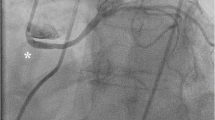
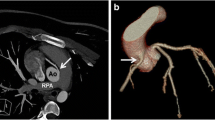
Abstract
Williams-Beuren syndrome (WBS) affects young infants and children. The underlying etiopathogenesis of this rare disease is due to the mutation of the elastin gene that is responsible for the elasticity of the arterial wall. As a result of inadequate elastin production, the major systemic arteries become abnormally rigid and can be manifested by an impediment to the blood flow. The most common cardiovascular abnormalities encountered in WBS are supravalvular aortic stenosis, pulmonary arterial stenosis, and mitral valve prolapse. Less frequently observed cardiovascular abnormalities include coarctation of the aorta, ventricular septal defect, patent ductus, subaortic stenosis, and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Coronary artery stenosis and severe impediment to the bi-ventricular outflow as a result of supravalvular aortic and pulmonary artery stenosis predispose patients to sudden death. Patients with progressed arterial stenosis and severe stenosis are likely to require intervention to prevent serious complications. Rarely, imaging findings may precede clinical presentation, which allows the radiologist to participate in the patient care. However, to be more prudent, the radiologist must be accustomed to the imaging characteristics of WBS as well as the patient’s clinical information, which could raise the suspicion of WBS. We performed a retrospective analysis of all the available images from patients diagnosed with WBS in last 4 years at our institution, and present key imaging findings along with a review of the literature to summarize the clinically relevant features as demonstrated by multidetector computed tomography in WBS. Cross-sectional imaging plays a vital role in the diagnosis of WBS cases with equivocal clinical features. MDCT evaluation of complex cardiovascular abnormalities of WBS including coronary artery disease is feasible with modern MDCT scanners and in the future, this approach could provide accurate information for planning, navigation, and noninvasive assessment of the secondary arterial changes in WBS and thus reducing the dependence upon invasive contrast catherization techniques.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad Z, Vettukattil J (2010) Pulmonary artery diverticulum: an angiographic marker for Williams syndrome. Pediatr Cardiol 31:611–614
Amenta S, Sofocleous C, Kolialexi A, Thomaidis L, Giouroukos S, Karavitakis E et al (2005) Clinical manifestations and molecular investigation of 50 patients with Williams syndrome in the Greek population. Pediatr Res 57(6):789–795
Bennett CJ, Maleszewski JJ, Araoz PA (2012) CT and MR imaging of the aortic valve: radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiographics 32(5):1399–1420
Berdon WE, Clarkson PM, Teele RL (2011) Williams-Beuren syndrome. Pediatric Radiol 41(2):262–266
Beuren AJ, Apitz J, Harmjanz D (1962) Supravalvular aortic stenosis in association with mental retardation and a certain facial appearance. Circulation 26:1235–1240
Bird LM, Billman GF, Lacro RV, Spicer RL, Jariwala LK, Hoyme HE et al (1996) Sudden death in Williams syndrome: report of ten cases. J Pediatr 129(6):926–931
Blomberg S, Rosander M, Andersson G (2006) Fears, hyperacusis and musicality in Williams syndrome. Res Dev Disabil 27(6):668–680
Bragg K, Fedel GM, DiProsperis A (2005) Cardiac arrest under anesthesia in a pediatric patient with Williams syndrome: a case report. AANA J 73(4):287–293
Collins RT II (2013) Cardiovascular disease in Williams syndrome. Circulation 127:2125–2134
Collins RT II, Kaplan P, Somes GW, Rome JJ (2010) Long-term outcomes of patients with cardiovascular abnormalities and Williams syndrome. Am J Cardiol 105:874–878
Colquitt JL, Noonan JA (2013) Cardiac findings in Noonan syndrome on long-term follow-up. Congenit Heart Dis 10. doi:10.1111/chd.12102
Daniels RS, Loggie MH, Schwartz C, Strife L, Kaplan S (1985) Systemic hypertension secondary to vascular anomalies in patients with Williams syndrome. J Pediatr 106:249–251
De Leersnyder H (2013) Smith-Magenis syndrome. Handb Clin Neurol 111:295–296
Del Pasqua A, Rinelli G, Toscano A, Iacobelli R, Digilio C, Marino B, Saffirio C et al (2009) New findings concerning cardiovascular manifestations emerging from long-term follow-up of 150 patients with the Williams-Beuren-Beuren syndrome. Cardiol Young 19(6):563–567
Ergul Y, Nisli K, Kayserili H, Karaman B, Basaran S, Dursun M et al (2012) Evaluation of coronary artery abnormalities in Williams syndrome patients using myocardial perfusion scintigraphy and CT angiography. Cardiol J 19(3):301–308
Eronen M, Peippo M, Hiippala A, Raatikka M, Arvio M, Johansson R et al (2002) Cardiovascular manifestations in 75 patients with Williams syndrome. J Med Genet 39:554–558
Ewart AK, Morris CA, Atkinson D, Jin W, Sternes K, Spallone P et al (1993) Hemizygosity at the elastin locus in a developmental disorder, Williams syndrome. Nat Genet 5:11–16
Figueroa J, Rodríguez LM, Hach JL, Del Castillo Ruíz V, Martínez HO (2008) Cardiovascular spectrum in Williams-Beuren syndrome: the Mexican experience in 40 patients. Tex Heart Inst J 35(3):279–285
Gallo FJ, Klein-Tasman BP, Gaffrey MS, Curran P (2008) Expecting the worst: Observations of reactivity to sound in young children with Williams syndrome. Res Dev Disabil 29(6):567–581
Geggel RL, Gauvreau K, Lock JE (2001) Balloon dilation angioplasty of peripheral pulmonary stenosis associated with Williams syndrome. Circulation 103:2165–2170
Goo HW (2013) Current trends in cardiac CT in children. Acta Radiol 54(9):1055–1062
Hallidie-Smith KA, Karas S (1988) Cardiac anomalies in Williams-Beuren syndrome. Arch Dis Child 63(7):809–813
Gray JC 3rd, Krazinski AW, Schoepf UJ, Meinel FG, Pietris NP, Suranyi P, et al.(2013) Cardiovascular manifestations of Williams syndrome: imaging findings. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr Nov-Dec;7(6):400-407.
Han BK, Lindberg J, Overman D, Schwartz RS, Grant K, Lesser JR (2012) Safety and accuracy of dual-source coronary computed tomography angiography in the pediatric population. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr 6(4):252–259
Kaplan P, Wang PP, Francke U (2001) Williams (Williams Beuren) syndrome: a distinct neurobehavioral disorder. J Child Neurol 16:177–190
Kasdon BD, Fox JE (2012) Kabuki syndrome diagnostic and treatment considerations. Ment Health Fam Med 9(3):171–179
Keane JF, Fellows KE, La Farge CG, Nadas AS, Bernhard WF (1976) The surgical management of discrete and diffuse supra-valvular aortic stenosis. Circulation 54:112–117
Keating MT (1995) Genetic approaches to cardiovascular disease: supravalvular aortic stenosis, Williams syndrome and long-QT syndrome. Circulation 92:142–147
Kim YM, Yoo SJ, Choi JY, Kim SH, Bae EJ, Lee YT (1999) Natural course of supravalvular aortic stenosis and peripheral pulmonary arterial stenosis in Williams’ syndrome. Cardiol Young 9:37–41
Kobayashi D, Sallaam S, Humes RA (2013) Tetralogy of Fallot with complete DiGeorge syndrome: report of a case and a review of the literature. Congenit Heart Dis 8(4):E119–E126
Lee WD, Hsu JJ, Huang FC, Chao MC, Chang YL, Huang MH (2009) Ischemic stroke in Williams-Beuren syndrome: a case report. Kaohsiung J Med Sci 25(4):212–216
Li DY, Faury G, Taylor DG, Davis EC, Boyle WA, Mecham RP et al (1998) Novel arterial pathology in mice and humans hemizygous for elastin. J Clin Invest 102:1783–1787
Lopez-Rangel E, Maurice M, McGillivray B, Friedman JM (1992) Williams syndrome in adults. Am J Med Genet 44(6):720–729
Matsuyama S, Watanabe T, Watabe T, Kuribayashi Y, Tina T, Shohtsu A et al (1977) Pulmonary artery diverticulum associated with tetralogy of Fallot. Tokai J Exp Clin Med 2:113–121
McGoon DC, Mankin HT, Vlad P, Kirklin JW (1961) The surgical treatment of supravalvular aortic stenosis. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 41:125–133
Mervis CB, Robinson BF, Bertrand J, Morris CA, Klein-Tasman BP, Armstrong SC (2000) The Williams syndrome cognitive profile. Brain Cogn 44(3):604–628
Morris CA, Pagon RA, Adam MP, Bird TD, Dolan CR, Fong CT, et al (1999) editors. GeneRevieWBS™ (Internet). Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993-2013.
Morrow AG, Waldhausen JA, Peters RL, Bloodwell RD, Braunwald E (1959) Supravalvular aortic stenosis: clinical, hemo-dynamic and pathologic observations. Circulation 20:1003–1010
Paul JF, Rohnean A, Sigal-Cinqualbre A (2010) Multidetector CT for congenital heart patients: what a paediatric radiologist should know. Pediatr Radiol 6:869–875
Perou ML (1961) Congenital supravalvular aortic stenosis. A morphological study with attempt at classification. Arch Pathol 71:453–466
Peterson TA, Todd DB, Edwards JE (1965) Supravalvular aortic stenosis. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 50:734–741
Pham PP, Moller JH, Hills C, Larson V, Pyles L (2009) Cardiac catheterization and operative outcomes from a multicenter consortium for children with Williams syndrome. Pediatr Cardiol 30:9–14
Pober BR. Williams-Beuren syndrome (2001) N Engl J Med 362:239–252
Pober BR, Johnson M, Urban Z (2008) Mechanisms and treatment of cardiovascular disease in Williams-Beuren syndrome. J Clin Invest 118:1606–1615
Radford DJ, Pohlner PG (2000) The middle aortic syndrome: an important feature of Williams’ syndrome. Cardiol Young 10:597–602
Rose C, Wessel A, Pankau R, Partsch CJ, Bürsch J (2001) Anomalies of the Abdominal aorta in Williams-Beuren syndrome—another cause of arterial hypertension. Eur J Pediatr 160:655–658
Sadler LS, Pober BR, Grandinetti A, Scheiber D, Fekete G, Sharma AN et al (2001) Differences by sex in cardiovascular disease in Williams syndrome. J Pediatr 139(6):849–853
Schaefer BM, Lewin MB, Stout KK, Byers PH, Otto CM (2007) Usefulness of bicuspid aortic valve phenotype to predict elastic properties of the ascending aorta. Am J Cardiol 99(5):686–690
Stamm C, Li J, Ho SY, Redington AN, Anderson RH (1997) The aortic root in supravalvular aortic stenosis: the potential surgical relevance of morphologic findings. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 114:16–24
van Pelt NC, Wilson NJ, Lear G (2005) Severe coronary artery disease in the absence of supravalvular stenosis in a patient with Williams syndrome. Pediatr Cardiol 26(5):665–667
van Son JAM, Edwards WD, Danielson GK (1994) Pathology of coronary arteries, myocardium, and great arteries in supravalvular aortic stenosis. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 108:21–28
Vincent WR, Buckberg GD, Hoffman JI (1974) Left ventricular subendocardial ischemia in severe valvular and supravalvular aortic stenosis: a common mechanism. Circulation 49:326–333
Watson TG, Mah E, Joseph Schoepf U, King L, Huda W, Hlavacek AM (2013) Effective radiation dose in computed tomographic angiography of the chest and diagnostic cardiac catheterization in pediatric patients. Pediatr Cardiol 34(3):518–524
Wessel A, Gravenhorst V, Buchhorn R (2004) Risk of sudden death in the Williams-Beuren syndrome. Am J Med Genet A 127(3):234–237
Williams JC, Barratt-Boyes BG, Lowe JB (1961) Supravalvular aortic stenosis. Circulation 24:1311–1318
Yau EK, Lo IF, Lam ST (2004) Williams-Beuren syndrome in the Hong Kong Chinese population: retrospective study. Hong Kong Med J. Feb 10(1):22-27.
Zaghloul N, Hutcheon RG, Tepperberg JH (2001) Visual diagnosis: monozygotic twins who have congenital heart disease and distinctive facial features. Pediatr Rev 23(10):365–367
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Das, K.M., Momenah, T.S., Larsson, S.G. et al. Williams-Beuren Syndrome: Computed Tomography Imaging Review. Pediatr Cardiol 35, 1309–1320 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-014-0998-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-014-0998-z