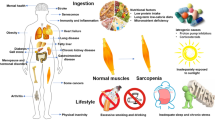
Abstract
Sarcopenia is a major global public health problem that harms individual physical function. In 2018, the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in the Elderly 2 classified sarcopenia into primary and secondary sarcopenia. However, information on the pathogenesis and effective treatment of primary and secondary sarcopenia is limited. Traditional herbal active ingredients have biological activities that promote skeletal muscle health, showing potential preventive and therapeutic effects on sarcopenia. Therefore, this narrative review aims to provide a comprehensive overview of global traditional herbal active ingredients’ beneficial therapeutic effects and molecular mechanisms on sarcopenia-related animal models. For this purpose, we conducted a literature search in three databases, PubMed, Web of Science, and Embase, consistent with the review objectives. After the screening, 12 animal studies met the review themes. The review results showed that the pathological mechanisms in sarcopenia-related animal models include imbalanced protein metabolism, oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis, insulin resistance, endoplasmic reticulum stress, impaired mitochondrial biogenesis, and autophagy-lysosome system aggravation. Eleven traditional herbal active ingredients exerted positive anti-sarcopenic effects by ameliorating these pathological mechanisms. This narrative review will provide meaningful insight into future studies regarding traditional herbal active ingredients for treating sarcopenia.
Graphical abstract



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- AI:
-
Atractylenolide I
- Akt:
-
Protein kinase B
- ALK:
-
Activin receptor-like kinase
- ATF6:
-
Activating transcription factor 6
- Bax:
-
Bcl2-associated X protein
- Bcl2:
-
B-cell lymphoma 2 protein
- BMP:
-
Bone morphogenetic protein
- CHOP:
-
C/EBP homologous protein
- CK:
-
Ginsenoside compound K
- CKD:
-
Chronic kidney disease
- COPD:
-
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- CS:
-
Carnosol
- DCS:
-
Dimethyl-carnosol
- DCSD:
-
Dimethyl-carnosol-D6
- DEXA:
-
Dexamethasone
- DHM:
-
Dihydromyricetin
- DMF:
-
5,7-Dimethoxyflavone
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- FOXO3a:
-
Forkhead box class O 3a
- GPx:
-
Glutathione peroxidase
- GR:
-
Glutathione reductase
- GSK-3β:
-
Glycogen synthase kinase 3β
- IGF-1:
-
Insulin-like growth factor 1
- IKB:
-
Inhibitor of κB
- IKK:
-
IκB kinase
- JAK:
-
Janus kinase
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharides
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- MHC:
-
Major histocompatibility complex
- mTOR:
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin
- MSTN:
-
Myostatin
- MuRF1:
-
Muscle RING-finger protein-1
- MyHC:
-
Myosin heavy chain
- MyoD:
-
Myogenic differentiation antigen
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor-kappa B
- NRF-1:
-
Nuclear factor erythroid 2 related factor 1
- ORX:
-
Orchiectomized
- Pax7:
-
Paired box protein Pax-7
- PGC-1α:
-
Proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha
- PI3K:
-
Phosphoinositide 3-kinases
- PKM2:
-
Pyruvate kinase isozyme M2
- S-Rg3:
-
20(S)-Ginsenoside Rg3
- SNAP23:
-
Synaptosome-associated protein 23
- STAT:
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription
- TFAM:
-
Mitochondrial transcription factor A
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha
- WOS:
-
Web of Science
- XIAP:
-
X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein
References
Acharyya S, Butchbach MER, Sahenk Z et al (2005) Dystrophin glycoprotein complex dysfunction: a regulatory link between muscular dystrophy and cancer cachexia. Cancer Cell 8:421–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2005.10.004
Akaberi M, Sahebkar A, Emami SA (2021) Turmeric and curcumin: from traditional to modern medicine. Adv Exp Med Biol 1291:15–39. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-56153-6_2
Attaix D, Ventadour S, Codran A et al (2005) The ubiquitin-proteasome system and skeletal muscle wasting. Essays Biochem 41:173–186. https://doi.org/10.1042/EB0410173
Bagherniya M, Mahdavi A, Shokri-Mashhadi N et al (2022) The beneficial therapeutic effects of plant-derived natural products for the treatment of sarcopenia. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 13:2772–2790. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcsm.13057
Barbalho SM, Flato UAP, Tofano RJ et al (2020) Physical exercise and myokines: relationships with sarcopenia and cardiovascular complications. Int J Mol Sci 21:3607. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21103607
Bar-Shai M, Carmeli E, Ljubuncic P, Reznick AZ (2008) Exercise and immobilization in aging animals: the involvement of oxidative stress and NF-kappaB activation. Free Radic Biol Med 44:202–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2007.03.019
Bauer J, Morley JE, Schols AMWJ et al (2019) Sarcopenia: a time for action. An SCWD position paper. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 10:956–961. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcsm.12483
Befroy DE, Petersen KF, Dufour S et al (2007) Impaired mitochondrial substrate oxidation in muscle of insulin-resistant offspring of type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes 56:1376–1381. https://doi.org/10.2337/db06-0783
Bruyère O, Beaudart C, Ethgen O et al (2019) The health economics burden of sarcopenia: a systematic review. Maturitas 119:61–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.maturitas.2018.11.003
Bryner RW, Woodworth-Hobbs ME, Williamson DL, Alway SE (2012) Docosahexaenoic acid protects muscle cells from palmitate-induced atrophy. ISRN Obes 2012:647348. https://doi.org/10.5402/2012/647348
Carneiro RCV, Ye L, Baek N et al (2021) Vine tea (Ampelopsis grossedentata): a review of chemical composition, functional properties, and potential food applications. J Funct Foods 76:104317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2020.104317
Cawthon PM, Lui L-Y, Taylor BC et al (2017) Clinical definitions of sarcopenia and risk of hospitalization in community-dwelling older men: the osteoporotic fractures in men study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 72:1383–1389. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/glw327
Chung C-L, Chen J-H, Huang W-C et al (2022) Glabridin, a bioactive flavonoid from licorice, effectively inhibits platelet activation in humans and mice. Int J Mol Sci 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms231911372
Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Kiesswetter E, Drey M, Sieber CC (2017) Nutrition, frailty, and sarcopenia. Aging Clin Exp Res 29:43–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-016-0709-0
Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Bahat G, Bauer J et al (2019) Sarcopenia: revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 48:601. https://doi.org/10.1093/ageing/afz046
Deng M, Chen H, Long J et al (2021) Atractylenolides (I, II, and III): a review of their pharmacology and pharmacokinetics. Arch Pharm Res 44:633–654. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-021-01342-6
Dhillon RJS, Hasni S (2017) Pathogenesis and management of sarcopenia. Clin Geriatr Med 33:17–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cger.2016.08.002
Ding K, Jiang W, Jia H, Lei M (2022) Synergistically anti-multiple myeloma effects: flavonoid, non-flavonoid polyphenols, and bortezomib. Biomolecules 12:1647. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom12111647
Fan M, Gu X, Zhang W et al (2022a) Atractylenolide I ameliorates cancer cachexia through inhibiting biogenesis of IL-6 and tumour-derived extracellular vesicles. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 13:2724–2739. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcsm.13079
Fan M, Sun W, Gu X et al (2022b) The critical role of STAT3 in biogenesis of tumor-derived exosomes with potency of inducing cancer cachexia in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene 41:1050–1062. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-021-02151-3
Fitts RH (1994) Cellular mechanisms of muscle fatigue. Physiol Rev 74:49–94. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.1994.74.1.49
Go G-Y, Lee S-J, Jo A et al (2017) Ginsenoside Rg1 from Panax ginseng enhances myoblast differentiation and myotube growth. J Ginseng Res 41:608–614. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgr.2017.05.006
Günther S, Kim J, Kostin S et al (2013) Myf5-positive satellite cells contribute to Pax7-dependent long-term maintenance of adult muscle stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 13:590–601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2013.07.016
Guo L-T, Wang S-Q, Su J et al (2019) Baicalin ameliorates neuroinflammation-induced depressive-like behavior through inhibition of toll-like receptor 4 expression via the PI3K/AKT/FoxO1 pathway. J Neuroinflammation 16:95. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-019-1474-8
He C, Wang Z, Shi J (2020) Pharmacological effects of icariin. Adv Pharmacol 87:179–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.apha.2019.10.004
Huang J, Zhang Y, Dong L et al (2018a) Ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry, and pharmacology of Cornus officinalis Sieb. et Zucc. J Ethnopharmacol 213:280–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2017.11.010
Huang Y, Chen K, Ren Q et al (2018b) Dihydromyricetin attenuates dexamethasone-induced muscle atrophy by improving mitochondrial function via the PGC-1α pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem 49:758–779. https://doi.org/10.1159/000493040
Hyatt H, Deminice R, Yoshihara T, Powers SK (2019) Mitochondrial dysfunction induces muscle atrophy during prolonged inactivity: a review of the causes and effects. Arch Biochem Biophys 662:49–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2018.11.005
Jiang W, Ding K, Yue R, Lei M (2023) Therapeutic effects of icariin and icariside II on diabetes mellitus and its complications. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 1–26. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2022.2159317
Kashyap D, Kumar G, Sharma A et al (2017) Mechanistic insight into carnosol-mediated pharmacological effects: recent trends and advancements. Life Sci 169:27–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2016.11.013
Kim C, Hwang J-K (2020a) Flavonoids: nutraceutical potential for counteracting muscle atrophy. Food Sci Biotechnol 29:1619–1640. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-020-00816-5
Kim C, Hwang J-K (2020b) The 5,7-dimethoxyflavone suppresses sarcopenia by regulating protein turnover and mitochondria biogenesis-related pathways. Nutrients 12:1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12041079
Kim JK, Mun S, Kim M-S et al (2012) 5,7-Dimethoxyflavone, an activator of PPARα/γ, inhibits UVB-induced MMP expression in human skin fibroblast cells: 5,7-DMF inhibits MMP expression. Exp Dermatol 21:211–216. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0625.2011.01435.x
Kim TJ, Pyun DH, Kim MJ et al (2022) Ginsenoside compound K ameliorates palmitate-induced atrophy in C2C12 myotubes via promyogenic effects and AMPK/autophagy-mediated suppression of endoplasmic reticulum stress. J Ginseng Res 46:444–453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgr.2021.09.002
Lee H, Kong G, Tran Q et al (2020) Relationship between ginsenoside Rg3 and metabolic syndrome. Front Pharmacol 11:130. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.00130
Li X-X, He G-R, Mu X et al (2012) Protective effects of baicalein against rotenone-induced neurotoxicity in PC12 cells and isolated rat brain mitochondria. Eur J Pharmacol 674:227–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.09.181
Li B, Wan L, Li Y et al (2014) Baicalin, a component of Scutellaria baicalensis, alleviates anorexia and inhibits skeletal muscle atrophy in experimental cancer cachexia. Tumour Biol 35:12415–12425. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2558-9
Li F, Li X, Peng X et al (2017) Ginsenoside Rg1 prevents starvation-induced muscle protein degradation via regulation of AKT/mTOR/FoxO signaling in C2C12 myotubes. Exp Ther Med 14:1241–1247. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2017.4615
Li J, Yi X, Yao Z et al (2020) TNF receptor-associated factor 6 mediates TNFα-induced skeletal muscle atrophy in mice during aging: TRAF6 induces muscle loss during aging. J Bone Miner Res 35:1535–1548. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.4021
Lin Y-A, Li Y-R, Chang Y-C et al (2021) Activation of IGF-1 pathway and suppression of atrophy related genes are involved in Epimedium extract (icariin) promoted C2C12 myotube hypertrophy. Sci Rep 11:10790. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-89039-0
Liu T, Zhu L, Wang L (2022) A narrative review of the pharmacology of ginsenoside compound K. Ann Transl Med 10:234. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm-22-501
Lu S, Li Y, Shen Q et al (2021) Carnosol and its analogues attenuate muscle atrophy and fat lipolysis induced by cancer cachexia. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 12:779–795. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcsm.12710
Ma K, Huang F, Qiao R, Miao L (2022) Pathogenesis of sarcopenia in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Front Physiol. 13:850964. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2022.850964
Mijnarends DM, Koster A, Schols JMGA et al (2016) Physical activity and incidence of sarcopenia: the population-based AGES—Reykjavik study. Age Ageing 45:614–620. https://doi.org/10.1093/ageing/afw090
Naseeb MA, Volpe SL (2017) Protein and exercise in the prevention of sarcopenia and aging. Nutr Res 40:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nutres.2017.01.001
Papadopoulou SK, Papadimitriou K, Voulgaridou G et al (2021) Exercise and nutrition impact on osteoporosis and sarcopenia-the incidence of osteosarcopenia: a narrative review. Nutrients 13:4499. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124499
Park W, Park MY, Song G, Lim W (2020) 5,7-Dimethoxyflavone induces apoptotic cell death in human endometriosis cell lines by activating the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway. Phytother Res 34:2275–2286. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.6677
Petermann-Rocha F, Balntzi V, Gray SR et al (2022) Global prevalence of sarcopenia and severe sarcopenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 13:86–99. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcsm.12783
Pyun DH, Kim TJ, Kim MJ et al (2021) Endogenous metabolite, kynurenic acid, attenuates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via AMPK/autophagy- and AMPK/ORP150-mediated signaling. J Cell Physiol 236:4902–4912. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.30199
Reddy SS, Shruthi K, Prabhakar YK et al (2018) Implication of altered ubiquitin-proteasome system and ER stress in the muscle atrophy of diabetic rats. Arch Biochem Biophys 639:16–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2017.12.015
Rhoads MG, Kandarian SC, Pacelli F et al (2010) Expression of NF-kappaB and IkappaB proteins in skeletal muscle of gastric cancer patients. Eur J Cancer 46:191–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2009.10.008
Rondanelli M, Miccono A, Peroni G et al (2016) A systematic review on the effects of botanicals on skeletal muscle health in order to prevent sarcopenia. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2016:5970367. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/5970367
Roshanravan B, Gamboa J, Wilund K (2017) Exercise and CKD: skeletal muscle dysfunction and practical application of exercise to prevent and treat physical impairments in CKD. Am J Kidney Dis 69:837–852. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2017.01.051
Sabatino A, Cuppari L, Stenvinkel P et al (2021) Sarcopenia in chronic kidney disease: what have we learned so far? J Nephrol 34:1347–1372. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-020-00840-y
Saokaew S, Wilairat P, Raktanyakan P et al (2017) Clinical effects of Krachaidum ( Kaempferia parviflora): a systematic review. J Evid Based Complementary Altern Med 22:413–428. https://doi.org/10.1177/2156587216669628
Schakman O, Gilson H, Thissen JP (2008) Mechanisms of glucocorticoid-induced myopathy. J Endocrinol 197:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1677/JOE-07-0606
Seok YM, Yoo J-M, Nam Y et al (2021) Mountain ginseng inhibits skeletal muscle atrophy by decreasing muscle RING finger protein-1 and atrogin1 through forkhead box O3 in L6 myotubes. J Ethnopharmacol 270:113557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2020.113557
Shen J, Cheng J, Zhu S et al (2019) Regulating effect of baicalin on IKK/IKB/NF-kB signaling pathway and apoptosis-related proteins in rats with ulcerative colitis. Int Immunopharmacol 73:193–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2019.04.052
Sieber CC (2019) Malnutrition and sarcopenia. Aging Clin Exp Res 31:793–798. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40520-019-01170-1
Simmler C, Pauli GF, Chen S-N (2013) Phytochemistry and biological properties of glabridin. Fitoterapia 90:160–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2013.07.003
Singh S, Meena A, Luqman S (2021) Baicalin mediated regulation of key signaling pathways in cancer. Pharmacol Res 164:105387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105387
Song Y, Kim M-B, Kim C et al (2016) 5,7-Dimethoxyflavone attenuates obesity by inhibiting adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and high-fat diet-induced obese C57BL/6J mice. J Med Food 19:1111–1119. https://doi.org/10.1089/jmf.2016.3800
Steffl M, Sima J, Shiells K, Holmerova I (2017) The increase in health care costs associated with muscle weakness in older people without long-term illnesses in the Czech Republic: results from the Survey of Health, Ageing and Retirement in Europe (SHARE). Clin Interv Aging 12:2003–2007. https://doi.org/10.2147/cia.s150826
Takemoto Y, Inaba S, Zhang L et al (2017) An herbal medicine, Go-sha-jinki-gan (GJG), increases muscle weight in severe muscle dystrophy model mice. Clin Nutr Exp 16:13–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yclnex.2017.08.003
Theeuwes WF, Gosker HR, Langen RCJ et al (2017) Inactivation of glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β) enhances skeletal muscle oxidative metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 1863:3075–3086. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.09.018
Thoma A, Lightfoot AP (2018) NF-kB and inflammatory cytokine signalling: role in skeletal muscle atrophy. Adv Exp Med Biol 1088:267–279. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-1435-3_12
Toda K, Hitoe S, Takeda S, Shimoda H (2016) Black ginger extract increases physical fitness performance and muscular endurance by improving inflammation and energy metabolism. Heliyon 2:e00115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2016.e00115
Traub J, Bergheim I, Eibisberger M, Stadlbauer V (2020) Sarcopenia and liver cirrhosis-comparison of the European Working Group on Sarcopenia criteria 2010 and 2019. Nutrients 12:547. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12020547
Vazeille E, Slimani L, Claustre A et al (2012) Curcumin treatment prevents increased proteasome and apoptosome activities in rat skeletal muscle during reloading and improves subsequent recovery. J Nutr Biochem 23:245–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2010.11.021
Wang D-T, Yin Y, Yang Y-J et al (2014) Resveratrol prevents TNF-α-induced muscle atrophy via regulation of Akt/mTOR/FoxO1 signaling in C2C12 myotubes. Int Immunopharmacol 19:206–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2014.02.002
Wang D, Sun H, Song G et al (2018a) Resveratrol improves muscle atrophy by modulating mitochondrial quality control in STZ-induced diabetic mice. Mol Nutr Food Res 62:1700941. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.201700941
Wang D, Yang Y, Zou X et al (2020) Curcumin ameliorates CKD-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress through inhibiting GSK-3β activity. J Nutr Biochem 83:108404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2020.108404
Wang M, Ren J, Chen X et al (2020) 20(S)-Ginsenoside Rg3 promotes myoblast differentiation and protects against myotube atrophy via regulation of the Akt/mTOR/FoxO3 pathway. Biochem Pharmacol 180:114145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114145
Wang J, Zeng L, Zhang Y et al (2022) Pharmacological properties, molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential of ginsenoside Rg3 as an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent. Front Pharmacol 13:975784. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.975784
Wang D, Wei L, Yang Y, Liu H (2018b) Dietary supplementation with ketoacids protects against CKD-induced oxidative damage and mitochondrial dysfunction in skeletal muscle of 5/6 nephrectomised rats. Skelet Muscle 8. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13395-018-0164-z
Wiedmer P, Jung T, Castro JP et al (2021) Sarcopenia - molecular mechanisms and open questions. Ageing Res Rev 65:101200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2020.101200
Woodworth-Hobbs ME, Perry BD, Rahnert JA et al (2017) Docosahexaenoic acid counteracts palmitate-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress in C2C12 myotubes: impact on muscle atrophy. Physiol Rep 5:e13530. https://doi.org/10.14814/phy2.13530
Xie W-Q, He M, Yu D-J et al (2021) Mouse models of sarcopenia: classification and evaluation. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 12:538–554. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcsm.12709
Xu M, Li X, Song L (2020) Baicalin regulates macrophages polarization and alleviates myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion injury via inhibiting JAK/STAT pathway. Pharm Biol 58:655–663. https://doi.org/10.1080/13880209.2020.1779318
Yang K-C, Bonini MG, Dudley SC Jr (2014) Mitochondria and arrhythmias. Free Radic Biol Med 71:351–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.03.033
Yang W-Y, Cao H-J, Li L et al (2022) A phytomolecule icariin protects from sarcopenia partially by suppressing myosin heavy chain degradation in orchiectomized rats. Adv Biol (Weinh) 6:e2200162. https://doi.org/10.1002/adbi.202200162
Yi X, Tao J, Qian Y et al (2022) Morroniside ameliorates inflammatory skeletal muscle atrophy via inhibiting canonical and non-canonical NF-κB and regulating protein synthesis/degradation. Front Pharmacol 13:1056460. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.1056460
Yoshioka Y, Kubota Y, Samukawa Y et al (2019) Glabridin inhibits dexamethasone-induced muscle atrophy. Arch Biochem Biophys 664:157–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2019.02.006
Yuan H, Ma Q, Ye L, Piao G (2016) The traditional medicine and modern medicine from natural products. Molecules 21:559. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21050559
Acknowledgements
Firstly, we would like to thank Prof. Huanan Jia, from Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Department of Geriatrics, for reviewing the initial version of this article. Secondly, we would like to thank Kaixi Ding’s parents (Xia Wang and Bing Ding), grandfather (Qingquan Ding), and uncle (Yi Ding), as they have inspired Kaixi Ding’s enthusiasm and pursuit of medical research from the beginning to the present.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Kaixi Ding and Wei Jiang. Methodology: Kaixi Ding and Wei Jiang. Software: Juejue Zhangwang and Yu Wang. Validation: Juejue Zhangwang and Yu Wang. Writing—original draft preparation: Kaixi Ding. Writing—review and editing: Kaixi Ding and Wei Jiang. Visualization: Wei Jiang. Supervision: Ming Lei. Project administration: Ming Lei and Jing Zhang. The authors confirm that no paper mill and artificial intelligence was used.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors unanimously approved the publication of this manuscript.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, K., Jiang, W., Zhangwang, J. et al. The potential of traditional herbal active ingredients in the treatment of sarcopenia animal models: focus on therapeutic effects and mechanisms. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 396, 3483–3501 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02639-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-023-02639-7