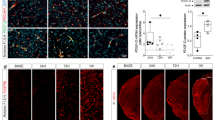
Abstract
Ischemic stroke followed by cerebral artery occlusion is a main cause of chronic disability worldwide. Recombinant human brain natriuretic peptide (rhBNP) has been reported to alleviate sepsis-induced cognitive dysfunction and brain I/R injury. However, the function and molecular mechanisms of rhBNP in ischemic brain injury have not been clarified. For establishment of an animal model of ischemic brain injury, C57BL/6 mice were treated with middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) surgery for 1 h and reperfusion for 24 h. After subcutaneous injection of rhBNP into model mice, neurologic deficits were assessed by evaluating behavior of mice according to Longa scoring system, and TTC staining was utilized to determine the brain infarct size of mice. The levels of oxidative stress markers, superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), glutathione (GSH) and malondialdehyde (MDA), were detected in hippocampal tissues of mice by corresponding kits. Cell apoptosis in hippocampus tissues was examined by TUNEL staining. Protein levels of antioxidant enzymes (HO-1 and NQO1) in cerebral cortex, apoptotic markers (Bax, Bcl-2, and cleaved caspase), and PI3K/AKT pathway-associated factors in hippocampus were tested by western blot analysis. The results revealed that injection of rhBNP decreased neurologic deficit scores, the percent of brain water content, and infarct volume. Additionally, rhBNP downregulated MDA level, upregulated the levels of SOD, CAT, and GSH in hippocampus of mice, and increased protein levels of HO-1 and NQO1 in the cortex. Cell apoptosis in hippocampus tissues of model mice was inhibited by rhBNP which was shown as the reduced TUNEL-positive cells, the decreased Bax, cleaved caspase-3, and cleaved caspase-9 protein levels, and the enhanced Bcl-2 protein level. In addition, rhBNP treatment activated the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and upregulated the protein levels of HO-1 and NRF2. Overall, rhBNP activates the PI3K/AKT/HO-1/NRF2 pathway to attenuate ischemic brain injury in mice after MCAO by suppression of cell apoptosis and oxidative stress.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included either in this article or in the supplementary information files.
References
Andrabi SS et al (2019) Pramipexole prevents ischemic cell death via mitochondrial pathways in ischemic stroke. Dis Model Mech 12(8):dmm033860
Avrutsky MI, Troy CM (2021) Caspase-9: a multimodal therapeutic target with diverse cellular expression in human disease. Front Pharmacol 12:701301
Cantley LC (2002) The phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway. Science 296(5573):1655–1657
Carpenter EL, Becker AL, Indra AK (2022) NRF2 and key transcriptional targets in melanoma redox manipulation. Cancers (basel) 14(6):1531
Chamorro Á et al (2012) The immunology of acute stroke. Nat Rev Neurol 8(7):401–410
Chan PH (2001) Reactive oxygen radicals in signaling and damage in the ischemic brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 21(1):2–14
Chen BH et al (2017) Pretreated quercetin protects gerbil hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons from transient cerebral ischemic injury by increasing the expression of antioxidant enzymes. Neural Regen Res 12(2):220–227
Chen X et al (2020) β-Arrestin-2 attenuates hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury by activating PI3K/Akt signaling. Aging (albany NY) 13(2):2251–2263
Chien MY et al (2016) Salvianolic acid A alleviates ischemic brain injury through the inhibition of inflammation and apoptosis and the promotion of neurogenesis in mice. Free Radic Biol Med 99:508–519
Cui HY et al (2018) Rosmarinic acid elicits neuroprotection in ischemic stroke via Nrf2 and heme oxygenase 1 signaling. Neural Regen Res 13(12):2119–2128
Forman HJ, Zhang H, Rinna A (2009) Glutathione: overview of its protective roles, measurement, and biosynthesis. Mol Aspects Med 30(1–2):1–12
Hausenloy DJ, Yellon DM (2006) Survival kinases in ischemic preconditioning and postconditioning. Cardiovasc Res 70(2):240–253
Hou JB et al (2021) Ubiquitin-specific protease 29 exacerbates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2021:6955628
Hu G et al (2014) Anti-inflammatory effect of B-type natriuretic peptide postconditioning during myocardial ischemia-reperfusion: involvement of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Inflammation 37(5):1669–1674
Iadecola C, Anrather J (2011) The immunology of stroke: from mechanisms to translation. Nat Med 17(7):796–808
Ikonomidou C, Kaindl AM (2011) Neuronal death and oxidative stress in the developing brain. Antioxid Redox Signal 14(8):1535–1550
Jiang M et al (2020) The caspase-3/GSDME signal pathway as a switch between apoptosis and pyroptosis in cancer. Cell Death Discov 6:112
Lee GA et al (2017) Interleukin 15 activates Akt to protect astrocytes from oxygen glucose deprivation-induced cell death. Cytokine 92:68–74
Lehr HA et al (1991) Leukotrienes as mediators in ischemia-reperfusion injury in a microcirculation model in the hamster. J Clin Invest 87(6):2036–2041
Leigh R et al (2018) Imaging the physiological evolution of the ischemic penumbra in acute ischemic stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 38(9):1500–1516
Li N et al (2014) Protective effect of recombinant human brain natriuretic peptide on acute renal injury induced by endotoxin in canines. Cell Biochem Biophys 70(2):1317–1324
Li L et al (2015) Overexpression of heme oxygenase 1 impairs cognitive ability and changes the plasticity of the synapse. J Alzheimers Dis 47(3):595–608
Li J et al (2018) Dexmedetomidine attenuates lung apoptosis induced by renal ischemia-reperfusion injury through α(2)AR/PI3K/Akt pathway. J Transl Med 16(1):78
Li KP et al (2020a) Recombinant human brain natriuretic peptide attenuates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting CD4(+) T cell proliferation via PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway activation. Cardiovasc Ther 2020:1389312
Li N et al (2020b) Therapeutic effects of recombinant human brain natriuretic peptide on sepsis-associated encephalopathy in mice. Int Immunopharmacol 81:106280
Liu Q et al (2018) Hydromorphine postconditioning protects isolated rat heart against ischemia-reperfusion injury via activating P13K/Akt/eNOS signaling. Cardiovasc Ther 36(6):e12481
Liu B et al (2020) Nobiletin alleviates ischemia/reperfusion injury in the kidney by activating PI3K/AKT pathway. Mol Med Rep 22(6):4655–4662
Longa EZ et al (1989) Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke 20(1):84–91
Lu D et al (2019) HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors attenuate neuronal damage by suppressing oxygen glucose deprivation-induced activated microglial cells. Neural Plast 2019:7675496
Mueller C et al (2004) Use of B-type natriuretic peptide in the evaluation and management of acute dyspnea. N Engl J Med 350(7):647–654
Niizuma K et al (2010) Mitochondrial and apoptotic neuronal death signaling pathways in cerebral ischemia. Biochim Biophys Acta 1802(1):92–99
Pandian JD et al (2018) Prevention of stroke: a global perspective. Lancet 392(10154):1269–1278
Ren B et al (2010) B-type natriuretic peptide pretreatment attenuates heart ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Transplant Proc 42(10):4496–4498
Roy MJ et al (2014) Cell death and the mitochondria: therapeutic targeting of the BCL-2 family-driven pathway. Br J Pharmacol 171(8):1973–1987
Schettler V et al (1999) Review: the oxidant/antioxidant balance during regular low density lipoprotein apheresis. Ther Apher 3(3):219–226
Shan SM, Pei L, Wang JK (2006) Effects of recombinant human morphogenetic protein-2 on pulmonary artery pressure in acute lung injury caused by endotoxin and mechanism thereof: experiment with rats. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 86(45):3201–3206
Silva F et al (2022) Caspase 3 and cleaved caspase 3 expression in tumorogenesis and its correlations with prognosis in head and neck cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Mol Sci 23(19):11937
Song Z et al (2013) Protective effects of recombinant human brain natriuretic peptide against LPS-Induced acute lung injury in dogs. Int Immunopharmacol 17(3):508–512
Song Z et al (2015) Recombinant human brain natriuretic peptide attenuates trauma-/haemorrhagic shock-induced acute lung injury through inhibiting oxidative stress and the NF-κB-dependent inflammatory/MMP-9 pathway. Int J Exp Pathol 96(6):406–413
Thompson BJ, Ronaldson PT (2014) Drug delivery to the ischemic brain. Adv Pharmacol 71:165–202
Van Opdenbosch N, Lamkanfi M (2019) Caspases in cell death, inflammation, and disease. Immunity 50(6):1352–1364
Wang J et al (2019) Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of chalcone analogues with novel dual antioxidant mechanisms as potential anti-ischemic stroke agents. Acta Pharm Sin B 9(2):335–350
Wu B et al (2009) Pretreatment with B-type natriuretic peptide protects the heart from ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting myocardial apoptosis. Tohoku J Exp Med 219(2):107–114
Wu S et al (2019) Stroke in China: advances and challenges in epidemiology, prevention, and management. Lancet Neurol 18(4):394–405
Xiao J et al (2020) Dexamethasone on alleviating lung ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats by regulating PI3K/AKT pathway. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue 32(2):188–193
Yang C et al (2009) Curcumin upregulates transcription factor Nrf2, HO-1 expression and protects rat brains against focal ischemia. Brain Res 1282:133–141
Yang H et al (2014) Protective effect of rhBNP on intestinal injury in the canine models of sepsis. Int Immunopharmacol 19(2):262–266
Yang J et al (2018) Berberine ameliorates MCAO induced cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via activation of the BDNF-TrkB-PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Neurochem Res 43(3):702–710
Zhang Z et al (2004) Bcl-2 homodimerization involves two distinct binding surfaces, a topographic arrangement that provides an effective mechanism for Bcl-2 to capture activated Bax. J Biol Chem 279(42):43920–43928
Zhang C et al (2018) Recombinant human brain natriuretic peptide regulates PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway through lncRNA EGOT to attenuate hypoxia-induced injury in H9c2 cardiomyocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 503(3):1186–1193
Zhang M et al (2020) MiR-506 alleviates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury via targeting PI3K/AKT. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 24(24):12896–12903
Zhao YR et al (2016) The PI3K/Akt, p38MAPK, and JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathways mediate the protection of SO2 against acute lung injury induced by limb ischemia/reperfusion in rats. J Physiol Sci 66(3):229–239
Acknowledgements
The authors appreciate all the participants providing supports for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TL and DJS were the main designers of this study. TL, DJS, HWL, YQG, YGL, SHW, YTH, KMQ, XTQ and YD performed the experiments and analyzed the data. TL, DJS, XPC, BLQ, ZJW and YD drafted the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All the experiments associated with animals were in line the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and had been approved by the Ethics Committee of Nanning Second People’s Hospital.
Additional information
Communicated by Sreedharan Sajikumar.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, T., Su, D., Lu, H. et al. Recombinant human brain natriuretic peptide attenuates ischemic brain injury in mice by inhibiting oxidative stress and cell apoptosis via activation of PI3K/AKT/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Exp Brain Res 241, 2751–2763 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-023-06716-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-023-06716-4