Abstract
The authors report on a disposable sensor for the differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetric (DPASV) determination of the ions Zn(II), Pb(II) and Cu(II). Simultaneous detection is accomplished by using a screen-printed carbon electrode (SPCE) co-modified with an in-situ plated bismuth (Bi)) film and gold nanoparticles (AuNPs). The synergistic effect of the Bi film, and the large surface and good electrical conductivity of the AuNPs strongly assist in the co-deposition of the three ions. Four well-defined and fully separated anodic stripping peaks, at 540 mV for Zn(II), 50 mV for Pb(II), 140 mV for Bi(III) and 295 mV for Cu(II), all vs. Ag/AgCl, can be seen. The modified SPCE was characterized by scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, cyclic voltammetry and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Under the optimized conditions, the sensor has a good response to these ions. The detection limits (at an S/N ratio of 3) are 50 ng·L−1 for Zn(II), 20 ng·L−1 for Pb(II), and 30 ng·L−1 for Cu(II). The method was applied to the determination of the 3 ions in spiked lake water samples.

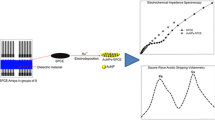
Schematic of screen-printed carbon electrode (SPCE) co-modified with a bismuth film and gold nanoparticles for electrochemical simultaneous determination of Zn(II), Pb(II) and Cu(II) by differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetric (DPASV).





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bulut Y, Tez Z (2007) Removal of heavy metals from aqueous solution by sawdust adsorption. J Environ Sci 19(2):160–166
Neagu D, Arduini F, Quintana JC, Di Cori P, Forni C, Moscone D (2014) Disposable electrochemical sensor to evaluate the phytoremediation of the aquatic plant Lemna Minor L. toward Pb2+ and/or Cd2+. Environ Sci Technol 48(13):7477–7485
Silva EL, Roldan P d S (2009) Simultaneous flow injection preconcentration of lead and cadmium using cloud point extraction and determination by atomic absorption spectrometry. J Hazard Mater 161(1):142–147
Ammann AA (2002) Speciation of heavy metals in environmental water by ion chromatography coupled to ICP–MS. Anal Bioanal Chem 372(3):448–452
Qian ZS, Shan XY, Chai LJ, Chen JR, Feng H (2015) A fluorescent nanosensor based on graphene quantum dots–aptamer probe and graphene oxide platform for detection of lead (II) ion. Biosens Bioelectron 68:225–231
Promphet N, Rattanarat P, Rangkupan R, Chailapakul O, Rodthongkum N (2015) An electrochemical sensor based on graphene/polyaniline/polystyrene nanoporous fibers modified electrode for simultaneous determination of lead and cadmium. Sensors Actuators B Chem 207:526–534
Mazloum-Ardakani M, Ganjipour B, Beitollahi H, Amini MK, Mirkhalaf F, Naeimi H, Nejati-Barzoki M (2011) Simultaneous determination of levodopa, carbidopa and tryptophan using nanostructured electrochemical sensor based on novel hydroquinone and carbon nanotubes: application to the analysis of some real samples. Electrochim Acta 56(25):9113–9120
Beitollahi H, Gholami A, Ganjali MR (2015) Preparation, characterization and electrochemical application of Ag–ZnO nanoplates for voltammetric determination of glutathione and tryptophan using modified carbon paste electrode. Mater Sci Eng C 57:107–112
Mohammadi S, Beitollahi H, Mohadesi A (2013) Electrochemical behaviour of a modified carbon nanotube paste electrode and its application for simultaneous determination of epinephrine, uric acid and folic acid. Sens Lett 11(2):388–394
Beitollahi H, Tajik S, Biparva P (2014) Electrochemical determination of sulfite and phenol using a carbon paste electrode modified with ionic liquids and graphene nanosheets: application to determination of sulfite and phenol in real samples. Measurement 56:170–177
Taleat Z, Mazloum Ardakani M, Naeimi H, Beitollahi H, Nejati M, Reza Zare H (2008) Electrochemical behavior of ascorbic acid at a 2,2′-[3,6-Dioxa-1,8-octanediylbis(nitriloethylidyne)]-bis-hydroquinone carbon paste electrode. Anal Sci 24(8):1039–1044
Beitollahi H, Taher MA, Ahmadipour M, Hosseinzadeh R (2014) Electrocatalytic determination of captopril using a modified carbon nanotube paste electrode: application to determination of captopril in pharmaceutical and biological samples. Measurement 47:770–776
Karimi-Maleh H, Ensafi AA, Beitollahi H, Nasiri V, Khalilzadeh MA, Biparva P (2012) Electrocatalytic determination of sulfite using a modified carbon nanotubes paste electrode: application for determination of sulfite in real samples. Ionics 18(7):687–694
Güell R, Aragay G, Fontàs C, Anticó E, Merkoçi A (2008) Sensitive and stable monitoring of lead and cadmium in seawater using screen-printed electrode and electrochemical stripping analysis. Anal Chim Acta 627(2):219–224
Ting SL, Ee SJ, Ananthanarayanan A, Leong KC, Chen P (2015) Graphene quantum dots functionalized gold nanoparticles for sensitive electrochemical detection of heavy metal ions. Electrochim Acta 172:7–11
de Oliveira MF, Saczk AA, Okumura LL, Fernandes AP, de Moraes M, Stradiotto NR (2004) Simultaneous determination of zinc, copper, lead, and cadmium in fuel ethanol by anodic stripping voltammetry using a glassy carbon–mercury-film electrode. Anal Bioanal Chem 380(1):135–140
Niu P, Fernández-Sánchez C, Gich M, Navarro-Hernández C, Fanjul-Bolado P, Roig A (2016) Screen-printed electrodes made of a bismuth nanoparticle porous carbon nanocomposite applied to the determination of heavy metal ions. Microchim Acta 183(2):617–623
Wang J, Lu J, Hocevar SB, Farias PAM, Ogorevc B (2000) Bismuth-coated carbon electrodes for anodic stripping voltammetry. Anal Chem 72(14):3218–3222
Barton J, García MBG, Santos DH, Fanjul-Bolado P, Ribotti A, McCaul M, Diamond D, Magni P (2016) Screen-printed electrodes for environmental monitoring of heavy metal ions: a review. Microchim Acta 183(2):503–517
Zhao G, Wang H, Liu G, Wang Z (2016) Box–Behnken response surface design for the optimization of electrochemical detection of cadmium by square wave anodic stripping voltammetry on bismuth film/glassy carbon electrode. Sensors Actuators B Chem 235:67–73
Sahoo S, Satpati AK, Reddy AVR (2015) Electrodeposited bi-au nanocomposite modified carbon paste electrode for the simultaneous determination of copper and mercury. RSC Adv 5(33):25794–25800
Toghill KE, Wildgoose GG, Moshar A, Mulcahy C, Compton RG (2008) The fabrication and characterization of a bismuth nanoparticle modified boron doped diamond electrode and its application to the simultaneous determination of cadmium(II) and lead(II). Electroanalysis 20(16):1731–1737
Chen C, Niu X, Chai Y, Zhao H, Lan M (2013) Bismuth-based porous screen-printed carbon electrode with enhanced sensitivity for trace heavy metal detection by stripping voltammetry. Sensors Actuators B Chem 178:339–342
Niu X, Chen C, Zhao H, Tang J, Li Y, Lan M (2012) Porous screen-printed carbon electrode. Electrochem Commun 22:170–173
Sosa V, Serrano N, Ariño C, Díaz-Cruz JM, Esteban M (2014) Sputtered bismuth screen-printed electrode: a promising alternative to other bismuth modifications in the voltammetric determination of cd(II) and Pb(II) ions in groundwater. Talanta 119:348–352
Wan H, Sun Q, Li H, Sun F, Hu N, Wang P (2015) Screen-printed gold electrode with gold nanoparticles modification for simultaneous electrochemical determination of lead and copper. Sensors Actuators B Chem 209:336–342
Kanyong P, Rawlinson S, Davis J (2016) Gold nanoparticle modified screen-printed carbon arrays for the simultaneous electrochemical analysis of lead and copper in tap water. Microchim Acta 183(8):2361–2368
Li Y, Wang J, Deng Z, Wu Y, Sun X, Yu D, Yang P (2001) Bismuth nanotubes: a rational low-temperature synthetic route. J Am Chem Soc 123(40):9904–9905
Xiong W, Zhou L, Liu S (2016) Development of gold-doped carbon foams as a sensitive electrochemical sensor for simultaneous determination of Pb (II) and cu (II). Chem Eng J 284:650–656
Chaiyo S, Mehmeti E, Zagar K, Siangproh W, Chailapakul O, Kalcher K (2016) Electrochemical sensors for the simultaneous determination of zinc, cadmium and lead using a Nafion/ionic liquid/graphene composite modified screen-printed carbon electrode. Anal Chim Acta 918:26–34
Fu L, Li X, Yu J, Ye J (2013) Facile and simultaneous stripping determination of zinc, cadmium and lead on disposable multiwalled carbon nanotubes modified screen-printed electrode. Electroanalysis 25(2):567–572
Ruecha N, Rodthongkum N, Cate DM, Volckens J, Chailapakul O, Henry CS (2015) Sensitive electrochemical sensor using a graphene–polyaniline nanocomposite for simultaneous detection of Zn(II), cd(II), and Pb(II). Anal Chim Acta 874:40–48
Injang U, Noyrod P, Siangproh W, Dungchai W, Motomizu S, Chailapakul O (2010) Determination of trace heavy metals in herbs by sequential injection analysis-anodic stripping voltammetry using screen-printed carbon nanotubes electrodes. Anal Chim Acta 668(1):54–60
Shi L, Li Y, Rong X, Wang Y, Ding S (2017) Facile fabrication of a novel 3D graphene framework/bi nanoparticle film for ultrasensitive electrochemical assays of heavy metal ions. Anal Chim Acta 968:21–29
Cheng Y-m, H-b F, Yin W, C-j H, D-q H, F-m L, Zhang Y, Chen C (2015) A sensitive electrochemical sensor for lead based on gold nanoparticles/nitrogen-doped graphene composites functionalized with l-cysteine-modified electrode. J Solid State Electrochem 20(2):327–335
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Guangzhou Science Technology and Innovation Commission (Project No. 201508020010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 8030 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, Z., Zhang, J., Dai, W. et al. A screen-printed carbon electrode modified with a bismuth film and gold nanoparticles for simultaneous stripping voltammetric determination of Zn(II), Pb(II) and Cu(II). Microchim Acta 184, 4731–4740 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2521-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2521-8