsipur M, Yeganeh-Faal A, Molaabasi F, Molaei K, Sarparast M (2019) A highly selective semiconducting polymer dots-based “off-on” fluorescent nanoprobe for iron, copper and histidine detection and imaging in living cells. Talanta 194:752–762. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.10.072
Zhong Z, Jia L (2019) Room temperature preparation of water-soluble polydopamine-polyethyleneimine copolymer dots for selective detection of copper ions. Talanta 197:584–591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.01.070
Chen H, Yu J, Men X, Zhang J, Ding Z, Jiang Y, Wu C, Chiu DT (2021) Reversible ratiometric NADH sensing using semiconducting polymer dots. Angew Chem Int Ed 60(21):12007–12012. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202100774
Jia J, Lu W, Cui S, Dong C, Shuang S (2021) Preparation of yellow-emitting carbon dots and their bifunctional detection of tetracyclines and Al3+ in food and living cells. Microchim Acta 188(12):418. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-05078-4
Bu W, Xu X, Wang Z, Jin N, Liu L, Liu J, Zhu S, Zhang K, Jelinek R, Zhou D, Sun H, Yang B (2020) Ascorbic acid-PEI carbon dots with osteogenic effects as mir-2861 carriers to effectively enhance bone regeneration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12(45):50287–50302. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.0c15425
Hou J, Wang W, Zhou T, Wang B, Li H, Ding L (2016) Synthesis and formation mechanistic investigation of nitrogen-doped carbon dots with high quantum yields and yellowish-green fluorescence. Nanoscale 8(21):11185–11193. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6nr02701f
Liu S, Liu H, Chen Q, Hou J, Yang G (2021) Preparation of boronic acid-modified polymer dots under mild conditions and their applications in pH and glucose detection. Mikrochim Acta 189(1):36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-05137-w
Liu SG, Luo D, Li N, Zhang W, Lei JL, Li NB, Luo HQ (2016) Water-soluble nonconjugated polymer nanoparticles with strong fluorescence emission for selective and sensitive detection of nitro-explosive picric acid in aqueous medium. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8(33):21700–21709. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b07407
Pathak A, Pv S, Stanley J, Satheesh Babu TG (2019) Multicolor emitting N/S-doped carbon dots as a fluorescent probe for imaging pathogenic bacteria and human buccal epithelial cells. Mikrochim Acta 186(3):157. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3270-7
Kwak BE, Yoo HJ, Kim DH (2019) Quenching-resistant polymer carbon dot preserving emission color consistency in solid-state. Adv Optical Mater 7(23):1900932. https://doi.org/10.1002/adom.201900932
Xia H, Chen X, Chen X, Cheng J, Liu Y, Chen X, Zhang Q, Zou G (2018) Chiral discrimination of amino acid enantiomers based on different interactions with Cu2+. Sens Actuators B Chem 254:44–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.06.143
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2572021BU05), Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province (LH2020E007), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC, No. 51803021), and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2018M641790).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Guang Yang: Project administration, Investigation, Funding acquisition, Writing-original draft. Zhongrui Wang: Investigation, Methodology, Writing-original draft. Xinxin Ji, Jingying Zhao, Jie Ji, and Guangyao Li: Investigation, Methodology, Validation. Hongyan Xia and Juan Hou: Investigation, Writing-review and editing, Supervision.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Ji, X., Zhao, J. et al. Preparation of fluorescein-modified polymer dots and their application in chiral discrimination of lysine enantiomers. Microchim Acta 190, 29 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05608-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05608-8