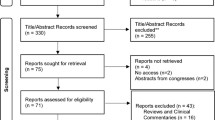
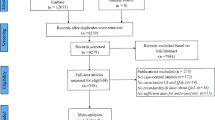
Abstract
Purpose
To explore the effectiveness of micturition interruption exercise in improving the incidence of urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy.
Materials and methods
With a retrospective case–control study, 96 patients admitted in the Second Affiliated Hospital of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University from August 2014 to August 2020 and underwent radical prostatectomy were collected as the subjects. Those patients who used micturition interruption exercise (n = 48) were set as the therapy group, and the control group was collected according to the ratio of 1:1; the patients used Kegel exercise (n = 48) to compare the rehabilitation of urinary incontinence in patients and the effect of training compliance on rehabilitation.
Results
The recovery time of urinary incontinence in the therapy group was significantly shorter than that of the control group. In the therapy group, 83.3% of patients with training compliance reached an average or above, while the control group only accounted for 58.3%. International Consultation on Incontinence Questionnaire Short-Form score of the therapy group was lower than that of the control group after surgery. Spearman analysis suggests that there is a negative correlation between the postoperative urinary incontinence recovery time and compliance with the micturition interruption exercise.
Conclusions
Micturition interruption exercise could not only improve the compliance of patients with exercise, but also significantly shorten the recovery time of urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this research period are included in published articles. Data are available on request to the authors.
References
Anderson CA, Omar MI, Campbell SE, Hunter KF, Cody JD, Glazener CM (2015) Conservative management for postprostatectomy urinary incontinence. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 20;1(1):CD001843
Comiter CV, Dobberfuhl AD (2016) The artificial urinary sphincter and male sling for postprostatectomy incontinence: which patient should get which procedure? Investig Clin Urol 57(1):3–13
Huang YC, Chang KV. Kegel exercises. Treasure Island , America, 2020
Mungovan SF, Carlsson SV, Gass GC, Graham PL, Sandhu JS, Akin O et al (2021) Preoperative exercise interventions to optimize continence outcomes following radical prostatectomy. Nat Rev Urol 18(5):259–281
Sandhu JS, Breyer B, Comiter C, Eastham JA, Gomez C, Kirages DJ et al (2019) Incontinence after prostate treatment: AUA/SUFU Guideline. J Urol 202(2):369–378
Soto González M, Da Cuña CI, Lantarón Caeiro EM, Gutiérrez Nieto M, López García S, Ojea Calvo A (2018) Correlation between the 1-hour and 24-hour pad test in the assessment of male patients with post-prostatectomy urinary incontinence. Prog Urol 28(11):536–541
Shein-Chung Chow,J Shao,H Wang,et al (2017) Sample size calculations in clinical research, third edition. Statistical Theory and Related Fields 1(2):265–266
Teber D, Sofikerim M, Ates M, Gözen AS, Güven O, Sanli O et al (2010) Is type 2 diabetes mellitus a predictive factor for incontinence after laparoscopic radical prostatectomy? A matched pair and multivariate analysis. J Urol 183(3):1087–1091
Latorre GFS, de Fraga R, Seleme MR, Mueller CV, Berghmans B (2019) An ideal e-health system for pelvic floor muscle training adherence: systematic review. Neurourol Urodyn38 (1):63–80
Fernández RA, García-Hermoso A, Solera-Martínez M, Correa MT, Morales AF, Martínez-Vizcaíno V (2015) Improvement of continence rate with pelvic floor muscle training post-prostatectomy: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Urol Int 94(2):125–132
Hodges PW, Stafford RE, Hall L, Neumann P, Morrison S, Frawley H et al (2020) Reconsideration of pelvic floor muscle training to prevent and treat incontinence after radical prostatectomy. Urol Oncol 38(5):354–371
Kegel AH (1948) Progressive resistance exercise in the functional restoration of the perineal muscles. Am J Obstet Gynecol 56(2):238–248
Moinzadeh A, Shunaigat AN, Libertino JA (2003) Urinary incontinence after radical retropubic prostatectomy: the outcome of a surgical technique. BJU Int 92(4):355–359
Bordoni B, Sugumar K, Leslie SW (2021) Anatomy, abdomen and pelvis, Pelvic Floor. Treasure Island ,FL
Grimes WR, Stratton M (2021) Pelvic floor dysfunction. Treasure Island ,FL
Bump RC, Hurt WG, Fantl JA, Wyman JF (1991) Assessment of Kegel pelvic muscle exercise performance after brief verbal instruction. Am J Obstet Gynecol 165(2):322–327
Ribeiro AM, Nammur LG, Mateus-Vasconcelos ECL, Ferreira CHJ, Muglia VF, de Oliveira HF (2021) Pelvic floor muscles after prostate radiation therapy: morpho-functional assessment by magnetic resonance imaging, surface electromyography and digital anal palpation. Int Braz J Urol 47(1):120–130
Stafford RE, Coughlin G, Lutton NJ, Hodges PW (2015) Validity of estimation of pelvic floor muscle activity from transperineal ultrasound imaging in men. PLoS One 10 (12):e0144342
Hall LM, Aljuraifani R, Hodges PW (2018) Design of programs to train pelvic floor muscles in men with urinary dysfunction: systematic review. Neurourol Urodyn 37(7):2053–2087
Yanmei Wen , Ping Ouyang, Huafeng Yang ,Shiwei Yang,Yi Song (2017) Efficacy of pelvic floor muscle training and micturition interruption training on prevention of urinary retention after radical operation of gynecological tumor:a Meta analysis. Chin J Mod Nurs 23 (33): 4244–4249
Acknowledgements
Thanks to everyone for their help.
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (project number: Y20H270024).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Kang-jie He carried out the questionnaire investigation, participated in the data analysis, and drafted the manuscript. Xiang-nan Yang carried out the questionnaire investigation and performed the statistical analysis. Yue Duan conceived of the study, participated in its design and coordination, and obtained funding. Zheng Zhu participated in the training of nursing in this research. Di Dai and Jia-cheng Zhang checked the correctness of the data. Jia-xing Chen proposed critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate
All authors have participated sufficiently in the work to take public responsibility for appropriate portions of the content after receiving permission from the human research ethics committee of the Hospital (IRB No.2020-KL-167-01). As this was a retrospective study, the ethics committee abandoned the requirement for informed consent.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent for publication was obtained from all participants.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, Kj., Yang, Xn., Zhu, Z. et al. Clinical effect of micturition interruption exercise on urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy. Support Care Cancer 30, 3241–3247 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-021-06780-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-021-06780-y