Abstract
Key message
A stable QTL qSalt-A04-1 for salt tolerance in the cotton seed germination stage, and two candidate genes, GhGASA1 and GhADC2, that play negative roles by modulating the GA and PA signalling pathways, respectively, were identified.
Abstract
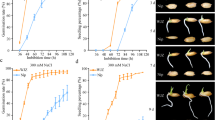
The successful transition of a seed into a seedling is a prerequisite for plant propagation and crop yield. Germination is a vulnerable stage in a plant’s life cycle that is strongly affected by environmental conditions, such as salinity. In this study, we identified a novel quantitative trait locus (QTL) qRGR-A04-1 associated with the relative germination rate (RGR) after salt stress treatment based on a high-density genetic map under phytotron and field conditions, with LOD values that ranged from 6.65 to 16.83 and 6.11–12.63% phenotypic variations in all five environmental tests. Two candidate genes with significantly differential expression between the two parents were finally identified through RNA-seq and qRT-PCR analyses. Further functional analyses showed that GhGASA1- and GhADC2-overexpression lines were more sensitive to salt stress than wild-type Arabidopsis based on the regulation of the transcript levels of gibberellic acid (GA)- and polyamine (PA)- related genes in GA and PA biosynthesis and the reduction in the accumulation of GA and PA, respectively, under salt stress. Virus-induced gene silencing analysis showed that TRV:GASA1 and TRV:ADC2 were more tolerant to salt stress than TRV:00 based on the increased expression of GA synthesis genes and decreased H2O2 content, respectively. Taken together, our results suggested that QTL qRGR-A04-1 and its two harboured genes, GhGASA1 and GhADC2, are promising candidates for salt tolerance improvement in cotton.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashraf M, Foolad MR (2013) Crop breeding for salt tolerance in the era of molecular markers and marker-assisted selection. Plant Breed 132:10–20. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbr.12000
Biswas MS, Mano J (2015) Lipid peroxide-derived short-chain carbonyls mediate hydrogen peroxide-induced and salt-induced programmed cell death in plants. Plant Physiol 168:885–898. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.115.256834
Cai CP, Zhu GZ, Zhang TZ, Guo WZ (2017) High-density 80 K SNP array is a powerful tool for genotyping G. hirsutum accessions and genome analysis. BMC Genomics 18:654. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-017-4062-2
Clough SJ, Ben AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16:735–743. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313x.1998.00343.x
Diouf L, Pan Z, He SP, Gong WF, Jia YH, Magwanga RO, Romy KRE, Or Rashid H, Kirungu JN, Du X (2017) High-density linkage map construction and mapping of salt-tolerant QTLs at seedling stage in upland cotton using genotyping by sequencing (GBS). Int J Mol Sci 18:2622. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122622
Diouf L, Magwanga RO, Gong WF, He SP, Pan ZE, Jia YH, Kirungu JN, Du XM (2018) QTL mapping of fiber quality and yield-related traits in an intra-specific upland cotton using genotype by sequencing (GBS). Int J Mol Sci 19:441. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020441
Farooq M, Gogoi N, Barthakur S, Baroowa B, Bharadwaj N, Alghamdi SS, Siddique KHM (2017) Drought stress in grain legumes during reproduction and grain filling. J Agron Crop Sci 203:81–102. https://doi.org/10.1111/jac.12169
Gao X, Shan L (2013) Functional genomic analysis of cotton genes with agrobacterium-mediated virus-induced gene silencing. Methods Mol Biol 975:157–165. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-62703-278-0_12
Gu QS, Ke HF, Liu ZW, Lv X, Sun ZW, Zhang M, Chen LT, Yang J, Zhang Y, Wu LQ, Li ZK, Wu JH, Wang GN, Meng CS, Zhang GY, Wang XF, Ma ZY (2020) A high-density genetic map and multiple environmental tests reveal novel quantitative trait loci and candidate genes for fibre quality and yield in cotton. Theor Appl Genet 133:3395–3408. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-020-03676-z
Hamwieh A, Tuyen DD, Cong H, Benitez ER, Takahashi R, Xu DH (2011) Identification and validation of a major QTL for salt tolerance in soybean. Euphytica 179:451–459. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-011-0347-8
Han J, Shi J, Zeng L, Xu J, Wu L (2015) Effects of nitrogen fertilization on the acidity and salinity of greenhouse soils. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:2976–2986. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3542-z
Hu Y, Chen JD, Fang L, Zhang ZY, Ma W, Niu YC, Ju LZ, Deng JQ, Zhao T, Lian JM, Baruch K, Fang D, Liu X, Ruan YL, Rahman MU, Han JL, Wang K, Wang Q, Wu HT, Mei GF, Zang YH, Han ZG, Xu CY, Shen WJ, Yang DF, Si ZF, Dai F, Zou LF, Huang F, Bai YL, Zhang YG, Brodt A, Ben-Hamo H, Zhu XF, Zhou BL, Guan XY, Zhu SJ, Chen XY, Zhang TZ (2019) Gossypium barbadense and Gossypium hirsutum genomes provide insights into the origin and evolution of allotetraploid cotton. Nat Genet 51:739–748. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-019-0371-5
Huang ZB, Sun ZJ, Lu ZH (2013) Effects of soil amendments on coastal saline-alkali soil improvement and the growth of plants. Adv Mater Res 634–638:152–159
Jiang ZM, Xu G, Jing YJ, Tang WJ, Lin RC (2016) Phytochrome B and REVEILLE1/2-mediated signalling controls seed dormancy and germination in Arabidopsis. Nat Commun 7:12377. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms12377
Kubiś J, Floryszak-Wieczorek J, Arasimowicz-Jelonek M (2013) Polyamines induce adaptive responses in water deficit stressed cucumber roots. J Plant Res 127:151–158. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-013-0585-z
Liu JH, Wang W, Wu H, Gong XQ, Moriguchi T (2015) Polyamines function in stress tolerance: from synthesis to regulation. Front Plant Sci 6:827. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00827
Luo XB, Xu L, Wang Y, Dong JH, Chen YL, Tang MJ, Fan LX, Zhu YL, Liu LW (2019) An ultra-high density genetic map provides insights into genome synteny, recombination landscape and taproot skin color in radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Plant Biotechnol J 18:274–286. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.13195
Ma ZY, He SP, Wang XF, Sun JL, Zhang Y, Zhang GY, Wu LQ, Li ZK, Liu ZH, Sun GF, Yan YY, Jia YH, Yang J, Pan ZE, Gu QS, Li XY, Sun ZW, Dai PH, Liu ZW, Gong WF, Wu JH, Wang M, Liu HW, Feng KY, Ke HF, Wang JD, Lan HY, Wang GN, Peng J, Wang N, Wang LR, Pang BY, Peng Z, Li RQ, Tian SL, Du XM (2018) Resequencing a core collection of upland cotton identifies genomic variation and loci influencing fiber quality and yield. Nat Genet 50:803–813. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-018-0119-7
Ma JJ, Pei WF, Ma QF, Geng YH, Liu GY, Liu J, Cui YP, Zhang X, Wu M, Li XL, Li D, Zang XS, Song JK, Tang SR, Zhang JF, Yu SX, Yu JW (2019) QTL analysis and candidate gene identification for plant height in cotton based on an interspecific backcross inbred line population of Gossypium hirsutum × Gossypium barbadense. Theor Appl Genet 132:2663–2676. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-019-03380-7
Millar AA, Jacobsen JV, Ross JJ, Helliwell CA, Poole AT, Scofield G, Reid JB, Gubler F (2006) Seed dormancy and ABA metabolism in Arabidopsis and barley: the role of ABA 8′-hydroxylase. Plant J 45:942–954. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02659.x
Mo HJ, Wang XF, Zhang Y, Zhang GY, Zhang JF, Ma ZY (2015) Cotton polyamine oxidase is required for spermine and camalexin signalling in the defence response toVerticillium dahliae. Plant J 83:962–975. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12941
Moschou PN, Delis ID, Paschalidis KA, Roubelakis-Angelakis KA (2008) Transgenic tobacco plants overexpressing polyamine oxidase are not able to cope with oxidative burst generated by abiotic factors. Physiol Plant 133:140–156. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-3054.2008.01049.x
Munns R, Tester M (2008) Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:651–681. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.59.032607.092911
Nahirñak V, Almasia NI, Hopp HE, Vazquez-Rovere C (2012) Snakin/GASA proteins: involvement in hormone crosstalk and redox homeostasis. Plant Signal Behav 7:1004–1008. https://doi.org/10.4161/psb.20813
Oluoch G, Zheng JY, Wang XX, Khan MKR, Zhou ZL, Cai XY, Wang CY, Wang YH, Li XY, Wang H, Liu F, Wang KB (2016) QTL mapping for salt tolerance at seedling stage in the interspecific cross of Gossypium tomentosum with Gossypium hirsutum. Euphytica 209:223–235. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-016-1674-6
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29:45–50. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/29.9.e45
Poland JA, Bradbury PJ, Buckler ES, Nelson RJ (2011) Genome-wide nested association mapping of quantitative resistance to northern leaf blight in maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:6893–6898. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1010894108
Roy SJ, Negrao S, Tester M (2014) Salt resistant crop plants. Curr Opin Biotechnol 26:115–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2013.12.004
Shu K, Liu XD, Xie Q, He ZH (2015) Two faces of one seed: hormonal regulation of dormancy and germination. Mol Plant 9:34–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2015.08.010
Sun ZW, Wang XF, Liu ZW, Gu QS, Zhang Y, Li ZK, Ke HF, Yang J, Wu JH, Wu LQ, Zhang GY, Zhang CY, Ma ZY (2017) Genome-wide association study discovered genetic variation and candidate genes of fibre quality traits in Gossypium hirsutum L. Plant Biotechnol J 15:982–996. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12693
Sun ZW, Li HL, Zhang Y, Li ZK, Ke HF, Wu LQ, Zhang GY, Wang XF, Ma ZY (2018) Identification of SNPs and candidate genes associated with salt tolerance at the seedling stage in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Front Plant Sci 9:1011. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01011
Urano K, Yoshiba Y, Nanjo T, Ito T, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (2004) Arabidopsis stress-inducible gene for arginine decarboxylase AtADC2 is required for accumulation of putrescine in salt tolerance. Bioph Res Co 313:369–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2003.11.119
Wang W, Vinocur B, Altman A (2003) Plant responses to drought, salinity and extreme temperatures: towards genetic engineering for stress tolerance. Planta 218:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-003-1105-5
Wang S, Basten CJ, Zeng ZB (2011) Windows QTL Cartographer 2.5. North Carolina State University, Department of statistics, Raleigh
Wang MJ, Tu LL, Yuan DJ, Zhu D, Shen C, Li JY, Liu FY, Pei LL, Wang PC, Zhao GN, Ye ZX, Huang H, Yan FL, Ma YZ, Zhang L, Liu M, You JQ, Yang YC, Liu ZP, Huang F, Li BQ, Qiu P, Zhang QH, Zhu LF, Jin SX, Yang XY, Min L, Li GL, Chen LL, Zheng HK, Lindsey K, Lin ZX, Udall JA, Zhang XL (2018) Reference genome sequences of two cultivated allotetraploid cottons, Gossypium hirsutum and Gossypium barbadense. Nat Genet 52:224–229. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-018-0282-x
Wu H, Fu B, Sun PP, Xiao C, Liu JH (2016) A NAC transcription factor represses putrescine biosynthesis and affects drought tolerance1. Plant Physiol 172:1532–1547. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.16.01096
Yamaguchi S (2008) Gibberellin metabolism and its regulation. Annu Rev Plant Biol 59:225–251. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.arplant.59.032607.092804
Yano K, Yamamoto E, Aya K, Takeuchi H, Lo PC, Hu L, Yamasaki M, Yoshida S, Kitano H, Hirano K, Matsuoka M (2016) Genome-wide association study using whole-genome sequencing rapidly identifies new genes influencing agronomic traits in rice. Nat Genet 48:927–934. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3596
Zhang TZ, Hu Y, Jiang WK, Fang L, Guan XY, Chen JD, Zhang JB, Saski CA, Scheffler BE, Stelly DM, Hulse-Kemp AM, Wan Q, Liu BL, Liu CX, Wang S, Pan MQ, Wang YK, Wang DW, Ye WX, Chang LJ, Zhang WP, Song QX, Kirkbride RC, Chen XY, Dennis E, Llewellyn DJ, Peterson DG, Thaxton P, Jones DC, Wang Q, Xu XY, Zhang H, Wu HT, Zhou L, Mei GF, Chen SQ, Tian Y, Xiang D, Li XH, Ding J, Zuo QY, Tao LN, Liu YC, Li J, Lin Y, Hui YY, Cao ZS, Cai CP, Zhu XF, Jiang Z, Zhou BL, Guo WZ, Li RQ, Chen ZJ (2015) Sequencing of allotetraploid cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L. acc. TM-1) provides a resource for fiber improvement. Nat Biotechnol 33:531–537. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.3207
Zhou JH, Li ZY, Xiao GQ, Zhai MJ, Pan XW, Huang RF, Zhang HW (2020) CYP71D8L is a key regulator involved in growth and stress responses by mediating gibberellin homeostasis in rice. J Exp Bot 71:1160–1170. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erz491
Zhu T, Liang CZ, Meng ZG, Sun GQ, Meng ZH, Guo SD, Zhang R (2017) CottonFGD: an integrated functional genomics database for cotton. BMC Plant Biol 17:9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-017-1039-x
Acknowledgments
We thank Professor Tianzhen Zhang of Zhejiang University for releasing RNA-seq data.
Funding
This work was supported by the Fund of the Science and Technology Support Programme of Hebei Province (16226307D) and the Top Talent Fund of Hebei Province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZM designed the research; QG, HK, CL, XL, ZS, ZL, WR, JY, YZ, LW, GZ, XW performed experiments; QG, XW analyzed data; QG wrote the manuscript; ZM, XW revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of intersts.
Ethical approval
The experiments were performed in compliance with the current laws of China.
Additional information
Communicated by Tianzhen Zhang.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, Q., Ke, H., Liu, C. et al. A stable QTL qSalt-A04-1 contributes to salt tolerance in the cotton seed germination stage. Theor Appl Genet 134, 2399–2410 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-021-03831-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-021-03831-0