Abstract
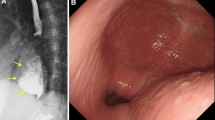
Esophageal epiphrenic diverticula (EED) are rare pulsion-type outpouchings at the lower end of esophagus. Traditionally, surgery has been performed in EED. More recently, per-oral endoscopic myotomy with septotomy (D-POEM) has emerged as an option in these cases. In this study, we aim to determine the efficacy and safety of D-POEM in cases with EED. The data of cases who underwent D-POEM in cases with EED from March 2013 to Nov 2020 were analyzed, retrospectively. The primary outcome of the study was clinical success. Secondary outcomes included technical success, procedure duration, reflux esophagitis, and adverse events. 13 patients (males 9, 48.07 ± 17.55 years) with EED underwent D-POEM during the study period. Median size of the EED was 45 mm (range 25–70). Associated esophageal motility disorder was found in 10 (76.9%) cases including type II achalasia (3), type I (3), hypercontractile esophagus (2), and unspecified (2). Technical success was achieved in 12 (92.3%) cases. Median length of total and gastric myotomies were 10 cm (range 6–20) and 3 cm (1–3), respectively. At a median follow-up of 25 months, clinical success was achieved in 84.6% cases. Mean integrated relaxation pressures reduced significantly after POEM procedure (25.80 ± 13.24 vs 9.40 ± 3.10, p = 0.001). There was one major adverse event requiring surgical intervention. D-POEM is an effective procedure in cases with EED. Long-term follow-up studies are required to ascertain the durability of response in these cases.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fisichella PM, Jalilvand A, Dobrowolsky A. Achalasia and epiphrenic diverticulum. World J Surg. 2015;39:1614–9.
Tapias LF, Morse CR, Mathisen DJ, et al. Surgical management of esophageal epiphrenic diverticula: a transthoracic approach over four decades. Ann Thorac Surg. 2017;104:1123–30.
Andrasi L, Paszt A, Simonka Z, et al. Laparoscopic surgery for epiphrenic esophageal diverticulum. JSLS. 2018;22:e2017.
Yang J, Zeng X, Yuan X, et al. An international study on the use of peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) in the management of esophageal diverticula: the first multicenter D-POEM experience. Endoscopy. 2019;51:346–9.
Samanta J, Mandavdhare HS, Kumar N, et al. Per oral endoscopic myotomy for the management of large esophageal diverticula (D-POEM): safe and effective modality for complete septotomy. Dysphagia. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-021-10252-0.
Zeng X, Bai S, Zhang Y, et al. Peroral endoscopic myotomy for the treatment of esophageal diverticulum: an experience in China. Surg Endosc. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-020-07593-6.
Maydeo A, Patil GK, Dalal A. Operative technical tricks and 12-month outcomes of diverticular peroral endoscopic myotomy (D-POEM) in patients with symptomatic esophageal diverticula. Endoscopy. 2019;51:1136–40.
Nabi Z, Ramchandani M, Sayyed M, et al. Comparison of short versus long esophageal myotomy in cases with idiopathic achalasia: a randomized controlled trial. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2020. https://doi.org/10.5056/jnm20022.
Nabi Z, Reddy DN, Ramchandani M. Adverse events during and after per-oral endoscopic myotomy: prevention, diagnosis, and management. Gastrointest Endosc. 2018;87:4–17.
Chan DSY, Foliaki A, Lewis WG, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of surgicaltreatment of non-zenker’s oesophageal diverticula. J Gastrointest Surg. 2017;21:1067–75.
Basile P, Gonzalez JM, Le Mouel JP, et al. Per-oral endoscopic myotomy with septotomy for the treatment of distal esophageal diverticula (D-POEM). Surg Endosc. 2020;34:2321–5.
Demeter M, Duricek M, Vorcak M, et al. S-POEM in treatment of achalasia and esophageal epiphrenic diverticula: single center experience. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2020;55:509–14.
Kinoshita M, Tanaka S, Kawara F, et al. Peroral endoscopic myotomy alone is effective for esophageal motility disorders and esophageal epiphrenic diverticulum: a retrospective single-center study. Surg Endosc. 2020;34:5447–54.
Nabi Z, Ramchandani M, Reddy DN. Per-oral endoscopic myotomy and gastroesophageal reflux: Where do we stand after a decade of “POETRY”? Indian J Gastroenterol. 2019;38:287–94.
Funding
The authors did not receive any kind of funding for the publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZN was responsible for designing the study, conducting the analysis, and paper writing. RC and JB were responsible for study conception and revising the manuscript. MR, SD, and RG contributed to data collection and interpretation of data. DNR performed critical revision of the manuscript. All authors revised and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1964 and later versions. Informed consent or substitute for it was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Informed Consent
Informed consent or substitute for it was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file1: Suppl Video: D-POEM in a case with giant epiphrenic diverticulum.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nabi, Z., Chavan, R., Asif, S. et al. Per-oral Endoscopic Myotomy with Division of Septum (D-POEM) in Epiphrenic Esophageal Diverticula: Outcomes at a Median Follow-Up of Two Years. Dysphagia 37, 839–847 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-021-10339-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-021-10339-8