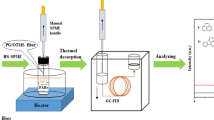
Abstract
Metal–organic framework-derived carbon materials have shown extensive application in the sensitive extraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), but more active sites for its adsorption were still a tireless pursuit. In this study, ZIF-nanoleaf-derived carbon (NLCs) was synthesized and developed as a solid-phase microextraction (SPME) fiber (NLCs-F). The extraction performance was compared with ZIF-dodecahedron-derived carbon (DHCs) coated fiber (DHCs-F), which was prepared by only changing the ratio of the reactants. The unique morphology of NLCs provided abundant adsorption active sites for the selected PAHs, while the large average aperture facilitated selective extraction of high molecular weight analytes. Additionally, the high carbon content enhanced the strong enrichment capability for hydrophobic PAHs. Hence, the prepared NLCs-F coupled with GC–MS showed a good correlation coefficient (0.9975) in a wide linear range, low limits of detection (0.3–1.8 ng L−1), satisfactory repeatability, and reproducibility, which made it apply in the enrichment of PAHs in actual tea and coffee samples.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ncube S, Madikizela L, Cukrowska E, Chimuka L. Recent advances in the adsorbents for isolation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) from environmental sample solutions. TrAC, Trends Anal Chem. 2018;99:101–16.
Wei S, Lin W, Xu J, Wang Y, Liu S, Zhu F, Liu Y, Ouyang G. Fabrication of a polymeric composite incorporating metal-organic framework nanosheets for solid-phase microextraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from water samples. Anal Chim Acta. 2017;971:48–54.
Tang S, Zhang H, Lee HK. Advances in sample extraction. Anal Chem. 2016;88(1):228–49.
Fazli Z, Nakhodchi S, Alizadeh N. Electrochemically controlled solid-phase microextraction based on conductive molecularly imprinted polymer combined with ion mobility spectrometry for separation and determination of thiopental. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2022;414(29–30):8413–21.
Hu H, Liu S, Chen C, Wang J, Zou Y, Lin L, Yao S. Two novel zeolitic imidazolate frameworks (ZIFs) as sorbents for solid-phase extraction (SPE) of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in environmental water samples. Analyst. 2014;139(22):5818–26.
Liu M, Liu J, Guo C, Li Y. Metal azolate framework-66-coated fiber for headspace solid-phase microextraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. J Chromatogr A. 2019;1584:57–63.
Wu T, Wang J, Liang W, Zang X, Wang C, Wu Q, Wang Z. Single layer graphitic carbon nitride-modified graphene composite as a fiber coating for solid-phase microextraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Microchim Acta. 2017;184(7):2171–80.
Hu X, Liu C, Li J, Luo R, Jiang H, Sun X, Shen J, Han W, Wang L. Hollow mesoporous carbon spheres-based fiber coating for solid-phase microextraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. J Chromatogr A. 2017;1520:58–64.
Spietelun A, Kloskowski A, Chrzanowski W, Namiesnik J. Understanding solid-phase microextraction: key factors influencing the extraction process and trends in improving the technique. Chem Rev. 2013;113(3):1667–85.
Zheng J, Huang J, Yang Q, Ni C, Xie X, Shi Y, Sun J, Zhu F, Ouyang G. Fabrications of novel solid phase microextraction fiber coatings based on new materials for high enrichment capability. TrAC, Trends Anal Chem. 2018;108:135–53.
Lashgari M, Yamini Y. An overview of the most common lab-made coating materials in solid phase microextraction. Talanta. 2019;191:283–306.
Hu Y, Li Y, Shi Y, Kuang Y, Zhou S, Peng Y, Liu Y, Chen L, Zhou N, Zheng J, Zhu F, Ouyang G. A robust and ultra-high-surface hydrogen-bonded organic framework promoting high-efficiency solid phase microextraction of multiple persistent organic pollutants from beverage and tea. Food Chem. 2023;415: 135790.
Wang C, Kim J, Malgras V, Na J, Lin J, You J, Zhang M, Li J, Yamauchi Y. Metal-organic frameworks and their derived materials: emerging catalysts for a sulfate radicals-based advanced oxidation process in water purification. Small. 2019;15(16): e1900744.
Yang W, Li X, Li Y, Zhu R, Pang H. Applications of metal-organic-framework-derived carbon materials. Adv Mater. 2019;31(6): e1804740.
Zhao Z, Zhang M, Ruan J, Wang L, Wang J, Zhang W, Qiao W. An ideal confined catalytic model via MOFs derived yolk-shell nanoreactors: the formation mechanism and catalytic performance for single-core and multi-core. Appl Surf Sci. 2023;623:156958.
Hao L, Wang C, Wu Q, Li Z, Zang X, Wang Z. Metal-organic framework derived magnetic nanoporous carbon: novel adsorbent for magnetic solid-phase extraction. Anal Chem. 2014;86(24):12199–205.
Zhang S, Yang Q, Li Z, Wang W, Wang C, Wang Z. Zeolitic imidazole framework templated synthesis of nanoporous carbon as a novel fiber coating for solid-phase microextraction. Analyst. 2016;141(3):1127–35.
Zhang S, Yang Q, Yang X, Wang W, Li Z, Zhang L, Wang C, Wang Z. A zeolitic imidazolate framework based nanoporous carbon as a novel fiber coating for solid-phase microextraction of pyrethroid pesticides. Talanta. 2017;166:46–53.
Wei F, He Y, Qu X, Xu Z, Zheng S, Zhu D, Fu H. In situ fabricated porous carbon coating derived from metal-organic frameworks for highly selective solid-phase microextraction. Anal Chim Acta. 2019;1078:70–7.
Hu Q, Liu S, Chen X, Xu J, Zhu F, Ouyang G. Enhancing enrichment ability of a nanoporous carbon based solid-phase microextraction device by a morphological modulation strategy. Anal Chim Acta. 2019;1047:1–8.
Zhang M, Wang C, Yan X, Kwame KP, Chen S, Xiao C, Qi J, Sun X, Wang L, Li J. Metal organic framework-derived hollow cactus-like carbon sheets for oxygen reduction. Journal of Materials Chemistry A. 2019;7(35):20162–8.
Kaneti YV, Dutta S, Hossain MSA, Shiddiky MJA, Tung KL, Shieh FK, Tsung CK, Wu KC, Yamauchi Y. Strategies for improving the functionality of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks: tailoring nanoarchitectures for functional applications. Adv Mater. 2017;29(38):1700213.
Ruan J, Dou T, Zhang M, Shao W, Chen Z, Guo H, Wang J, Wei W, Qiao W. Tailored design of 2D MOF derived carbon boosting the low temperature plasma catalysis for water treatment: The role of graphitization and hierarchical porous structure. Chem Eng J. 2023;470:144316.
Kong L, Zhu J, Shuang W, Bu X-H. Nitrogen-doped wrinkled carbon foils derived from MOF nanosheets for superior sodium storage. Adv Energy Mater. 2018;8(25):1801515.
Li J, Xia W, Tang J, Tan H, Wang J, Kaneti YV, Bando Y, Wang T, He J, Yamauchi Y. MOF nanoleaves as new sacrificial templates for the fabrication of nanoporous Co–Nx/C electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction. Nanoscale Horizons. 2019;4(4):1006–13.
Wang C, Liu C, Li J, Sun X, Shen J, Han W, Wang L. Electrospun metal-organic framework derived hierarchical carbon nanofibers with high performance for supercapacitors. Chem Commun. 2017;53(10):1751–4.
Wang L, Feng X, Ren L, Piao Q, Zhong J, Wang Y, Li H, Chen Y, Wang B. Flexible solid-state supercapacitor based on a metal-organic framework interwoven by electrochemically-deposited PANI. J Am Chem Soc. 2015;137(15):4920–3.
Liu S, Zheng L, Yu P, Han S, Fang X. Novel composites of α-Fe2O3 tetrakaidecahedron and graphene oxide as an effective photoelectrode with enhanced photocurrent performances. Adv Func Mater. 2016;26(19):3331–9.
Wang D, Li X, Zheng LL, Qin LM, Li S, Ye P, Li Y, Zou JP. Size-controlled synthesis of CdS nanoparticles confined on covalent triazine-based frameworks for durable photocatalytic hydrogen evolution under visible light. Nanoscale. 2018;10(41):19509–16.
Dong H, Guo X, Yang C, Ouyang Z. Synthesis of g-C3N4 by different precursors under burning explosion effect and its photocatalytic degradation for tylosin. Appl Catal B. 2018;230:65–76.
Kuang Y, Xie X, Zhou S, Chen L, Zheng J, Ouyang G. Customized oxygen-rich biochar with ultrahigh microporosity for ideal solid phase microextraction of substituted benzenes. Sci Total Environ. 2023;870: 161840.
Fu H, Zhu D. In situ hydrothermal grown silicalite-1 coating for solid-phase microextraction. Anal Chem. 2012;84(5):2366–72.
Gu Z-Y, Yang C-X, Chang N, Yan X-P. Metal-Organic frameworks for analytical chemistry: from sample collection to chromatographic separation. Acc Chem Res. 2012;45(5):734–45.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge support from Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Chemical Pollution Control and Resources Reuse, Nanjing University of Science and Technology.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51878352).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Chaohai Wang and Jiansheng Li contributed equally to this study and share corresponding author.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, X., Pang, L., Wu, M. et al. Nanoleaf-derived carbon materials as a sensitivity coating for solid‑phase microextraction of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Anal Bioanal Chem 416, 277–285 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-023-05016-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-023-05016-8