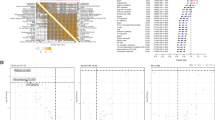
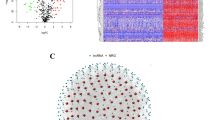
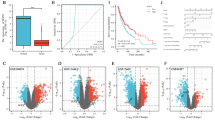
Abstract
Background
The incidence of skin cutaneous melanoma (SKCM), one of the most aggressive and lethal skin tumors, is increasing worldwide. However, for advanced SKCM, we still lack an accurate and valid way to predict its prognosis, as well as novel theories to guide the planning of treatment options for SKCM patients. Lactylation (LAC), a novel post-translational modification of histones, has been shown to promote tumor growth and inhibit the antitumor response of the tumor microenvironment (TME) in a variety of ways. We hope that this study will provide new ideas for treatment options for SKCM patients, as well as research on the molecular mechanisms of SKCM pathogenesis and development.
Methods
At the level of the RNA sequencing set (TCGA, GTEx), we used differential expression analysis, LASSO regression analysis, and multifactor Cox regression analysis to screen for prognosis-related genes and calculate the corresponding LAC scores. The content of TME cells in the tumor tissue was calculated using the CIBERSORT algorithm, and the TME score was calculated based on its results. Finally, the LAC–TME classifier was established and further analyzed based on the two scores, including the construction of a prognostic model, analysis of clinicopathological characteristics, and correlation analysis of tumor mutation burden (TMB) and immunotherapy. Based on single-cell RNA sequencing data, this study analyzed the cellular composition in SKCM tissues and explored the role of LAC scores in intercellular communication. To validate the functionality of the pivotal gene CLPB in the model, cellular experiments were ultimately executed.
Results
We screened a total of six prognosis-related genes (NDUFA10, NDUFA13, CLPB, RRM2B, HPDL, NARS2) and 7 TME cells with good prognosis. According to Kaplan–Meier survival analysis, we found that the LAClow/TMEhigh group had the highest overall survival (OS) and the LAChigh/TMElow group had the lowest OS (p value < 0.05). In further analysis of immune infiltration, tumor microenvironment (TME), functional enrichment, tumor mutational load and immunotherapy, we found that immunotherapy was more appropriate in the LAClow/TMEhigh group. Moreover, the cellular assays exhibited substantial reductions in proliferation, migration, and invasive potentials of melanoma cells in both A375 and A2058 cell lines upon CLPB knockdown.
Conclusions
The prognostic model using the combined LAC score and TME score was able to predict the prognosis of SKCM patients more consistently, and the LAC–TME classifier was able to significantly differentiate the prognosis of SKCM patients across multiple clinicopathological features. The LAC–TME classifier has an important role in the development of immunotherapy regimens for SKCM patients.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All the data in our study can be accessed from the online databases.
References
Banach K, Kowalska J, Rzepka Z, Beberok A, Rok J, Wrześniok D (2021) The role of UVA radiation in ketoprofen-mediated BRAF-mutant amelanotic melanoma cells death: a study at the cellular and molecular level. Toxicol in Vitro 72:105108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tiv.2021.105108
Banh RS, Kim ES, Spillier Q, Biancur DE, Yamamoto K, Sohn ASW, Shi G, Jones DR, Kimmelman AC, Pacold ME (2021) The polar oxy-metabolome reveals the 4-hydroxymandelate CoQ10 synthesis pathway. Nature 597:420–425. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-03865-w
Binnewies M, Roberts EW, Kersten K, Chan V, Fearon DF, Merad M, Coussens LM, Gabrilovich DI, Ostrand-Rosenberg S, Hedrick CC et al (2018) Understanding the tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) for effective therapy. Nat Med 24:541–550. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41591-018-0014-x
Brand A, Singer K, Koehl GE, Kolitzus M, Schoenhammer G, Thiel A, Matos C, Bruss C, Klobuch S, Peter K et al (2016) LDHA-associated lactic acid production blunts tumor immunosurveillance by T and NK cells. Cell Metab 24:657–671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2016.08.011
Brown TP, Ganapathy V (2020) Lactate/GPR81 signaling and proton motive force in cancer: role in angiogenesis, immune escape, nutrition, and Warburg phenomenon. Pharmacol Ther 206:107451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2019.107451
Cardoso Alves L, Corazza N, Micheau O, Krebs P (2021) The multifaceted role of TRAIL signaling in cancer and immunity. FEBS J 288:5530–5554. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.15637
Carlino MS, Larkin J, Long GV (2021) Immune checkpoint inhibitors in melanoma. Lancet 398:1002–1014. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01206-X
Cha J-H, Chan L-C, Li C-W, Hsu JL, Hung M-C (2019) Mechanisms controlling PD-L1 expression in cancer. Mol Cell 76:359–370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2019.09.030
Chae YK, Anker JF, Carneiro BA, Chandra S, Kaplan J, Kalyan A, Santa-Maria CA, Platanias LC, Giles FJ (2016) Genomic landscape of DNA repair genes in cancer. Oncotarget 7:23312–23321. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.8196
Chang L, Guo R, Huang Q, Yen Y (2013) Chromosomal instability triggered by Rrm2b loss leads to IL-6 secretion and plasmacytic neoplasms. Cell Rep 3:1389–1397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2013.03.040
Chen X, Glytsou C, Zhou H, Narang S, Reyna DE, Lopez A, Sakellaropoulos T, Gong Y, Kloetgen A, Yap YS et al (2019) Targeting mitochondrial structure sensitizes acute myeloid leukemia to venetoclax treatment. Cancer Discov 9:890–909. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-19-0117
Chen S, Zhou X, Yang X, Li W, Li S, Hu Z, Ling C, Shi R, Liu J, Chen G et al (2021) Dual blockade of lactate/GPR81 and PD-1/PD-L1 pathways enhances the anti-tumor effects of metformin. Biomolecules 11:1373. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11091373
Choi J-E, Sebastian C, Ferrer CM, Lewis CA, Sade-Feldman M, LaSalle T, Gonye A, Lopez BGC, Abdelmoula WM, Regan MS et al (2021) A unique subset of glycolytic tumour-propagating cells drives squamous cell carcinoma. Nat Metab 3:182–195. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42255-021-00350-6
Davis LE, Shalin SC, Tackett AJ (2019) Current state of melanoma diagnosis and treatment. Cancer Biol Ther 20:1366–1379. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384047.2019.1640032
de la Cruz-López KG, Castro-Muñoz LJ, Reyes-Hernández DO, García-Carrancá A, Manzo-Merino J (2019) Lactate in the regulation of tumor microenvironment and therapeutic approaches. Front Oncol 9:1143. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2019.01143
Deng D, Shah K (2020) TRAIL of hope meeting resistance in cancer. Trends Cancer 6:989–1001. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trecan.2020.06.006
Deng H, Kan A, Lyu N, He M, Huang X, Qiao S, Li S, Lu W, Xie Q, Chen H et al (2021) Tumor-derived lactate inhibit the efficacy of lenvatinib through regulating PD-L1 expression on neutrophil in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Immunother Cancer 9:e002305. https://doi.org/10.1136/jitc-2020-002305
Deng J, Lin J, Liu C, Li J, Cai J, Zhou X, Li X (2022) N7-methylguanosine methylation-related regulator genes as biological markers in predicting prognosis for melanoma. Sci Rep 12:21082. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-25698-x
Foskolou IP, Jorgensen C, Leszczynska KB, Olcina MM, Tarhonskaya H, Haisma B, D’Angiolella V, Myers WK, Domene C, Flashman E et al (2017) Ribonucleotide reductase requires subunit switching in hypoxia to maintain DNA replication. Mol Cell 66:206-220.e9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2017.03.005
Huang AC, Zappasodi R (2022) A decade of checkpoint blockade immunotherapy in melanoma: understanding the molecular basis for immune sensitivity and resistance. Nat Immunol 23:660–670. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41590-022-01141-1
Iqbal W, Demidova EV, Serrao S, ValizadehAslani T, Rosen G, Arora S (2021) RRM2B is frequently amplified across multiple tumor types: implications for DNA repair, cellular survival, and cancer therapy. Front Genet 12:628758. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2021.628758
Jovic D, Liang X, Zeng H, Lin L, Xu F, Luo Y (2022) Single-cell RNA sequencing technologies and applications: a brief overview. Clin Transl Med 12:e694. https://doi.org/10.1002/ctm2.694
Kamenisch Y, Ivanova I, Drexler K, Berneburg M (2018) UVA, metabolism and melanoma: UVA makes melanoma hungry for metastasis. Exp Dermatol 27:941–949. https://doi.org/10.1111/exd.13561
Katikaridis P, Römling U, Mogk A (2021) Basic mechanism of the autonomous ClpG disaggregase. J Biol Chem 296:100460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100460
Kędzierska-Mieszkowska S, Arent Z (2020) AAA+ molecular chaperone ClpB in Leptospira interrogans: its role and significance in leptospiral virulence and pathogenesis of leptospirosis. Int J Mol Sci 21:6645. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21186645
Kumagai S, Koyama S, Itahashi K, Tanegashima T, Lin Y-T, Togashi Y, Kamada T, Irie T, Okumura G, Kono H et al (2022) Lactic acid promotes PD-1 expression in regulatory T cells in highly glycolytic tumor microenvironments. Cancer Cell 40:201-218.e9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2022.01.001
Li X-Y, Zhao Z-J, Wang J-B, Shao Y-H, Hui-Liu, You J-X, Yang X-T (2022a) m7G methylation-related genes as biomarkers for predicting overall survival outcomes for hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2022.849756
Li Y, Li T, Zhai D, Xie C, Kuang X, Lin Y, Shao N (2022b) Quantification of ferroptosis pathway status revealed heterogeneity in breast cancer patients with distinct immune microenvironment. Front Oncol 12:956999. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.956999
Liu D, Yang X, Wu X (2021) Tumor immune microenvironment characterization identifies prognosis and immunotherapy-related gene signatures in melanoma. Front Immunol 12:663495. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.663495
Longhitano L, Giallongo S, Orlando L, Broggi G, Longo A, Russo A, Caltabiano R, Giallongo C, Barbagallo I, Di Rosa M et al (2022) Lactate rewrites the metabolic reprogramming of uveal melanoma cells and induces quiescence phenotype. Int J Mol Sci 24:24. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010024
López-Cortés A, Cabrera-Andrade A, Vázquez-Naya JM, Pazos A, Gonzáles-Díaz H, Paz-Y-Miño C, Guerrero S, Pérez-Castillo Y, Tejera E, Munteanu CR (2020) Prediction of breast cancer proteins involved in immunotherapy, metastasis, and RNA-binding using molecular descriptors and artificial neural networks. Sci Rep 10:8515. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-65584-y
Marzagalli M, Ebelt ND, Manuel ER (2019) Unraveling the crosstalk between melanoma and immune cells in the tumor microenvironment. Semin Cancer Biol 59:236–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.08.002
Masugi Y, Nishihara R, Yang J, Mima K, da Silva A, Shi Y, Inamura K, Cao Y, Song M, Nowak JA et al (2017) Tumour CD274 (PD-L1) expression and T cells in colorectal cancer. Gut 66:1463–1473. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2016-311421
Momynaliev KT, Kashin SV, Chelysheva VV, Selezneva OV, Demina IA, Serebryakova MV, Alexeev D, Ivanisenko VA, Aman E, Govorun VM (2010) Functional divergence of Helicobacter pylori related to early gastric cancer. J Proteome Res 9:254–267. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr900586w
Moyers JT, Glitza Oliva IC (2021) Immunotherapy for Melanoma. Adv Exp Med Biol 1342:81–111. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-79308-1_3
Okumura H, Natsugoe S, Yokomakura N, Kita Y, Matsumoto M, Uchikado Y, Setoyama T, Owaki T, Ishigami S, Aikou T (2006) Expression of p53R2 is related to prognosis in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 12:3740–3745. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-2416
Rivalta B, Torraco A, Martinelli D, Luciani M, Carrozzo R, Finocchi A (2022) Biallelic CLPB mutation associated with isolated neutropenia and 3-MGA-uria. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 33:e13782. https://doi.org/10.1111/pai.13782
Rui X, Shao S, Wang L, Leng J (2019) Identification of recurrence marker associated with immune infiltration in prostate cancer with radical resection and build prognostic nomogram. BMC Cancer 19:1179. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-019-6391-9
Shahbandi A, Chiu F-Y, Ungerleider NA, Kvadas R, Mheidly Z, Sun MJS, Tian D, Waizman DA, Anderson AY, Machado HL et al (2022) Breast cancer cells survive chemotherapy by activating targetable immune-modulatory programs characterized by PD-L1 or CD80. Nat Cancer 3:1513–1533. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43018-022-00466-y
Singh D, Tewari M, Singh S, Narayan G (2021) Revisiting the role of TRAIL/TRAIL-R in cancer biology and therapy. Future Oncol 17:581–596. https://doi.org/10.2217/fon-2020-0727
Song B, Peng Y, Zheng Y, Zhu Y, Liu W, Wang K, Cui Z, Song B (2023a) Role of single-cell ferroptosis regulation in intercellular communication and skin cutaneous melanoma progression and immunotherapy. Cancer Immunol Immunother. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-023-03504-5
Song B, Liu W, Zhu Y, Peng Y, Cui Z, Gao B, Chen L, Yu Z, Song B (2023b) Deciphering the contributions of cuproptosis in the development of hypertrophic scar using single-cell analysis and machine learning techniques. Front Immunol 14:1207522. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1207522
Strashilov S, Yordanov A (2021) Aetiology and pathogenesis of cutaneous melanoma: current concepts and advances. Int J Mol Sci 22:6395. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22126395
Thevarajan I, Zolkiewski M, Zolkiewska A (2020) Human CLPB forms ATP-dependent complexes in the mitochondrial intermembrane space. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 127:105841. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2020.105841
Vinasco K, Mitchell HM, Kaakoush NO, Castaño-Rodríguez N (2019) Microbial carcinogenesis: lactic acid bacteria in gastric cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer 1872:188309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2019.07.004
Wang Y, Zhao Z-J, Kang X-R, Bian T, Shen Z-M, Jiang Y, Sun B, Hu H-B, Chen Y-S (2020) lncRNA DLEU2 acts as a miR-181a sponge to regulate SEPP1 and inhibit skeletal muscle differentiation and regeneration. Aging (albany NY) 12:24033–24056. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.104095
Wang Z-H, Peng W-B, Zhang P, Yang X-P, Zhou Q (2021) Lactate in the tumour microenvironment: from immune modulation to therapy. EBioMedicine 73:103627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103627
Xin Q, Wang H, Li Q, Liu S, Qu K, Liu C, Zhang J (2022) Lactylation: a passing fad or the future of posttranslational modification. Inflammation 45:1419–1429. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-022-01637-w
Yang Z, Yan C, Ma J, Peng P, Ren X, Cai S, Shen X, Wu Y, Zhang S, Wang X et al (2023) Lactylome analysis suggests lactylation-dependent mechanisms of metabolic adaptation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Metab 5:61–79. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42255-022-00710-w
Ye X, Wei X, Liao J, Chen P, Li X, Chen Y, Yang Y, Zhao Q, Sun H, Pan L et al (2020) 4-Hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase-like protein promotes pancreatic cancer cell progression and is associated with glutamine-mediated redox balance. Front Oncol 10:617190. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.617190
Yi M, Zheng X, Niu M, Zhu S, Ge H, Wu K (2022) Combination strategies with PD-1/PD-L1 blockade: current advances and future directions. Mol Cancer 21:28. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-021-01489-2
Yu J, Chai P, Xie M, Ge S, Ruan J, Fan X, Jia R (2021) Histone lactylation drives oncogenesis by facilitating m6A reader protein YTHDF2 expression in ocular melanoma. Genome Biol 22:85. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-021-02308-z
Zaki MS, Eid OM, Eid MM, Mohamed AM, Sayed ISM, Abdel-Hamid MS, Abdel-Salam GMH (2019) Bilateral calcification of basal ganglia in a patient with duplication of both 11q13.1q22.1 and 4q35.2 with new phenotypic features. Cytogenet Genome Res 159:130–136. https://doi.org/10.1159/000504075
Zhang X, Wang Y (2019) Identification of hub genes and key pathways associated with the progression of gynecological cancer. Oncol Lett 18:6516–6524. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2019.11004
Zhang W, Kong Y, Li Y, Shi F, Lyu J, Sheng C, Wang S, Wang Q (2021) Novel molecular determinants of response or resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitor therapies in melanoma. Front Immunol 12:798474. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.798474
Zhao Z, Li T, Dong X, Wang X, Zhang Z, Zhao C, Kang X, Zheng R, Li X (2021) Untargeted metabolomic profiling of cuprizone-induced demyelination in mouse corpus callosum by UPLC-Orbitrap/MS reveals potential metabolic biomarkers of CNS demyelination disorders. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2021:7093844. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/7093844
Zhao Z-J, Zheng R-Z, Wang X-J, Li T-Q, Dong X-H, Zhao C-Y, Li X-Y (2022) Integrating lipidomics and transcriptomics reveals the crosstalk between oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in central nervous system demyelination. Front Aging Neurosci 14:870957. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2022.870957
Zhao S, Wang L, Ding W, Ye B, Cheng C, Shao J, Liu J, Zhou H (2023a) Crosstalk of disulfidptosis-related subtypes, establishment of a prognostic signature and immune infiltration characteristics in bladder cancer based on a machine learning survival framework. Front Endocrinol (lausanne) 14:1180404. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2023.1180404
Zhao S, Zhang X, Gao F, Chi H, Zhang J, Xia Z, Cheng C, Liu J (2023b) Identification of copper metabolism-related subtypes and establishment of the prognostic model in ovarian cancer. Front Endocrinol (lausanne) 14:1145797. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2023.1145797
Zhao S, Wang Q, Ni K, Zhang P, Liu Y, Xie J, Ji W, Cheng C, Zhou Q (2023c) Combining single-cell sequencing and spatial transcriptome sequencing to identify exosome-related features of glioblastoma and constructing a prognostic model to identify BARD1 as a potential therapeutic target for GBM patients. Front Immunol 14:1263329. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1263329
Zhao Z, Ding Y, Tran LJ, Chai G, Lin L (2023d) Innovative breakthroughs facilitated by single-cell multi-omics: manipulating natural killer cell functionality correlates with a novel subcategory of melanoma cells. Front Immunol 14:1196892. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1196892
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82072182, 82002061).
Funding
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China, Grant numbers [82002061, 82072182].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and design: YZ, BS; data curation and methodology: ZY and YP; BS carried out the in vitro studies. Analysis and interpretation of data: ZC; writing of the manuscript: YZ, BS; review of the manuscript: ZY, YP and ZC; study supervision: LC and BS. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Y., Song, B., Yang, Z. et al. Integrative lactylation and tumor microenvironment signature as prognostic and therapeutic biomarkers in skin cutaneous melanoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 17897–17919 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05483-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05483-7