Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the risk factors of second primary malignant tumor (SPMT) in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC) and establish a competing risk nomogram to predict the probability of SPMT occurrence.
Methods
We retrieved data from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database for patients diagnosed with DTC between 2000 and 2019. The Fine and Gray subdistribution hazard model was employed to identify SPMT risk factors in the training set and develop a competing risk nomogram. Model evaluation was performed using area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC), calibration curve, and decision curve analysis (DCA).
Results
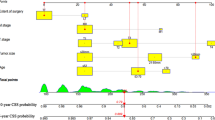
A total of 112,257 eligible patients were included in the study and randomized into a training set (n = 112,256) and a validation set (n = 33,678). The cumulative incidence rate of SPMT was 15% (n = 9528). Age, sex, race, tumor multifocality, and TNM stage were independent risk factors of SPMT. The calibration plots showed good agreement between the predicted and observed SPMT risks. The 10-year AUCs of the calibration plots were 70.2 (68.7–71.6) in the training set and 70.2 (68.7–71.5) in the validation set. Moreover, DCA showed that our proposed model resulted in higher net benefits within a defined range of risk thresholds. The cumulative incidence rate of SPMT differed among risk groups, classified according to nomogram risk scores.
Conclusion
The competing risk nomogram developed in this study exhibits high performance in predicting the occurrence of SPMT in patients with DTC. These findings may help clinicians identify patients at distinct levels of risk of SPMT and develop corresponding clinical management strategies.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
SEER Stat 8.4.1 software was used to extract our data online, and data in our study is available at SEER database: https://seer.cancer.gov/. In addition, the raw data for this study are available in the supplementary material.
References
Al Afif A, Williams BA, Rigby MH, Bullock MJ, Taylor SM, Trites J, Hart RD (2015) Multifocal papillary thyroid cancer increases the risk of central lymph node metastasis. Thyroid 25(9):1008–1012. https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2015.0130
Alarid ET, Preisler-Mashek MT, Solodin NM (2003) Thyroid hormone is an inhibitor of estrogen-induced degradation of estrogen receptor-alpha protein: estrogen-dependent proteolysis is not essential for receptor transactivation function in the pituitary. Endocrinology 144(8):3469–3476. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2002-0092
An JH, Hwangbo Y, Ahn HY, Keam B, Lee KE, Han W, Park DJ, Park IA, Noh DY, Youn YK, Cho BY, Im SA, Park YJ (2015) A possible association between thyroid cancer and breast cancer. Thyroid 25(12):1330–1338. https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2014.0561
Bassi P, Sacco E (2009) Cancer and aging: the molecular pathways. Urol Oncol 27(6):620–627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urolonc.2009.07.013
Bassily MN, Wilson R, Pompei F, Burmistrov D (2010) Cancer survival as a function of age at diagnosis: a study of the surveillance, epidemiology and end results database. Cancer Epidemiol 34(6):667–681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canep.2010.04.013
Bellini MI, Lori E, Forte F, Lauro A, Tripodi D, Amabile MI, Cantisani V, Varanese M, Ferent IC, Baldini E, Ulisse S, D’Andrea V, Pironi D, Sorrenti S (2022) Thyroid and renal cancers: a bidirectional association. Front Oncol 12:951976. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.951976
Borgoni S, Kudryashova KS, Burka K, de Magalhaes JP (2021) Targeting immune dysfunction in aging. Ageing Res Rev 70:101410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2021.101410
Brown AP, Chen J, Hitchcock YJ, Szabo A, Shrieve DC, Tward JD (2008) The risk of second primary malignancies up to three decades after the treatment of differentiated thyroid cancer. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93(2):504–515. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2007-1154
Cerbon MA, Pichon MF, Milgrom E (1981) Thyroid hormone receptors in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 41(10):4167–4173
Curtis RE, Freedman DM, Ron E, Ries LAG, Hacker DG, Edwards BK, Tucker MA, Fraumeni Jr JF (eds) (2006) New malignancies among cancer survivors: SEER cancer registries, 1973–2000. National Cancer Institute, Bethesda. NIH Publ. No. 05-5302
Dawson DM, Lawrence EG, MacLennan GT, Amini SB, Kung HJ, Robinson D, Resnick MI, Kursh ED, Pretlow TP, Pretlow TG (1998) Altered expression of RET proto-oncogene product in prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and prostate cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 90(7):519–523. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/90.7.519
Derwahl M, Nicula D (2014) Estrogen and its role in thyroid cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer 21(5):T273–T283. https://doi.org/10.1530/ERC-14-0053
Fine JP, Gray RJ (1999) A proportional hazards model for the subdistribution of a competing risk. Publ Am Stat Assoc 94(446):496–509
Hirsch D, Shohat T, Gorshtein A, Robenshtok E, Shimon I, Benbassat C (2016) Incidence of nonthyroidal primary malignancy and the association with(131)I treatment in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid 26(8):1110–1116. https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2016.0037
Hsu CH, Huang CL, Hsu YH, Iqbal U, Nguyen PA, Jian WS (2014) Co-occurrence of second primary malignancy in patients with thyroid cancer. QJM 107(8):643–648. https://doi.org/10.1093/qjmed/hcu051
Institute, National Cancer (2010) SEER cancer statistics review, 1975–2007 [online]. https://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2007/
Izkhakov E, Barchana M, Liphshitz I, Silverman BG, Stern N, Keinan-Boker L (2017) Trends of second primary malignancy in patients with thyroid cancer: a population-based cohort study in Israel. Thyroid 27(6):793–801. https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2016.0481
Jia H, Li Q, Yuan J, Sun X, Wu Z (2020) second primary malignancies in patients with colorectal cancer: a population-based analysis. Oncologist 25(4):e644–e650. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2019-0266
Johnson CH, Peace S, Adamo P, Fritz A, Percy-Laurry A, Edwards BK (2007) The 2007 multiple primary and histology coding rules. National Cancer Institute, Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results Program, Bethesda
Keegan THM, Bleyer A, Rosenberg AS, Li Q, Goldfarb M (2017) Second primary malignant neoplasms and survival in adolescent and young adult cancer survivors. JAMA Oncol 3(11):1554–1557. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.0465
Kim C, Bi X, Pan D, Chen Y, Carling T, Ma S, Udelsman R, Zhang Y (2013) The risk of second cancers after diagnosis of primary thyroid cancer is elevated in thyroid microcarcinomas. Thyroid 23(5):575–582. https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2011.0406
Kim M, Kim H, Park S, Joo J, Kim IJ, Kim BH (2022a) Risk factors for second primary malignancies following thyroid cancer: a nationwide cohort study. Eur J Endocrinol 186(5):561–571. https://doi.org/10.1530/EJE-21-1208
Kim S, Bang JI, Boo D, Kim B, Choi IY, Ko S, Yoo IR, Kim K, Kim J, Joo Y, Ryoo HG, Paeng JC, Park JM, Jang W, Kim B, Chung Y, Yang D, Yoo S, Lee HY (2022b) Second primary malignancy risk in thyroid cancer and matched patients with and without radioiodine therapy analysis from the observational health data sciences and informatics. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 49(10):3547–3556. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-022-05779-9
Kim KJ, Kim KJ, Choi J, Kim NH, Kim SG (2023) Linear association between radioactive iodine dose and second primary malignancy risk in thyroid cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djad040
Lang BH, Lo CY, Wong IO, Cowling BJ (2010) Impact of second primary malignancy on outcomes of differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Surgery 148(6):1191–1196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surg.2010.09.022
Li J, Peng F, Huang H, Cai Z (2022) Trends in the risk of second primary malignances after non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Am J Cancer Res 12(6):2863–2875
Lloyd KM 2nd, Dennis M (1963) Cowden’s disease. A possible new symptom complex with multiple system involvement. Ann Intern Med 58:136–142. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-58-1-136
Lu CH, Lee KD, Chen PT, Chen CC, Kuan FC, Huang CE, Chen MF, Chen MC (2013) Second primary malignancies following thyroid cancer: a population-based study in Taiwan. Eur J Endocrinol 169(5):577–585. https://doi.org/10.1530/EJE-13-0309
Malchoff CD, Sarfarazi M, Tendler B, Forouhar F, Whalen G, Joshi V, Arnold A, Malchoff DM (2000) Papillary thyroid carcinoma associated with papillary renal neoplasia: genetic linkage analysis of a distinct heritable tumor syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85(5):1758–1764. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.85.5.6557
Nikiforov YE, Rowland JM, Bove KE, Monforte-Munoz H, Fagin JA (1997) Distinct pattern of ret oncogene rearrangements in morphological variants of radiation-induced and sporadic thyroid papillary carcinomas in children. Cancer Res 57(9):1690–1694
Nogueira CR, Brentani MM (1996) Triiodothyronine mimics the effects of estrogen in breast cancer cell lines. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 59(3–4):271–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0960-0760(96)00117-3
Nose N, Sugio K, Oyama T, Nozoe T, Uramoto H, Iwata T, Onitsuka T, Yasumoto K (2009) Association between estrogen receptor-beta expression and epidermal growth factor receptor mutation in the postoperative prognosis of adenocarcinoma of the lung. J Clin Oncol 27(3):411–417. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2008.18.3251
Pietras RJ, Marquez DC, Chen HW, Tsai E, Weinberg O, Fishbein M (2005) Estrogen and growth factor receptor interactions in human breast and non-small cell lung cancer cells. Steroids 70(5–7):372–381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.steroids.2005.02.017
Pizzato M, Li M, Vignat J, Laversanne M, Singh D, La Vecchia C, Vaccarella S (2022) The epidemiological landscape of thyroid cancer worldwide: GLOBOCAN estimates for incidence and mortality rates in 2020. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 10(4):264–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(22)00035-3
Ronckers CM, McCarron P, Ron E (2005) Thyroid cancer and multiple primary tumors in the SEER cancer registries. Int J Cancer 117(2):281–288. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.21064
Rubino C, de Vathaire F, Dottorini ME, Hall P, Schvartz C, Couette JE, Dondon MG, Abbas MT, Langlois C, Schlumberger M (2003) Second primary malignancies in thyroid cancer patients. Br J Cancer 89(9):1638–1644. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6601319
Salvatore D, Santoro M, Schlumberger M (2021) The importance of the RET gene in thyroid cancer and therapeutic implications. Nat Rev Endocrinol 17(5):296–306. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41574-021-00470-9
Sandeep TC, Strachan MW, Reynolds RM, Brewster DH, Scelo G, Pukkala E, Hemminki K, Anderson A, Tracey E, Friis S, McBride ML, Kee-Seng C, Pompe-Kirn V, Kliewer EV, Tonita JM, Jonasson JG, Martos C, Boffetta P, Brennan P (2006) Second primary cancers in thyroid cancer patients: a multinational record linkage study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91(5):1819–1825. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2005-2009
Sawka AM, Thabane L, Parlea L, Ibrahim-Zada I, Tsang RW, Brierley JD, Straus S, Ezzat S, Goldstein DP (2009) Second primary malignancy risk after radioactive iodine treatment for thyroid cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Thyroid 19(5):451–457. https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2008.0392
Silva JM, Dominguez G, Gonzalez-Sancho JM, Garcia JM, Silva J, Garcia-Andrade C, Navarro A, Munoz A, Bonilla F (2002) Expression of thyroid hormone receptor/erbA genes is altered in human breast cancer. Oncogene 21(27):4307–4316. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1205534
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71(3):209–249. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660
Teng CJ, Hu YW, Chen SC, Yeh CM, Chiang HL, Chen TJ, Liu CJ (2016) Use of radioactive iodine for thyroid cancer and risk of second primary malignancy: a nationwide population-based study. J Natl Cancer Inst. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djv314
Travis LB, Demark Wahnefried W, Allan JM, Wood ME, Ng AK (2013) Aetiology, genetics and prevention of secondary neoplasms in adult cancer survivors. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 10(5):289–301. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2013.41
Vaccarella S, Dal Maso L, Laversanne M, Bray F, Plummer M, Franceschi S (2015) The impact of diagnostic changes on the rise in thyroid cancer incidence: a population-based study in selected high-resource countries. Thyroid 25(10):1127–1136. https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2015.0116
Wang W, Su X, He K, Wang Y, Wang H, Wang H, Zhao Y, Zhao W, Zarnegar R, Fahey TJ 3rd, Teng X, Teng L (2016) Comparison of the clinicopathologic features and prognosis of bilateral versus unilateral multifocal papillary thyroid cancer: an updated study with more than 2000 consecutive patients. Cancer 122(2):198–206. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.29689
Zheng R, Zhang S, Zeng H, Wang S, Sun K, Chen R, Li L, Wei W, He J (2022) Cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2016. J Natl Cancer Center 2(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jncc.2022.02.002
Acknowledgements
We express our appreciation to Bullet Edits (http://www.bulletedits.cn/) for their expert language services.
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, Grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript. This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation, Regional Science Foundation Project (Grant numbers: 81960322 and 82160343), Joint Program of Applied Basic Research of Yunnan Provincial Department of Science and Technology—Kunming Medical University (Grant number: NO. 202301AY070001-106), and "Famous Doctor" Special Project of Ten Thousand People Plan of Yunnan Province (Grant number: YNWR-MY-2020-095).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Data preparation and collection were performed by FH, TC, CL, XDS and JL. Data analysis was carried out by FH, CLY and ZXY. Manuscript writing was performed by FH. Study supervision and revision of the manuscript were performed by ZYD and CL. And all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethics approval
As the data from the SEER database are publicly available, our study was exempt from ethical committee approval. Furthermore, we declare that all methods were performed in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations.
Consent for publication
All authors have given their consent to publish the paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
432_2023_5135_MOESM2_ESM.pdf
Supplementary file2Fig. S2 Time-dependent ROC curves of the competing risk nomogram for predicting 3-, 5-, and 10-year SPMT’s probabilities in the training set (a) and validation set (b) (PDF 280 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, F., Cheng, T., Yang, CL. et al. Risk prediction of second primary malignant tumor in primary differentiated thyroid cancer patients: a population-based study. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 149, 12379–12391 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05135-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-023-05135-w