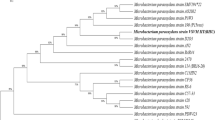
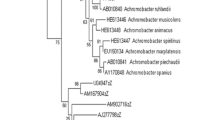
Abstract
Heavy metal pollution is a global problem that affects both the environment and human health. Microorganisms play an important role in remediation. Most studies on the use of microorganisms for heavy metal remediation focus on single heavy metals. In this study, a strain of Penicillium amphipolaria, XK11 with high resistance to both antimony (Sb III) and cadmium (Cd II) was screened from the mineral slag. The strain also had a high phosphate solubilization capacity. The single-factor adsorption experiment results showed that the initial pH (pH0), adsorption time (T), and initial solution concentration (C0) all affected the adsorption of Sb and Cd by XK11. When the initial pH0 (Cd = 6, Sb = 4) and adsorption time (T = 7 d) were constant, XK11 achieved the maximum removal rate of Cd (45.6%) and Sb (34.6%). These results confirm that XK11 has potential as a biomaterial or remediation of Sb and Cd pollution.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article and the supplementary information file.
Change history
24 April 2023
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-023-03543-7
References
Aleksandra B, Patryk O (2020) Effect of biochar addition to sewage sludge on cadmium, copper and lead speciation in sewage sludge-amended soil. Chemosphere 239:124719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124719
Amirnia S, Ray MB, Margaritis A (2015) Heavy metals removal from aqueous solutions using Saccharomyces cerevisiae in a novel continuous bioreactor–biosorption system. Chem Eng J 264:863–872. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.12.016
Anna CP, Justyna SB, Wojciech Ł (2018) Optimization of copper, lead and cadmium biosorption onto newly isolated bacterium using a Box-Behnken design. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 149:275–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.12.008
Aryal M, Liakopoulou-Kyriakides M (2015) Bioremoval of heavy metals by bacterial biomass. Environ Monit Assess 187:4173. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-014-4173-z
Ayansina SA, Olubukola OB (2017) A new strategy for heavy metal polluted environments: a review of microbial biosorbents. Int J Environ Res Public Health 14:94. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14010094
Bargagli R, Baldi F (1984) Mercury and methyl mercury in higher fungi and their relation with the substrata in a cinnabar mining area. Chemosphere 13:1059–1071. https://doi.org/10.1016/0045-6535(84)90065-1
Bashir S, Hussain Q, Zhu J, Fu QL, Houben D, Hu HQ (2020) Efficiency of KOH-modified rice straw-derived biochar for reducing cadmium mobility, bioaccessibility and bioavailability risk index in red soil. Pedosphere 30:874–882. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1002-0160(20)60043-1
Cai Y, Li XP, Liu DY, Xu CL, Ai YW, Sun XM, Zhang M, Gao Y, Zhang YC, Yang T, Wang JZ, Wang LJ, Li XY, Yu YT (2018) A novel Pb-resistant Bacillus subtilis Bacterium isolate for co-biosorption of hazardous Sb(III) and Pb(II): thermodynamics and application strategy. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15:702. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph15040702
Cao X, Wang CL (2010) Screening of microorganisms resistant to heavy metals lead and cadmium. J Green Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1674-9944.2010.07.050
Chien CC, Lin BC, Wu CH (2013) Biofilm formation and heavy metal resistance by an environmental Pseudomonas sp. Biochem Eng J 78:132–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2013.01.014
Demey H, Vincent T, Guibal E (2018) A novel algal-based sorbent for heavy metal removal. Chem Eng J 332:582–595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.09.083
Deng YN, Wang LF, Luo K, Peng D, Jiang HD, Jin CZ, Zhou XM, Bai LY (2017) Heavy Metals; Studies from X.M. Zhou and Colleagues Yield New Information about Heavy Metals (Screening and identifying a cadmium-resistant fungus and characterizing its cadmium adsorption). Pol J Environ Stud 26:1101–1021. https://doi.org/10.15244/pjoes/67655
Du LD, Wang YN, Li YS, Yu TQ, Lu P, Liang W (2008) Study on accumulation of lead in soil by Microbes. J Beijing Univ Agric 23:38–41. https://doi.org/10.13473/j.cnki.issn.1002-3186.2008.01.005
Durali M, Mustafa T, Mustafa S (2007) A biosorption system for metal ions on Penicillium italicum–loaded on Sepabeads SP 70 prior to flame atomic absorption spectrometric determinations. J Hazard Mater 152:1171–1178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.07.097
Fang X, Tang ZJ, Tian DL, Xiang WH, Sun WJ (2012) Distributioan and ecological risk assessment of 7 heavy metals in urban forest soils in ChangSha city. Acta Ecol Sin 32:7595–7606. https://doi.org/10.5846/stxb201201130073
Fomina MA, Alexander IJ, Colpaert JV, Gadd GM (2004) Solubilization of toxic metal minerals and metal tolerance of mycorrhizal fungi. Soil Biol Biochem 37:851–866. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2004.10.013
Harms H, Schlosser D, Wick LY (2011) Untapped potential: exploiting fungi in bioremediation of hazardous chemicals. Nat Rev Microbiol 9:177–192. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2519
Hassan SHA, Mostafa K, Nivien AN, Elhagag AH (2018) Potentiality of Neopestalotiopsis clavispora ASU1 in biosorption of cadmium and zinc. Chemosphere 202(7):750–756. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.03.114
Hilbe JM (2003) A review of current SPSS products. Am Stat 57:310–315. https://doi.org/10.1198/0003130032495
Hong SQ, Niu MX, Qin X, Zhang LH (2022) Research progress on antimony removal from printing and dyeing wastewater by adsorption. J xi’an Polytech Univ 36:63–70. https://doi.org/10.13338/j.issn.1674-649x.2022.03.008
Huang HJ (2020) Comparison of Adsorption Capacity and Adsorption Mechanism of Three Microorganisms to Cadmium. Shanxi University
Huang MS, Zheng YP, Zhu L (2000) Adsorption and Desorption of Heavy Metals by Microorganisms. Chem Equip Technol. https://doi.org/10.16759/j.cnki.issn.1007-7251.2000.02.008
Huang HM, Zhao YL, Xu ZG, Ding Y, Zhang W, Wu L (2018) Biosorption characteristics of a highly Mn(II)-resistant Ralstonia pickettii strain isolated from Mn ore. PLoS ONE 13:e0203285. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0203285
Huang HM, Fan L, Zhao YL, Jin Q, Yang GY, Zhao D, Xu ZG (2022) Integrating Broussonetia papyrifera and two bacillus species to repair soil antimony pollutions. Front Microbiol 13:871581. https://doi.org/10.3389/FMICB.2022.871581
Ianis M, Tsekova K, Vasileva S (2006) Copper Biosorption by Penicillium Cyclopium: Equilibrium and Modelling Study. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 20:195–201. https://doi.org/10.1080/13102818.2006.10817332
Ibrahim F, Halttunen T, Tahvonen R, Salminen S (2006) Probiotic bacteria as potential detoxification tools: assessing their heavy metal binding isotherms. Can J Microbiol 52:877–885. https://doi.org/10.1139/w06-043
Jovancicevic V, Bockris JOm, Carbajal JL, Zelenay YP, Mizuno T (1987) ChemInform abstract: adsorption and absorption of chloride ions on passive iron systems. ChemInform. https://doi.org/10.1002/chin.198711027
Lenka S, Marketa S, Martin K, Eric G (2006) Cadmium, lead and mercury biosorption on waste fungal biomass issued from fermentation industry. I. Equilibrium studies. Sep Purif Technol 52:142–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2006.03.024
Li CY (2020) The research on optimum selection of cadmium tolerant fungi in the background of high antimony content and its biosorption characteristics of antimony and cadmium. Central South University of Forestry and Technology
Li SS, Dai YZ, Luo CX, Li FC, S L (2009) Morphologic changes of antimony in water and status quo of antimony-removal technologies. Environ Prot Chem Ind 29:131-134. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1006-1878.2009.02.008
Li X, Zhang YX, Liu JG, Chai TY (2013) Isolation and characterization of cadmium-resistant Penicillium SP. from coal mining areas. Microbiology China 40(8):1347–1355. https://doi.org/10.13344/j.microbiol.china.2013.08.008
Li H, Luo N, Zhang LJ, Zhao HM, Li YW, Cai QW, Hung WM, Hui MC (2016a) Do arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi affect cadmium uptake kinetics, subcellular distribution and chemical forms in rice? Sci Total Environ 571:1183–1190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.07.124
Li YC, Hu XX, Ren BZ (2016b) Treatment of antimony mine drainage: challenges and opportunities with special emphasis on mineral adsorption and sulfate reducing bacteria. Water Sci Technol 73:2039–2051. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2016.044
Li JX, Zhang YX, Zheng SL, Liu FH, Wang GJ (2019) Anaerobic bacterial immobilization and removal of toxic Sb(III) coupled with Fe(II)/Sb(III) oxidation and denitrification. Front Microbiol 10:360. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.00360
Li XX, Lan X, Feng XW, Luan XY, Cao XF, Cui ZJ (2021) Biosorption capacity of Mucor circinelloides bioaugmented with Solanum nigrum L. for the cleanup of lead, cadmium and arsenic. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 212:112014. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ECOENV.2021.112014
Liao J, Feng CL, Xiang J, Li J (2015) Influence factors and absorption mechanism of Pb(II) and Zn(II) by resistant fungus HA. Microbiol China 42:254–263. https://doi.org/10.13344/j.microbiol.china.140503
Lu X, Xu XJ, Zhu W, Huang QY, Chen WL (2015) A comparative study on the biosorption of Cd2+ onto Paecilomyces lilacinus XLA and Mucoromycote sp. XLC Int J Mol Sci 16:15670–15687. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160715670
Lu YC, Cheng JQ, Wang JN, Zhang FF, Tian YJ, Liu CX, Cao LC, Zhou YM (2022) Efficient remediation of cadmium contamination in soil by functionalized biochar: recent advances, challenges, and future prospects. Processes 10:1627. https://doi.org/10.3390/PR10081627
Luo SL, Wan Y, Xiao X, Guo HJ, Chen L, Xi Q, Zeng GM, Liu CB, Chen JL (2011) Isolation and characterization of endophytic bacterium LRE07 from cadmium hyperaccumulator Solanum nigrum L. and its potential for remediation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89:1637–1644. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2927-2
Mishra SP (2022) Removal of heavy metal ions from copper and zinc industrial effluents using Penicillium sp. Int J Environ Sci Technol 19:9107–9114. https://doi.org/10.1007/S13762-021-03607-5
Mohite BV, Koli SH, Patil SV (2018) Heavy metal stress and its consequences on exopolysaccharide (EPS)-producing Pantoea agglomerans. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 186:199–216. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-018-2727-1
Njoku KL, Akinyede OR, Obidi OF (2020) Microbial remediation of heavy metals contaminated media by Bacillus megaterium and Rhizopus stolonifer. Sci Afr 10:e00545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sciaf.2020.e00545
Ogbodu RO, Omorogie MO, Unuabonah EI, Babalola JO (2015) Biosorption of heavy metals from aqueous solutions by P arkia biglobosa biomass: equilibrium, kinetics, and thermodynamic studies. Environ Prog Sustain Energy 34:1694–1704. https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.12175
Omotayo RA, Jonathan OO, Renate RD (2006) A new approach to chemical modification protocols of Aspergillus niger and sorption of lead ion by fungal species. Electron J Biotechnol 9:340–348. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0717-34582006000400001
Ren ZT (2021) Study on Removal of Heavy Metals Lead and Cadmium by Penicillium sp. PC1. China University of Geosciences
Say R, Yilmaz N, Denizli A (2004) Removal of chromium(VI) ions from synthetic solutions by the fungus Penicillium purpurogenum. Eng Life Sci 4:276–280. https://doi.org/10.1002/elsc.200420032
Shi F, Liu ZG, Li JL, Gao HW, Qin S, Guo JJ (2022) Alterations in microbial community during the remediation of a black-odorous stream by acclimated composite microorganisms. J Environ Sci 118:181–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JES.2021.12.034
Sun L, Cheng XH, Li WH, Ou SO, Yang T (2015) Comparison of colony diameter diffusion method and dry weight method in optimizing the culture conditions of Hypsizygus marmoreus strain. Edible Fungi China 34:28–32. https://doi.org/10.13629/j.cnki.53-1054.2015.03.008
Sundararaju S, Manjula A, Kumaravel V, Muneeswaran T, Vennila T (2020) Biosorption of nickel ions using fungal biomass Penicillium sp. MRF1 for the treatment of nickel electroplating industrial effluent. Biomass Convers Biorefinery 12:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-020-00679-0
Tan TW, Cheng P (2003) Biosorption of metal ions with Penicillium chrysogenum. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 104:119–128. https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:104:2:119
Umair A, Huma A, Hafsa S, Muhammad B, Muhammad SMh, Muhammad S, Muhammad A, Afaq H, Nova R, Saravanan R, Muhammad M, Shiong KK (2022) Remediation techniques for elimination of heavy metal pollutants from soil: A review. Environ Res 214:113918. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENVRES.2022.113918
Wan MW, Kan CC, Rogel BD, Dalida MLp (2009) Adsorption of copper (II) and lead (II) ions from aqueous solution on chitosan-coated sand. Carbohyd Polym 80:891–899. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2009.12.048
Wang C (2015) Study on Interaction Mechanism between Bacillus atrophaeus and uranium and chromium. Southwest University of Science and Technology.
Wang JL, Chen C (2009) Biosorbents for heavy metals removal and their future. Biotechnol Adv 27:195–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2008.11.002
Wang JL, Chen C (2015) The current status of heavy metal pollution and treatment technology development in China. Environ Technol Rev 4:39–53. https://doi.org/10.1080/21622515.2015.1051136
Wang NN, Xu XJ, Li HY, Wang QY, Yuan LZ, Yu HW (2017) High performance and prospective application of xanthate-modified thiourea chitosan sponge-combined Pseudomonas putida and Talaromyces amestolkiae biomass for Pb(II) removal from wastewater. Biores Technol 233:58–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.02.069
Wang X, Li D, Gao P, Gu W, He X, Yang W, Tang W (2020) Analysis of biosorption and biotransformation mechanism of Pseudomonas chengduensis strain MBR under Cd(II) stress from genomic perspective. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 198:110655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110655
Wen Y, Leng Y, Li SW (2020) Research progress on microbial tolerance to heavy metal and its mechanism. Environ Sci Technol 43:79–86. https://doi.org/10.19672/j.cnki.1003-6504.2020.09.012
Wu SJ, Xia X, Wang D, Zhou ZJ, Wang GJ (2019) Gene function and expression regulation of RuvRCAB in bacterial Cr(VI), As(III), Sb(III), and Cd(II) resistance. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103:2701–2713. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-09666-6
Wu YJ, Ma LY, Liu QZ, Vestergard M, Topalovic O, Wang Q, Zhou QY, Huang LK, Yang XE, Feng Y (2020) The plant-growth promoting bacteria promote cadmium uptake by inducing a hormonal crosstalk and lateral root formation in a hyperaccumulator plant Sedum alfredii. J Hazard Mater 395:122661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122661
Xia L, Xu XJ, Zhu W, Huang QY, Chen WL (2015) A comparative study on the biosorption of Cd2+ onto Paecilomyces lilacinus XLA and Mucoromycote sp. XLC Int J Mol Sci 16:15670–15687. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160715670
Xu Z, Dong M, Peng X, Ku W, Zhao Y, Yang G (2019) New insight into the molecular basis of cadmium stress responses of wild paper mulberry plant by transcriptome analysis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 171:301–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.12.084
Yang TY, Tian J, Zhang MX, Zhang L (2019) Ion beam mutagenesis and phosphate solubilizing mechanism on PSF YTH isolated from rhizospheric soil. J Nucl Agric Sci 33:1072–1078. https://doi.org/10.27327/d.cnki.gshnu.2019.000230
Yao Y, Hu L, Li SZ, Zeng Q, Zhong H, He ZG (2020) Exploration on the bioreduction mechanisms of Cr(VI) and Hg(II) by a newly isolated bacterial strain Pseudomonas umsongensis CY-1. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 201:110850. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.110850
Zhang WL, Lei MT, Li Y, Wang PF, Wang C, Gao Y, Wu HN, Xu C, Niu LH, Wang LF, Zhang HJ (2019) Determination of vertical and horizontal assemblage drivers of bacterial community in a heavily polluted urban river. Water Res 161:98–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2019.05.107
Zhang YJ, Du L, Xie JL (2021) Study on the ability of Lactobacillus plantarum X7021 in the adsorption heavy metals and degradation of nitrite. J Food Saf Qual 12:4786–4792. https://doi.org/10.19812/j.cnki.jfsq11-5956/ts.2021.12.012
Zhao XF, He YF, Li C (2021) Study on adsorption characteristics of a lead-tolerant lactic acid bacteria. J Chinese Inst Food Sci Technol 21:58–64. https://doi.org/10.16429/j.1009-7848.2021.01.007
Zhao D, Li CY, Zheng MX, Zhao YL, Xu ZG, Yang GY (2022) Curvularia coatesiae XK8, a potential bioadsorbent material for adsorbing Cd(II) and Sb(III) compound pollution: characteristics and effects. Front Microbiol 12:816312. https://doi.org/10.3389/FMICB.2021.816312
Zheng XC, Yan YR, Luo W, Tang J (2021) Preparation of CS/PVA microspheres and their adsorption of heavy metal ions. Saf Environ Eng 28:196–203. https://doi.org/10.13578/j.cnki.issn.1671-1556.2021.02.026
Zhou YP (2022) Microorganisms also have different tolerances to different heavy metals. Shandong Jianzhu University
Ziagova M, Dimitriadis G, Aslanidou D, Papaioannou X, Litopoulou TE, Liakopoulou-Kyriakides M (2007) Comparative study of Cd(II) and Cr(VI) biosorption on Staphylococcus xylosus and Pseudomonas sp. in single and binary mixtures. Biores Technol 98:2859–2865. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2006.09.043
Funding
This study was supported by the Key Projects of National Forestry and Grassland Bureau (201801), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2020M682602), and Longnan Socially Funded Science and Technology Plan Project (2022-S·SZ-03). The funding bodies played no role in the design of the study and collection, analysis, and interpretation of data and in writing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by DJ, LC, SY, and HH. The data analysis and original writing were completed by DJ. XZ, MY, and ZY completed the revision and review of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Communicated by Yusuf Akhter.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jingyi, D., Chaoyang, L., Yu, S. et al. Adsorption capacity of Penicillium amphipolaria XK11 for cadmium and antimony. Arch Microbiol 205, 139 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-023-03484-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-023-03484-1