Abstract
Key message
A novel QTL qGLF5 from Oryza rufipogon Griff. improves yield per plant and plant architecture in rice.
Abstract
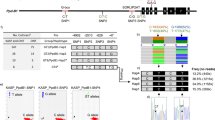
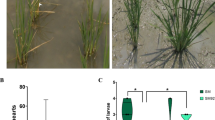
Kernel size and plant architecture are critical agronomic traits that are key targets for improving crop yield. From the single-segment substitution lines of Oryza rufipogon Griff. in the indica cultivar Huajingxian74 (HJX74) background, we identified a novel quantitative trait locus (QTL), named qGLF5, which improves kernel shape, plant architecture, and yield per plant in rice. Compared with the control HJX74, the plant height, panicles per plant, panicle length, primary branches per panicle, secondary branches per panicle, and kernels per plant of the near-isogenic line-qGLF5 (NIL-qGLF5) are significantly increased. NIL-qGLF5 has long and narrow kernels by regulating cell number, cell length and width in the spikelet hulls. Yield per plant of NIL-qGLF5 is increased by 35.02% compared with that of HJX74. In addition, qGLF5 significantly improves yield per plant and plant architecture of NIL-gw5 and NIL-GW7. These results indicate that qGLF5 might be beneficial for improving plant architecture and kernel yield in rice breeding by molecular design.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arseneau JR, Steeves R, Laflamme M (2017) Modified low-salt CTAB extraction of high-quality DNA from contaminant-rich tissues. Mol Ecol Resour 17(4):686–693. https://doi.org/10.1111/1755-0998.12616
Ashikari M, Sakakibara H, Lin SY, Yamamoto T, Takashi T, Nishimura A, Angeles ER, Qian Q, Kitano H, Matsuoka M (2005) Cytokinin oxidase regulates rice grain production. Science 309(5735):741–745. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1113373
Cao ZB, Tang HW, Cai YH, Zeng BH, Zhao JL, Tang XY, Lu M, Wang HM, Zhu XJ, Wu XF, Yuan LF, Wan JL (2022) Natural variation of HTH5 from wild rice, Oryza rufipogon Griff., is involved in conferring high-temperature tolerance at the heading stage. Plant Biotechnol J 20(8):1591–1605. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.13835
Duan PG, Ni S, Wang JM, Zhang BL, Xu R, Wang YX, Chen HQ, Zhu XD, Li YH (2016) Regulation of OsGRF4 by OsmiR396 controls grain size and yield in rice. Nat Plants 2(1):1038. https://doi.org/10.1038/nplants.2015.203
Eshed Y, Zamir D (1995) An introgression line population of Lycopersicon pennellii in the cultivated tomato enables the identification and fine mapping of yield-associated QTL. Genetics 141(3):1147–1162. https://doi.org/10.1093/genetics/141.3.1147
Fan YW, Li YB (2019) Molecular, cellular and Yin-Yang regulation of grain size and number in rice. Mol Breeding 39(12):163. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-019-1078-0
Hao JQ, Wang DK, Wu YB, Huang K, Duan PG, Li N, Xu R, Zeng DL, Dong GJ, Zhang BL, Zhang LM, Inze D, Qian Q, Li YH (2021) The GW2-WG1-OsbZIP47 pathway controls grain size and weight in rice. Mol Plant 14(8):1266–1280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2021.04.011
He Y, Li LY, Shi WB, Tan JH, Luo XX, Zheng SY, Chen WT, Li J, Zhuang CX, Jiang DG (2022) Florigen repression complexes involving rice CENTRORADIALIS2 regulate grain size. Plant Physiol 190(2):1260–1274. https://doi.org/10.1093/plphys/kiac338
Hu J, Wang YX, Fang YX, Zeng LJ, Xu J, Yu HP, Shi ZY, Pan JJ, Zhang D, Kang SJ, Zhu L, Dong GJ, Guo LB, Zeng DL, Zhang GH, Xie LH, Xiong GS, Li JY, Qian Q (2015) A rare allele of gs2 enhances grain size and grain yield in rice. Mol Plant 8(10):1455–1465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2015.07.002
Jiang HZ, Zhang AP, Liu XT, Chen JG (2022) Grain size associated genes and the molecular regulatory mechanism in rice. Int J Mol Sci 23(6):3169. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23063169
Jiao YQ, Wang YH, Xue DW, Wang J, Yan MX, Liu GF, Dong GJ, Zeng DL, Lu ZF, Zhu XD, Qian Q, Li JY (2010) Regulation of OsSPL14 by OsmiR156 defines ideal plant architecture in rice. Nat Genet 42(6):541-U536. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.591
Jin J, Huang W, Gao JP, Yang J, Shi M, Zhu MZ, Luo D, Lin HX (2008) Genetic control of rice plant architecture under domestication. Nat Genet 40(11):1365–1369. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.247
Kaur P, Neelam K, Sarao PS, Babbar A, Kumar K, Vikal Y, Khanna R, Kaur R, Mangat GS, Singh K (2022) Molecular mapping and transfer of a novel brown planthopper resistance gene bph42 from Oryza rufipogon (Griff.) To cultivated rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Biol Rep 49(9):8597–8606. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07692-8
Li N, Li YH (2016) Signaling pathways of seed size control in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 33:23–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2016.05.008
Li YB, Fan CC, Xing YZ, Jiang YH, Luo LJ, Sun L, Shao D, Xu CJ, Li XH, Xiao JH, He YQ, Zhang QF (2011) Natural variation in GS5 plays an important role in regulating grain size and yield in rice. Nat Genet 43(12):1266. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.977
Li N, Xu R, Li YH (2019) Molecular networks of seed size control in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 70:435–463. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-050718-095851
Li ZY, Wei XJ, Tong XH, Zhao J, Liu XX, Wang HM, Tang LQ, Shu YZ, Li GH, Wang YF, Ying JZ, Jiao GA, Hu HH, Hu PS, Zhang J (2022) The OsNAC23-Tre6P-SnRK1a feed-forward loop regulates sugar homeostasis and grain yield in rice. Mol Plant 15(4):706–722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2022.01.016
Li Y, Wu S, Huang Y, Ma X, Tan L, Liu F, Lv Q, Zhu Z, Hu M, Fu Y, Zhang K, Gu P, Xie D, Sun H, Sun C (2023) OsMADS17 simultaneously increases grain number and grain weight in rice. Nat Commun 14(1):3098. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-38726-9
Lin SJ, Liu ZP, Zhang K, Yang WF, Zhan PL, Tan QY, Gou YJ, Ma SP, Luan X, Huang CB, Xiao ZL, Liu YY, Zhu BH, Liang RQ, Zhou WQ, Zhu HT, Bu SH, Liu GF, Zhang GQ, Wang SK (2023) GL9 from Oryza glumaepatula controls grain size and chalkiness in rice. Crop J 11(1):198–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2022.06.006
Liu JF, Chen J, Zheng XM, Wu FQ, Lin QB, Heng YQ, Tian P, Cheng ZJ, Yu XW, Zhou KN, Zhang X, Guo XP, Wang JL, Wang HY, Wan JM (2017) GW5 acts in the brassinosteroid signalling pathway to regulate grain width and weight in rice. Nat Plants 3(5):17043. https://doi.org/10.1038/nplants.2017.43
Liu ZP, Chen G, Gao F, Xu R, Li N, Zhang YY, Li YH (2019) Transcriptional repression of the APC/C activator genes CCS52A1/A2 by the mediator complex subunit MED16 controls endoreduplication and cell growth in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 31(8):1899–1912. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00811
Liu ZP, Li N, Zhang YY, Li YH (2020) Transcriptional repression of GIF1 by the KIX-PPD-MYC repressor complex controls seed size in Arabidopsis. Nat Commun 11(1):1846. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-15603-3
Lyu J, Wang DK, Duan PG, Lu YP, Huang K, Zeng DL, Zhang LM, Dong GJ, Li YJ, Xu R, Zhang BL, Huang XH, Li N, Wang YC, Qian Q, Li YH (2020) Control of grain size and weight by the GSK2-LARGE1/OML4 pathway in rice. Plant Cell 32(6):1905–1918. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.19.00468
Mao HL, Sun SY, Yao JL, Wang CR, Yu SB, Xu CG, Li XH, Zhang QF (2010) Linking differential domain functions of the GS3 protein to natural variation of grain size in rice. P Natl Acad Sci USA 107(45):19579–19584. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1014419107
Miura K, Ikeda M, Matsubara A, Song XJ, Ito M, Asano K, Matsuoka M, Kitano H, Ashikari M (2010) OsSPL14 promotes panicle branching and higher grain productivity in rice. Nat Genet 42(6):545-U102. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.592
Rangan GK, Tesch GH (2007) Quantification of renal pathology by image analysis. Nephrology 12(6):553–558. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1797.2007.00855.x
Ren DY, Ding CQ, Qian Q (2023) Molecular bases of rice grain size and quality for optimized productivity. Sci Bull 68(3):314–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scib.2023.01.026
Shan JX, Zhu MZ, Shi M, Gao JP, Lin HX (2009) Fine mapping and candidate gene analysis of spd6, responsible for small panicle and dwarfness in wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.). Theor Appl Genet 119(5):827–836. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-009-1092-4
Si LZ, Chen JY, Huang XH, Gong H, Luo JH, Hou QQ, Zhou TY, Lu TT, Zhu JJ, Shangguan YY, Chen EW, Gong CX, Zhao Q, Jing YF, Zhao Y, Li Y, Cui LL, Fan DL, Lu YQ, Weng QJ, Wang YC, Zhan QL, Liu KY, Wei XH, An K, An G, Han B (2016) OsSPL13 controls grain size in cultivated rice. Nat Genet 48(4):447. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3518
Song XJ, Huang W, Shi M, Zhu MZ, Lin HX (2007) A QTL for rice grain width and weight encodes a previously unknown RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase. Nat Genet 39(5):623–630. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng2014
Song XG, Meng XB, Guo HY, Cheng Q, Jing YH, Chen MJ, Liu GF, Wang B, Wang YH, Li JY, Yu H (2022) Targeting a gene regulatory element enhances rice grain yield by decoupling panicle number and size. Nat Biotechnol 40(9):1403. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-022-01281-7
Sun XM, Xiong HY, Jiang CH, Zhang DM, Yang ZL, Huang YP, Zhu WB, Ma SS, Duan JZ, Wang X, Liu W, Guo HF, Li GL, Qi JW, Liang CB, Zhang ZY, Li JJ, Zhang HL, Han LJ, Zhou YH, Peng YL, Li ZC (2022) Natural variation of DROT1 confers drought adaptation in upland rice. Nat Commun 13(1):4265. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-31844-w
Tan LB, Li XR, Liu FX, Sun XY, Li CG, Zhu ZF, Fu YC, Cai HW, Wang XK, Xie DX, Sun CQ (2008) Control of a key transition from prostrate to erect growth in rice domestication. Nat Genet 40(11):1360–1364. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.197
Tan QY, Bu SH, Chen GD, Yan ZG, Chang ZY, Zhu HT, Yang WF, Zhan PL, Lin SJ, Xiong L, Chen SL, Liu GF, Liu ZP, Wang SK, Zhang GQ (2022) Reconstruction of the high stigma exsertion rate trait in rice by pyramiding multiple QTLs. Front Plant Sci 13:921700. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.921700
Wang SK, Li S, Liu Q, Wu K, Zhang JQ, Wang SS, Wang Y, Chen XB, Zhang Y, Gao CX, Wang F, Huang HX, Fu XD (2015) The OsSPL16-GW7 regulatory module determines grain shape and simultaneously improves rice yield and grain quality. Nat Genet 47(8):949. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3352
Xi ZY, He FH, Zeng RZ, Zhang ZM, Ding XH, Li WT, Zhang GQ (2006) Development of a wide population of chromosome single-segment substitution lines in the genetic background of an elite cultivar of rice (Oryza sativa L). Genome 49(5):476–484. https://doi.org/10.1139/G06-005
Xing YZ, Zhang QF (2010) Genetic and molecular bases of rice yield. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61(61):421–442. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-042809-112209
Xue WY, Xing YZ, Weng XY, Zhao Y, Tang WJ, Wang L, Zhou HJ, Yu SB, Xu CG, Li XH, Zhang QF (2008) Natural variation in Ghd7 is an important regulator of heading date and yield potential in rice. Nat Genet 40(6):761–767. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.143
Yang W, Xiong L, Liang J, Hao Q, Luan X, Tan Q, Lin S, Zhu H, Liu G, Liu Z, Bu S, Wang S, Zhang G (2021a) Substitution mapping of two closely linked QTLs on chromosome 8 controlling grain chalkiness in rice. Rice (n Y) 14(1):85. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12284-021-00526-4
Yang WF, Liang JY, Hao QW, Luan X, Tan QY, Lin SW, Zhu HT, Liu GF, Liu ZP, Bu SH, Wang SK, Zhang GQ (2021b) Fine mapping of two grain chalkiness QTLs sensitive to high temperature in rice. Rice 14(1):33. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12284-021-00476-x
Yang WF, Hao QW, Liang JY, Tan QY, Luan X, Lin SJ, Zhu HT, Bu SH, Liu ZP, Liu GF, Wang SK, Zhang GQ (2022) Fine Mapping of two major quantitative trait loci for rice chalkiness With high temperature-enhanced additive effects. Front Plant Sci 13:957863. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.957863
Zhan PL, Ma SP, Xiao ZL, Li FP, Wei X, Lin SJ, Wang XL, Ji Z, Fu Y, Pan JH, Zhou M, Liu Y, Chang ZY, Li L, Bu SH, Liu ZP, Zhu HT, Liu GF, Zhang GQ, Wang SK (2022) Natural variations in grain length 10 (GL10) regulate rice grain size. J Genet Genomics 49(5):405–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgg.2022.01.008
Zhang GQ (2019) The platform of breeding by design based on the SSSL library in rice. Yi Chuan 41(8):754–760. https://doi.org/10.16288/j.yczz.19-105
Zhang GQ (2021) Target chromosome-segment substitution: a way to breeding by design in rice. Crop J 9(3):658–668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2021.03.001
Zhang XJ, Wang JF, Huang J, Lan HX, Wang CL, Yin CF, Wu YY, Tang HJ, Qian Q, Li JY, Zhang HS (2012) Rare allele of OsPPKL1 associated with grain length causes extra-large grain and a significant yield increase in rice. P Natl Acad Sci USA 109(52):21534–21539. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1219776110
Funding
This research was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (2023A1515012083), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32201742), the Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangzhou (2023A04J1962), the double first-class discipline promotion project (2021B10564001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YJ Wang and XY Liang conducted most of the experiments. GY Gong, HY Zhao, ZW Zheng, CH Wang, HT Zhu, and JY Huang took part in the experiments. Z Li, SH Bu, and GF Liu: Data analysis, review, and editing. GQ Zhang: Conceptualization, resources, review, and editing; ZP Liu and SK Wang: Conceptualization, project administration, data analysis, resources, supervision, writing, review, and editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Additional information
Communicated by Takuji Sasaki.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Liang, X., Gong, G. et al. qGLF5 from Oryza rufipogon Griff. improves kernel shape, plant architecture, and yield in rice. Theor Appl Genet 136, 225 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-023-04478-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-023-04478-9