Abstract
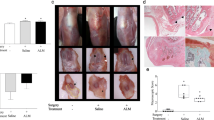
In this study, the effects of tranexamic acid (TXA) on the knee’s articular cartilage, anterior cruciate ligament (ACL), and joint capsule were assessed histologically. There were 15 rats in each of the 3 groups, totaling 45 rats. Intraarticular (IA) saline injections were applied for the first group, IA TXA injections for the second group, and intravenous (IV) TXA injections for the third group. Using samples taken from the knee joint 3 weeks later, the medial/lateral femoral condyle and medial/lateral tibial plateau articular cartilages were evaluated with Osteoarthritis Research Society International (OARSI) scoring, while ACL diameter and joint capsule thickness were analyzed histologically. In comparisons of OARSI scores for the medial/lateral femoral condyle and medial/lateral tibial plateau cartilage regions, the scores obtained for the IV TXA group were significantly higher than those of the IA saline group (P < 0.001, P = 0.001, P = 0.003, P = 0.011). In comparisons of medial/lateral femoral condyle and medial/lateral tibial plateau OARSI scores, the scores obtained for the IV TXA group were again significantly higher than those of the IA TXA group (P < 0.001, P < 0.001, P < 0.001, P = 0.002). When ACL diameters were compared, a significant decrease was observed in the ACL diameters of the IV TXA group compared to the IA saline and IA TXA groups (P < 0.001, P = 0.039). Histologically, IV TXA damages the articular cartilage and ACL more than IA TXA. IA administration of TXA is more protective when the articular cartilage and ACL are preserved.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets analyzed in the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Alshryda S, Sukeik M, Sarda P et al (2014) A systematic review and meta-analysis of the topical administration of tranexamic acid in total hip and knee replacement. Bone Joint J 96-B(8):1005–1015. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.96B8.33745
Ambra LF, de Girolamo L, Niu W et al (2019) No effect of topical application of tranexamic acid on articular cartilage. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 27(3):931–935. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-017-4746-9
Bahl V, Goyal A, Jain V et al (2013) Effect of haemarthrosis on the rehabilitation of anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction—single bundle versus double bundle. J Orthop Surg Res 8:5. https://doi.org/10.1186/1749-799X-8-5
Birisik F Sr, Bayram S, Çakmak M et al (2021) Investigation of the Effects of Intra-articular Tranexamic Acid on Intact Cartilage Tissue and Cartilage Formation in Osteochondral Defects of the Rabbit Knee: An Experimental Study. Cureus 13(5):e14873. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.14873
Bolam SM, O’Regan-Brown A, Paul Monk A et al (2021) Toxicity of tranexamic acid (TXA) to intra-articular tissue in orthopaedic surgery: a scoping review. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 29(6):1862–1871. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-020-06219-7
Bolam SM, O’Regan-Brown A, Konar S et al (2022) Cytotoxicity of tranexamic acid to tendon and bone in vitro: Is there a safe dosage? J Orthop Surg Res 17(1):273. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-022-03167-5
Çevik HB, Eceviz E, Çilingir Kaya ÖT et al (2020) The effect of topical and systemic tranexamic acid on fracture healing in rats. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc 54(2):207–212. https://doi.org/10.5152/j.aott.2020.02.44
Charan J, Kantharia ND (2013) How to calculate sample size in animal studies? J Pharmacol Pharmacother 4(4):303–306. https://doi.org/10.4103/0976-500X.119726
Chiang ER, Chen KH, Wang ST et al (2019) Intra-articular injection of tranexamic acid reduced postoperative hemarthrosis in arthroscopic anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: a prospective randomized study. Arthroscopy 35(7):2127–2132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arthro.2019.02.018
Felli L, Revello S, Burastero G et al (2019) Single intravenous administration of tranexamic acid in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction to reduce postoperative hemarthrosis and increase functional outcomes in the early phase of postoperative rehabilitation: a randomized controlled trial. Arthroscopy 35(1):149–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arthro.2018.07.050
Gandhi R, Evans HM, Mahomed SR et al (2013) Tranexamic acid and the reduction of blood loss in total knee and hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. BMC Res Notes 6:184. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-0500-6-184
Gerwin N, Bendele AM, Glasson S et al (2010) The OARSI histopathology initiative - recommendations for histological assessments of osteoarthritis in the rat. Osteoarthr Cartil 18(Suppl 3):S24-34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2010.05.030
Gianakos AL, Hurley ET, Haring RS et al (2018) Reduction of blood loss by tranexamic acid following total hip and knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. JBJS Rev 6(5):e1. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.RVW.17.00103
Goderecci R, Giusti I, Necozione S et al (2019) Short exposure to tranexamic acid does not affect, in vitro, the viability of human chondrocytes. Eur J Med Res 24(1):15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40001-019-0373-x
Goldring MB (2000) The role of the chondrocyte in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum 43(9):1916–1926. https://doi.org/10.1002/1529-0131(200009)43:9%3c1916::AID-ANR2%3e3.0.CO;2-I
Hamilton PT, Jansen MS, Ganesan S et al (2013) Improved bone morphogenetic protein-2 retention in an injectable collagen matrix using bifunctional peptides. PLoS One 8(8):e70715. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0070715
Johns WL, Walley KC, Hammoud S et al (2021) Tranexamic Acid in Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Am J Sports Med 49(14):4030–4041. https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546521988943
Karaaslan F, Karaoğlu S, Yurdakul E (2015) Reducing intra-articular hemarthrosis after arthroscopic anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction by the administration of intravenous tranexamic acid: a prospective, randomized controlled trial. Am J Sports Med 43(11):2720–2726. https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546515599629
Kim C, Park SS, Davey JR (2015) Tranexamic acid for the prevention and management of orthopedic surgical hemorrhage: current evidence. J Blood Med 6:239–244. https://doi.org/10.2147/JBM.S61915
Lee JW, Kim SG, Kim SH et al (2020) Intra-articular administration of tranexamic acid has no effect in reducing intra-articular hemarthrosis and postoperative pain after primary ACL reconstruction using a quadruple hamstring graft: a randomized controlled trial. Orthop J Sports Med 8(7):2325967120933135. https://doi.org/10.1177/2325967120933135
Ma R, Wu M, Li Y et al (2021) The comparative efficacies of intravenous administration and intra-articular injection of tranexamic acid during anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction for reducing postoperative hemarthrosis: a prospective randomized study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 22(1):114. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-021-03990-7
Maniar RN, Kumar G, Singhi T et al (2012) Most effective regimen of tranexamic acid in knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized controlled study in 240 patients. Clin Orthop Relat Res 470(9):2605–2612. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-012-2310-y
Mao Z, Yue B, Wang Y et al (2016) A comparative, retrospective study of peri-articular and intra-articular injection of tranexamic acid for the management of postoperative blood loss after total knee arthroplasty. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 17(1):438. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-016-1293-3
McLean M, McCall K, Smith IDM et al (2019) Tranexamic acid toxicity in human periarticular tissues. Bone Joint Res 8(1):11–18. https://doi.org/10.1302/2046-3758.81.BJR-2018-0181.R1
Melvin JS, Stryker LS, Sierra RJ (2015) Tranexamic acid in hip and knee arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 23(12):732–740. https://doi.org/10.5435/JAAOS-D-14-00223
Morrison RJM, Tsang B, Fishley W et al (2017) Dose optimisation of intravenous tranexamic acid for elective hip and knee arthroplasty: the effectiveness of a single pre-operative dose. Bone Joint Res 6(8):499–505. https://doi.org/10.1302/2046-3758.68.BJR-2017-0005.R1
Murkin JM, Falter F, Granton J et al (2010) High-dose tranexamic acid is associated with nonischemic clinical seizures in cardiac surgical patients. Anesth Analg 110(2):350–353. https://doi.org/10.1213/ANE.0b013e3181c92b23
Na Y, Jia Y, Shi Y et al (2022) Administration of Tranexamic Acid to Reduce Intra-articular Hemarthrosis in ACL Reconstruction: A Systematic Review. Orthop J Sports Med 10(1):23259671211061730. https://doi.org/10.1177/23259671211061726
Nilsson IM (1980) Clinical pharmacology of aminocaproic and tranexamic acids. J Clin Pathol Suppl (r Coll Pathol) 14:41–47
Nugent M, May JH, Parker JD et al (2019) Does tranexamic acid reduce knee swelling and improve early function following arthroscopic meniscectomy? A double-blind randomized controlled trial. Orthop J Sports Med 7(8):2325967119866122. https://doi.org/10.1177/2325967119866122
Parker JD, Lim KS, Kieser DC et al (2018) Is tranexamic acid toxic to articular cartilage when administered topically? Bone Joint J 100-B(3):404–412. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.100B3.BJJ-2017-1135.R1
Pongcharoen B, Ruetiwarangkoon C (2016) Does tranexamic acid reduce blood loss and transfusion rates in unicompartmental knee arthroplasty? J Orthop Sci 21(2):211–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jos.2015.12.006
Salzler MJ, Lin A, Miller CD et al (2014) Complications after arthroscopic knee surgery. Am J Sports Med 42(2):292–296. https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546513510677
Sassoon A, Nam D, Jackups R et al (2016) Tranexamic acid: optimal blood loss management in surface replacement arthroplasty. Bone Joint J 98-B(2):173–178. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.98B2.36776
Schwab PE, Lavand’homme P, Yombi JC et al (2015) Lower blood loss after unicompartmental than total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 23(12):3494–3500. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-014-3188-x
Sukur E, Kucukdurmaz F (2018) Comparison of Cytotoxic Effects of Intra-Articular Use of Tranexamic Acid versus Epinephrine on Rat Cartilage. Med Sci Monit. 24:1166–1170. https://doi.org/10.12659/msm.908560
Wang H, Shen B, Zeng Y (2014) Comparison of topical versus intravenous tranexamic acid in primary total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled and prospective cohort trials. Knee 21(6):987–993. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knee.2014.09.010
Wang S, Gao X, An Y (2017) Topical versus intravenous tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int Orthop 41(4):739–748. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-016-3296-y
Xie J, Hu Q, Ma J, Huang Q et al (2017) Multiple boluses of intravenous tranexamic acid to reduce hidden blood loss and the inflammatory response following enhancedrecovery primary total hip arthroplasty: a randomised clinical trial. Bone Joint J 99-B(11):1442–1449. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.99B11.BJJ-2017-0488.R1
Xiong H, Liu Y, Zeng Y et al (2018) The efficacy and safety of combined administration of intravenous and topical tranexamic acid in primary total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 19(1):321. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-018-2181-9
Yuan ZF, Yin H, Ma WP et al (2016) The combined effect of administration of intravenous and topical tranexamic acid on blood loss and transfusion rate in total knee arthroplasty: combined tranexamic acid for TKA. Bone Joint Res 5(8):353–361. https://doi.org/10.1302/2046-3758.58.BJR-2016-0001.R2
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grants from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by S.A., Y.A., G.A., and A.Ç.T. The first draft of the manuscript was written by C.Ç. M.A. and M.D. played leading roles in the critical revision. The authors declare that all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The Research Ethics Committee for Animal Experiments approved the study (Date: 20.01.2022, Number: 0069).
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Çağlar, C., Akçaalan, S., Akçaalan, Y. et al. Tranexamic acid administered intraarticularly to the knee is safer for the articular cartilage and anterior cruciate ligament compared to intravenous administration: Histological analysis of an experimental rat model. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 397, 1045–1051 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02666-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02666-4