Abstract
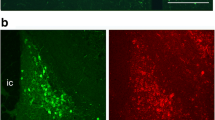
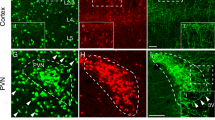
We examined the morphological features of corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) neurons in a mouse line in which modified yellow fluorescent protein (Venus) was expressed under the CRF promoter. We previously generated the CRF-Venus knock-in mouse, in which Venus is inserted into the CRF gene locus by homologous recombination. In the present study, the neomycin phosphotransferase gene (Neo), driven by the pgk-1 promoter, was deleted from the CRF-Venus mouse genome, and a CRF-Venus∆Neo mouse was generated. Venus expression is much more prominent in the CRF-Venus∆Neo mouse when compared to the CRF-Venus mouse. In addition, most Venus-expressing neurons co-express CRF mRNA. Venus-expressing neurons constitute a discrete population of neuroendocrine neurons in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus (PVH) that project to the median eminence. Venus-expressing neurons were also found in brain regions outside the neuroendocrine PVH, including the olfactory bulb, the piriform cortex (Pir), the extended amygdala, the hippocampus, the neocortices, Barrington’s nucleus, the midbrain/pontine dorsal tegmentum, the periaqueductal gray, and the inferior olivary nucleus (IO). Venus-expressing perikarya co-expressing CRF mRNA could be observed clearly even in regions where CRF-immunoreactive perikarya could hardly be identified. We demonstrated that the CRF neurons contain glutamate in the Pir and IO, while they contain gamma-aminobutyric acid in the neocortex, the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, the hippocampus, and the amygdala. A population of CRF neurons was demonstrated to be cholinergic in the midbrain tegmentum. The CRF-Venus∆Neo mouse may be useful for studying the structural and functional properties of CRF neurons in the mouse brain.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alheid GF, Shammah-Lagnado SJ, Beltramino CA (1999) The interstitial nucleus of the posterior limb of the anterior commissure: a novel layer of the central division of extended amygdala. Ann N Y Acad Sci 877:645–654
Alon T, Zhou L, Pérez CA, Garfield AS, Friedman JM, Heisler LK (2009) Transgenic mice expressing green fluorescent protein under the control of the corticotropin-releasing hormone promoter. Endocrinology 150:5626–5632
Andres AL, Regev L, Phi L, Seese RR, Chen Y, Gall CM, Baram TZ (2013) NMDA receptor activation and calpain contribute to disruption of dendritic spines by the stress neuropeptide CRH. J Neurosci 33:16945–16960
Arase K, York DA, Shimizu H, Shargill N, Bray GA (1988) Effects of corticotropin-releasing factor on food intake and brown adipose tissue thermogenesis in rats. Am J Physiol 255:E255–E259
Asan E, Yilmazer-Hanke DM, Eliava M, Hantsch M, Lesch KP, Schmitt A (2005) The corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF)-system and monoaminergic afferents in the central amygdala: investigations in different mouse strains and comparison with the rat. Neuroscience 131:953–967
Bale TL, Vale WW (2004) CRF and CRF receptors: role in stress responsivity and other behaviors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 44:525–557
Biag J, Huang Y, Gou L, Hintiryan H, Askarinam A, Hahn JD, Toga AW, Dong HW (2012) Cyto- and chemoarchitecture of the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus in the C57BL/6 J male mouse: a study of immunostaining and multiple fluorescent tract tracing. J Comp Neurol 520:6–33
Borelli KG, Brandão ML (2008) Effects of ovine CRF injections into the dorsomedial, dorsolateral and lateral columns of the periaqueductal gray: a functional role for the dorsomedial column. Horm Behav 53:40–50
Chalmers DT, Lovenberg TW, Grigoriadis DE, Behan DP, De Souza EB (1996) Corticotrophin-releasing factor receptors: from molecular biology to drug design. Trends Pharmacol Sci 17:166–172
Chang D, Yi SJ, Baram TZ (1996) Developmental profile of corticotropin releasing hormone messenger RNA in the rat inferior olive. Int J Dev Neurosci 14:69–76
Chen Y, Bender RA, Frotscher M, Baram TZ (2001) Novel and transient populations of corticotropin-releasing hormone-expressing neurons in developing hippocampus suggest unique functional roles: a quantitative spatiotemporal analysis. J Neurosci 21:7171–7181
Chen Y, Brunson KL, Adelmann G, Bender RA, Frotscher M, Baram TZ (2004) Hippocampal corticotropin releasing hormone: pre- and postsynaptic location and release by stress. Neuroscience 126:533–540
Chen Y, Molet J, Gunn BG, Ressler K, Baram TZ (2015) Diversity of reporter expression patterns in transgenic mouse lines targeting corticotropin-releasing hormone-expressing neurons. Endocrinology 156:4769–4780
Chung RY, Mason P, Strassman A, Maciewicz R (1987) Edinger–Westphal nucleus: cells that project to spinal cord contain corticotropin-releasing factor. Neurosci Lett 83:13–19
Cummings S, Elde R, Ells J, Lindall A (1983) Corticotropin-releasing factor immunoreactivity is widely distributed within the central nervous system of the rat: an immunohistochemical study. J Neurosci 3:1355–1368
Deli L, Wittmann G, Kalló I, Lechan RM, Watanabe M, Liposits Z, Fekete C (2009) Type1 cannabinoid receptor-containing axons innervate hypophysiotropic thyrotropin-releasing hormone-synthesizing neurons. Endocrinology 150:98–103
Erb S, Stewart J (1999) A role for the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis, but not the amygdala, in the effects of corticotropin-releasing factor on stress-induced reinstatement of cocaine seeking. J Neurosci 19:RC35
Franklin KBJ, Paxinos G (2008) The mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 3rd edn. Elsevier, New York
Fukaya M, Tsujita M, Yamazaki M, Kushiya E, Abe M, Akashi K, Natsume R, Kano M, Kamiya H, Watanabe M, Sakimura K (2006) Abundant distribution of TARP gamma-8 in synaptic and extrasynaptic surface of hippocampal neurons and its major role in AMPA receptor expression on spines and dendrites. Eur J Neurosci 24:2177–2190
Gallopin T, Geoffroy H, Rossier J, Lambolez B (2006) Cortical sources of CRF, NKB, and CCK and their effects on pyramidal cells in the neocortex. Cereb Cortex 16:1440–1452
Garcia I, Bhullar PK, Tepe B, Ortiz-Guzman J, Huang L, Herman AM, Chaboub L, Deneen B, Justice NJ, Arenkiel BR (2016) Local corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH) signals to its receptor CRHR1 during postnatal development of the mouse olfactory bulb. Brain Struct Funct 221:1–20
Grieder TE, Herman MA, Contet C, Tan LA, Vargas-Perez H, Cohen A, Chwalek M, Maal-Bared G, Freiling J, Schlosburg JE, Clarke L, Crawford E, Koebel P, Repunte-Canonigo V, Sanna PP, Tapper AR, Roberto M, Kieffer BL, Sawchenko PE, Koob GF, van der Kooy D, George O (2014) VTA CRF neurons mediate the aversive effects of nicotine withdrawal and promote intake escalation. Nat Neurosci 17:1751–1758
Gundersen HJ, Jensen EB, Kiêu K, Nielsen J (1999) The efficiency of systematic sampling in stereology—reconsidered. J Microsc 193:199–211
Hauger RL, Risbrough V, Oakley RH, Olivares-Reyes JA, Dautzenberg FM (2009) Role of CRF receptor signaling in stress vulnerability, anxiety, and depression. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1179:120–143
Helmreich DL, Itoi K, Lopez-Figueroa MO, Akil H, Watson SJ (2001) Norepinephrine-induced CRH and AVP gene transcription within the hypothalamus: differential regulation by corticosterone. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 88:62–73
Hioki H, Fujiyama F, Taki K, Tomioka R, Furuta T, Tamamaki N, Kaneko T (2003) Differential distribution of vesicular glutamate transporters in the rat cerebellar cortex. Neuroscience 117:1–6
Hisano S (2003) Vesicular glutamate transporters in the brain. Anat Sci Int 78:191–204
Hisano S, Sawada K, Kawano M, Kanemoto M, Xiong G, Mogi K, Sakata-Haga H, Takeda J, Fukui Y, Nogami H (2002) Expression of inorganic phosphate/vesicular glutamate transporters (BNPI/VGLUT1 and DNPI/VGLUT2) in the cerebellum and precerebellar nuclei of the rat. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 107:23–31
Huang L, Garcia I, Jen HI, Arenkiel BR (2013) Reciprocal connectivity between mitral cells and external plexiform layer interneurons in the mouse olfactory bulb. Front Neural Circuits 7:32
Imaki T, Nahon JL, Sawchenko PE, Vale W (1989) Widespread expression of corticotropin-releasing factor messenger RNA and immunoreactivity in the rat olfactory bulb. Brain Res 496:35–44
Itoi K, Mouri T, Takahashi K, Murakami O, Imai Y, Sasaki S, Yoshinaga K, Sasano N (1987) Suppression by glucocorticoid of the immunoreactivity of corticotropin-releasing factor and vasopressin in the paraventricular nucleus of rat hypothalamus. Neurosci Lett 73:231–236
Itoi K, Jiang YQ, Iwasaki Y, Watson SJ (2004) Regulatory mechanisms of corticotropin-releasing hormone and vasopressin gene expression in the hypothalamus. J Neuroendocrinol 16:348–355
Itoi K, Talukder AH, Fuse T, Kaneko T, Ozawa R, Sato T, Sugaya T, Uchida K, Yamazaki M, Abe M, Natsume R, Sakimura K (2014) Visualization of corticotropin-releasing factor neurons by fluorescent proteins in the mouse brain and characterization of labeled neurons in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus. Endocrinology 155:4054–4560
Joëls M, Baram TZ (2009) The neuro-symphony of stress. Nat Rev Neurosci 10:459–466
Kaneko T, Fujiyama F, Hioki H (2002) Immunohistochemical localization of candidates for vesicular glutamate transporters in the rat brain. J Comp Neurol 444:39–62
Keegan CE, Karolyi IJ, Knapp LT, Bourbonais FJ, Camper SA, Seasholtz AF (1994) Expression of corticotropin-releasing hormone transgenes in neurons of adult and developing mice. Mol Cell Neurosci 5:505–514
Kiss JZ, Mezey E, Skirboll L (1984) Corticotropin-releasing factor-immunoreactive neurons of the paraventricular nucleus become vasopressin positive after adrenalectomy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:1854–1858
Klausner AP, Steers WD (2004) Corticotropin releasing factor: a mediator of emotional influences on bladder function. J Urol 172:2570–2573
Kolber BJ, Boyle MP, Wieczorek L, Kelley CL, Onwuzurike CC, Nettles SA, Vogt SK, Muglia LJ (2010) Transient early-life forebrain corticotropin-releasing hormone elevation causes long-lasting anxiogenic and despair-like changes in mice. J Neurosci 30:2571–2581
Koob GF (2015) The dark side of emotion: the addiction perspective. Eur J Pharmacol 753:73–87
Levy BH, Tasker JG (2012) Synaptic regulation of the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis and its modulation by glucocorticoids and stress. Front Cell Neurosci 6:24
Lu A, Steiner MA, Whittle N, Vogl AM, Walser SM, Ableitner M, Refojo D, Ekker M, Rubenstein JL, Stalla GK, Singewald N, Holsboer F, Wotjak CT, Wurst W, Deussing JM (2008) Conditional mouse mutants highlight mechanisms of corticotropin-releasing hormone effects on stress-coping behavior. Mol Psychiatry 13:1028–1042
Martin EI, Ressler KJ, Jasnow AM, Dabrowska J, Hazra R, Rainnie DG, Nemeroff CB, Owens MJ (2010) A novel transgenic mouse for gene-targeting within cells that express corticotropin-releasing factor. Biol Psychiatry 67:1212–1216
Merchenthaler I (1984) Corticotropin releasing factor (CRF)-like immunoreactivity in the rat central nervous system. Extrahypothalamic distribution. Peptides 5(Suppl 1):53–69
Merchenthaler I, Vigh S, Petrusz P, Schally AV (1983) The paraventriculo-infundibular corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) pathway as revealed by immunocytochemistry in long-term hypophysectomized or adrenalectomized rats. Regul Pept 5:295–305
Mishina M, Sakimura K (2007) Conditional gene targeting on the pure C57BL/6 genetic background. Neurosci Res 58:105–112
Miura E, Fukaya M, Sato T, Sugihara K, Asano M, Yoshioka K, Watanabe M (2006) Expression and distribution of JNK/SAPK-associated scaffold protein JSAP1 in developing and adult mouse brain. J Neurochem 97:1431–1446
Miyata M, Okada D, Hashimoto K, Kano M, Ito M (1999) Corticotropin-releasing factor plays a permissive role in cerebellar long-term depression. Neuron 22:763–775
Miyazaki T, Fukaya M, Shimizu H, Watanabe M (2003) Subtype switching of vesicular glutamate transporters at parallel fibre-Purkinje cell synapses in developing mouse cerebellum. Eur J Neurosci 17:2563–2572
Morin SM, Ling N, Liu XJ, Kahl SD, Gehlert DR (1999) Differential distribution of urocortin- and corticotropin-releasing factor-like immunoreactivities in the rat brain. Neuroscience 92:281–291
Nahar J, Haam J, Chen C, Jiang Z, Glatzer NR, Muglia LJ, Dohanich GP, Herman JP, Tasker JG (2015) Rapid nongenomic glucocorticoid actions in male mouse hypothalamic neuroendocrine cells are dependent on the nuclear glucocorticoid receptor. Endocrinology 156:2831–2842
Narushima M, Uchigashima M, Fukaya M, Matsui M, Manabe T, Hashimoto K, Watanabe M, Kano M (2007) Tonic enhancement of endocannabinoid-mediated retrograde suppression of inhibition by cholinergic interneuron activity in the striatum. J Neurosci 27:496–506
Olson EN, Arnold HH, Rigby PW, Wold BJ (1996) Know your neighbors: three phenotypes in null mutants of the myogenic bHLH gene MRF4. Cell 85:1–4
Overton JM, Fisher LA (1989) Central nervous system actions of corticotropin-releasing factor on cardiovascular function in the absence of locomotor activity. Regul Pept 25:315–324
Padilla SL, Reef D, Zeltser LM (2012) Defining POMC neurons using transgenic reagents: impact of transient Pomc expression in diverse immature neuronal populations. Endocrinology 153:1219–1231
Palkovits M, Léránth C, Görcs T, Young WS 3rd (1987) Corticotropin-releasing factor in the olivocerebellar tract of rats: demonstration by light- and electron-microscopic immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization histochemistry. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:3911–3915
Pavcovich LA, Yang M, Miselis RR, Valentino RJ (1998) Novel role for the pontine micturition center, Barrington’s nucleus: evidence for coordination of colonic and forebrain activity. Brain Res 784:355–361
Paxinos G, Franklin KBJ (2013) The mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 4th edn. Elsevier, New York
Pleil KE, Rinker JA, Lowery-Gionta EG, Mazzone CM, McCall NM, Kendra AM, Olson DP, Lowell BB, Grant KA, Thiele TE, Kash TL (2015) NPY signaling inhibits extended amygdala CRF neurons to suppress binge alcohol drinking. Nat Neurosci 18:545–552
Puder BA, Papka RE (2001) Distribution and origin of corticotropin-releasing factor-immunoreactive axons in the female rat lumbosacral spinal cord. J Neurosci Res 66:1217–1225
Regev L, Tsoory M, Gil S, Chen A (2012) Site-specific genetic manipulation of amygdala corticotropin-releasing factor reveals its imperative role in mediating behavioral response to challenge. Biol Psychiatry 71:317–326
Roozendaal B, Brunson KL, Holloway BL, McGaugh JL, Baram TZ (2002) Involvement of stress-released corticotropin-releasing hormone in the basolateral amygdala in regulating memory consolidation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:13908–13913
Rubin AN, Alfonsi F, Humphreys MP, Choi CK, Rocha SF, Kessaris N (2010) The germinal zones of the basal ganglia but not the septum generate GABAergic interneurons for the cortex. J Neurosci 30:12050–12062
Sakanaka M, Shibasaki T, Lederis K (1986) Distribution and efferent projections of corticotropin-releasing factor-like immunoreactivity in the rat amygdaloid complex. Brain Res 382:213–238
Sakanaka M, Shibasaki T, Lederis K (1987) Corticotropin releasing factor-like immunoreactivity in the rat brain as revealed by a modified cobalt-glucose oxidase-diaminobenzidine method. J Comp Neurol 260:256–298
Sasaki M, Sato H (2013) Polysynaptic connections between Barrington’s nucleus and sacral preganglionic neurons. Neurosci Res 75:150–156
Sawchenko PE, Swanson LW, Vale WW (1984a) Co-expression of corticotropin-releasing factor and vasopressin immunoreactivity in parvocellular neurosecretory neurons of the adrenalectomized rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:1883–1887
Sawchenko PE, Swanson LW, Vale WW (1984b) Corticotropin-releasing factor: co-expression within distinct subsets of oxytocin-, vasopressin-, and neurotensin-immunoreactive neurons in the hypothalamus of the male rat. J Neurosci 4:1118–1129
Silberman Y, Winder DG (2013) Corticotropin releasing factor and catecholamines enhance glutamatergic neurotransmission in the lateral subdivision of the central amygdala. Neuropharmacology 70:316–323
Stenzel-Poore MP, Heinrichs SC, Rivest S, Koob GF, Vale WW (1994) Overproduction of corticotropin-releasing factor in transgenic mice: a genetic model of anxiogenic behavior. J Neurosci 14:2579–2584
Studeny S, Vizzard MA (2005) Corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) expression in postnatal and adult rat sacral parasympathetic nucleus (SPN). Cell Tissue Res 322:339–352
Swanson LW, Sawchenko PE, Rivier J, Vale WW (1983) Organization of ovine corticotropin-releasing factor immunoreactive cells and fibers in the rat brain: an immunohistochemical study. Neuroendocrinology 36:165–186
Takasaki C, Yamasaki M, Uchigashima M, Konno K, Yanagawa Y, Watanabe M (2010) Cytochemical and cytological properties of perineuronal oligodendrocytes in the mouse cortex. Eur J Neurosci 32:1326–1336
Tamamaki N, Yanagawa Y, Tomioka R, Miyazaki J, Obata K, Kaneko T (2003) Green fluorescent protein expression and colocalization with calretinin, parvalbumin, and somatostatin in the GAD67-GFP knock-in mouse. J Comp Neurol 467:60–79
Taniguchi H, He M, Wu P, Kim S, Paik R, Sugino K, Kvitsiani D, Fu Y, Lu J, Lin Y, Miyoshi G, Shima Y, Fishell G, Nelson SB, Huang ZJ (2011) A resource of Cre driver lines for genetic targeting of GABAergic neurons in cerebral cortex. Neuron 71:995–1013
Tian JB, Bishop GA (2003) Frequency-dependent expression of corticotropin releasing factor in the rat’s cerebellum. Neuroscience 121:363–377
Vale W, Spiess J, Rivier C, Rivier J (1981) Characterization of a 41-residue ovine hypothalamic peptide that stimulates secretion of corticotropin and beta-endorphin. Science 213:1394–1397
Valentino RJ, Kosboth M, Colflesh M, Miselis RR (2000) Transneuronal labeling from the rat distal colon: anatomic evidence for regulation of distal colon function by a pontine corticotropin-releasing factor system. J Comp Neurol 417:399–414
Valentino RJ, Liouterman L, Van Bockstaele EJ (2001) Evidence for regional heterogeneity in corticotropin-releasing factor interactions in the dorsal raphe nucleus. J Comp Neurol 435:450–463
Wamsteeker Cusulin JI, Füzesi T, Watts AG, Bains JS (2013) Characterization of corticotropin-releasing hormone neurons in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus of Crh-IRES-Cre mutant mice. PLoS One 8:e64943
Wang HL, Morales M (2009) Pedunculopontine and laterodorsal tegmental nuclei contain distinct populations of cholinergic, glutamatergic and GABAergic neurons in the rat. Eur J Neurosci 29:340–358
Wang L, Goebel-Stengel M, Stengel A, Wu SV, Ohning G, Taché Y (2011) Comparison of CRF-immunoreactive neurons distribution in mouse and rat brains and selective induction of Fos in rat hypothalamic CRF neurons by abdominal surgery. Brain Res 1415:34–46
Yamasaki M, Yamada K, Furuya S, Mitoma J, Hirabayashi Y, Watanabe M (2001) 3-Phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase, a key enzyme for l-serine biosynthesis, is preferentially expressed in the radial glia/astrocyte lineage and olfactory ensheathing glia in the mouse brain. J Neurosci 21:7691–7704
Yan XX, Toth Z, Schultz L, Ribak CE, Baram TZ (1998) Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH)-containing neurons in the immature rat hippocampal formation: light and electron microscopic features and colocalization with glutamate decarboxylase and parvalbumin. Hippocampus 8:231–243
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the Research Grants from JSPS (K.I., K.S., M.W.), JST (K.I., K.S., M.W.), and Comprehensive Brain Research Network (K.I., K.S., M.W.). Anti-CRF antibodies were generously donated by Drs. Wylie Vale and Paul Sawchenko, Salk Institute, Ca, USA, and Dr. Tamotsu Shibasaki, Nippon Medical School, Tokyo, Japan. Anti-thyrotropin-releasing hormone antibody was a gift from Dr. Fekete, Hungarian Academy of Sciences. We thank Dr. Sadayoshi Ito, Tohoku University, and Shinji Ohara, Matsumoto Medical Center, for encouragements. Address any requests to K.I. for mice generated in his laboratory and presented in the present manuscript. The CRF-Venus mouse is also available from Experimental Animal Division, RIKEN BRC (Access Number: RBRC06519).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution or practice at which the studies were conducted.
Additional information
J. Kono, K. Konno and A. H. Talukder contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Fig. 1 Generation of the Actb-FLPe mouse by homologous recombination. The Actb-FLPe mouse was generated by inserting the CAG promoter-driven FLPe-IRES-Flag-EGFP-Neo construct, into the 3′ downstream region of the β-actin gene (Actb) by homologous recombination using RENKA embryonic stem cells, which are of C57BL6/N genetic background (Mishina and Sakimura 2007). The neomycin phosphotransferase gene (Neo), driven by the pgk-1 promoter, is flanked by loxP sites. The Actb gene locus, targeting vector for homologous recombination, and the targeted allele are shown schematically.
Supplementary Fig. 2 Venus-expressing neurons in the cingulate cortex. An inverted monochrome image of Venus-expressing neurons in the cingulate cortex (Cg) is shown in a (immunofluorescence). A cresyl violet (Nissl) staining of the same section in a, is shown in a’. Venus-expressing neurons were observed mainly in layers 2/3 of the Cg. Scale bar = 200 μm.
Supplementary Fig. 3 Venus-expressing neurons in the hippocampus. a-a’: an inverted monochrome image of Venus-expressing neurons and fibers in the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus is shown in a (immunofluorescence). A cresyl violet (Nissl) staining of the same section in a, is shown in a’. b-b’: most Venus-expressing neurons co-expressed glutamic acid decarboxylase 67 (GAD67) mRNA. A single image of GAD67 mRNA is shown in b’, and a merged image for Venus and GAD67 mRNA in b (dually stained cells are indicated by arrows). c–c’: Venus-containing puncta, which co-expressed vesicular inhibitory amino acid transporter (VIAAT) immunoreactivity, were observed in close proximity to the somata of granule cells (arrows). GrDG, granule cell layer of dentate gyrus; PoDG, polymorphic cell layer of the dentate gyrus. Scale bars = 200 μm for a-a’, 20 μm for b-b’, and 5 μm for c–c’.
Supplementary Fig. 4 Venus-expressing neurons in the shell of the nucleus accumbens. An inverted monochrome image of Venus-expressing neurons in the nucleus accumbens is shown in a (immunofluorescence). A cresyl violet (Nissl) staining of the same section in a, is shown in a’. Venus-expressing neurons are present in the shell of the nucleus accumbens (AcbSh). aca, anterior part of the anterior commissure; Pir, piriform cortex. Scale bar = 200 μm.
Supplementary Fig. 5 Venus-expressing neurons in the periaqueductal gray and mesencephalic reticular formation. Inverted monochrome images of Venus-expressing neurons in the periaqueductal gray (PAG) and the adjacent mesencephalic reticular formation (mRt) are shown in a and b, respectively (immunofluorescence). The same sections in a and b are stained with cresyl violet (Nissl) and shown in a’ and b’, respectively. In the PAG, Venus-expressing neurons and fibers tended to be localized in the ventral half of this structure (a-a’). Scale bars = 200 μm.
Supplementary Fig. 6 Venus-expressing neurons in the interpeduncular nucleus and median raphe nucleus. a-a’, b-b’: inverted monochrome images of Venus-expressing neurons and fibers in the caudal subnucleus of interpeduncular nucleus (IPC) and the median raphe nucleus (MnR) are shown in a and b, respectively (immunofluorescence). The same sections in a and b are stained with cresyl violet (Nissl) and shown in a’ and b’, respectively. Numerous small-sized neurons expressed Venus in the IPC (a) and the MnR (b). c–c’: most Venus-expressing neurons co-expressed CRF mRNA in the MnR. A single image of CRF mRNA is shown in c’, and merged image for Venus and CRF mRNA in c. Arrows indicate the cells that co-express Venus and CRF mRNA. ml, medial lemniscus; PMnR, paramedian raphe nucleus; ts, tectospinal tract. Scale bars = 200 μm for a-a’ and b-b’, and 10 μm for c–c’.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kono, J., Konno, K., Talukder, A.H. et al. Distribution of corticotropin-releasing factor neurons in the mouse brain: a study using corticotropin-releasing factor-modified yellow fluorescent protein knock-in mouse. Brain Struct Funct 222, 1705–1732 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-016-1303-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-016-1303-0