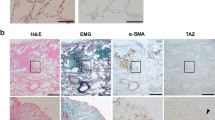
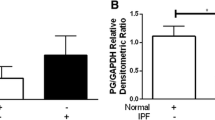
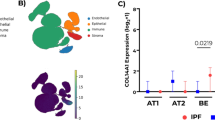
Abstract
Intermediate filaments (IF), a subfamily of the cytoskeletal filaments, provide structural support to cells. Human diseases related to mutations in IF proteins in which their tissue-specific expression is reflected have been found in a broad range of patients. The properties of identified IF mutants are well-studied in vitro in cultured cells and in vivo using transgenic mice expressing IF mutants. However, the association of IF proteins with diseases of the lung is not fully studied yet. Epithelial cells in normal lung express vimentin and various keratins, and the patterns of their expression are altered depending on the progression of the lung diseases. A growing number of studies performed in alveolar epithelial cells demonstrated IF involvement in disease-related aspects including their usefulness as tumor marker, in epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cell migration. However, the lung disease-associated IF functions in animal models are poorly understood, and IF mutations associated with lung diseases in humans have not been reported. In this review, we summarize recent studies that show the significance of IF proteins in lung epithelial cells. Understanding these aspects is an important prerequisite for further investigations on the role of lung IF in animal models and human lung diseases.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AEC:
-
Alveolar epithelial cell
- EMT:
-
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition
- GFAP:
-
Glial fibrillary acidic protein
- IF:
-
Intermediate filament
- K:
-
Keratin
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small cell lung carcinoma
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SCLC:
-
Small cell lung carcinoma
- TGFβ1:
-
Transforming growth factor beta 1
References
Blobel GA, Moll R, Franke WW, Vogt-Moykopf I (1984) Cytokeratins in normal lung and lung carcinomas. I. Adenocarcinomas, squamous cell carcinomas and cultured cell lines. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol 45:407–429
Blobel GA, Gould VE, Moll R, Lee I, Huszar M, Geiger B, Franke WW (1985) Coexpression of neuroendocrine markers and epithelial cytoskeletal proteins in bronchopulmonary neuroendocrine neoplasms. Lab Invest 52:39–51
Castanon MJ, Walko G, Winter L, Wiche G (2013) Plectin-intermediate filament partnership in skin, skeletal muscle, and peripheral nerve. Histochem Cell Biol 140:33–53
Chen Y, Cui T, Yang L, Mireskandari M, Knoesel T, Zhang Q, Pacyna-Gengelbach M, Petersen I (2011) The diagnostic value of cytokeratin 5/6, 14, 17, and 18 expression in human non-small cell lung cancer. Oncology 80:333–340
Coulombe PA, Kerns ML, Fuchs E (2009) Epidermolysis bullosa simplex: a paradigm for disorders of tissue fragility. J Clin Invest 119:1784–1793
Dauphin M, Barbe C, Lemaire S, Nawrocki-Raby B, Lagonotte E, Delepine G, Birembaut P, Gilles C, Polette M (2013) Vimentin expression predicts the occurrence of metastases in non small cell lung carcinomas. Lung Cancer. pii: S0169-5002(13)00116-5. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2013.03.011. [Epub ahead of print]
Eriksson JE, Dechat T, Grin B, Helfand B, Mendez M, Pallari HM, Goldman RD (2009) Introducing intermediate filaments: from discovery to disease. J Clin Invest 119:1763–1771
Esue O, Rupprecht L, Sun SX, Wirtz D (2010) Dynamics of the bacterial intermediate filament crescentin in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One 5:e8855
Fukunaga Y, Bandoh S, Fujita J, Yang Y, Ueda Y, Hojo S, Dohmoto K, Tojo Y, Takahara J, Ishida T (2002) Expression of cytokeratin 8 in lung cancer cell lines and measurement of serum cytokeratin 8 in lung cancer patients. Lung Cancer 38:31–38
Goldfarb LG, Dalakas MC (2009) Tragedy in a heartbeat: malfunctioning desmin causes skeletal and cardiac muscle disease. J Clin Invest 119:1806–1813
Herrmann H, Bar H, Kreplak L, Strelkov SV, Aebi U (2007) Intermediate filaments: from cell architecture to nanomechanics. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:562–573
Herrmann H, Strelkov SV, Burkhard P, Aebi U (2009) Intermediate filaments: primary determinants of cell architecture and plasticity. J Clin Invest 119:1772–1783
Horn S, Moersig W, Moll R, Oelert H, Lorenz J (1996) Expression of cell adhesion molecules in lung cancer cell lines. Exp Toxicol Pathol 48:535–540
Ishii T, Bandoh S, Fujita J, Ohtsuki Y, Tojo Y, Kanaji N, Fukunaga Y, Ueda Y, Ishida T, Kubo A (2008) Full-length cytokeratin 8 is released and circulates in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Tumour Biol 29:57–62
Iyonaga K, Miyajima M, Suga M, Saita N, Ando M (1997) Alterations in cytokeratin expression by the alveolar lining epithelial cells in lung tissues from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J Pathol 182:217–224
Kanaji N, Bandoh S, Ishii T, Fujita J, Ishida T, Matsunaga T, Kubo A (2011) Cytokeratins negatively regulate the invasive potential of lung cancer cell lines. Oncol Rep 26:763–768
Kasai H, Allen JT, Mason RM, Kamimura T, Zhang Z (2005) TGF-beta1 induces human alveolar epithelial to mesenchymal cell transition (EMT). Respir Res 6:56
Ku NO, Zhou X, Toivola DM, Omary MB (1999) The cytoskeleton of digestive epithelia in health and disease. Am J Physiol 277:G1108–G1137
Ku NO, Strnad P, Zhong BH, Tao GZ, Omary MB (2007) Keratins let liver live: mutations predispose to liver disease and crosslinking generates Mallory-Denk bodies. Hepatology 46:1639–1649
Liem RK, Messing A (2009) Dysfunctions of neuronal and glial intermediate filaments in disease. J Clin Invest 119:1814–1824
Moll R, Franke WW, Schiller DL, Geiger B, Krepler R (1982) The catalog of human cytokeratins: patterns of expression in normal epithelia, tumors and cultured cells. Cell 31:11–24
Moll R, Krepler R, Franke WW (1983) Complex cytokeratin polypeptide patterns observed in certain human carcinomas. Differentiation 23:256–269
Moll R, Divo M, Langbein L (2008) The human keratins: biology and pathology. Histochem Cell Biol 129:705–753
Muller M, Bhattacharya SS, Moore T, Prescott Q, Wedig T, Herrmann H, Magin TM (2009) Dominant cataract formation in association with a vimentin assembly disrupting mutation. Hum Mol Genet 18:1052–1057
Na N, Chandel NS, Litvan J, Ridge KM (2010) Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species are required for hypoxia-induced degradation of keratin intermediate filaments. FASEB J 24:799–809
Omary MB (2009) “IF-pathies”: a broad spectrum of intermediate filament-associated diseases. J Clin Invest 119:1756–1762
Omary MB, Coulombe PA, McLean WH (2004) Intermediate filament proteins and their associated diseases. N Engl J Med 351:2087–2100
Omary MB, Ku NO, Strnad P, Hanada S (2009) Toward unraveling the complexity of simple epithelial keratins in human disease. J Clin Invest 119:1794–1805
Ridge KM, Linz L, Flitney FW, Kuczmarski ER, Chou YH, Omary MB, Sznajder JI, Goldman RD (2005) Keratin 8 phosphorylation by protein kinase C delta regulates shear stress-mediated disassembly of keratin intermediate filaments in alveolar epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 280:30400–30405
Rogel MR, Soni PN, Troken JR, Sitikov A, Trejo HE, Ridge KM (2011) Vimentin is sufficient and required for wound repair and remodeling in alveolar epithelial cells. FASEB J 25:3873–3883
Sivaramakrishnan S, Schneider JL, Sitikov A, Goldman RD, Ridge KM (2009) Shear stress induced reorganization of the keratin intermediate filament network requires phosphorylation by protein kinase C zeta. Mol Biol Cell 20:2755–2765
Strnad P, Stumptner C, Zatloukal K, Denk H (2008) Intermediate filament cytoskeleton of the liver in health and disease. Histochem Cell Biol 129:735–739
Waschke J (2008) The desmosome and pemphigus. Histochem Cell Biol 130:21–54
Worman HJ, Fong LG, Muchir A, Young SG (2009) Laminopathies and the long strange trip from basic cell biology to therapy. J Clin Invest 119:1825–1836
Zeisberg M, Neilson EG (2009) Biomarkers for epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. J Clin Invest 119:1429–1437
Zwerger M, Medalia O (2013) From lamins to lamina: a structural perspective. Histochem Cell Biol 140:3–12
Acknowledgments
We thank Sujin Kim for assistance with immune staining. This work was supported by Korean Research WCU project (R31-10086) from the Korean Ministry of Education, Science and Technology, and Health grant (A111769) from Korea Health Industry Development Institute (N.-O. K).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yi, H., Ku, NO. Intermediate filaments of the lung. Histochem Cell Biol 140, 65–69 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-013-1105-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-013-1105-x