Abstract
The authors describe a fluorometric assay for microRNA. It is based on two-step amplification involving (a) strand displacement replication and (b) rolling circle amplification. The strand displacement amplification system is making use of template DNA (containing a sequence that is complementary to microRNA-21) and nicking enzyme sites. After hybridization, the microRNA strand becomes extended by DNA polymerase chain reaction and then cleaved by the nicking enzyme. The DNA thus produced acts as a primer in rolling circle amplification. Then, the DNA probe SYBR Green II is added to bind to ssDNA to generate a fluorescent signal which increases with increasing concentration of microRNA. The method has a wide detection range that covers the10 f. to 0.1 nM microRNA concentration range and has a detection limit as low as 1.0 fM. The method was successfully applied to the determination of microRNA-21 in the serum of healthy and breast cancer patients.

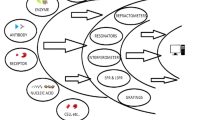
Schematic of a fluorometric microRNA assay based on two-step amplification involving strand displacement replication and rolling circle amplification. DNA probe SYBR Green II is then bound to ssDNA to generate a fluorescent signal which increases with increasing concentration of microRNA.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V (1993) The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell 75(5):843–854. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(93)90529-Y
Tay Y, Zhang J, Thomson AM, Lim B, Rigoutsos I (2008) MicroRNAs to Nanog, Oct4 and Sox2 coding regions modulate embryonic stem cell differentiation. Nature 455(7216):1124–1128. doi:10.1038/nature07299
Bartels CL, Tsongalis GJ (2009) MicroRNAs: novel biomarkers for human cancer. Clin Chem 55(4):623–631. doi:10.1373/clinchem.2008.112805
Kato M, Castro NE, Natarajan R (2013) MicroRNAs: potential mediators and biomarkers of diabetic complications. Free Radical Bio Med 64:85–94. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.06.009
Cortez MA, Bueso-Ramos C, Ferdin J, Lopez-Berestein G, Sood AK, Calin GA (2011) MicroRNAs in body fluids-the mix of hormones and biomarkers. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 8(8):467–477. doi:10.1038/nrclinonc.2011.76
Dong H, Lei J, Ding L, Wen Y, Ju H, Zhang X (2013) MicroRNA: function, detection, and bioanalysis. Chem Rev 113(8):6207–6233. doi:10.1021/cr300362f
Li W, Hou T, Wu M, Li F (2016) Label-free fluorescence strategy for sensitive microRNA detection based on isothermal exponential amplification and graphene oxide. Talanta 148:116–121. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2015.10.078
Sang Y, Xu Y, Xu L, Cheng W, Li X, Wu J, Ding S (2017) Colorimetric and visual determination of microRNA via cycling signal amplification using T7 exonuclease. Microchim Acta 184(7):2465–2471. doi:10.1007/s00604-017-2238-8
Xu Y, Li D, Cheng W, Hu R, Sang Y, Yin Y, Ding S, Ju H (2016) Chemiluminescence imaging for microRNA detection based on cascade exponential isothermal amplification machinery. Anal Chim Acta 936:229–235. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2016.07.007
Zeng K, Li H, Peng Y (2017) Gold nanoparticle enhanced surface plasmon resonance imaging of microRNA-155 using a functional nucleic acid-based amplification machine. Microchim Acta. doi:10.1007/s00604-017-2276-2
Zhang H, Liu Y, Fu X, Yuan L, Zhu Z (2015) Microfluidic bead-based assay for microRNAs using quantum dots as labels and enzymatic amplification. Microchim Acta 182(3):661–669. doi:10.1007/s00604-014-1372-9
Zhou L, Wang J, Chen Z, Li J, Wang T, Zhang Z, Xie G (2017) A universal electrochemical biosensor for the highly sensitive determination of microRNAs based on isothermal target recycling amplification and a DNA signal transducer triggered reaction. Microchim Acta 184(5):1305–1313. doi:10.1007/s00604-017-2129-z
Liu H, Bei X, Xia Q, Fu Y, Zhang S, Liu M, Fan K, Zhang M, Yang Y (2016) Enzyme-free electrochemical detection of microRNA-21 using immobilized hairpin probes and a target-triggered hybridization chain reaction amplification strategy. Microchim Acta 183(1):297–304. doi:10.1007/s00604-015-1636-z
Yang J, Tang M, Diao W, Cheng W, Zhang Y, Yan Y (2016) Electrochemical strategy for ultrasensitive detection of microRNA based on MNAzyme-mediated rolling circle amplification on a gold electrode. Microchim Acta 183(11):3061–3067. doi:10.1007/s00604-016-1958-5
Hou T, Li W, Liu X, Li F (2015) Label-free and enzyme-free homogeneous electrochemical biosensing strategy based on hybridization chain reaction: a facile, sensitive, and highly specific microRNA assay. Anal Chem 87(22):11368–11374. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.5b02790
Wang M, Yang Z, Guo Y, Wang X, Yin H, Ai S (2015) Visible-light induced photoelectrochemical biosensor for the detection of microRNA based on Bi2S3 nanorods and streptavidin on an ITO electrode. Microchim Acta 182(1):241–248. doi:10.1007/s00604-014-1324-4
Yu Y-Q, Wang J-P, Zhao M, Hong L-R, Chai Y-Q, Yuan R, Zhuo Y (2016) Target-catalyzed hairpin assembly and intramolecular/intermolecular co-reaction for signal amplified electrochemiluminescent detection of microRNA. Biosens Bioelectron 77:442–450. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2015.09.056
Liu T, Chen X, Hong C-Y, Xu X-P, Yang H-H (2014) Label-free and ultrasensitive electrochemiluminescence detection of microRNA based on long-range self-assembled DNA nanostructures. Microchim Acta 181(7):731–736. doi:10.1007/s00604-013-1113-5
Liu H, Tian T, Zhang Y, Ding L, Yu J, Yan M (2017) Sensitive and rapid detection of microRNAs using hairpin probes-mediated exponential isothermal amplification. Biosens Bioelectron 89:710–714. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2016.10.099
Nie J, Zhang D-W, Tie C, Zhou Y-L, Zhang X-X (2014) G-quadruplex based two-stage isothermal exponential amplification reaction for label-free DNA colorimetric detection. Biosens Bioelectron 56:237–242. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2014.01.032
Tan E, Wong J, Nguyen D, Zhang Y, Erwin B, Van Ness LK, Baker SM, Galas DJ, Niemz A (2005) Isothermal DNA amplification coupled with DNA nanosphere-based colorimetric detection. Anal Chem 77(24):7984–7992. doi:10.1021/ac051364i
Dong H, Zhang J, Ju H, Lu H, Wang S, Jin S, Hao K, Du H, Zhang X (2012) Highly sensitive multiple microRNA detection based on fluorescence quenching of graphene oxide and isothermal strand-displacement polymerase reaction. Anal Chem 84(10):4587–4593. doi:10.1021/ac300721u
Liu H, Li L, Duan L, Wang X, Xie Y, Tong L, Wang Q, Tang B (2013) High specific and ultrasensitive isothermal detection of microRNA by padlock probe-based exponential rolling circle amplification. Anal Chem 85(16):7941–7947. doi:10.1021/ac401715k
Xu Z, Yin H, Tian Z, Zhou Y, Ai S (2014) Electrochemical immunoassays for the detection the activity of DNA methyltransferase by using the rolling circle amplification technique. Microchim Acta 181(3):471–477. doi:10.1007/s00604-013-1141-1
Shen B, Li J, Cheng W, Yan Y, Tang R, Li Y, Ju H, Ding S (2015) Electrochemical aptasensor for highly sensitive determination of cocaine using a supramolecular aptamer and rolling circle amplification. Microchim Acta 182(1):361–367. doi:10.1007/s00604-014-1333-3
Gu H, Hao L, Duan N, Wu S, Xia Y, Ma X, Wang Z (2017) A competitive fluorescent aptasensor for okadaic acid detection assisted by rolling circle amplification. Microchim Acta. doi:10.1007/s00604-017-2293-1
Rafiee-Pour H-A, Behpour M, Keshavarz M (2016) A novel label-free electrochemical miRNA biosensor using methylene blue as redox indicator: application to breast cancer biomarker miRNA-21. Biosens Bioelectron 77:202–207. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2015.09.025
Huang YL, Mo S, Gao ZF, Chen JR, Lei JL, Luo HQ, Li NB (2017) Amperometric biosensor for microRNA based on the use of tetrahedral DNA nanostructure probes and guanine nanowire amplification. Microchim Acta. doi:10.1007/s00604-017-2246-8
Chi B-Z, Liang R-P, Qiu W-B, Yuan Y-H, Qiu J-D (2017) Direct fluorescence detection of microRNA based on enzymatically engineered primer extension poly-thymine (EPEPT) reaction using copper nanoparticles as nano-dye. Biosens Bioelectron 87:216–221. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2016.08.042
Lv W, Zhao J, Situ B, Li B, Ma W, Liu J, Wu Z, Wang W, Yan X, Zheng L (2016) A target-triggered dual amplification strategy for sensitive detection of microRNA. Biosens Bioelectron 83:250–255. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2016.04.053
Niu C, Song Q, He G, Na N, Ouyang J (2016) Near-infrared-fluorescent probes for bioapplications based on silica-coated gold nanobipyramids with distance-dependent plasmon-enhanced fluorescence. Anal Chem 88(22):11062–11069. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.6b03034
Yin H, Zhou Y, Li B, Li X, Yang Z, Ai S, Zhang X (2016) Photoelectrochemical immunosensor for microRNA detection based on gold nanoparticles-functionalized g-C3N4 and anti-DNA:RNA antibody. Sens Actuators, B-Chem 222:1119–1126. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2015.08.019
Li B, Li X, Wang M, Yang Z, Yin H, Ai S (2015) Photoelectrochemical biosensor for highly sensitive detection of microRNA based on duplex-specific nuclease-triggered signal amplification. J Solid State Electrochem 19(5):1301–1309. doi:10.1007/s10008-015-2747-5
Chen Y, Xiang Y, Yuan R, Chai Y (2015) Intercalation of quantum dots as the new signal acquisition and amplification platform for sensitive electrochemiluminescent detection of microRNA. Anal Chim Acta 891:130–135. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2015.07.059
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong province, China (No. ZR2014BQ029, ZR2017MD023), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21375079), and the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFD0800304).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 222 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Y., Li, B., Wang, M. et al. Fluorometric determination of microRNA based on strand displacement amplification and rolling circle amplification. Microchim Acta 184, 4359–4365 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2450-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2450-6