Abstract
This work describes the synthesis of red-emitting copper nanoclusters (CuNCs) by using DNA as the template. DNA-templated CuNCs combined with blue-emitting carbon dots (CDs) form the self-assembled complex DNA-CuNC/CDs through electrostatic interactions. In the presence of arginine (Arg), the blue fluorescence of CDs (with excitation/emission maxima at 350/440 nm) is quenched. Addition of acetaminophen (AP) induces the competitive combination of Arg and AP for the CDs. This results in the release of Arg from CDs and the recovery of blue fluorescence. On addition of both Arg and AP, the red fluorescence of CuNCs (with excitation/emission maxima at 350/670 nm) undergoes only slight changes. Hence, the DNA-CuNC/CD complex can serve as a dually emitting ratiometric probe to determine both Arg and AP, with detection limits of 0.35 μM and 0.26 μM, respectively. The probe also enables on-site, visual determination of Arg and AP in aqueous samples, best by placing the system in cuvettes or dropping it onto filter paper strips. An “INHIBIT” logic gate was designed based on this ratiometric and visual fluorometric assay, with Arg and AP as the inputs.

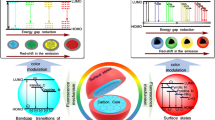
Schematic presentation of self-assembly of DNA-templated copper nanoclusters and carbon dots to construct novel dual-emitting nanoprobes for ratiometric fluorometric and visual determination of arginine and acetaminophen in aqueous solutions and on wetting filter paper strips.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chu Q, Jiang L, Tian X, Ye J (2008) Rapid determination of acetaminophen and p-aminophenol in pharmaceutical formulations using miniaturized capillary electrophoresis with amperometric detection. Anal Chim Acta 606:246–251
Prabakar SJR, Narayanan SS (2007) Amperometric determination of paracetomol by a surface modified cobalt hexacyanoferrate graphite wax composite electrode. Talanta 72:1818–1827
Zhao G, Yang L, Wu S, Zhao H, Tang E, Li CP (2017) The synthesis of amphiphilic pillar[5]arene functionalized reduced graphene oxide and its application as novel fluorescence sensing platform for the determination of acetaminophen. Biosens Bioelectron 91:863–869
Tsierkezos NG, Othman SH, Ritter U (2013) Nitrogen-doped multi-walled carbon nanotubes for paracetamol sensing. Ionics 19:1897–1905
Toklu HZ, Sehirli AO, Velioglu-Ogunc A, Cetinel S, Sener G (2006) Acetaminophen-induced toxicity is prevented by β-D-glucan treatment in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 543:133–140
Abdelaleem EA, Abdelwahab NS (2013) Validated stability indicating RP-HPLC method for determination of paracetamol, methocarbamol and their related substances. Anal Methods 5:541–545
Issa YM, Hassoun MEM, Zayed AG (2012) Simultaneous determination of paracetamol, caffeine, domperidone, ergotamine tartrate, propyphenazone, and drotaverine HCl by high performance liquid chromatography. J Liq Chromatogr R T 35:2148–2161
Baranowska I, Wilczek A (2009) Simultaneous RP-HPLC determination of sotalol, metoprolol, alpha- hydroxymetoprolol, paracetamoland its glucuronide and sulfate metabolites in human urine. Anal Sci 25:769–772
Mendez-Albores A, Tarin C, Rebollar-Perez G, Dominguez-Ramirez L, Torres E (2015) Biocatalytic spectrophotometric method to detect paracetamol in water samples. J Environ Sci Health A 50:1046–1056
Ruiz-Medina A, Fernández-de Córdova ML, Ayora-Cañada MJ, Pascual-Reguera MI, Molina-Díaz A (2000) A flow-through solid phase UV spectrophotometric biparameter sensor for the sequential determination of ascorbic acid and paracetamol. Anal Chim Acta 404:131–139
Abirami G, Vetrichelvan T (2013) Simultaneous determination of tolperisone and paracetamol in pure and fixed dose combination by UV – spectrophotometry. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 5:488–492
Easwaramoorthy D, Yu YC, Huang HJ (2001) Chemiluminescence detection of paracetamol by a luminol- permanganate based reaction. Anal Chim Acta 439:95–100
Dai Y, Li X, Lu X, Kan X (2016) Voltammetric determination of paracetamol using a glassy carbon electrode modified with Prussian blue and a molecularly imprinted polymer, and ratiometric read-out of two signals. Microchim Acta 183:2771–2778
Kalambate PK, Sanghavi BJ, Karna SP, Srivastava AK (2015) Simultaneous voltammetric determination of paracetamol and domperidone based on a graphene/platinum nanoparticles/nafion composite modified glassy carbon electrode. Sensors Actuators B Chem 213:285–294
Liu X, Zhang XY, Wang LL, Wang YY (2014) A sensitive electrochemical sensor for paracetamol based on a glassy carbon electrode modified with multiwalled carbon nanotubes and dopamine nanospheres functionalized with gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 181:1439–1446
Teng Y, Fan LM, Dai YL, Zhong M, Lu XJ, Kan XW (2015) Electrochemical sensor for paracetamol recognition and detection based on catalytic and imprinted composite film. Biosens Bioelectron 71:137–142
Lentini G, Habtemariam S (2014) Microchip capillary electrophoresis–electrospray ionizationmass spectrometry analysis of paracetamol metabolites in human urine: an intriguing case. J Chromatogr A 1327:160
Khanmohammadi M, Soleimani M, Morovvat F, Garmarudi AB, Khalafbeigi M, Ghasemi K (2012) Simultaneous determination of paracetamol and codeine phosphate in tablets by TGA and chemometrics. Thermochim Acta 530:128–132
Gui R, Jin H, Bu X, Fu Y, Wang Z, Liu Q (2019) Recent advances in dual-emission ratiometric fluorescence probes for chemo/biosensing and bioimaging of biomarkers. Coord Chem Rev 383:82–103
Jin H, Gui R, Yu J, Lv W, Wang Z (2017) Fabrication strategies, sensing modes and analytical applications of ratiometric electrochemical biosensors. Biosens Bioelectron 91:523–537
He W, Gui R, Jin H, Wang B, Bu X, Fu Y (2018) Ratiometric fluorescence and visual imaging detection of dopamine based on carbon dots/copper nanoclusters dual-emitting nanohybrids. Talanta 178:109–115
Kong W, Niu Y, Liu M, Zhang K, Xu G, Wang Y, Wang X, Xu Y, Li J (2019) One-step hydrothermal synthesis of fluorescent MXene-like titanium carbonitride quantum dots. Inorg Chem Commun 105:151–157
Yang H, Zhao W, Deng S, Zhang K, Zhao Z, Deng R, He Q, Li J (2019) Intrinsic conformation-induced fluorescence resonance energy transfer aptasensor. ACS Appl Bio Mater. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsabm.9b00738
Sheng L, Lu Y, Deng S, Liao X, Zhang K, Ding T, Gao H, Liu D, Deng R, Li J (2019) A transcription aptasensor: amplified, label-free and culture-independent detection of foodborne pathogens via light-up RNA aptamers. Chem Commun 55:10096–10099
Fu Y, Jin H, Bu X, Gui R (2018) Melamine-induced decomposition and anti-FRET effect from self-assembled complex of rhodamine 6G and DNA-stabilized silver nanoclusters used for dual-emitting ratiometric and naked-eye visual fluorescence detection. J Agric Food Chem 66:9819–9827
Gui R, Bu X, He W, Jin H (2018) Ratiometric fluorescence, solution-phase and filter-paper visualization detection of ciprofloxacin based on dual-emitting carbon dots/silicon dots hybrids. New J Chem 42:16217–16225
Bu X, Fu Y, Jin H, Gui R (2018) Specific enzymatic synthesis of 2,3-diaminophenazine and copper nanoclusters used for dual-emission ratiometric and naked-eye visual fluorescence sensing of choline. New J Chem 42:17323–17330
Sachdev A, Matai I, Gopinath P (2014) Implications of surface passivation on physicochemical and bioimaging properties of carbon dots. RSC Adv 4:20915–20921
Wang G, Wan J, Zhang X (2017) TTE DNA-Cu NPs: enhanced fluorescence and application in a target DNA triggered dual-cycle amplification biosensor. Chem Commun 53:5629–5632
Zhu HW, Dai WX, Yu XD, Xu JJ, Chen HY (2015) Poly thymine stabilized copper nanoclusters as a fluorescence probe for melamine sensing. Talanta 144:642–647
Wang M, Lin Z, Liu Q, Jiang S, Liu H, Su X (2018) DNA-hosted copper nanoclusters/graphene oxide based fluorescent biosensor for protein kinase activity detection. Anal Chim Acta 1012:66–73
Chen J, Ji X, Tinnefeld P, He Z (2016) Multifunctional dumbbell-shaped DNA-templated selective formation of fluorescent silver nanoclusters or copper nanoparticles for sensitive detection of biomolecules. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:1786–1794
Li ZY, Wu YT, Tseng WL (2015) UV-light-induced improvement of fluorescence quantum yield of DNA- templated gold nanoclusters: application to ratiometric fluorescent sensing of nucleic acids. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:23708–23716
Ramírez-Herrera DE, Tirado-Guízar A, Paraguay-Delgado F, Pina-Luis G (2017) Ratiometric arginine assay based on FRET between CdTe quantum dots and Cresyl violet. Microchim Acta 184:1997–2005
Liu M, Li N, He Y, Ge Y, Song G (2018) Dually emitting gold-silver nanoclusters as viable ratiometric fluorescent probes for cysteine and arginine. Microchim Acta 185:147
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong, China (no. ZR2019MB026), and the Source Innovation Plan Application Basic Research Project of Qingdao, China (no. 18-2-2-26 jch).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 131 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bu, X., Fu, Y., Jiang, X. et al. Self-assembly of DNA-templated copper nanoclusters and carbon dots for ratiometric fluorometric and visual determination of arginine and acetaminophen with a logic-gate operation. Microchim Acta 187, 154 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-4146-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-4146-6