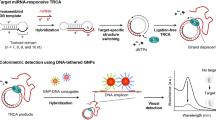
Abstract
MicroRNA (miRNA) sensing strategies employing rolling circle amplification (RCA) coupled with the hairpin DNA (HD) probe–mediated FRET assay have shown promise, but achieving rapid, sensitive, and specific detection of target miRNA remains a challenge in clinical diagnostics. Herein, we incorporate PstI endonuclease cleavage (PEC) into a conventional RCA-based HD probe FRET assay to develop an effective and feasible method. Long single-stranded RCA products are synthesized from miRNA-21 loaded on a circular dumbbell DNA, and the resultant RCA products self-assemble to generate long HD structures with double-stranded stem regions that are specifically recognized and cleaved by PstI endonucleases when incubated with PstI enzymes. This releases large amounts of short single-stranded DNA fragments that hybridize and open to the complementary loop-stem regions of HD probes labeled with FAM at one end and BHQ-1 at the other, resulting in a reduction in FRET efficiency. This assay achieves a 39.7 aM detection limit for target miRNA-21, approximately 37-fold higher than that of the conventional assay (1.5 fM). Moreover, quantitative detection is possible in a wide range from 1 aM to 1 pM within 90 min with high sequence specificity. We demonstrate the assay with the detection of target miRNA-21 in total RNA extracted from MCF-7 cancer cells.
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ozdogan S, Yaltirik CK, Yilmaz SG, Akdeniz FT, Sumerkent K, Ali HD, Ture U, Isbir T. Investigation of the effects of MicroRNA-221 expression levels in glioblastoma multiforme tumors. Anticancer Res. 2020;40:3265–70.
Martin HC, Wani S, Steptoe AL, Krishnan K, Nones K, Nourbaksh E, Vlassov A, Grimmond SM, Cloonan N. Imperfect centered miRNA binding sites are common and can mediate repression of target mRNAs. Genome Biol. 2014;15:R51.
O’Brien J, Hayder H, Zayed Y, Peng C. Overview of MicroRNA biogenesis, mechanisms of actions, and circulation. Front Endocrinol. 2018;9:402.
Kakumani PK, Ponia SS, Rajgokul KS, Sood V, Chinnappan M, Banerjea AC, Medigeshi GR, Malhotra P, Mukherjee SK, Bhatnagar RK. Role of RNA interference (RNAi) in dengue virus replication and identification of NS4B as an RNAi suppressor. J Virol. 2013;87:8870–83.
Peng Y, Croce CM. The role of microRNAs in human cancer. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2016;1:15004.
Otmani K, Lewalle P. Tumor suppressor miRNA in cancer cells and the tumor microenvironment: mechanism of deregulation and clinical implications. Front Oncol. 2021;11:708765.
Zhao Q, Chen S, Zhu Z, Yu L, Ren Y, Jiang M, Weng J, Li B. miR-21 promotes EGF-induced pancreatic cancer cell proliferation by targeting Spry2. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9:1157.
Liu T, Liu D, Guan S, Dong M. Diagnostic role of circulating miR-21 in colorectal cancer: a update meta-analysis. Ann Med. 2021;53:87–102.
Jang JY, Kim YS, Kang KN, Kim KH, Park YJ, Kim CW. Multiple microRNAs as biomarkers for early breast cancer diagnosis. Mol Clin Oncol. 2020;14:31.
Wu Y, Li Q, Zhang R, Dai X, Chen W, Xing D. Circulating microRNAs: biomarkers of disease. Clin Chim Acta. 2021;516:46–54.
Rana S, Valbuena GN, Curry E, Bevan CL, Keun HC. MicroRNA as biomarkers for prostate cancer prognosis: a systematic review and a systematic reanalysis of public data. Br J Cancer. 2022;126:502–13.
Porzycki P, Ciszkowicz E, Semik M, Tyrka M. Combination of three miRNA (miR-141, miR-21, and miR-375) as potential diagnostic tool for prostate cancer recognition. Int Urol Nephrol. 2018;50:1619–26.
Lu H, Yang F, Liu B, Zhang K, Cao Y, Dai W, Li W, Dong H. Intracellular low-abundance microRNA imaging by a NIR-assisted entropy-driven DNA system. Nanoscale Horiz. 2018;4:472–9.
Jacroux T, Rieck DC, Cui R, Ouyang Y, Dong WJ. Enzymatic amplification of DNA/RNA hybrid molecular beacon signaling in nucleic acid detection. Anal Biochem. 2013;432:106–14.
Balcells I, Cirera S, Busk PK. Specific and sensitive quantitative RT-PCR of miRNAs with DNA primers. BMC Biotechnol. 2011;11:70.
Asa TA, Kumara GSR, Seo YJ. Highly sensitive, selective, and rapid detection of miRNA-21 using an RCA/G-quadruplex/QnDESA probing system. Anal Methods. 2022;14:97–100.
Zhang K, Zhang H, Cao H, Jiang Y, Mao K, Yang Z. Rolling circle amplification as an efficient analytical tool for rapid detection of contaminants in aqueous environments. Biosensors-Basel. 2021;11:352.
James AM, Baker MB, Bao G, Searles CD. MicroRNA detection using a double molecular beacon approach: distinguishing between miRNA and pre-miRNA. Theranostics. 2017;7:634–46.
Petralia S, Conoci S. PCR technologies for point of care testing: progress and perspectives. ACS Sens. 2017;2:876–91.
Deng S, Hoog GS, Pan W, Chen M, van den Ende AHG, Yang L, Sun J, Najafzadeh MJ, Liao W, Li R. Three isothermal amplification techniques for rapid identification of cladophialophora carrionii, an agent of human chromoblastomycosis. J Clin Microbiol. 2014;52:3531–5.
Wang X, Yu X, Wang X, Suzuki M, Asanuma H, Dong P, Wu W, Liang X. Highly specific DNA detection from massive background nucleic acids based on rolling circle amplification of target dsDNA. RSC Adv. 2014;4:38293–9.
Gao Z, Wu C, Lv S, Wang C, Zhang N, Xiao S, Han Y, Xu H, Zhang Y, Li F, Lyu J, Shen Z. Nicking-enhanced rolling circle amplification for sensitive fluorescent detection of cancer-related microRNAs. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2018;410:6819–26.
Hong CA, Jang B, Jeong EH, Jeong H, Lee H. Self-assembled DNA nanostructures prepared by rolling circle amplification for the delivery of siRNA conjugates. Chem Commun. 2014;50:13049–51.
Yao C, Zhang R, Tang J, Yang D. Rolling circle amplification (RCA)-based DNA hydrogel. Nature. 2021;16:5460–83.
Zhang B, Li S, Guan Y, Yuan Y. Accurate detection of target microRNA in mixed species of high sequence homology using target-protection rolling circle amplification. ACS Omega. 2021;6:1516–22.
Fang C, Ouyang P, Yang Y, Qing Y, Han J, Shang W, Chen Y, Du J. MiRNA detection using a rolling circle amplification and RNA-cutting allosteric deoxyribozyme dual signal amplification strategy. Biosensors-Basel. 2021;11:222.
Liu Y, Li S, Zhang L, Zhao Q, Li N, Wu Y. Catalytic hairpin assembly-assisted rolling circle amplification for high-sensitive telomerase activity detection. ACS Omega. 2020;5:11836–41.
Xu H, Zhang Y, Zhang S, Sun M, Li W, Jiang Y, Wu ZS. Ultrasensitive assay based on a combined cascade amplification by nicking-mediated rolling circle amplification and symmetric strand-displacement amplification. Anal Chim Acta. 2018;1047:172–8.
Lee H, Kim DM, Kim DE. Label-free fluorometric detection of influenza viral RNA by strand displacement coupled with rolling circle amplification. Analyst. 2020;145:8002–7.
Xiao F, Liu J, Guo Q, Du Z, Li H, Sun C, Du W. Dual-signal amplification strategy sensitive microRNA detection based on rolling circle amplification and enzymatic repairing amplification. ACS Omega. 2020;5:32738–43.
Cui L, Zhu Z, Lin N, Zhang H, Guan Z, Yang CJ. A T7 exonuclease-assisted cyclic enzymatic amplification method coupled with rolling circle amplification: a dual-amplification strategy for sensitive and selective microRNA detection. Chem Commun. 2014;50:1576–8.
Zhu J, Kempenaers W, Straeten D, Contreras R, Fiers W. A method for fast and pure DNA elution from agarose gels by centrifugal filtration. Nature. 1985;3:1014–6.
Funding
This work was supported by a Yeungnam University Research Grant (219A580020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yun Jin Lee and Ji Yun Jeong: conceptualization; methodology; investigation; validation; and writing—original draft preparation. Ji Yoon Do: methodology, validation, and resources. Cheol Am Hong: supervision; project administration; conceptualization; methodology; funding acquisition; and writing—reviewing and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, Y.J., Jeong, J.Y., Do, J.Y. et al. Rapid and ultrasensitive miRNA detection by combining endonuclease reactions in a rolling circle amplification (RCA)–based hairpin DNA fluorescent assay. Anal Bioanal Chem 415, 1991–1999 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-023-04618-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-023-04618-6