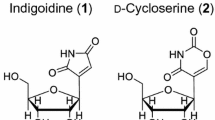
Abstract
Genome sequencing has revealed that each Streptomyces contains a wide range of biosynthetic gene clusters (BGCs) and has the capability to produce more novel natural products than what is expected. However, most gene clusters for secondary metabolite biosynthesis are cryptic under normal growth conditions. In Streptomyces tsukubaensis, combining overexpression of the putative SARPs (Streptomyces antibiotic regulatory proteins) and bioactivity-guided screening, the silent gene cluster (tsu) was successfully activated and a novel bioactive anthracycline tsukubarubicin was further isolated and identified. Biological activity assays demonstrated that tsukubarubicin possessed much better antitumor bioactivities against various human cancer cell lines (especially the breast cancer cell lines) than clinically used doxorubicin. Moreover, the previously unreported gene cluster (tsu) for biosynthesis of tsukubarubicin was first characterized and detailed annotations of this gene cluster were also conducted. Our strategy presented in this work is broadly applicable in other Streptomyces and will assist in enriching the natural products for potential drug leads.
Key points
• Generally scalable strategy to activate silent gene clusters by manipulating SARPs.
• The novel anthracycline tsukubarubicin with potent antitumor bioactivities.
• Identification and annotation of the previously uncharacterized tsu gene cluster.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25(17):3389–3402. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/25.17.3389
Aoki M, Shirai H, Nakayama N, Itezono Y, Mori M, Satoh T, Ohshima S, Watanabe J, Yokose K, Seto H (1991) Structural studies on avidinorubicin, a novel anthracycline with platelet aggregation inhibitory activity. J Antibiot 44(6):635–645. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.44.635
Asbell PA, Sanfilippo CM, Sahm DF, DeCory HH (2020) Trends in antibiotic resistance among ocular microorganisms in the United States from 2009 to 2018. JAMA Ophthalmol 138(5):439–450. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2020.0155
Barzkar N, Tamadoni Jahromi S, Poorsaheli HB, Vianello F (2019) Metabolites from marine microorganisms, micro, and macroalgae: immense scope for pharmacology. Mar Drugs 17(8). https://doi.org/10.3390/md17080464
Bentley SD, Chater KF, Cerdeno-Tarraga AM, Challis GL, Thomson NR, James KD, Harris DE, Quail MA, Kieser H, Harper D, Bateman A, Brown S, Chandra G, Chen CW, Collins M, Cronin A, Fraser A, Goble A, Hidalgo J, Hornsby T, Howarth S, Huang CH, Kieser T, Larke L, Murphy L, Oliver K, O'Neil S, Rabbinowitsch E, Rajandream MA, Rutherford K, Rutter S, Seeger K, Saunders D, Sharp S, Squares R, Squares S, Taylor K, Warren T, Wietzorrek A, Woodward J, Barrell BG, Parkhill J, Hopwood DA (2002) Complete genome sequence of the model actinomycete Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Nature 417(6885):141–147. https://doi.org/10.1038/417141a
Bhuyan BK, Dietz A (1965) Fermentation, taxonomic, and biological studies on nogalamycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 5:836–844
Bierman M, Logan R, O'Brien K, Seno ET, Rao RN, Schoner BE (1992) Plasmid cloning vectors for the conjugal transfer of DNA from Escherichia coli to Streptomyces spp. Gene 116(1):43–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/0378-1119(92)90627-2
Blin K, Medema MH, Kazempour D, Fischbach MA, Breitling R, Takano E, Weber T (2013) AntiSMASH 2.0—a versatile platform for genome mining of secondary metabolite producers. Nucleic Acids Res 41(Web Server issue):204–212. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt449
Bruender NA, Thoden JB, Holden HM (2010) X-ray structure of Kijd3, a key enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of D-kijanose. Biochemistry-Us 49(17):3517–3524. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi100318v
Bruheim P, Sletta H, Bibb MJ, White J, Levine DW (2002) High-yield actinorhodin production in fed-batch culture by a Streptomyces lividans strain overexpressing the pathway-specific activator gene actll-ORF4. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 28(2):103–111. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj/jim/7000219
Camacho C, Coulouris G, Avagyan V, Ma N, Papadopoulos J, Bealer K, Madden TL (2009) BLAST+: architecture and applications. Bmc Bioinformatics 10:421. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-10-421
Challinor VL, Bode HB (2015) Bioactive natural products from novel microbial sources. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1354:82–97. https://doi.org/10.1111/nyas.12954
Cragg GM, Newman DJ (2013) Natural products: a continuing source of novel drug leads. Biochim Biophys Acta 1830(6):3670–3695. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.02.008
Fenical WB (2020) Marine microbial natural products: the evolution of a new field of science. J Antibiot 73(8):481–487. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41429-020-0331-4
Grocholski T, Yamada K, Sinkkonen J, Tirkkonen H, Niemi J, Metsa-Ketela M (2019) Evolutionary trajectories for the functional diversification of anthracycline methyltransferases. ACS Chem Biol 14(5):850–856. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.9b00238
Guerra SM, Rodriguez-Garcia A, Santos-Aberturas J, Vicente CM, Payero TD, Martin JF, Aparicio JF (2012) LAL regulators SCO0877 and SCO7173 as pleiotropic modulators of phosphate starvation response and actinorhodin biosynthesis in Streptomyces coelicolor. PLoS One 7(2):31475. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0031475
Guo F, Xiang S, Li L, Wang B, Rajasarkka J, Grondahl-Yli-Hannuksela K, Ai G, Metsa-Ketela M, Yang K (2015) Targeted activation of silent natural product biosynthesis pathways by reporter-guided mutant selection. Metab Eng 28:134–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2014.12.006
Ishii K, Kondo S, Nishimura Y, Hamada M, Takeuchi T, Umezawa H (1983a) Decilorubicin, a new anthracycline antibiotic. J Antibiot 36(4):451–453. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.36.451
Ishii K, Nishimura Y, Kondo S, Umezawa H (1983b) Decilonitrose and 4-O-succinyl-L-diginose, sugar components of decilorubicin. J Antibiot 36(4):454–456. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.36.454
Ishii K, Nishimura Y, Naganawa H, Kondo S, Umezawa H (1984) The structure of decilorubicin. J Antibiot 37(4):344–353. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.37.344
Izawa T, Nishimura Y, Kondo S (1991) 3-Amino-5-C-phenyl-D-altrofuranose and 3-amino-5-C-[3-carboxy-4-(carboxymethyl)-2-oxo-3-cyclohexen-1-yl]-D-altrofuranose, possible intermediates for synthesis of the anthracycline antibiotic decilorubicin. Carbohydr Res 211(1):137–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/0008-6215(91)84152-5
Jones SE, Elliot MA (2018) Exploring the regulation of Streptomyces growth and development. Curr Opin Microbiol 42:25–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2017.09.009
Kieser T, Bibb M, Chater K, Butter M, Hopwood D, Bittner M, Buttner M (2000) Practical Streptomyces genetics. John Innes Centre, England
Kong D, Wang X, Nie J, Niu G (2019) Regulation of antibiotic production by signaling molecules in Streptomyces. Front Microbiol 10:2927. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.02927
Kren V, Martinkova L (2001) Glycosides in medicine: “the role of glycosidic residue in biological activity”. Curr Med Chem 8(11):1303–1328. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867013372193
Lee N, Kim W, Hwang S, Lee Y, Cho S, Palsson B, Cho BK (2020) Thirty complete Streptomyces genome sequences for mining novel secondary metabolite biosynthetic gene clusters. Sci Data 7(1):55. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-020-0395-9
Li Y, Kong L, Shen J, Wang Q, Liu Q, Yang W, Deng Z, You D (2019) Characterization of the positive SARP family regulator PieR for improving piericidin A1 production in Streptomyces piomogeues var. Hangzhouwanensis. Synth Syst Biotechnol 4(1):16–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.synbio.2018.12.002
Li Y, Zhang J, Zheng J, Guan H, Liu W, Tan H (2020) Co-expression of a SARP family activator ChlF2 and a type II thioesterase ChlK led to high production of chlorothricin in Streptomyces antibioticus DSM 40725. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 8:1013. https://doi.org/10.3389/fbioe.2020.01013
Liu G, Chater KF, Chandra G, Niu G, Tan H (2013) Molecular regulation of antibiotic biosynthesis in Streptomyces. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 77(1):112–143. https://doi.org/10.1128/MMBR.00054-12
Ma D, Wang C, Chen H, Wen J (2018) Manipulating the expression of SARP family regulator BulZ and its target gene product to increase tacrolimus production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 102(11):4887–4900. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-018-8979-4
Macneil DJ, Klapko LM (1987) Transformation of Streptomyces avermitilis by plasmid DNA. J Ind Microbiol 2(4):209–218. https://doi.org/10.1007/Bf01569542
Mao XM, Zhou Z, Cheng LY, Hou XP, Guan WJ, Li YQ (2009) Involvement of SigT and RstA in the differentiation of Streptomyces coelicolor. FEBS Lett 583(19):3145–3150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2009.09.025
Mao D, Okada BK, Wu Y, Xu F, Seyedsayamdost MR (2018) Recent advances in activating silent biosynthetic gene clusters in bacteria. Curr Opin Microbiol 45:156–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2018.05.001
Martin JF, Liras P (2010) Engineering of regulatory cascades and networks controlling antibiotic biosynthesis in Streptomyces. Curr Opin Microbiol 13(3):263–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2010.02.008
Mo S, Yoon YJ (2016) Interspecies complementation of the LuxR family pathway-specific regulator involved in macrolide biosynthesis. J Microbiol Biotechnol 26(1):66–71. https://doi.org/10.4014/jmb.1510.10085
Newman DJ, Cragg GM (2016) Natural products as sources of new drugs from 1981 to 2014. J Nat Prod 79(3):629–661. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jnatprod.5b01055
Nishimura Y, Ishii K (1990) The absolute-configuration of decilonitrose, a sugar component of decilorubicin, is undoubtedly 2,3,6-trideoxy-3-C-methyl-3-nitro-L-ribo-hexopyranose. J Antibiot 43(1):54–61. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.43.54
Ohnishi Y, Ishikawa J, Hara H, Suzuki H, Ikenoya M, Ikeda H, Yamashita A, Hattori M, Horinouchi S (2008) Genome sequence of the streptomycin-producing microorganism Streptomyces griseus IFO 13350. J Bacteriol 190(11):4050–4060. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00204-08
Panthee S, Kito N, Hayashi T, Shimizu T, Ishikawa J, Hamamoto H, Osada H, Takahashi S (2020) Beta-carboline chemical signals induce reveromycin production through a LuxR family regulator in Streptomyces sp. SN-593. Sci Rep 10(1):10230. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-66974-y
Romero-Rodriguez A, Robledo-Casados I, Sanchez S (2015) An overview on transcriptional regulators in Streptomyces. Biochim Biophys Acta 1849(8):1017–1039. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagrm.2015.06.007
Rossiter SE, Fletcher MH, Wuest WM (2017) Natural products as platforms to overcome antibiotic resistance. Chem Rev 117(19):12415–12474. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00283
Rutledge PJ, Challis GL (2015) Discovery of microbial natural products by activation of silent biosynthetic gene clusters. Nat Rev Microbiol 13(8):509–523. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro3496
Siitonen V, Selvaraj B, Niiranen L, Lindqvist Y, Schneider G, Metsa-Ketela M (2016) Divergent non-heme iron enzymes in the nogalamycin biosynthetic pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 113(19):5251–5256. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1525034113
Smith CK, Davies GJ, Dodson EJ, Moore MH (1995) DNA-nogalamycin interactions: the crystal structure of d(TGATCA) complexed with nogalamycin. Biochemistry-Us 34(2):415–425. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00002a005
Tanaka Y, Hosaka T, Ochi K (2010) Rare earth elements activate the secondary metabolite-biosynthetic gene clusters in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J Antibiot 63(8):477–481. https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2010.53
Tang L, Grimm A, Zhang YX, Hutchinson CR (1996) Purification and characterization of the DNA-binding protein DnrI, a transcriptional factor of daunorubicin biosynthesis in Streptomyces peucetius. Mol Microbiol 22(5):801–813. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2958.1996.01528.x
Temperini C, Cirilli M, Aschi M, Ughetto G (2005) Role of the amino sugar in the DNA binding of disaccharide anthracyclines: crystal structure of the complex MAR70/d(CGATCG). Bioorg Med Chem 13(5):1673–1679. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2004.12.007
Thorson JS, Hosted TJ, Jiang JQ, Biggins JB, Ahlert J (2001) Nature’s carbohydrate chemists: the enzymatic glycosylation of bioactive bacterial metabolites. Curr Org Chem 5(2):139–167. https://doi.org/10.2174/1385272013375706
Wang YY, Zhang XS, Luo HD, Ren NN, Jiang XH, Jiang H, Li YQ (2016) Characterization of discrete phosphopantetheinyl transferases in Streptomyces tsukubaensis L19 unveils a complicate phosphopantetheinylation network. Sci Rep 6:24255. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep24255
Williams LD, Egli M, Qi G, Bash P, Vandermarel GA, Vanboom JH, Rich A, Frederick CA (1990) Structure of nogalamycin bound to a DNA hexamer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 87(6):2225–2229. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.87.6.2225
Xia H, Li X, Li Z, Zhan X, Mao X, Li Y (2020) The application of regulatory cascades in Streptomyces: yield enhancement and metabolite mining. Front Microbiol 11:406. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.00406
Xu G, Yang S (2019) Regulatory and evolutionary roles of pseudo gamma-butyrolactone receptors in antibiotic biosynthesis and resistance. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103(23-24):9373–9378. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-10219-0
Yang K, Qi LH, Zhang M, Hou XF, Pan HX, Tang GL, Wang W, Yuan H (2015) The SARP family regulator Txn9 and two-component response regulator Txn11 are key activators for trioxacarcin biosynthesis in Streptomyces bottropensis. Curr Microbiol 71(4):458–464. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-015-0868-9
Yang C, Qian R, Xu Y, Yi J, Gu Y, Liu X, Yu H, Jiao B, Lu X, Zhang W (2019) Marine actinomycetes-derived natural products. Curr Top Med Chem 19(31):2868–2918. https://doi.org/10.2174/1568026619666191114102359
Zhang XS, Luo HD, Tao Y, Wang YY, Jiang XH, Jiang H, Li YQ (2016) FkbN and Tcs7 are pathway-specific regulators of the FK506 biosynthetic gene cluster in Streptomyces tsukubaensis L19. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 43(12):1693–1703. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10295-016-1849-0
Zhang MM, Wong FT, Wang Y, Luo S, Lim YH, Heng E, Yeo WL, Cobb RE, Enghiad B, Ang EL, Zhao H (2017) CRISPR-Cas9 strategy for activation of silent Streptomyces biosynthetic gene clusters. Nat Chem Biol 13:607–609. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.2341
Zhong X, Tian Y, Niu G, Tan H (2013) Assembly and features of secondary metabolite biosynthetic gene clusters in Streptomyces ansochromogenes. Sci China Life Sci 56(7):609–618. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-013-4506-0
Zhou Z, Xu Q, Bu Q, Guo Y, Liu S, Liu Y, Du Y, Li Y (2015) Genome mining-directed activation of a silent angucycline biosynthetic gene cluster in Streptomyces chattanoogensis. Chembiochem 16(3):496–502. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbic.201402577
Acknowledgements
We thank every people participating in this work.
Funding
This research was sponsored by the NSFC key projects (no. 31520103901 and no. 31730002) and the National Key R&D Program of China (no. 2019YFA09005400).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QBW carried out the experiments and wrote the manuscript. ZYL, XYZ, and YL assisted with the experiments (fermentation, construction of plasmids, and analysis of NMR data, respectively). QBW, YQL, and XAC conceived and designed the experiments. QBW and YQL revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(PDF 1221 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, QB., Chen, XA., Lv, ZY. et al. Activation and discovery of tsukubarubicin from Streptomyces tsukubaensis through overexpressing SARPs. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 105, 4731–4741 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11344-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-021-11344-5