Abstract
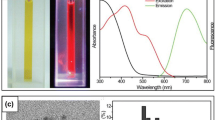
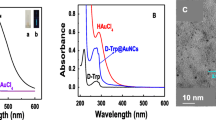
An interesting phenomenon is described that the fluorescence signal of poly(adenine) (A) DNA-templated gold nanoclusters (AuNCs) is greatly improved in the presence of l-histidine by means of l-histidine-DNA interaction. The modified nanoclusters display strong fluorescence emission with excitation/emission maxima at 290/475 nm. The fluorescence quantum yield (QY) is improved from 1.9 to 6.5%. Fluorescence enhancement is mainly ascribed to the l-histidine-DNA interaction leading to conformational changes of the poly(A) DNA template, which offer a better microenvironment to protect AuNCs. The assay enables l-histidine to be determined with good sensitivity and a linear response that covers the 1 to 50 nM l-histidine concentration range with a 0.3 nM limit of detection. The proposed method has been applied to the determination of imidazole-containing drugs in pharmaceutical samples.
Graphical abstract

A turn-on fluorescent method has been designed for the sensitive detection of l-histidine as well as imidazole-containing drugs on the basis of the l-histidine-DNA interaction.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li JJ, Zhu JJ, Xu K (2014) Fluorescent metal nanoclusters: from synthesis to applications. Trends Anal Chem 58:90–98
Zhang LB, Wang EK (2014) Metal nanoclusters: new fluorescent probes for sensors and bioimaging. Nano Today 9:132–157
Liu JW (2014) DNA-stabilized, fluorescent, metal nanoclusters for biosensor development. Trends Anal Chem 58:99–111
Cai YY, Wang J, Liu CY, Yang SQ, Zhang YJ, Liu AH (2020) Histidine-triggered turning-on of gold/copper nanocluster fluorescence for the sensitive and selective detection of histidine. Chem Commun 56:11637–11640
Zhang ZQ, Liu TT, Wang SS, Ma J, Zhou T, Wang F, Wang XF, Zhang GD (2019) DNA-templated gold nanocluster as a novel fluorometric sensor for glutathione determination. J Photoch Photobio A 370:89–93
Gu ZF, Cao ZJ (2018) Molecular switch-modulated fluorescent copper nanoclusters for selective and sensitive detection of histidine and cysteine. Anal Bioanal Chem 410:4991–4999
Zhou Y, Zhou TS, Zhang M, Shi GY (2014) A DNA-scaffolded silver nanocluster/Cu2+ ensemble as a turn-on fluorescent probe for histidine. Analyst 139:3122–3126
Tao Y, Li MQ, Ren JS, Qu XG (2015) Metal nanoclusters: novel probes for diagnostic and therapeutic applications. Chem Soc Rev 44:8636–8663
Liu R, Wang CQ, Hu JY, Su YY, Lv Y (2018) DNA-templated copper nanoparticles: versatile platform for label-free bioassays. Trends Anal Chem 105:436–452
Zhang LL, Zhao JJ, Zhang H, Jiang JH, Yu RQ (2013) Double strand DNA-templated copper nanoparticle as a novel fluorescence indicator for label-free detection of polynucleotide kinase activity. Biosens Bioelectron 44:6–9
Lian JY, Liu Q, Jin Y, Li BX (2017) Histone-DNA interaction: an effective approach to improve the fluorescence intensity and stability of DNA-templated Cu nanoclusters. Chem Commun 53:12568–12571
Zhang L, Cai QY, Li J, Ge J, Wang JY, Dong ZZ, Li ZH (2015) A label-free method for detecting biothiols based on poly(thymine)-templated copper nanoparticles. Biosens Bioelectron 69:77–82
Liu G, Li J, Feng DQ, Zhu JJ, Wang W (2017) Silver nanoclusters beacon as stimuli-responsive versatile platform for multiplex DNAs detection and aptamer-substrate complexes sensing. Anal Chem 89:1002–1008
Wang HB, Zhang HD, Chen Y, Liu YM (2015) A fluorescent biosensor for protein detection based on poly(thymine)-templated copper nanoparticles and terminal protection of small molecule-linked DNA. Biosens Bioelectron 74:581–586
Shen CC, Xia XD, Hu SQ, Yang MH, Wang JX (2015) Silver nanoclusters-based fluorescence assay of protein kinase activity and inhibition. Anal Chem 87:693–698
Petty JT, Zheng J, Hud NV, Dickson RM (2004) DNA-templated Ag nanocluster formation. J Am Chem Soc 126:5207–5212
Rotaru A, Dutta S, Jentzsch E, Gothelf K, Mokhir A (2010) Selective dsDNA-templated formation of copper nanoparticles in solution. Angew Chem Int Ed 49:5665–5667
Qing ZH, He XX, He DG, Wang KM, Xu FZ, Qing TP, Yang XH (2013) Poly(thymine)-templated selective formation of fluorescent copper nanoparticles. Angew Chem Int Ed 52:9719–9722
Chen J, Ji X, He ZK (2017) Smart composite reagent composed of double-stranded DNA-templated copper nanoparticle and SYBR green I for hydrogen peroxide related biosensing. Anal Chem 89:3988–3995
Qing ZH, Bai A, Xing S, Zou Z, He X, Wang KM, Yang RH (2019) Progress in biosensor based on DNA-templated copper nanoparticles. Biosens Bioelectron 137:96–109
Lyu D, Li J, Wang X, Guo WW, Wang EK (2019) Cationic-polyelectrolyte- modified fluorescent DNA-silver nanoclusters with enhanced emission and higher stability for rapid bioimaging. Anal Chem 91:2050–2057
Tian X, Kong XJ, Zhu ZM, Chen TT, Chu X (2015) A new label-free and turn-on strategy for endonuclease detection using a DNA-silver nanocluster probe. Talanta 131:116–120
Guo LY, Tang T, Hu LS, Yang MH, Chen X (2017) Fluorescence assay of Fe (III) in human serum samples based on pH dependent silver nanoclusters. Sensors Actuators B Chem 241:773–778
Wang GF, Wan J, Zhang XJ (2017) TTE DNA-Cu NPs: enhanced fluorescence and application in a target DNA triggered dual-cycle amplification biosensor. Chem Commun 53:5629–5632
Wang HB, Zhang HD, Chen Y, Huang KJ, Liu YM (2015) A label-free and ultrasensitive fluorescent sensor for dopamine detection based on double-stranded DNA templated copper nanoparticles. Sensors Actuators B Chem 220:146–153
Qing ZH, Zhu L, Yang S, Cao Z, He X, Wang KM, Yang RH (2016) In situ formation of fluorescent copper nanoparticles for ultrafast zero-background Cu2+ detection and its toxicides screening. Biosens Bioelectron 78:471–476
Yeh H, Sharma J, Shih I, Vu DM, Martinez JS, Werner JH (2012) A fluorescence light-up Ag nanocluster probe that discriminates single-nucleotide variants by emission color. J Am Chem Soc 134:11550–11558
Yuan Y, Li W, Liu Z, Nie Z, Huang Y, Yao S (2014) A versatile biosensing system for DNA-related enzyme activity assay via the synthesis of silver nanoclusters using enzymatically-generated DNA as template. Biosens Bioelectron 61:321–327
Li J, Si L, Bao J, Wang Z, Dai ZH (2017) Fluorescence regulation of poly(thymine)-Templated copper nanoparticles via an enzyme-triggered reaction toward sensitive and selective detection of alkaline phosphatase. Anal Chem 89:3681–3686
Li ZY, Wu YT, Tseng WL (2015) UV-light-induced improvement of fluorescence quantum yield of DNA-templated gold nanoclusters: application to ratiometric fluorescent sensing of nucleic acids. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:23708–23716
Wang HB, Li Y, Bai HY, Liu YM (2018) DNA-templated Au nanoclusters and MnO2 sheets: a label-free and universal fluorescence biosensing platform. Sensors Actuators B Chem 259:204–210
Wang HB, Bai HY, Dong GL, Liu YM (2019) DNA-templated Au nanoclusters coupled with proximity-dependent hybridization and guanine-rich DNA induced quenching: a sensitive fluorescent biosensing platform for DNA detection. Nanoscale Adv 1:1482–1488
Wang HB, Zhang HD, Chen Y, Liu YM (2015) Inhibition of double-stranded DNA templated copper nanoparticles as label-free fluorescent sensors for L-histidine detection. New J Chem 39:8896–8900
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. U1704153), 1000 Talents Program of Zhongyuan, Plan for Young Excellent Teachers in Universities of Henan Province (No. 2017GGJS100), Nanhu Scholars Program for Young Scholars of XYNU.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(PDF 132 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, HB., Mao, AL., Tao, BB. et al. l-Histidine-DNA interaction: a strategy for the improvement of the fluorescence signal of poly(adenine) DNA-templated gold nanoclusters. Microchim Acta 188, 198 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04853-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04853-7