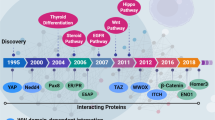
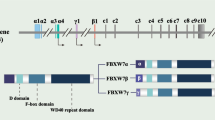
Abstract
Background
Breast cancer is considered the number one killer of women both in China and abroad, and the leading cause of cancer death. It severely affects female health-related quality of life. Broad-complex, tramtrack, bric à brac (BTB) protein family was first discovered in drosophila as early as in 1993 by Godt D and peers, since then, more family members and their critical biological functions were uncovered. Moreover, researchers around the world have recently demonstrated that numerous signaling pathways connect BTB family members and human breast cancer.
Purpose
In this review, we critically discuss these findings regarding the essential mechanisms and functions of the BTB protein family in mediating the organic processes of human breast cancer. Meanwhile, we summarize the signaling pathways the BTB protein family participates in. And we address that BTB proteins regulate the growth, apoptosis, and other behaviors of breast cancer cells. We also point out the future directions for further studies in this field.
Methods
The relevant online literatures have been reviewed for this article.
Conclusion
This review could offer an update on novel molecular targets for treating human breast cancer and new insights into BTB protein family research.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no new data were created or analyzed in this study.
Abbreviations
- AEG-1:
-
Astrocyte elevated gene-1
- AKT:
-
Protein kinase B
- BACH1:
-
BTB and CNC homology 1
- BCL6:
-
B cell leukemia/lymphoma 6
- BOZF1:
-
BTB and zinc finger domains factor on chromosome 1
- BRCA1:
-
Breast cancer susceptibility gene 1
- BTB:
-
Broad-complex, tramtrack, bric à brac
- BTBD7:
-
BTB domain containing 7
- bZIP:
-
Basic region/leucine zipper
- cAMP:
-
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate
- CDKN1A:
-
Cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor 1A
- cIAP2:
-
Cellular inhibitor of apoptosis proteins 2
- CNC:
-
Cap 'n' collar
- CUL3:
-
Cullin3
- CXCL14:
-
C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 14
- CXCL4:
-
C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 4
- CXCR3-B:
-
C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 3-B
- CXCR4:
-
C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 4
- DBC2:
-
Deleted in breast cancer 2
- EMT:
-
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition
- ERα:
-
Estrogen receptor alpha
- GPCR:
-
Gprotein-coupled receptor
- GPER1:
-
G protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1
- GTPases:
-
Guanosine triphosphate pases
- HER2:
-
Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2
- HMGA2:
-
High mobility group AT-hook 2
- HO-1:
-
Heme oxygenase-1
- ICAM-1:
-
Intercellular adhesion molecule-1
- KCTD10:
-
Potassium channel tetramerization domain containing 10
- MAP:
-
Mitogen-activated protein
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinases
- METTL7A:
-
Methyltransferase like 7A
- METTL7B:
-
Methyltransferase like 7B
- MMP1:
-
Matrix metallopeptidase 1
- MSI2:
-
Musashi RNA binding protein 2
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor kappa B
- Nrf2:
-
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2
- OPN:
-
Osteopontin
- PARP:
-
Polyadenosine-diphosphate-ribose polymerase
- PATZ1:
-
POZ and AT hook containing zinc finger 1
- PCNA:
-
Proliferating cell nuclear antigen
- PDIP1:
-
Polymerase delta-interacting protein 1
- PI3K:
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase
- PKA:
-
Protein kinase A
- PLZF:
-
Promyelocytic leukemia zinc finger
- POK:
-
Poxvirus and zinc finger and Kruppel
- POZ:
-
Pox virus and zinc finger
- PTEN:
-
Phosphatase and tensin homolog
- RARα:
-
Retinoid acid receptor alpha
- Rbx1:
-
Ring-box 1
- Rho:
-
Rhodopsin
- RhoBTB1:
-
Rho related BTB domain containing 1
- RhoBTB2:
-
Rho related BTB domain containing 2
- RKIP:
-
Raf kinase inhibitory protein
- ROCK:
-
Rho-associated, coiled-coil containing protein kinase
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- Sp:
-
Specificity protein
- SPOP:
-
Speckle type POZ protein
- SRC-3:
-
Steroid receptor co-activator-3
- TCF/LEF:
-
T-cell factor/lymphoid enhancer-binding factor
- TGF-β:
-
Transforming growth factor-beta
- TNBC:
-
Triple negative breast cancer
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha
- TNM:
-
Tumor-node-metastasis
- ZBTB1:
-
Zinc finger and BTB domain containing 1
- ZBTB16:
-
Zinc finger and BTB domain containing 16
- ZBTB27:
-
Zinc finger and BTB domain containing 27
- ZBTB28:
-
Zinc finger and BTB domain containing 28
- ZBTB3:
-
Zinc finger and BTB domain containing 3
- ZBTB33:
-
Zinc finger and BTB domain containing 33
- ZBTB4:
-
Zinc finger and BTB domain containing 4
- ZBTB7A:
-
Zinc finger and BTB domain containing 7A
- ZBTB8A:
-
Zinc finger and BTB domain containing 8A
References
Aggarwal A, Hunter WJ 3rd, Aggarwal H, Silva ED, Davey MS, Murphy RF, Agrawal DK (2010) Expression of leukemia/lymphoma-related factor (LRF/POKEMON) in human breast carcinoma and other cancers. Exp Mol Pathol 89(2):140–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexmp.2010.05.002
Androutsellis-Theotokis A, Leker RR, Soldner F, Hoeppner DJ, Ravin R, Poser SW, McKay RD (2006) Notch signalling regulates stem cell numbers in vitro and in vivo. Nature 442(7104):823–826. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04940
Ang L, Zheng L, Wang J, Huang J, Hu HG, Zou Q, Wu ZS (2017) Expression of and correlation between BCL6 and ZEB family members in patients with breast cancer. Exp TherApy Med 14(5):3985–3992. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2017.5101
Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Rand MD, Lake RJ (1999) Notch signaling: cell fate control and signal integration in development. Science 284(5415):770–776. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.284.5415.770
Aznar N, Midde KK, Dunkel Y, Lopez-Sanchez I, Pavlova Y, Marivin A, Ghosh P (2015) Daple is a novel non-receptor GEF required for trimeric G protein activation in Wnt signaling. Elife 4:e07091. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.07091
Bardwell VJ, Treisman R (1994) The POZ domain: a conserved protein-protein interaction motif. Genes Dev 8(14):1664–1677. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.8.14.1664
Barrett CW, Smith JJ, Lu LC, Markham N, Stengel KR, Short SP, Williams CS (2012) Kaiso directs the transcriptional corepressor MTG16 to the Kaiso binding site in target promoters. PLoS ONE 7(12):e51205. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0051205
Bassey-Archibong BI, Rayner LG, Hercules SM, Aarts CW, Dvorkin-Gheva A, Bramson JL, Daniel JM (2017) Kaiso depletion attenuates the growth and survival of triple negative breast cancer cells. Cell Death Dis 8(3):e2689. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2017.92
Berthold J, Schenkova K, Rivero F (2008) Rho GTPases of the RhoBTB subfamily and tumorigenesis. Acta Pharmacol Sin 29(3):285–295. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-7254.2008.00773.x
Bi Y, Wei L, Mao HT, Zhang L, Zuo WS (2008) Expressions of Fas, CTLA-4 and RhoBTB2 genes in breast carcinoma and their relationship with clinicopathological factors. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi 30(10):749–753
Borri F, Granaglia A (2021) Pathology of triple negative breast cancer. Semin Cancer Biol 72:136–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2020.06.005
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68(6):394–424. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492
Buluwela L, Pike J, Mazhar D, Kamalati T, Hart SM, Al-Jehani R, Ali S (2005) Inhibiting estrogen responses in breast cancer cells using a fusion protein encoding estrogen receptor-alpha and the transcriptional repressor PLZF. Gene Ther 12(5):452–460. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302421
Bunz F, Dutriaux A, Lengauer C, Waldman T, Zhou S, Brown JP, Vogelstein B (1998) Requirement for p53 and p21 to sustain G2 arrest after DNA damage. Science 282(5393):1497–1501. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.282.5393.1497
Chaharbakhshi E, Jemc JC (2016) Broad-complex, tramtrack, and bric-à-brac (BTB) proteins: critical regulators of development. Genesis 54(10):505–518. https://doi.org/10.1002/dvg.22964
Chandrashekar DS, Bashel B, Balasubramanya SAH, Creighton CJ, Ponce-Rodriguez I, Chakravarthi B, Varambally S (2017) UALCAN: a portal for facilitating tumor subgroup gene expression and survival analyses. Neoplasia 19(8):649–658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neo.2017.05.002
Chandrashekar DS, Karthikeyan SK, Korla PK, Patel H, Shovon AR, Athar M, Varambally S (2022) UALCAN: an update to the integrated cancer data analysis platform. Neoplasia 25:18–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neo.2022.01.001
Chen HY, Chen RH (2016) Cullin 3 ubiquitin ligases in cancer biology: functions and therapeutic implications. Front Oncol 6:113. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2016.00113
Chen Z, Brand NJ, Chen A, Chen SJ, Tong JH, Wang ZY, Zelent A (1993) Fusion between a novel Krüppel-like zinc finger gene and the retinoic acid receptor-alpha locus due to a variant t(11;17) translocation associated with acute promyelocytic leukaemia. Embo J 12(3):1161–1167
Chen J, Lai YH, Ooi S, Song Y, Li L, Liu TY (2020) BTB domain-containing 7 predicts low recurrence and suppresses tumor progression by deactivating Notch1 signaling in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 184(2):287–300. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-020-05857-2
Chin KV, Yang WL, Ravatn R, Kita T, Reitman E, Vettori D, Iacono L (2002) Reinventing the wheel of cyclic AMP: novel mechanisms of cAMP signaling. Ann N Y Acad Sci 968:49–64. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.2002.tb04326.x
Cho JH, Kim MJ, Kim KJ, Kim JR (2012) POZ/BTB and AT-hook-containing zinc finger protein 1 (PATZ1) inhibits endothelial cell senescence through a p53 dependent pathway. Cell Death Differ 19(4):703–712. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2011.142
Choi WI, Yoon JH, Kim MY, Koh DI, Licht JD, Kim K, Hur MW (2014) Promyelocytic leukemia zinc finger-retinoic acid receptor α (PLZF-RARα), an oncogenic transcriptional repressor of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A (p21WAF/CDKN1A) and tumor protein p53 (TP53) genes. J Biol Chem 289(27):18641–18656. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.538777
Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours (2012) Nature 490(7418): 61–70. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11412
Corbit KC, Trakul N, Eves EM, Diaz B, Marshall M, Rosner MR (2003) Activation of Raf-1 signaling by protein kinase C through a mechanism involving Raf kinase inhibitory protein. J Biol Chem 278(15):13061–13068. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M210015200
Dangi-Garimella S, Yun J, Eves EM, Newman M, Erkeland SJ, Hammond SM, Rosner MR (2009) Raf kinase inhibitory protein suppresses a metastasis signalling cascade involving LIN28 and let-7. Embo J 28(4):347–358. https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2008.294
Daniel JM, Spring CM, Crawford HC, Reynolds AB, Baig A (2002) The p120(ctn)-binding partner Kaiso is a bi-modal DNA-binding protein that recognizes both a sequence-specific consensus and methylated CpG dinucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res 30(13):2911–2919. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkf398
Del Valle-Pérez B, Casagolda D, Lugilde E, Valls G, Codina M, Dave N, Duñach M (2011) Wnt controls the transcriptional activity of Kaiso through CK1ε-dependent phosphorylation of p120-catenin. J Cell Sci 124(Pt 13):2298–2309. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.082693
DiBello PR, Withers DA, Bayer CA, Fristrom JW, Guild GM (1991) The Drosophila Broad-Complex encodes a family of related proteins containing zinc fingers. Genetics 129(2):385–397
Donovan SL, Schweers B, Martins R, Johnson D, Dyer MA (2006) Compensation by tumor suppressor genes during retinal development in mice and humans. BMC Biol 4:14. https://doi.org/10.1186/1741-7007-4-14
Fan L, Strasser-Weippl K, Li JJ, St Louis J, Finkelstein DM, Yu KD, Goss PE (2014) Breast cancer in China. Lancet Oncol 15(7):e279-289. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(13)70567-9
Furth PA, Nakles RE, Millman S, Diaz-Cruz ES, Cabrera MC (2011) Signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 as a key signaling pathway in normal mammary gland developmental biology and breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 13(5):220. https://doi.org/10.1186/bcr2921
Gao K, Jin X, Tang Y, Ma J, Peng J, Yu L, Wang C (2015) Tumor suppressor SPOP mediates the proteasomal degradation of progesterone receptors (PRs) in breast cancer cells. Am J Cancer Res 5(10):3210–3220
Godt D, Couderc JL, Cramton SE, Laski FA (1993) Pattern formation in the limbs of Drosophila: bric à brac is expressed in both a gradient and a wave-like pattern and is required for specification and proper segmentation of the tarsus. Development 119(3):799–812
Granovsky AE, Rosner MR (2008) Raf kinase inhibitory protein: a signal transduction modulator and metastasis suppressor. Cell Res 18(4):452–457. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2008.43
Győrffy B (2021) Survival analysis across the entire transcriptome identifies biomarkers with the highest prognostic power in breast cancer. Comput Struct Biotechnol J 19:4101–4109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csbj.2021.07.014
Haga RB, Garg R, Collu F, Borda D’Agua B, Menéndez ST, Colomba A, Ridley AJ (2019) RhoBTB1 interacts with ROCKs and inhibits invasion. Biochem J 476(17):2499–2514. https://doi.org/10.1042/bcj20190203
Hamaguchi M, Meth JL, von Klitzing C, Wei W, Esposito D, Rodgers L, Wigler MH (2002) DBC2, a candidate for a tumor suppressor gene involved in breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(21):13647–13652. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.212516099
Han L, Hou L, Song J, Lin D, Wu L, Ge Y, Ma Z (2013) Decreased expression of the DBC2 gene and its clinicopathological significance in breast cancer: correlation with aberrant DNA methylation. Biotechnol Lett 35(8):1175–1181. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-013-1190-x
Harrison SD, Travers AA (1990) The tramtrack gene encodes a Drosophila finger protein that interacts with the ftz transcriptional regulatory region and shows a novel embryonic expression pattern. Embo j 9(1):207–216
Hatzi K, Melnick A (2014) Breaking bad in the germinal center: how deregulation of BCL6 contributes to lymphomagenesis. Trends Mol Med 20(6):343–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2014.03.001
He J, Wu M, Xiong L, Gong Y, Yu R, Peng W, Xiang T (2020) BTB/POZ zinc finger protein ZBTB16 inhibits breast cancer proliferation and metastasis through upregulating ZBTB28 and antagonizing BCL6/ZBTB27. Clin Epigenetics 12(1):82. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13148-020-00867-9
Hernández-Muñoz I, Lund AH, van der Stoop P, Boutsma E, Muijrers I, Verhoeven E, van Lohuizen M (2005) Stable X chromosome inactivation involves the PRC1 Polycomb complex and requires histone MACROH2A1 and the CULLIN3/SPOP ubiquitin E3 ligase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(21):7635–7640. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0408918102
Jin X, Wang J, Li Q, Zhuang H, Yang J, Lin Z, Gao K (2019) SPOP targets oncogenic protein ZBTB3 for destruction to suppress endometrial cancer. Am J Cancer Res 9(12):2797–2812
Kim SW, Park JI, Spring CM, Sater AK, Ji H, Otchere AA, McCrea PD (2004) Non-canonical Wnt signals are modulated by the Kaiso transcriptional repressor and p120-catenin. Nat Cell Biol 6(12):1212–1220. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1191
Kim K, Chadalapaka G, Lee SO, Yamada D, Sastre-Garau X, Defossez PA, Safe S (2012) Identification of oncogenic microRNA-17–92/ZBTB4/specificity protein axis in breast cancer. Oncogene 31(8):1034–1044. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.296
Kim MK, Jeon BN, Koh DI, Kim KS, Park SY, Yun CO, Hur MW (2013) Regulation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A gene (CDKN1A) by the repressor BOZF1 through inhibition of p53 acetylation and transcription factor Sp1 binding. J Biol Chem 288(10):7053–7064. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.416297
Kim H, Dejsuphong D, Adelmant G, Ceccaldi R, Yang K, Marto JA, D’Andrea AD (2014) Transcriptional repressor ZBTB1 promotes chromatin remodeling and translesion DNA synthesis. Mol Cell 54(1):107–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2014.02.017
Kirschner LS, Yin Z, Jones GN, Mahoney E (2009) Mouse models of altered protein kinase A signaling. Endocr Relat Cancer 16(3):773–793. https://doi.org/10.1677/erc-09-0068
Kriegsmann M, Endris V, Wolf T, Pfarr N, Stenzinger A, Loibl S, Weichert W (2014) Mutational profiles in triple-negative breast cancer defined by ultradeep multigene sequencing show high rates of PI3K pathway alterations and clinically relevant entity subgroup specific differences. Oncotarget 5(20):9952–9965. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.2481
Kwon JE, La M, Oh KH, Oh YM, Kim GR, Seol JH, Chung CH (2006) BTB domain-containing speckle-type POZ protein (SPOP) serves as an adaptor of Daxx for ubiquitination by Cul3-based ubiquitin ligase. J Biol Chem 281(18):12664–12672. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M600204200
Lee J, Yesilkanal AE, Wynne JP, Frankenberger C, Liu J, Yan J, Rosner MR (2019) Effective breast cancer combination therapy targeting BACH1 and mitochondrial metabolism. Nature 568(7751):254–258. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1005-x
Li C, Ao J, Fu J, Lee DF, Xu J, Lonard D, O’Malley BW (2011) Tumor-suppressor role for the SPOP ubiquitin ligase in signal-dependent proteolysis of the oncogenic co-activator SRC-3/AIB1. Oncogene 30(42):4350–4364. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.151
Liang Y, Wu H, Lei R, Chong RA, Wei Y, Lu X, Kang Y (2012) Transcriptional network analysis identifies BACH1 as a master regulator of breast cancer bone metastasis. J Biol Chem 287(40):33533–33544. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.392332
Liang X, Zhao Q, Geng T, Luo S, He Q (2018) MiR-106b regulates the apoptosis and tumorigenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma via targeting Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 7A (Zbtb7a). J Biochem Mol Toxicol 32(8):e22169. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbt.22169
Lim JH (2014) Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 3 is essential for the growth of cancer cells. BMB Rep 47(7):405–410. https://doi.org/10.5483/bmbrep.2014.47.7.075
Liu XS, Haines JE, Mehanna EK, Genet MD, Ben-Sahra I, Asara JM, Yuan ZM (2014) ZBTB7A acts as a tumor suppressor through the transcriptional repression of glycolysis. Genes Dev 28(17):1917–1928. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.245910.114
Lo Nigro C, Vivenza D, Monteverde M, Lattanzio L, Gojis O, Garrone O, Crook T (2012) High frequency of complex TP53 mutations in CNS metastases from breast cancer. Br J Cancer 106(2):397–404. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2011.464
Logarajah S, Hunter P, Kraman M, Steele D, Lakhani S, Bobrow L, Wagner S (2003) BCL-6 is expressed in breast cancer and prevents mammary epithelial differentiation. Oncogene 22(36):5572–5578. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206689
Lorenz K, Lohse MJ, Quitterer U (2003) Protein kinase C switches the Raf kinase inhibitor from Raf-1 to GRK-2. Nature 426(6966):574–579. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02158
Luo FY, Liu ZH, Hu QH, Lin GQ, Tang CE, Zhang WX, Zhuang W (2015) Association of BTBD7 with metastasis and poor prognosis in non-small-cell lung cancer patients. J Cancer 6(5):477–481. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.11715
Mansoori B, Mohammadi A, Asadzadeh Z, Shirjang S, Minouei M, Abedi Gaballu F, Baradaran B (2019) HMGA2 and Bach-1 cooperate to promote breast cancer cell malignancy. J Cell Physiol 234(10):17714–17726. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.28397
Mao H, Qu X, Yang Y, Zuo W, Bi Y, Zhou C, Zhang L (2010) A novel tumor suppressor gene RhoBTB2 (DBC2): frequent loss of expression in sporadic breast cancer. Mol Carcinog 49(3):283–289. https://doi.org/10.1002/mc.20598
Mao A, Chen M, Qin Q, Liang Z, Jiang W, Yang W, Wei C (2019) ZBTB7A promotes migration, invasion and metastasis of human breast cancer cells through NF-κB-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in vitro and in vivo. J Biochem 166(6):485–493. https://doi.org/10.1093/jb/mvz062
Mastrangelo T, Modena P, Tornielli S, Bullrich F, Testi MA, Mezzelani A, Sozzi G (2000) A novel zinc finger gene is fused to EWS in small round cell tumor. Oncogene 19(33):3799–3804. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1203762
McKenzie PP, Guichard SM, Middlemas DS, Ashmun RA, Danks MK, Harris LC (1999) Wild-type p53 can induce p21 and apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells but the DNA damage-induced G1 checkpoint function is attenuated. Clin Cancer Res 5(12):4199–4207
McKinnon CM, Mellor H (2017) The tumor suppressor RhoBTB1 controls Golgi integrity and breast cancer cell invasion through METTL7B. BMC Cancer 17(1):145. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-017-3138-3
McKinnon CM, Lygoe KA, Skelton L, Mitter R, Mellor H (2008) The atypical Rho GTPase RhoBTB2 is required for expression of the chemokine CXCL14 in normal and cancerous epithelial cells. Oncogene 27(54):6856–6865. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.317
Mittal S, Subramanyam D, Dey D, Kumar RV, Rangarajan A (2009) Cooperation of Notch and Ras/MAPK signaling pathways in human breast carcinogenesis. Mol Cancer 8:128. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-4598-8-128
Molloy ME, Lewinska M, Williamson AK, Nguyen TT, Kuser-Abali G, Gong L, Yuan ZM (2018) ZBTB7A governs estrogen receptor alpha expression in breast cancer. J Mol Cell Biol 10(4):273–284. https://doi.org/10.1093/jmcb/mjy020
Murakami A, Maekawa M, Kawai K, Nakayama J, Araki N, Semba K, Higashiyama S (2019) Cullin-3/KCTD10 E3 complex is essential for Rac1 activation through RhoB degradation in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive breast cancer cells. Cancer Sci 110(2):650–661. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.13899
Ogden SR, Wroblewski LE, Weydig C, Romero-Gallo J, O’Brien DP, Israel DA, Peek RM Jr (2008) p120 and Kaiso regulate Helicobacter pylori-induced expression of matrix metalloproteinase-7. Mol Biol Cell 19(10):4110–4121. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.e08-03-0283
Park JI, Kim SW, Lyons JP, Ji H, Nguyen TT, Cho K, McCrea PD (2005) Kaiso/p120-catenin and TCF/beta-catenin complexes coordinately regulate canonical Wnt gene targets. Dev Cell 8(6):843–854. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2005.04.010
Park JI, Ji H, Jun S, Gu D, Hikasa H, Li L, McCrea PD (2006) Frodo links Dishevelled to the p120-catenin/Kaiso pathway: distinct catenin subfamilies promote Wnt signals. Dev Cell 11(5):683–695. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2006.09.022
Paysan-Lafosse T, Blum M, Chuguransky S, Grego T, Pinto BL, Salazar GA, Bateman A (2023) InterPro in 2022. Nucleic Acids Res 51(D1):D418-d427. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac993
Perez-Torrado R, Yamada D, Defossez PA (2006) Born to bind: the BTB protein-protein interaction domain. BioEssays 28(12):1194–1202. https://doi.org/10.1002/bies.20500
Punwani D, Simon K, Choi Y, Dutra A, Gonzalez-Espinosa D, Pak E, Puck JM (2012) Transcription factor zinc finger and BTB domain 1 is essential for lymphocyte development. J Immunol 189(3):1253–1264. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1200623
Qu YH, Liu HT, Zheng LJ, Qin Z, Li HX (2017) Effects of microRNA-373 on the proliferation and invasiveness of breast carcinoma and its mechanisms. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 97(8):603–607. https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2017.08.009
Ren K, Yuan J, Yang M, Gao X, Ding X, Zhou J, Zhang J (2014) KCTD10 is involved in the cardiovascular system and Notch signaling during early embryonic development. PLoS ONE 9(11):e112275. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0112275
Sahai E, Marshall CJ (2002) RHO-GTPases and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2(2):133–142. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc725
Sahlgren C, Lendahl U (2006) Notch signaling and its integration with other signaling mechanisms. Regen Med 1(2):195–205. https://doi.org/10.2217/17460751.1.2.195
Shah SP, Roth A, Goya R, Oloumi A, Ha G, Zhao Y, Aparicio S (2012) The clonal and mutational evolution spectrum of primary triple-negative breast cancers. Nature 486(7403):395–399. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10933
Shen Y, Cao R, Liu W, Zhou Y, Wu Y, Tan J, Zu X (2017) Negative feedback loop between ZBTB7A and TGF-β in breast cancer. Oncol Lett 14(2):1403–1410. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2017.6291
Silwal-Pandit L, Vollan HK, Chin SF, Rueda OM, McKinney S, Osako T, Langerod A (2014) TP53 mutation spectrum in breast cancer is subtype specific and has distinct prognostic relevance. Clin Cancer Res 20(13):3569–3580. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-2943
Song L, Tao X, Lin L, Chen C, Yao H, He G, Deng X (2018) Cerasomal lovastatin nanohybrids for efficient inhibition of triple-negative breast cancer stem cells to improve therapeutic efficacy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10(8):7022–7030. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b01633
Stagni V, Manni I, Oropallo V, Mottolese M, Di Benedetto A, Piaggio G, Barilà D (2015) ATM kinase sustains HER2 tumorigenicity in breast cancer. Nat Commun 6:6886. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms7886
Stogios PJ, Downs GS, Jauhal JJ, Nandra SK, Privé GG (2005) Sequence and structural analysis of BTB domain proteins. Genome Biol 6(10):R82. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2005-6-10-r82
Tamagnone L, Zacchigna S, Rehman M (2018) Taming the notch transcriptional regulator for cancer therapy. Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23020431
Tamma R, Ruggieri S, Annese T, Simone G, Mangia A, Rega S, Ribatti D (2018) Bcl6/p53 expression, macrophages/mast cells infiltration and microvascular density in invasive breast carcinoma. Oncotarget 9(32):22727–22740. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.25220
Tang W, Wang C, Fu F, Chen Q (2014) RhoBTB2 gene in breast cancer is silenced by promoter methylation. Int J Mol Med 33(3):722–728. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2013.1593
Tao YM, Huang JL, Zeng S, Zhang S, Fan XG, Wang ZM, Shen H (2013) BTB/POZ domain-containing protein 7: epithelial-mesenchymal transition promoter and prognostic biomarker of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 57(6):2326–2337. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.26268
Thirkettle HJ, Mills IG, Whitaker HC, Neal DE (2009) Nuclear LYRIC/AEG-1 interacts with PLZF and relieves PLZF-mediated repression. Oncogene 28(41):3663–3670. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.223
Tian X, Sun D, Zhang Y, Zhao S, Xiong H, Fang J (2008) Zinc finger protein 278, a potential oncogene in human colorectal cancer. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (shanghai) 40(4):289–296. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-7270.2008.00405.x
Trakul N, Menard RE, Schade GR, Qian Z, Rosner MR (2005) Raf kinase inhibitory protein regulates Raf-1 but not B-Raf kinase activation. J Biol Chem 280(26):24931–24940. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M413929200
Tran TH, Utama FE, Lin J, Yang N, Sjolund AB, Ryder A, Rui H (2010) Prolactin inhibits BCL6 expression in breast cancer through a Stat5a-dependent mechanism. Cancer Res 70(4):1711–1721. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-09-2314
Valentino T, Palmieri D, Vitiello M, Pierantoni GM, Fusco A, Fedele M (2013) PATZ1 interacts with p53 and regulates expression of p53-target genes enhancing apoptosis or cell survival based on the cellular context. Cell Death Dis 4(12):e963. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2013.500
vant Veer LJ, Dai H, van de Vijver MJ, He YD, Hart AA, Mao M, Friend SH (2002) Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of breast cancer. Nature 415(6871):530–536. https://doi.org/10.1038/415530a
Vega FM, Ridley AJ (2008) Rho GTPases in cancer cell biology. FEBS Lett 582(14):2093–2101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2008.04.039
Vermeulen JF, van de Ven RA, Ercan C, van der Groep P, van der Wall E, Bult P, Derksen PW (2012) Nuclear Kaiso expression is associated with high grade and triple-negative invasive breast cancer. PLoS ONE 7(5):e37864. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0037864
von Karstedt S, Conti A, Nobis M, Montinaro A, Hartwig T, Lemke J, Walczak H (2015) Cancer cell-autonomous TRAIL-R signaling promotes KRAS-driven cancer progression, invasion, and metastasis. Cancer Cell 27(4):561–573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2015.02.014
Walker SR, Nelson EA, Frank DA (2007) STAT5 represses BCL6 expression by binding to a regulatory region frequently mutated in lymphomas. Oncogene 26(2):224–233. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209775
Walker SR, Nelson EA, Zou L, Chaudhury M, Signoretti S, Richardson A, Frank DA (2009) Reciprocal effects of STAT5 and STAT3 in breast cancer. Mol Cancer Res 7(6):966–976. https://doi.org/10.1158/1541-7786.Mcr-08-0238
Wang G, Lunardi A, Zhang J, Chen Z, Ala U, Webster KA, Pandolfi PP (2013) Zbtb7a suppresses prostate cancer through repression of a Sox9-dependent pathway for cellular senescence bypass and tumor invasion. Nat Genet 45(7):739–746. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2654
Weber A, Marquardt J, Elzi D, Forster N, Starke S, Glaum A, Eilers M (2008) Zbtb4 represses transcription of P21CIP1 and controls the cellular response to p53 activation. Embo J 27(11):1563–1574. https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2008.85
Wu ZS, Wu Q, Wang CQ, Wang XN, Wang Y, Zhao JJ, Xu XC (2010) MiR-339–5p inhibits breast cancer cell migration and invasion in vitro and may be a potential biomarker for breast cancer prognosis. BMC Cancer 10:542. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-10-542
Wu Q, Liu X, Yan H, He YH, Ye S, Cheng XW, Wu ZS (2014) B-cell lymphoma 6 protein stimulates oncogenicity of human breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer 14:418. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-14-418
Yan H, Zhao M, Huang S, Chen P, Wu WY, Huang J, Wu Q (2016) Prolactin inhibits BCL6 expression in breast cancer cells through a MicroRNA-339–5p-dependent pathway. J Breast Cancer 19(1):26–33. https://doi.org/10.4048/jbc.2016.19.1.26
Yang WL, Ravatn R, Kudoh K, Alabanza L, Chin KV (2010) Interaction of the regulatory subunit of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase with PATZ1 (ZNF278). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 391(3):1318–1323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.12.026
Yang T, Yao H, He G, Song L, Liu N, Wang Y, Deng X (2016) Effects of lovastatin on MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells: an antibody microarray analysis. J Cancer 7(2):192–199. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.13414
Yang L, Wang T, Zhang J, Wang X (2017) BTBD7 silencing inhibited epithelial- mesenchymal transition (EMT) via regulating Slug expression in human salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma. Cancer Biomark 20(4):461–468. https://doi.org/10.3233/cbm-170262
Yeung KC, Rose DW, Dhillon AS, Yaros D, Gustafsson M, Chatterjee D, Sedivy JM (2001) Raf kinase inhibitor protein interacts with NF-kappaB-inducing kinase and TAK1 and inhibits NF-kappaB activation. Mol Cell Biol 21(21):7207–7217. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.21.21.7207-7217.2001
Yu JM, Sun W, Hua F, Xie J, Lin H, Zhou DD, Hu ZW (2015) BCL6 induces EMT by promoting the ZEB1-mediated transcription repression of E-cadherin in breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett 365(2):190–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2015.05.029
Yun J, Frankenberger CA, Kuo WL, Boelens MC, Eves EM, Cheng N, Rosner MR (2011) Signalling pathway for RKIP and Let-7 regulates and predicts metastatic breast cancer. Embo J 30(21):4500–4514. https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2011.312
Zeng L, Imamoto A, Rosner MR (2008) Raf kinase inhibitory protein (RKIP): a physiological regulator and future therapeutic target. Expert Opin Ther Targets 12(10):1275–1287. https://doi.org/10.1517/14728222.12.10.1275
Zhang Q, Wei T, Shim K, Wright K, Xu K, Palka-Hamblin HL, Khare S (2016) Atypical role of sprouty in colorectal cancer: sprouty repression inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncogene 35(24):3151–3162. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.365
Zhang P, Yang Y, Qian K, Li L, Zhang C, Fu X, Cui J (2020) A novel tumor suppressor ZBTB1 regulates tamoxifen resistance and aerobic glycolysis through suppressing HER2 expression in breast cancer. J Biol Chem 295(41):14140–14152. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA119.010759
Zhang N, Sun P, Xu Y, Li H, Liu H, Wang L, Wang T (2021) The GPER1/SPOP axis mediates ubiquitination-dependent degradation of ERα to inhibit the growth of breast cancer induced by oestrogen. Cancer Lett 498:54–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2020.10.019
Zhou J, Ren K, Liu X, Xiong X, Hu X, Zhang J (2005) A novel PDIP1-related protein, KCTD10, that interacts with proliferating cell nuclear antigen and DNA polymerase delta. Biochim Biophys Acta 1729(3):200–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbaexp.2005.05.005
Zhou L, Zhong Y, Yang FH, Li ZB, Zhou J, Liu XH, Hu F (2016) Kaiso represses the expression of glucocorticoid receptor via a methylation-dependent mechanism and attenuates the anti-apoptotic activity of glucocorticoids in breast cancer cells. BMB Rep 49(3):167–172. https://doi.org/10.5483/bmbrep.2016.49.3.151
Zhu Z, Wang S, Zhu J, Yang Q, Dong H, Huang J (2016) MicroRNA-544 down-regulates both Bcl6 and Stat3 to inhibit tumor growth of human triple negative breast cancer. Biol Chem 397(10):1087–1095. https://doi.org/10.1515/hsz-2016-0104
Zollman S, Godt D, Privé GG, Couderc JL, Laski FA (1994) The BTB domain, found primarily in zinc finger proteins, defines an evolutionarily conserved family that includes several developmentally regulated genes in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91(22):10717–10721. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.91.22.10717
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CO contributed to the conception of the study and designed the study plan; HZ performed the research, analyzed data, and wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Ouyang, C. BTB protein family and human breast cancer: signaling pathways and clinical progress. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 16213–16229 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05314-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05314-9