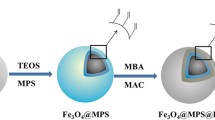
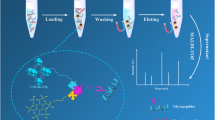
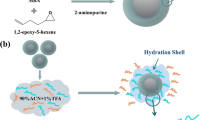
Abstract
Protein glycosylation of human serum exosomes can reveal significant physiological information, and the development of large-scale identification strategies is crucial for the in-depth investigation of the serum exosome glycoproteome. In this study, using surface functionalization techniques, an ultra-hydrophilic mesoporous silica magnetic nanosphere (denoted as Fe3O4-CG@mSiO2) was synthesized for the quick and accurate detection of glycopeptides from HRP digests. The Fe3O4-CG@mSiO2 nanospheres demonstrated outstanding enrichment capability, high sensitivity (5 amol/μL), good size exclusion effect (HRP digests/BSA proteins, 1:10,000), stable reusability (at least 10 times), and an excellent recovery rate (108.6 ± 5.5%). Additionally, after enrichment by Fe3O4-CG@mSiO2, 156 glycopeptides assigned to 64 proteins derived from human serum exosomes were successfully identified, which demonstrates that the nanospheres have great potential for the research of the large-scale serum exosome glycoproteome.
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kalluri R, LeBleu VS. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science. 2020;367(6478):eaau6977. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aau6977
Chen IH, Xue L, Hsu CC, Paez JS, Pan L, Andaluz H, Wendt MK, Iliuk AB, Zhu JK, Tao WA. Phosphoproteins in extracellular vesicles as candidate markers for breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2017;114(12):3175–80. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1618088114
Zhao YM, Jensen ON. Modification-specific proteomics: strategies for characterization of post-translational modifications using enrichment techniques. Proteomics. 2009;9(20):4632–41. https://doi.org/10.1002/pmic.200900398
Smith LM, Kelleher NL. Proteoforms as the next proteomics currency. Science. 2018;359(6380):1106–7. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aat1884
Qing GY, Yan JY, He XN, Li XL, Liang XM. Recent advances in hydrophilic interaction liquid interaction chromatography materials for glycopeptide enrichment and glycan separation. Trac-trends Anal Chem. 2020;124:115570–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2019.06.020
Chen CC, Su WC, Huang BY, Chen YJ, Tai HC, Obena RP. Interaction modes and approaches to glycopeptide and glycoprotein enrichment. Analyst. 2014;139(4):688–704. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3an01813j
Chen YJ, Xiong ZC, Zhang LY, Zhao JY, Zhang QQ, Peng L, Zhang WB, Ye ML, Zou HF. Facile synthesis of zwitterionic polymer-coated core-shell magnetic nanoparticles for highly specific capture of N-linked glycopeptides. Nanoscale. 2015;7(7):3100–8. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4nr05955g
Zhang YY, Fonslow BR, Shan B, Baek MC, Yates JR. Protein analysis by shotgun/bottom-up proteomics. Chem Rev. 2013;113(4):2343–94. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr3003533
Gao CH, Bai J, He YT, Zheng Q, Ma WD, Lei ZX, Zhang MY, Wu J, Fu FF, Lin Z. Postsynthetic functionalization of Zr4+-immobilized core-shell structured magnetic covalent organic frameworks for selective enrichment of phosphopeptides. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(14):13735–41. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b03330
Novotny MV, Alley WR. Recent trends in analytical and structural glycobiology. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2013;17(5):832–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2013.05.029
Wang YL, Liu MB, Xie LQ, Fang CY, Xiong HM, Lu HJ. Highly efficient enrichment method for glycopeptide analyses: using specific and nonspecific nanoparticles synergistically. Anal Chem. 2014;86(4):2057–64. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac403236q
Yao JZ, Wang JW, Sun NR, Deng CH. One-step functionalization of magnetic nanoparticles with 4-mercaptophenylboronic acid for a highly efficient analysis of N-glycopeptides. Nanoscale. 2017;9(41):16024–9. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7nr04206j
Su P, Wang Z, Li X, Li M, Li G, Gong Z, Song JY, Yang Y. Fabrication of magnetic dual-hydrophilic metal organic framework for highly efficient glycopeptide enrichment. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2021;413(21):5267–78. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-021-03535-w
Hua SW, Feng QS, Xie ZH, Mao HJ, Zhou YP, Yan YH, Ding CF. Post-synthesis of covalent organic frameworks with dual-hydrophilic groups for specific capture of serum exosomes. J Chromatogr A. 2022;1679:463406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2022.463406
Saleem S, Sajid MS, Hussain D, Jabeen F, Najam-ul-Haq M, Saeed A. Boronic acid functionalized MOFs as HILIC material for N-linked glycopeptide enrichment. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2020;412(7):1509–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-020-02427-9
Li YL, Deng CH, Sun NR. Hydrophilic probe in mesoporous pore for selective enrichment of endogenous glycopeptides in biological samples. Anal Chim Acta. 2018;1024:84–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2018.04.030
Sun NR, Wu H, Chen HM, Shen XZ, Deng CH. Advances in hydrophilic nanomaterials for glycoproteomics. Chem Commun. 2019;55(70):10359–75. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9cc04124a
Feng XY, Deng CH, Gao MX, Zhang XM. Facile and easily popularized synthesis of l-cysteine-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles based on one-step functionalization for highly efficient enrichment of glycopeptides. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2020;410(3):989–98. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-017-0602-5
Yeh CH, Chen SH, Li DT, Lin HP, Huang HJ, Chang CI, Shih WL, Chern CL, Shi FK, Hsu JL. Magnetic bead-based hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography for glycopeptide enrichments. J Chromatogr A. 2012;1224:70–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2011.12.057
Zhang Y, Jing HY, Meng B, Qian XH, Ying WT. L-cysteine functionalized straticulate C3N4 for the selective enrichment of glycopeptides. J Chromatogr A. 2020;1610:460545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2019.460545
Wu WR, Tang RZ, Pan L, Wang CY, Zhang JJ, Ma SJ, Shen YH, Ou JJ. Fabrication of hydrophilic zwitterionic microspheres via inverse suspension polymerization for the enrichment of N-glycopeptides. Microchim Acta. 2021;188(10):348. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-05010-w
Li XW, Zhang HY, Zhang N, Ma SJ, Ou JJ, Ye ML. One-step preparation of zwitterionic-rich hydrophilic hydrothermal carbonaceous materials for enrichment of n-glycopeptides. ACS Sustain Chem Eng. 2019;7(13):11511–20. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b01382
Ji YS, Lv RH, Song SH, Huang JF, Zhang LW, Huang G, Li JA, Ou JJ. Facile fabrication of zwitterionic magnetic composites by one-step distillation-precipitation polymerization for highly specific enrichment of glycopeptides. Anal Chim Acta. 2019;1053:43–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2018.12.003
Yi LH, Shao YF, Fu MY, Yan YH, Ding CF, Tang KQ. One-step preparation of magnetic zwitterionic-hydrophilic dual functional nanospheres for in-depth glycopeptides analysis in Alzheimer's disease patients' serum. J Chromatogr A. 2022;1669:462929. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2022.462929
Tian Y, Tang RZ, Liu LY, Yu Y, Ma SJ, Gong BL, Ou JJ. Glutathione-modified ordered mesoporous silicas for enrichment of N-linked glycopeptides by hydrophilic interaction chromatography. Talanta. 2020;217:121082. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2020.121082
Yan YY, Han RL, Hou YF, Zhang HJ, Yu JC, Gao WQ, Xu L, Tang KQ. Bowl-like mesoporous polydopamine with size exclusion for highly selective recognition of endogenous glycopeptides. Talanta. 2021;233:122468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2021.122468
Zhang QQ, Huang YY, Jiang BY, Hu YJ, Xie JJ, Gao X, Jia B, Shen HL, Zhang WJ, Yang PY. In situ synthesis of magnetic mesoporous phenolic resin for the selective enrichment of glycopeptides. Anal Chem. 2021;90(12):7357–63. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b00708
Kong SY, Zhang QQ, Yang LJ, Huang YY, Liu MQ, Yan GQ, Zhao HH, Wu MX, Zhang XM, Yang PY, Cao WQ. Effective enrichment strategy using boronic acid-functionalized mesoporous graphene-silica composites for intact n- and o-linked glycopeptide analysis in human serum. Anal Chem. 2021;93(17):6682–91. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.0c05482
Zheng Y, Pu CL, Zhao HL, Gu QY, Zhu TY, Lan MB. Hydrophilic arginine-functionalized mesoporous polydopamine-graphene oxide composites for glycopeptides analysis. Anal Chem. 2022;1189:123049. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2021.123049
Wang ZD, Wu RQ, Chen HM, Sun NR, Deng CH. Synthesis of zwitterionic hydrophilic magnetic mesoporous silica materials for endogenous glycopeptide analysis in human saliva. Nanoscale. 2018;10(11):5335–41. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7nr08613j
Chen HM, Li YL, Wu H, Sun NR, Deng CH. Smart hydrophilic modification of magnetic mesoporous silica with zwitterionic l-cysteine for endogenous glycopeptides recognition. ACS Sustain Chem Eng. 2019;7(2):2844–51. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b06258
Li DP, Zhang JH, Xie GS, Ji FF, Shao XJ, Zhu L, Cai ZW. A dual-zwitterion functionalized ultra-hydrophilic metal–organic framework with ingenious synergy for enhanced enrichment of glycopeptides. Chem Commun. 2019;55(93):13967–70. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9cc06785j
Sun NR, Wang JW, Yao JZ, Deng CH. Hydrophilic mesoporous silica materials for highly specific enrichment of n-linked glycopeptide. Anal Chem. 2017;89(3):1764–71. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.6b04054
Zhang Y, Kuang M, Zhang LJ, Yang PY, Lu HJ. An accessible protocol for solid-phase extraction of N-linked glycopeptides through reductive amination by amine-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles. Anal Chem. 2013;85(11):5535–41. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac400733y
Deng H, Li XL, Peng Q, Wang X, Chen JP, Li YD. Monodisperse magnetic single-crystal ferrite microspheres. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2005;44(18):2782–5. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200462551
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by Ningbo major science and technology project (2022Z133), the medical health Project of Health Department of Zhejiang Province (2021KY1045), Ningbo public welfare science and technology project (2021S104).
Ethically approved human serum samples used in this research were collected with the consent of volunteers. The study was conducted with the approval of the experimental ethics committee of Ningbo University and its affiliated hospital.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Consent for publication
All of the authors have given approval for the final version of the manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yi, L., Wang, B., Feng, Q. et al. Surface functionalization modification of ultra-hydrophilic magnetic spheres with mesoporous silica for specific identification of glycopeptides in serum exosomes. Anal Bioanal Chem 415, 1741–1749 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-023-04575-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-023-04575-0