Abstract
Purpose
To determine the long-term natural history of size change in SBRT-treated HCC to identify an imaging biomarker to help assess treatment response.
Methods
This was a retrospective cohort study of consecutive HCCs treated with SBRT from January 2008 to December 2016 with either 2 years post-treatment MRI follow-up or post-treatment resection histology. Size, major features for HCC, and mRECIST and LI-RADS v.2018 treatment response criteria were assessed at each post-treatment MRI. Local progression, distant progression, and survival were modeled with Kaplan Meier analyses.
Results
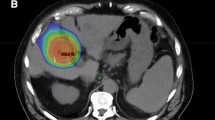
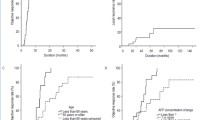
56 HCCs met inclusion criteria. Mean baseline HCC diameter was 30 mm (range: 9–105 mm). At 3 months, 76% (N = 43) of treated HCCs decreased in size (mean reduction: 8 mm, range: 5–99 mm) and 0% (N = 0) increased in size. By 24 months, 11% (N = 5) had increased in size and were considered local progression. APHE remained in 77% (43/56) at 3 months, 38% (19/50) at 12 months, and 23% (11/47) at 24 months. mRECIST-defined viable disease was observed in 77% (43/56) at 3 months and 20% (9/47) at 24 months. LI-RADS v.2018 criteria identified viable or equivocal disease in 0% at 3 months and 10% (5/47) at 24 months.
Conclusion
Gradual loss of APHE and slow decrease in size are normal findings in HCCs treated with SBRT, and persistent APHE does not indicate viable disease. mRECIST is not accurate in the assessment of HCC after SBRT due to an overreliance on APHE to define viable disease. Increasing mass size or new nodular APHE at the treatment site may indicate local progression.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bosetti C, Turati F, La Vecchia C. Hepatocellular carcinoma epidemiology. Best Pract Res Clinc Gastroenterol, 2014; 28:753-770.
Bruix J, Sherman M. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma: an update. Hepatology, 2011; 3:1020-1022.
El-Serag HB. Hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med, 2011; 365:1118-1127.
Bruix J, Sherman M, Llovet JM, et al. Clinical management of hepatocellular carcinoma: conclusions of the Barcelona-2000 EASL conference. J Hepatol 2001; 35:421-430.
Lencioni R, Llovet JM. Modified RECIST (mRECIST assessment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Liver Dis 2010; 30:52-60.
Kielar A, Fowler K, Lewis S, Yaghmai V, Miller F, Yarmohammadi H, Kim C, Chernyak V, Yokoo T, Meyer J, Newton I, Do R. Locoregional therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma and the new LI-RADS treatment response algorithm. Abdominal Radiology, 2018; 43 (1): 218-230.
Oldrini G, Huertas A, Renard-Oldrini S, Taste-George H, Guillaume V, Laurent V, Salleron J, Henrot P. Tumor response assessment by MRI following stereotactic body radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Plos One, 2017; e01766118
Mendiratta-Lala M, Masch W, Shankar PR, Hartman HE, Davenport MS, Schipper MJ, Maurino C, Cuneo KC, Lawrence TS, Owen D. Magnetic resonance imaging evaluation of hepatocellular carcinoma treated with stereotactic body radiation therapy: long term imaging follow-up. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 2019; 103(1):169-179.
Mendiratta-Lala M, Gu E, Owen D, Cuneo KC, Bazzi L, Lawrence TS, Hussain H, Davenport MS. Imaging findings within the first 12 months of hepatocellular carcinoma treated with stereotactic body radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 2018; 102(4):1063-1069.
Herfarth KK, Hof H, Bahner ML, et al. Assessment of focal liver reaction by multiphasic CT after stereotactic single-dose radiotherapy of liver tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2003;57:444-51.
Yip C, Cook GJR, Owczarczyk K, Goh V. Challenges in imaging assessment following liver stereotactic body radiotherapy: pitfalls to avoid in clinical practice. Chinese Clinical Oncology, 2017; 6(2):S11.
Sanuki, N, Takeda, A, Mizuno, T. Tumor response on CT following hypofractionated stereotactic ablative body radiotherapy for small hypervascular hepatocellular carcinoma with cirrhosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2013;201(6):W812–W820.
Park, MJ, Kim, SY, Yoon, SM. Stereotactic body radiotherapy-induced arterial hypervascularity of non-tumorous hepatic parenchyma in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: potential pitfalls in tumor response evaluation on multiphase computed tomography. PLoS One. 2014;9(2):e90327.
Kimura, T, Takahashi, S, Takahashi, I. The time course of dynamic computed tomographic appearance of radiation injury to the cirrhotic liver following stereotactic body radiation therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. PLos One. 2015;10(6):e0125231.
Yang JF, Lo CH. Is stereotactic body radiotherapy better than radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma? J Clin Oncol 2016; 34 (23): 3797-3798.
Price TR, Perkins SM, Sandrasegaran K, et al. Evaluation of response after stereotactic body radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer, 2012; 118:3191-3198.
Sheu JC, Sung JL, Chen DS, et al. Growth rate of asymptomatic hepatocellular carcinoma and its clinical implications. Gastroenterology, 1985; 89:259-266.
Kubota K, Ina H, Okada Y, Irie T. Growth rate of primary single hepatocellular carcinoma: determining optimal screening interval with contrast enhanced computed tomography. Digestive Diseases and Sciences, 2003; 48(3):581-586.
An C, Choi YA, Choi D, Paik YH, et al. Growth rate of early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic liver disease. Clinical and molecular hepatology, 2015; 21:279-286.
Barbara L, Benzi G, Gaiani S, et al. Natural history of small untreated hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: a multivariate analysis of prognostic factors of tumor growth rate and patient survival. Hepatology 1992; 16:132–137.
Kubota K, Ina H, Okada Y, Irie T. Growth rate of primary single hepatocellular carcinoma: determining optimal screening interval with contrast enhanced computed tomography. Dig Dis Sci 2003; 48:581–586.
Okazaki N, Yoshino M, Yoshida T, et al. Evaluation of the prognosis for small hepatocellular carcinoma based on tumor volume doubling time: a preliminary report. Cancer 1989; 63:2207–2210.
Poon RT, Fan ST, Lo CM, Liu CL, Wong J. Longterm survival and pattern of recurrence after resection of small hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with preserved liver function: implications for a strategy of salvage transplantation. Ann Surg 2002; 235:373–382.
Poon RT, Fan ST, Lo CM, Liu CL, Wong J. Intrahepatic recurrence after curative resection of hepatocellular carcinoma: long-term results of treatment and prognostic factors. Ann Surg 1999; 229:216–222.
Tezuka M, Hayashi K, Kubota K, et al. Growth rate of locally recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization: comparing the growth rate of locally recurrent tumor with that of primary hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Dis Sci 2007; 52:783–788.
Wald C, Russo MW, Heimbach JK, et al. New OPTN/UNOS Policy for liver transplant allocation: Standardization of liver imaging, diagnosis, classification and reporting of hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiology 2013; 266:376-382.
Vincenzi, B, Di Maio, M, Silletta, M. Prognostic relevance of objective response according to easl criteria and mrecist criteria in hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated with loco-regional therapies: a literature-based meta-analysis. PLos One. 2015;10(7): e0133488.
Mannina, EM, Cardenes, HR, Lasley, FD. Role of stereotactic body radiation therapy before orthotopic liver transplantation: retrospective evaluation of pathologic response and outcomes. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2017;97(5):931–938.
Wahl DR, Stenmark MH, Tao Y, Pollom EL, Caoili EM, Lawrence TS, Schipper MJ, Feng M. Outcomes After Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy or Radiofrequency Ablation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2016 Feb 10;34(5):452-9. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2015.61.4925. Epub 2015 Nov 30. PMID: 26628466; PMCID: PMC4872011.
Funding
This study was not funded by a grant; however, a few authors (Mishal Mendiratta-Lala, Dawn Owen, Kyle Cuneo, Theodore S. Lawrence, Matthew J. Schipper) are Co-PI’s on grant: P01 CA59827 (NIH funded).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors made substantial contributions to the conception or design of the work, or acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data; drafted work or revised it critically; approved the version to be published; and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy and integrity are appropriately resolved.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
Institutional review board approval was obtained and informed consent waived for this Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)-compliant retrospective cohort study. This research was conducted retrospectively from data obtained for clinical purposes.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mendiratta-Lala, M., Masch, W., Owen, D. et al. Natural history of hepatocellular carcinoma after stereotactic body radiation therapy. Abdom Radiol 45, 3698–3708 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-020-02532-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-020-02532-4