Abstract
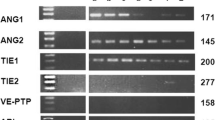
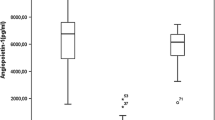
Chronic inflammation has been identified in leukemias as an essential regulator of angiogenesis. B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) cells secrete high levels of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha (HIF1α). The aim was to assess the role of inflammation in activation of angiogenic factors: endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS), HIF1α and VEGF via proliferation related signaling pathways and VEGF autocrine control. We isolated mononuclear cells (MNC) and CD19+ cells from peripheral blood of 60 patients with CLL. MNC were treated with pro-inflammatory interleukin-6 (IL-6) and VEGF, in combination with inhibitors of JAK1/2 (Ruxolitinib), mTOR (Rapamycin), NF-κB (JSH23), SMAD (LDN-193189) and PI3K/AKT (Ly294002) signaling pathways, to evaluate eNOS, VEGF and HIF1α expression by immunoblotting, immunocytochemistry and RT-qPCR. Also, we investigated IL-6 dependent neovascularization in human microvascular endothelial cells (HMEC-1) in co-culture with MNC of CLL. The angiogenic factors eNOS, VEGF and HIF1α had significantly higher frequencies in MNC of CLL in comparison to healthy controls (p < 0.001) and CD19+ cells of CLL. IL-6 increased the quantity of HIF1α (p < 0.05) and VEGF positive cells in the presence of JSH23 (p < 0.01). VEGF increased HIF1α (p < 0.05), and decreased eNOS gene expression (p < 0.01) in MNC of CLL. VEGF significantly (p < 0.001) increased the number of HIF1α positive MNC of CLL, prevented by inhibitors of JAK1/2, PI3K and mTOR signaling pathways. VEGF stimulation of SMAD (p < 0.05) and STAT5 (p < 0.01) signaling has been prevented by inhibitors of JAK1/2, mTOR, PI3K and SMAD signaling, individually (p < 0.01) or mutually (p < 0.001). Also, we showed that MNC of CLL and IL-6 individually stimulate neovascularization in co-culture with HMEC-1, without a cumulative effect. We demonstrated elevated angiogenic factors in CLL, while VEGF and IL-6 independently stimulated HIF1α. VEGF stimulation of HIF1α was mostly mTOR dependent, while IL-6 stimulation was NF-κB dependent.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data available on request by email to corresponding author.
References
Darwiche W, Gubler B, Marolleau JP (2018) Ghamlouch H (2018) Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia B-Cell Normal Cellular Counterpart: Clues from a Functional Perspective. Front Immunol 9:683. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.00683
Strati P, Shanafelt TD (2015) Monoclonal B-cell lymphocytosis and early-stage chronic lymphocytic leukemia: diagnosis, natural history, and risk stratification. Blood 126(4):454–462. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2015-02-585059
Aguilar-Cazares D, Chavez-Dominguez R, Carlos-Reyes A, Lopez-Camarillo C, Hernadez de la Cruz ON, Lopez-Gonzalez JS (2019) Contribution of Angiogenesis to Inflammation and Cancer. Front Oncol 9:1399. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2019.01399
MitrovićAjtić O, Subotički T, Diklić M, Đikić D, Vukotić M, Dragojević T, Živković E, Antić D, Čokić V (2022) Regulation of S100As Expression by Inflammatory Cytokines in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Int J Mol Sci 23(13):6952. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23136952
Han Y, Wang X, Wang B, Jiang G (2016) The progress of angiogenic factors in the development of leukemias. Intractable Rare Dis Res 5(1):6–16. https://doi.org/10.5582/irdr.2015.01048
Montemagno C, Pagès G (2020) Resistance to Anti-angiogenic Therapies: A Mechanism Depending on the Time of Exposure to the Drugs. Front Cell Dev Biol 8:584. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2020.00584
Adams J, Carder PJ, Downey S, Forbes MA, MacLennan K, Allgar V, Kaufman S, Hallam S, Bicknell R, Walker JJ, Cairnduff F, Selby PJ, Perren TJ, Lansdown M, Banks RE (2000) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in breast cancer: comparison of plasma, serum, and tissue VEGF and microvessel density and effects of tamoxifen. Cancer Res 60:2898–2905
Kay NE, Bone ND, Tschumper RC, Howell KH, Geyer SM, Dewald GW, Hanson CA, Jelinek DF (2002) B-CLL cells are capable of synthesis and secretion of both pro- and anti-angiogenic molecules. Leukemia 16:911–919. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2402467
Griggio V, Vitale C, Todaro M, Riganti C, Kopecka J, Salvetti C, Bomben R, Bo MD, Magliulo D, Rossi D, Pozzato G, Bonello L, Marchetti M, Omedè P, Kodipad AA, Laurenti L, Del Poeta G, Mauro FR, Bernardi R, Zenz T, Gattei V, Gaidano G, Foà R, Massaia M, Boccadoro M, Coscia M (2020) HIF-1α is over-expressed in leukemic cells from TP53-disrupted patients and is a promising therapeutic target in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Haematologica 105(4):1042–1054. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2019.217430
Ghosh AK, Shanafelt TD, Cimmino A, Taccioli C, Volinia S, Liu CG, Calin GA, Croce CM, Chan DA, Giaccia AJ, Secreto C, Wellik LE, Lee YK, Mukhopadhyay D, Kay NE (2009) Aberrant regulation of pVHL levels by microRNA promotes the HIF/VEGF axis in CLL B cells. Blood 113(22):5568–5574. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2008-10-185686
Lopes-Coelho F, Martins F, Pereira SA, Serpa J (2021) Anti-Angiogenic Therapy: Current Challenges and Future Perspectives. Int J Mol Sci 22(7):3765. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22073765
Rafii S, Lyden D, Benezra R, Hattori K, Heissig B (2002) Vascular and haematopoietic stem cells: novel targets for anti-angiogenesis therapy? Nat Rev Cancer 2:826–835. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc925
Subotički T, MitrovićAjtić O, Živković E, Diklić M, Đikić D, Tošić M, Beleslin-Čokić B, Dragojević T, Gotić M, Santibanez JF, Čokić V (2021) VEGF Regulation of Angiogenic Factors via Inflammatory Signaling in Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. Int J Mol Sci 22(13):6671. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22136671
Darwiche W, Gubler B, Marolleau JP, Ghamlouch H (2018) Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia B-Cell Normal Cellular Counterpart: Clues From a Functional Perspective. Front Immunol 9:683. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.00683
Hoermann G, Greiner G, Valent P (2015) Cytokine Regulation of Microenvironmental Cells in Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. Mediat Inflamm 2015:869242. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/869242
Zhu F, McCaw L, Spaner DE, Gorczynski RM (2018) Targeting the IL-17/IL-6 axis can alter growth of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia in vivo/in vitro. Leuk Res 66:28–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leukres.2018.01.006
Maffei R, Martinelli S, Castelli I, Santachiara R, Zucchini P, Fontana M, Fiorcari S, Bonacorsi G, Ilariucci F, Torelli G, Marasca R (2010) Increased angiogenesis induced by chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells is mediated by leukemia derived Ang2 and VEGF. Leuk Res 34(3):312–321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leukres.2009.06.023
Frater JL, Kay NE, Goolsby CL, Crawford SE, Dewald GW, Peterson LC (2008) Dysregulated angiogenesis in B-chronic lymphocytic leukemia: morphologic, immunohistochemical, and flow cytometric evidence. Diagn Pathol 3:16. https://doi.org/10.1186/1746-1596-3-16
Ribatti D, Vacca A, De Falco G, Ria R, Roncali L, Damacco F (2001) Role of hematopoietic growth factors in angiogenesis. Acta Haematol 106:157–161. https://doi.org/10.1159/000046611
Kay NE, Strati P, LaPlant BR, Leis JF, Nikcevich D, Call TG, Pettinger AM, Lesnick CE, Hanson CA, Shanafelt TD (2016) A randomized phase II trial comparing chemoimmunotherapy with or without bevacizumab in previously untreated patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Oncotarget 7(48):78269–78280. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.13412
Lu J, Cannizzaro E, Meier-Abt F, Scheinost S, Bruch PM, Giles HA, Lütge A, Hüllein J, Wagner L, Giacopelli B, Nadeu F, Delgado J, Campo E, Mangolini M, Ringshausen I, Böttcher M, Mougiakakos D, Jacobs A, Bodenmiller B, Dietrich S, Oakes CC, Zenz T, Huber W (2021) Multi-omics reveals clinically relevant proliferative drive associated with mTOR-MYC-OXPHOS activity in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Nat Cancer 2(8):853–864. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43018-021-00216-6
Zent CS, LaPlant BR, Johnston PB, Call TG, Habermann TM, Micallef IN, Witzig TE (2010) The treatment of recurrent/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL) with everolimus results in clinical responses and mobilization of CLL cells into the circulation. Cancer 116:2201–2207. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.25005
Blunt MD, Carter MJ, Larrayoz M, Smith LD, Aguilar-Hernandez M, Cox KL, Tipton T, Reynolds M, Murphy S, Lemm E, Dias S, Duncombe A, Strefford JC, Johnson PW, Forconi F, Stevenson FK, Packham G, Cragg MS, Steele AJ (2015) The PI3K/mTOR inhibitor PF-04691502 induces apoptosis and inhibits microenvironmental signaling in CLL and the Eμ-TCL1 mouse model. Blood 25:4032–4041. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2014-11-610329
Chen Y, Chen L, Yu J, Ghia EM, Choi MY, Zhang L, Zhang S, Sanchez-Lopez E, Widhopf GF 2nd, Messer K, Rassenti LZ, Jamieson C, Kipps TJ (2019) Cirmtuzumab blocks Wnt5a/ROR1 stimulation of NF-κB to repress autocrine STAT3 activation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 134(13):1084–1094. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.2019001366
Farahani M, Treweeke AT, Toh CH, Till KJ, Harris RJ, Cawley JC, Zuzel M, Chen H (2005) Autocrine VEGF mediates the antiapoptotic effect of CD154 on CLL cells. Leukemia 19(4):524–530. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.leu.2403631
Okumura N, Yoshida H, Kitagishi Y, Murakami M, Nishimura Y, Matsuda S (2012) PI3K/AKT/PTEN Signaling as a Molecular Target in Leukemia Angiogenesis. Adv Hematol 843085. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/843085
Ellis L, Hammers H, Pili R (2009) Targeting tumor angiogenesis with histone deacetylase inhibitors. Cancer Lett 280(2):145–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2008.11.012
Li Q, Michaud M, Canosa S, Kuo A, Madri JA (2011) GSK-3β: a signaling pathway node modulating neural stem cell and endothelial cell interactions. Angiogenesis 14(2):173–185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-011-9201-9
Khodashenas M, Rajabian A, Attaranzadeh A, Lavi Arab F, Allahyari N (1992) Allahyari A (2022) Evaluation of cytokine levels as possible predicting elements in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Rev Assoc Med Bras 68(10):1364–1368. https://doi.org/10.1590/1806-9282.20220260
Bibi S, Arslanhan MD, Langenfeld F, Jeanningros S, Cerny-Reiterer S, Hadzijusufovic E, Tchertanov L, Moriggl R, Valent P, Arock M (2014) Co-operating STAT5 and AKT signaling pathways in chronic myeloid leukemia and mastocytosis: possible new targets of therapy. Haematologica 99(3):417–429. https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2013.098442
Matvieieva AS, Kovalevska LM, Ivanivska TS, Klein E, Kashuba EV (2019) The STAT5 transcription factor in B-cells of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Biopolym Cell 30–38. https://doi.org/10.7124/bc.000993
Witkowska M, Majchrzak A, Cebula-Obrzut B, Wawrzyniak E, Robak T, Smolewski P (2017) The distribution and potential prognostic value of SMAD protein expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Tumour Biol 39(3):1010428317694551. https://doi.org/10.1177/1010428317694551
Funding
This research was supported by The Ministry of Science, Technological Development and Innovation of the Republic of Serbia grant number 451–03-66/2024–03/200015.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, V.Č., D.A. and O.M.A.; methodology, T.S., O.M.A., M.D. and D.Đ.; formal analysis, T.S., O.M.A., E.Ž. and M.D.; investigation, T.S., O.M.A., M.V., T.D. and D.Đ.; data curation, O.M.A. and M.V., writing—original draft preparation, O.M.A., T.S., V.V., and V.Č.; writing—review & editing, O.M.A. and V.Č.; visualization, O.M.A. and E.Ž.; supervision, V.Č.; project administration, V.Č. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Institutional review board Statement
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the University Clinical Centre of Serbia, Belgrade (decision number 187/4) and the Ethics Committee of the Institute for Medical Research, Belgrade (decision number EO 117/2016).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mitrović-Ajtić, O., Živković, E., Subotički, T. et al. Inflammation mediated angiogenesis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Ann Hematol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-024-05781-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-024-05781-1