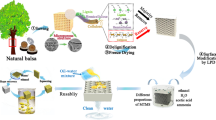
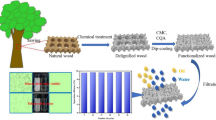
Abstract
Wood-derived materials have been utilized to develop filtration membranes for sustainable oil/water separation. However, it remains a significant challenge to manufacture durable wood-based membranes with high efficiency and ultra-high flux by simple methods. Herein, we report a facile strategy to fabricate a novel superhydrophobic hybrid wood membrane (PDMS@MOF-199/WS) with ultrahigh-flux and excellent oil/water separation performance. Firstly, copper-based metal organic frameworks (MOF-199) were in situ grown on the TEMPO-oxidized wood sponge (TO-WS) substrate to construct a hierarchical micro-nano structure with internal inherent microchannels. Secondly, a super-wetting surface was formed through soaking in polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) and heat treatment. Remarkably, the water contact angle (WCA) of PDMS@MOF-199/WS could reach 163° and the oil contact angle (OCA) was around 0°, which remained stable over a long period of ultrasonic treatment and tape peeling. More importantly, the as-prepared modified wood membrane can efficiently separate a wide range of immiscible oil/water mixtures, solely by tiny gravity, with ultra-high flux of 10,385 L m−2 h−1 (carbon tetrachloride/water) and separation efficiency of 99.6% (n-hexane). Furthermore, this novel membrane can also effectively separate surfactant-stabilized water-in-oil emulsions with an efficiency of as high as 97.8%. Meanwhile, the hybrid membrane displayed exceptional reusability, maintaining a high-flux of 8599.6 L m−2 h−1 and retaining WCA at 154.8° after 12 cycles. Our results demonstrate that the synergetic impact of MOF-199 and PDMS as a means of encoding on-surface wettability substantially improved the separation efficiency. This work opens a new avenue for the design of functional wood-derived filtration membranes for the ultrahigh flux oil–water separation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ávila-Ortega A, Avalos-Hernández JP, Trejo-Tzab R, Oliva AI, Juárez-Moreno JA (2021) Influence of deposited amine-functionalized Si-MCM-41 in polyacrylonitrile electrospun membranes applied for separation of water in oil emulsions. J Appl Polym Sci 138(30):50737. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.50737
Azama T, Pervaiz E, Javeda S, Amina SJ, Khalidc MS (2020) Tuning the hydrophobicity of MOF sponge for efficient oil/water separation. Chem Phys Impact 1:100001. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chphi.2020.100001
Barthwal S, Lim SH (2021) A durable, fluorine-free, and repairable superhydrophobic aluminum surface with hierarchical micro/nanostructures and its application for continuous oil-water separation. J Membr Sci 618:118716. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2020.118716
Barthwal S, Jeon YJ, Lim SH (2022) Superhydrophobic sponge decorated with hydrophobic MOF-5 nanocoating for efficient oil-water separation and antibacterial applications. Sustain Mater Technol 33:e00492. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.susmat.2022.e00492
Cai Y, Chen D, Li N, Xu Q, Li H, He J, Lu J (2020) A self-cleaning heterostructured membrane for efficient oil-in-water emulsion separation with stable flux. Adv Mater 32(25):2001265. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202001265
Chen C, Chen B (2019) Graphene oxide coated meshes with stable underwater superoleophobicity and anti-oil-fouling property for highly efficient oil/water separation. Sci Total Environ 696:133777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.133777
Chen C, Zhu X, Chen B (2019a) Durable superhydrophobic/superoleophilic graphene-based foam for high-efficiency oil spill cleanups and recovery. Environ Sci Technol 53(3):1509–1517. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b04642
Chen C, Weng D, Mahmood A, Chen S, Wang J (2019b) Separation mechanism and construction of surfaces with special wettability for oil/water separation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11(11):11006–11027. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b01293
Chen C-C, Wang ZL, Wang Y-R, Wan Z-M, Yang Q-L, Xu Z-Y, Li D-G, Jin Y-C (2022) Mechanically strong wood-based composite aerogels as oil adsorbents and sensors. Ind Crops Prod 187:115486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2022.115486
Cheng X, Ye Y, Li Z, Chen X, Bai Q, Wang K, Zhang Y, Drioli E, Ma J (2022) Constructing environmental-friendly “oil-diode” Janus membrane for oil/water separation. ACS Nano 16(3):4684–4692. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c11388
Cui Z, Wu J, Wu T, Xu Y, Li H, Yu Y, Tian D (2023) Novel wood membrane decorated with covalent organic frameworks and palladium nanoparticles for reduction of aromatic organic contaminants. Sep Purif Technol 319:124112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2023.124112
Deng Y-Y, Peng C-S, Dai M, Lin D-C, Ali I, Alhewairini SS, Zheng X-L, Chen G-Q, Li L-Y, Naz I (2020) Recent development of super-wettable materials and their applications in oil-water separation. J Clean Prod 266:121624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121624
Deng Y, Wu Y, Chen G, Zheng X, Dai M, Peng C (2021) Metal-organic framework membranes: Recent development in the synthesis strategies and their application in oil-water separation. Chem Eng J 405:127004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.127004
Du J, Zhang C, Pu H, Li Y, Jin S, Tan L, Zhou C, Dong L (2019) HKUST-1 MOFs decorated 3D copper foam with superhydrophobicity/superoleophilicity for durable oil/water separation. Colloid Surf A 573:222–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.04.064
Fang Y, Jing C, Li G, Ling S, Wang Z, Lu P, Chen W (2021) Wood-derived systems for sustainable oil/water separation. Adv Sustain Syst 5(7):2100039. https://doi.org/10.1002/adsu.202100039
Guan H, Cheng Z, Wang X (2018) Highly compressible wood sponges with a springlike lamellar structure as effective and reusable oil absorbents. ACS Nano 12(10):10365–10373. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.8b05763
Guo Y, Xie W, Li H, Li J, Hu J, Liu H (2022) Construction of hydrophobic channels on Cu (I)-MOF surface to improve selective adsorption desulfurization performance in presence of water. Sep Purif Technol 285:120287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.120287
Hao S-M, Qu J, Zhu Z-S, Zhang X-Y, Wang Q-Q, Yu Z-Z (2016) Hollow manganese silicate nanotubes with tunable secondary nanostructures as excellent fenton-type catalysts for dye decomposition at ambient temperature. Adv Funct Mater 26(40):7334–7342. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201603315
He K, Duan H, Chen G-Y, Liu X, Yang W, Wang D (2015) Cleaning of oil fouling with water enabled by zwitterionic polyelectrolyte coatings: overcoming the imperative challenge of oil–water separation membranes. ACS Nano 9(9):9188–9198. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.5b03791
He X-T, Li B-Y, Liu J-X, Tao W-Q, Li Z (2022) Facile fabrication of 2D MOF-Based membrane with hierarchical structures for ultrafast Oil-Water separation. Sep Purif Technol 297:121488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.121488
Hoang A, Nižetić S, Duong X, Rowinski L, Nguyen X (2021) Advanced super-hydrophobic polymer-based porous absorbents for the treatment of oil-polluted water. Chemosphere 277:130274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130274
Huang Z, Liu J, Liu Y, Xu Y, Li R, Hong H, Liao B (2021) Enhanced permeability and antifouling performance of polyether sulfone (PES) membrane via elevating magnetic Ni@MXene nanoparticles to upper layer in phase inversion process. J Membr Sci 623:119080. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2021.119080
Ivshina IB, Kuyukina MS, Krivoruchko AV, Elkin AA, Makarov SO, Cunningham CJ, Peshkur TA, Atlas RM, Philp JC (2015) Oil spill problems and sustainable response strategies through new technologies. Environ Sci Process Impacts 17(7):1201–1219. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5EM00070J
Jayaramulu K, Datta KKR, Rösler C, Petr M, Otyepka M, Zboril R, Fischer RA (2016) Biomimetic superhydrophobic/superoleophilic highly fluorinated graphene oxide and ZIF-8 composites for oil-water separation. Angew Chem Int Ed 55(3):1178–1182. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201507692
Li K, Wang S, Chen H, Yang X, Berglund LA, Zhou Q (2020) Self-densification of highly mesoporous wood structure into a strong and transparent film. Adv Mater 32(42):2003653. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202003653
Li H, Luo Y-D, Yu F-Y, Zhang H-M (2021a) In-situ construction of MOFs-based superhydrophobic/superoleophilic coating on filter paper with self-cleaning and antibacterial activity for efficient oil/water separation. Colloids Surf A 625:126976. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.126976
Li M, Liu H, Liu J, Pei Y, Zheng X, Tang K, Wang F (2021b) Hydrophobic and self-recoverable cellulose nanofibrils/N-alkylated chitosan/poly (vinyl alcohol) sponge for selective and versatile oil/water separation. Int J Biol Macromol 192:169–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.09.189
Li H, Luo Y, Yu F, Peng L (2022) Simple and scalable preparation of robust and magnetic superhydrophobic papers by one-step spray-coating for efficient oil-water separation. Colloids Surf A 640:128449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.128449
Li Y, Fan T, Cui W, Wang X, Ramakrishna S, Long Y (2023) Harsh environment-tolerant and robust PTFE@ ZIF-8 fibrous membrane for efficient photocatalytic organic pollutants degradation and oil/water separation. Sep Purif Technol 306:122586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.122586
Liu X, Liu Z, Wang X, Gao Y, Zhang J, Fan T, Long Y-Z (2022) Superhydrophobic nanofibrous sponge with hierarchically layered structure for efficient harsh environmental oil-water separation. J Hazard Mater 440:129790. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2022.129790
Ma W, Ding Y, Li Y, Gao S, Jiang Z, Cui J, Fu G (2021) Durable, self-healing superhydrophobic nanofibrous membrane with self-cleaning ability for highly-efficient oily wastewater purification. J Membr Sci 634:119402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2021.119402
Mahmoodi NM, Abdi J (2019) Nanoporous metal-organic framework (MOF-199): synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic degradation of Basic Blue 41. Microchem J 144:436–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2018.09.033
Mähringer A, Hennemann M, Clark T, Bein T, Medina DD (2021) Energy efficient ultrahigh flux separation of oily pollutants from water with superhydrophilic nanoscale metal-organic framework architectures. Angew Chem Int Ed 60(10):5519–5526. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202012428
Majhy B, Iqbal R, Sen AK (2018) Facile fabrication and mechanistic understanding of a transparent reversible superhydrophobic-superhydrophilic surface. Sci Rep 8(1):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-37016-5
Naghdi FG, Schenk PM (2016) Dissolved air flotation and centrifugation as methods for oil recovery from ruptured microalgal cells. Bioresour Technol 218:428–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.06.093
Nguyen JG, Cohen SM (2010) Moisture-resistant and superhydrophobic metal-organic frameworks obtained via postsynthetic modification. J Am Chem Soc 132(13):4560–4561. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja100900c
Owens D, Wendt R (1969) Estimation of the surface free energy of polymers. J Appl Polym Sci 13(8):1741–1747. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.1969.070130815
Qiao A, Huang R, Penkova A, Qi W, He Z, Su R (2022) Superhydrophobic, elastic and anisotropic cellulose nanofiber aerogels for highly effective oil/water separation. Sep Purif Technol 295:121266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2022.121266
Saththasivam J, Loganathan K, Sarp S (2016) An overview of oil–water separation using gas flotation systems. Chemosphere 144:671–680. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.08.087
Sayed K, Baloo L, Sharma NK (2021) Bioremediation of total petroleum hydrocarbons (TPH) by bioaugmentation and biostimulation in water with floating oil spill containment booms as bioreactor basin. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18(5):2226. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18052226
Shen T, Liu T, Mo H, Yuan Z, Cui F, Jin Y, Chen X (2020) Cu-based metal-organic framework HKUST-1 as effective catalyst for highly sensitive determination of ascorbic acid. RSC Adv 10(39):22881–22890. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ra01260b
Si Y, Dong Z, Jiang L (2018) Bioinspired designs of superhydrophobic and superhydrophilic materials. ACS Cent Sci 4(9):1102–1112. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscentsci.8b00504
Sun B, Kayal S, Chakraborty A (2014) Study of HKUST (copper benzene-1, 3, 5-tricarboxylate, Cu-BTC MOF)-1 metal organic frameworks for CH4 adsorption: an experimental Investigation with GCMC (grand canonical Monte-Carlo) simulation. Energy 76:419–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2014.08.033
Sun Y-X, Sun Q, Huang H-L, Aguila B, Niu Z, Perman J-A, Ma S-Q (2017) A molecular level superhydrophobic external surface to improve the stability of metal-organic frameworks. J Mater Chem A 5(35):18770–18776. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7TA05800D
Sutar RS, Latthe SS, Gharge NB, Gaikwad PP, Jundle AR, Ingole SS, Liu S (2023) Facile approach to fabricate a high-performance superhydrophobic PS/OTS modified SS mesh for oil-water separation. Colloids Surf A 657:130561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2022.130561
Tan Y-C, Zeng H-C (2017) Defect creation in HKUST-1 via molecular imprinting: attaining anionic framework property and mesoporosity for cation exchange applications. Adv Funct Mater 27(42):1703765. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201703765
Tao P, Shu L, Zhang J, Lee C, Ye Q, Guo H, Deng T (2018) Silicone oil-based solar-thermal fluids dispersed with PDMS-modified Fe3O4@ graphene hybrid nanoparticles. Prog Nat Sci Mater Int 28(5):554–562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnsc.2018.09.003
Todaro M, Buscarino G, Sciortino L, Alessi A, Messina F, Taddei M, Gelardi FM (2016) Decomposition process of carboxylate MOF HKUST-1 unveiled at the atomic scale level. J Phys Chem C 120(23):12879–12889. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b03237
Tu K, Puértolas B, Adobes-Vidal M, Wang Y, Sun J, Traber J, Keplinger T (2020) Green synthesis of hierarchical metal-organic framework/wood functional composites with superior mechanical properties. Adv Sci 7(7):1902897. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.201902897
Wang H, Li J, Yu X, Zhao X, Zeng X, Xu F, Tang X, Sun Y, Lin L (2021a) Facile fabrication of super-hydrophilic cellulose hydrogel-coated mesh using deep eutectic solvent for efficient gravity-driven oil/water separation. Cellulose 28:949–960. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03578-9
Wang S, Wang C, Zhou Q (2021b) Strong foam-like composites from highly mesoporous wood and metal-organic frameworks for efficient CO2 capture. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 13(25):29949–29959. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c06637
Wang P-L, Ma C, Yuan Q, Mai T, Ma GM (2022) Novel Ti3C2Tx MXene wrapped wood sponges for fast cleanup of crude oil spills by outstanding Joule heating and photothermal effect. J Colloid Interface Sci 606:971–982. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2021.08.092
Wu H, Simmons JM, Liu Y, Brown CM, Wang XS, Ma S, Zhou W (2010) Metal–organic frameworks with exceptionally high methane uptake: Where and how is methane stored? Chem A Eur J 16(17):5205–5214. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.200902719
Xue J, Zhu L, Zhu X, Li H, Ma C, Yu S, Xue Q (2021) Tetradecylamine-MXene functionalized melamine sponge for effective oil/water separation and selective oil adsorption. Sep Purif Technol 259:118106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2020.118106
Yang Y-Y, Guo Z-P, Huang W, Zhang S-Y, Huang J-J, Yang H-J, Zhou Y-S, Xu W-L, Gu S-J (2020) Fabrication of multifunctional textiles with durable antibacterial property and efficient oil-water separation via in situ growth of zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8) on cotton fabric. Appl Surf Sci 503:144079. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.144079
Zhan Y, He S, Hu J, Zhao S, Zeng G, Zhou M, Sengupta A (2020) Robust super-hydrophobic/super-oleophilic sandwich-like UIO-66-F4@ rGO composites for efficient and multitasking oil/water separation applications. J Hazard Mater 388:121752. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121752
Zhang Z, Sebe G, Rentsch D, Zimmermann T, Tingaut P (2014) Ultralightweight and flexible silylated nanocellulose sponges for the selective removal of oil from water. Chem Mater 26(8):2659–2668. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm5004164
Zhang H-Y, Yang C, Geng Q, Fan H-L, Wang B-J, Wu M-M, Tian Z (2019) Adsorption of hydrogen sulfide by amine-functionalized metal organic framework (MOF-199): an experimental and simulation study. Appl Surf Sci 497:143815. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.143815
Zhang L, Xie J, Luo X, Gong X, Zhu M (2023) Enhanced hydrophobicity of shell-ligand-exchanged ZIF-8/melamine foam for excellent oil-water separation. Chem Eng Sci 273:118663. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ces.2023.118663
Zhu M, Li Y, Chen G, Jiang F, Yang Z, Luo X, Hu L (2017) Tree-inspired design for high-efficiency water extraction. Adv Mater 29(44):1704107. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201704107
Funding
We gratefully acknowledge the financial support provided by the Yunnan Agricultural Joint Special General Project (202301BD070001-243), the Yunnan Province Natural Science Key Foundation (202201AS070152), the Key Laboratory of State Forestry and Grassland Administration on Highly Efficient Utilization of Forestry Biomass Resources in Southwest China (2022-KF04), the Scientific Research Fund Project of the Yunnan Provincial Department of Education (2023J0695), Distinguished Young Scholars in Yunnan Province (202001AV070008) and Special Project of “Top Young Talents” of Yunnan Ten Thousand Talents Plan (51900109).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XZ: Conceptualization, Investigation, Supervision, Writing-original draft. KL: Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing-review & editing. LG: Data curation, Methodology, Validation. XL: Investigation, Formal analysis, Validation. ZX: Software, Methodology. SD: Visualization, Methodology, Investigation. GZ: Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Writing-review & editing, Project administration.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file2 (MP4 4002 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, X., Li, K., Guo, L. et al. Construction of superhydrophobic PDMS@MOF-199/wood sponge hybrid membrane for ultrahigh-flux gravitational oil/water separation. Wood Sci Technol 57, 1421–1442 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-023-01502-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00226-023-01502-5