Abstract
Background
Gene variants have been identified in patients with familial or sporadic idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). These variants may partially account for the genetic risk of IPF. The aim of this study was to identify potential genes involved in both familial and sporadic IPF.
Methods
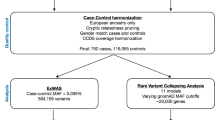
A Han family in northern China with four members diagnosed with IPF was investigated in this observational study. Whole-exome sequencing (WES) was used to identify germline variants underlying disease phenotypes in five members of this family. Candidate rare variants were validated by Sanger sequencing in samples from 16 family members and 119 patients with sporadic IPF. The plasma levels of proteins encoded by the above candidate genes were also examined in 16 family members, 119 other patients with sporadic IPF and 120 age- and sex-matched healthy controls.
Results
In a Chinese Han family, MMP19 c.1222 C > T was identified in all familial IPF patients and six offspring from generations III and IV. This variant introduces a premature stop codon, which may damage protein function. Sanger sequencing revealed that 7.6% (9/119) of sporadic IPF patients harbored three MMP19 variants. The genetic risk analysis for pulmonary fibrosis showed that MMP19 c.1499 C > T and c.1316G > A were significantly associated with an increased risk of IPF (OR 3.66, p = 0.028 and OR 8.64, p < 0.001, respectively). The plasma levels of MMP19 were significantly higher in patients with sporadic or familial IPF than in healthy controls (all p < 0.001).
Conclusions
MMP19 variants were identified in familial or sporadic IPF, thus providing a potential new clue into IPF pathogenesis.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 1000 G:
-
1000 Genomes Project
- COPD:
-
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- DLCO SB:
-
Diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide
- EAS:
-
East Asians
- FEV1 :
-
Forced expiratory volume in first second
- FVC:
-
Forced vital capacity
- GnomAD:
-
Genome Aggregation Database;
- IPF:
-
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- MMP19:
-
Matrix metalloproteinase-19
- OR:
-
Odds ratio
- PFTs:
-
Pulmonary function tests
- TERT:
-
Telomerase reverse transcriptase
References
Raghu G, Remy-Jardin M, Myers JL et al (2018) Diagnosis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT clinical practice guideline. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 198:e44–e68. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201807-1255ST
Lederer DJ, Martinez FJ (2018) Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. N Engl J Med 378:1811–1823. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1705751
Daccord C, Maher TM (2016) Recent advances in understanding Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.8209.1. F1000Res 5
Kropski JA, Blackwell TS, Loyd JE (2015) The genetic basis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Eur Respir J 45:1717–1727. https://doi.org/10.1183/09031936.00163814
King TJ, Pardo A, Selman M (2011) Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Lancet 378:1949–1961. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60052-4
Stuart BD, Choi J, Zaidi S et al (2015) Exome sequencing links mutations in PARN and RTEL1 with familial pulmonary fibrosis and telomere shortening. Nat Genet 47:512–517. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3278
Borie R, Kannengiesser C, Nathan N, Tabeze L, Pradere P, Crestani B (2015) Familial pulmonary fibrosis. Rev Mal Respir 32:413–434. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rmr.2014.07.017
Garcia-Sancho C, Buendia-Roldan I, Fernandez-Plata MR, Navarro C, Perez-Padilla R, Vargas MH, Loyd JE, Selman M (2011) Familial pulmonary fibrosis is the strongest risk factor for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Respir Med 105:1902–1907. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rmed.2011.08.022
Seibold MA, Wise AL, Speer MC et al (2011) A common MUC5B promoter polymorphism and pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med 364:1503–1512. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1013660
Allen RJ, Porte J, Braybrooke R et al (2017) Genetic variants associated with susceptibility to Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis in people of European ancestry: a genome-wide association study. Lancet Respir Med 5:869–880. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-2600(17)30387-9
Alder JK, Stanley SE, Wagner CL, Hamilton M, Hanumanthu VS, Armanios M (2015) Exome sequencing identifies mutant TINF2 in a family with pulmonary fibrosis. Chest 147:1361–1368. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.14-1947
Fingerlin TE, Murphy E, Zhang W et al (2013) Genome-wide association study identifies multiple susceptibility loci for pulmonary fibrosis. Nat Genet 45:613–620. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2609
Liu Q, Zhou Y, Cogan JD et al (2023) The genetic landscape of familial pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.202204-0781OC
Nogee LM, Dunbar AR, Wert SE, Askin F, Hamvas A, Whitsett JA (2001) A mutation in the surfactant protein C gene associated with familial interstitial lung Disease. N Engl J Med 344:573–579. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM200102223440805
Wang Y, Kuan PJ, Xing C et al (2009) Genetic defects in surfactant protein A2 are associated with pulmonary fibrosis and Lung cancer. Am J Hum Genet 84:52–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2008.11.010
Armanios MY, Chen JJ, Cogan JD et al (2007) Telomerase mutations in families with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. N Engl J Med 356:1317–1326. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa066157
Moore C, Blumhagen RZ, Yang IV et al (2019) Resequencing study confirms that host defense and cell senescence gene variants contribute to the risk of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 200:199–208. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201810-1891OC
Peljto AL, Blumhagen RZ, Walts AD et al (2023) Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis is associated with common genetic variants and limited rare variants. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.202207-1331OC
Petrovski S, Todd JL, Durheim MT et al (2017) An exome sequencing study to assess the role of rare genetic variation in pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 196:82–93. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201610-2088OC
Steele MP, Speer MC, Loyd JE et al (2005) Clinical and pathologic features of familial interstitial Pneumonia. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 172:1146–1152. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.200408-1104OC
Coghlan MA, Shifren A, Huang HJ, Russell TD, Mitra RD, Zhang Q, Wegner DJ, Cole FS, Hamvas A (2014) Sequencing of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis-related genes reveals Independent single gene associations. BMJ Open Respir Res 1:e57. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjresp-2014-000057
Kropski JA, Lawson WE, Young LR, Blackwell TS (2013) Genetic studies provide clues on the pathogenesis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Dis Model Mech 6:9–17. https://doi.org/10.1242/dmm.010736
Spagnolo P, Grunewald J, du Bois RM (2014) Genetic determinants of pulmonary fibrosis: evolving concepts. Lancet Respir Med 2:416–428. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-2600(14)70047-5
Deng Y, Li Z, Liu J et al (2018) Targeted resequencing reveals genetic risks in patients with sporadic Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Hum Mutat 39:1238–1245. https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.23566
Stracke JO, Hutton M, Stewart M, Pendas AM, Smith B, Lopez-Otin C, Murphy G, Knauper V (2000) Biochemical characterization of the catalytic domain of human matrix metalloproteinase 19. Evidence for a role as a potent basement membrane degrading enzyme. J Biol Chem 275:14809–14816. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.275.20.14809
Wu X, Qi H, Yang Y, Yin Y, Ma D, Li H, Qu Y (2016) Downregulation of matrix metalloproteinase19 induced by respiratory syncytial viral Infection affects the interaction between epithelial cells and fibroblasts. Mol Med Rep 13:167–173. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2015.4518
Jara P, Calyeca J, Romero Y et al (2015) Matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-19-deficient fibroblasts display a profibrotic phenotype. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 308:L511–L522. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajplung.00043.2014
Yu G, Kovkarova-Naumovski E, Jara P et al (2012) Matrix metalloproteinase-19 is a key regulator of lung fibrosis in mice and humans. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 186:752–762. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201202-0302OC
Gripp KW, Robbins KM, Sobreira NL et al (2015) Truncating mutations in the last exon of NOTCH3 cause lateral meningocele syndrome. Am J Med Genet A 167A:271–281. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.a.36863
Khajavi M, Inoue K, Lupski JR (2006) Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay modulates clinical outcome of genetic Disease. Eur J Hum Genet 14:1074–1081. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201649
Cong YS, Wright WE, Shay JW (2002) Human telomerase and its regulation. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 66:407–425. https://doi.org/10.1128/MMBR.66.3.407-425.2002
Lingner J, Hughes TR, Shevchenko A, Mann M, Lundblad V, Cech TR (1997) Reverse transcriptase motifs in the catalytic subunit of telomerase. Science 276:561–567. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.276.5312.561
Feng J, Funk WD, Wang SS et al (1995) The RNA component of human telomerase. Science 269:1236–1241. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.7544491
Armanios M, Blackburn EH (2012) The telomere syndromes. Nat Rev Genet 13:693–704. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg3246
Cronkhite JT, Xing C, Raghu G, Chin KM, Torres F, Rosenblatt RL, Garcia CK (2008) Telomere shortening in familial and sporadic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 178:729–737. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.200804-550OC
Tsakiri KD, Cronkhite JT, Kuan PJ, Xing C, Raghu G, Weissler JC, Rosenblatt RL, Shay JW, Garcia CK (2007) Adult-onset pulmonary fibrosis caused by mutations in telomerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:7552–7557. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0701009104
Arimura-Omori M, Kiyohara C, Yanagihara T et al (2020) Association between Telomere-related polymorphisms and the risk of IPF and COPD as a precursor lesion of Lung cancer: findings from the Fukuoka Tobacco-related lung Disease (FOLD) registry. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 21:667–673. https://doi.org/10.31557/APJCP.2020.21.3.667
Zheng CM, Zhan X, Yang YH, Jiang T, Ye Q, Lu Y (2018) A rare missense variant in telomerase reverse transcriptase is associated with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis in a Chinese Han family. Chin Med J (Engl) 131:2205–2209. https://doi.org/10.4103/0366-6999.240802
Sena P, Mariani F, Marzona L, Benincasa M, Ponz DLM, Palumbo C, Roncucci L (2012) Matrix metalloproteinases 15 and 19 are stromal regulators of Colorectal cancer development from the early stages. Int J Oncol 41:260–266. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2012.1441
Velinov N, Poptodorov G, Gabrovski N, Gabrovski S (2010) [the role of matrixmetalloproteinases in the tumor growth and metastasis], Khirurgiia (Sofiia) 44–49
Yu G, Herazo-Maya JD, Nukui T et al (2014) Matrix metalloproteinase-19 promotes metastatic behavior in vitro and is associated with increased mortality in non-small cell Lung cancer. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 190:780–790. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201310-1903OC
Chen Z, Wu G, Ye F, Chen G, Fan Q, Dong H, Zhu X, Wu C (2019) High expression of MMP19 is associated with poor prognosis in patients with Colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer 19:448. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-019-5673-6
Shen D, Zhao H, Zeng P, Song J, Yang Y, Gu X, Ji Q, Zhao W (2020) Circular RNA hsa_circ_0005556 accelerates gastric Cancer progression by sponging miR-4270 to increase MMP19 expression. J Gastric Cancer 20:300–312. https://doi.org/10.5230/jgc.2020.20.e28
Acknowledgements
We thank all participants who were involved in this study. We express our thanks to Miss Moyang Xu of University of Michigan, Ann Arbor for polishing language and grammas of the manuscript.
Funding
The work was supported by Reform and Development Program of Beijing Institute of Respiratory Medicine (Ggyfz202321) and by High Level Public Health Technology Talent Construction Project (DL-02-21).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YF and CZ designed the work, analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript. RM collected the data and contributed to analysis of data. JW and SY made contributions to the conception of the work and interpretation of data. QY participated in the study design and execution, as well as revising of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics Approval
The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of Beijing Chao-Yang Hospital (2018-KE-289).
Consent to Participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, Y., Zheng, C., Ma, R. et al. MMP19 Variants in Familial and Sporadic Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Lung 201, 571–580 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-023-00652-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-023-00652-4