Abstract
Key message
Map-based cloning identified GmHAD1, a gene which encodes a HAD-like acid phosphatase, associated with soybean tolerance to low phosphorus stress.
Abstract
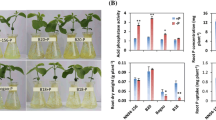
Phosphorus (P) deficiency in soils is a major limiting factor for crop growth worldwide. Plants may adapt to low phosphorus (LP) conditions via changes to root morphology, including the number, length, orientation, and branching of the principal root classes. To elucidate the genetic mechanisms for LP tolerance in soybean, quantitative trait loci (QTL) related to root morphology responses to LP were identified via hydroponic experiments. In total, we identified 14 major loci associated with these traits in a RIL population. The log-likelihood scores ranged from 2.81 to 7.43, explaining 4.23–13.98% of phenotypic variance. A major locus on chromosome 08, named qP8-2, was co-localized with an important P efficiency QTL (qPE8), containing phosphatase genes GmACP1 and GmACP2. Another major locus on chromosome 10 named qP10-2 explained 4.80–13.98% of the total phenotypic variance in root morphology. The qP10-2 contains GmHAD1, a gene which encodes an acid phosphatase. In the transgenic soybean hairy roots, GmHAD1 overexpression increased P efficiency by 8.4–16.5% relative to the control. Transgenic Arabidopsis plants had higher biomass than wild-type plants across both short- and long-term P reduction. These results suggest that GmHAD1, an acid phosphatase gene, improved the utilization of organic phosphate by soybean and Arabidopsis plants.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- APA:
-
Acid phosphatase activity
- cv.:
-
Cultivar
- CIM:
-
Composite interval mapping method
- LOD:
-
Log-likelihood
- QTL:
-
Quantitative trait loci
- RIL:
-
Recombinant inbred line
- RAD-seq:
-
Restriction-site-associated DNA sequencing
- SNP:
-
Single nucleotide polymorphism
- MAS:
-
Marker-assisted selection
- RSA:
-
Root system architecture
- LP:
-
Low phosphorus
- HAD:
-
Haloacid dehalogenase
- ρ-NPP:
-
ρ-Nitrophenol phosphate
References
Abdel-Haleem H, Lee GJ, Boerma RH (2011) Identification of QTL for increased fibrous roots in soybean. Theor Appl Genet 122(5):935–946
Ahsan M, Wright D, Virk DS (1996) Genetic analysis of salt tolerance in spring wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Cereal Res Commun 24:353–360
Baldwin JC, Karthikeyan AS, Raghothama KG (2001) LEPS2, a phosphorus starvation-induced novel acid phosphatase from tomato. Plant Physiol 125(2):728–737
Baldwin JC, Karthikeyan AS, Cao A et al (2008) Biochemical and molecular analysis of LePS2; 1: a phosphate starvation induced protein phosphatase gene from tomato. Planta 228(2):273
Barriga P, Marambio E (1995) Gene action and components of genetic variation of phosphorus content and phosphorus efficiency utilization in wheat. Agro Sur (Chile) 23:30–38
Cai Z, Cheng Y, Ma Z et al (2017) Fine-mapping of QTLs for individual and total isoflavone content in soybean (Glycine max L.) using a high-density genetic map. Theor Appl Genet 131(3):555–568
Cheng F, Cao G, Wang X et al (2008) The discovery and application of the efficient strains of soybean rhizobia in the acid low phosphorus soil in south China. Chin Sci Bull 23:2903–2910
Cheng Y, Ma Q, Ren H et al (2017) Fine mapping of a Phytophthora-resistance gene RpsWY in soybean (Glycine max L.) by high-throughput genome-wide sequencing. Theor Appl Genet 130(5):1041–1051
Chin JH, Gamuyao R, Dalid C et al (2011) Developing rice with high yield under phosphorus deficiency: Pup1 sequence to application. Plant Physiol 156(3):1202–1216
Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16(6):735–743
Cordell D, White S (2011) Peak phosphorus: clarifying the key issues of a vigorous debate about long-term phosphorus security. Sustainability 3(10):2027–2049
Elser JJ (2012) Phosphorus: a limiting nutrient for humanity? Curr Opin Biotechnol 23(6):833–838
FAO (2015) World fertilizer trends and outlook to 2018. http://www.fao.org/3/a-i4324e.pdf. Accessed 16 Feb 2015
Furlani AMC, Lima M, Nass LL (1998) Combining ability effects for P-efficiency characters in maize grown in low P nutrient [Zea mays L.-phosphorus]. Maydica (Italy) 43:169–174
Gamuyao R, Chin JH, Pariasca-Tanaka J et al (2012) The protein kinase Pstol1 from traditional rice confers tolerance of phosphorus deficiency. Nature 488(7412):535–539
Gao H, Bhattacharyya MK (2008) The soybean-Phytophthora resistance locus Rps1-k encompasses coiled coil-nucleotide binding-leucine rich repeat-like genes and repetitive sequences. BMC Plant Biol 8(1):29
Gaxiola RA, Sanchez CA, Paez-Valencia J et al (2012) Genetic manipulation of a “vacuolar” H+-PPase: from salt tolerance to yield enhancement under phosphorus-deficient soils. Plant Physiol 159(1):3–11
Geng X, Horst WJ, Golz JF et al (2017) LEUNIG_HOMOLOG transcriptional corepressor mediates aluminium sensitivity through PECTIN METHYLESTERASE46 modulated root cell wall pectin methylesterification in Arabidopsis. Plant J 90(3):491–504
Gohla A, Birkenfeld J, Bokoch GM (2005) Chronophin, a novel HAD-type serine protein phosphatase, regulates cofilin-dependent actin dynamics. Nat Cell Biol 7(1):21–29
Gutierrez-Gonzalez JJ, Wu X, Zhang J et al (2009) Genetic control of soybean seed isoflavone content: importance of statistical model and epistasis in complex traits. Theor Appl Genet 119(6):1069–1083
Gutierrez-Gonzalez JJ, Wu X, Gillman JD et al (2010) Intricate environment-modulated genetic networks control isoflavone accumulation in soybean seeds. BMC Plant Biol 10(1):105
Gutierrez-Gonzalez JJ, Vuong TD, Zhong R et al (2011) Major locus and other novel additive and epistatic loci involved in modulation of isoflavone concentration in soybean seeds. Theor Appl Genet 123(8):1375–1385
Haling RE, Brown LK, Bengough AG et al (2013) Root hairs improve root penetration, root–soil contact, and phosphorus acquisition in soils of different strength. J Exp Bot 64(12):3711–3721
Hufnagel B, de Sousa SM, Assis L et al (2014) Duplicate and conquer: multiple homologs of PHOSPHORUS-STARVATION TOLERANCE1 enhance phosphorus acquisition and sorghum performance on low-phosphorus soils. Plant Physiol 166(2):659–677
Jain A, Vasconcelos MJ, Raghothama KG et al (2007) Molecular mechanisms of plant adaptation to phosphate deficiency. Plant Breed Rev 29:359
Kereszt A, Li D, Indrasumunar A et al (2007) Agrobacterium rhizogenes-mediated transformation of soybean to study root biology. Nat Protoc 2(4):948–952
Kumar B, Abdel-Ghani AH, Pace J et al (2014) Association analysis of single nucleotide polymorphisms in candidate genes with root traits in maize (Zea mays L.) seedlings. Plant Sci 224:9–19
Kumar J, Gupta DS, Gupta S et al (2017) Quantitative trait loci from identification to exploitation for crop improvement. Plant Cell Rep 36(8):1187–1213
Kuznetsova E, Nocek B, Brown G et al (2015) Functional diversity of haloacid dehalogenase superfamily phosphatases from Saccharomyces cerevisiae biochemical, structural, and evolutionary insights. J Biol Chem 290(30):18678–18698
Lambers H, Shane MW, Cramer MD et al (2006) Root structure and functioning for efficient acquisition of phosphorus: matching morphological and physiological traits. Ann Bot 98(4):693–713
Li P, Chen F, Cai H et al (2015) A genetic relationship between nitrogen use efficiency and seedling root traits in maize as revealed by QTL analysis. J Exp Bot 66(11):3175–3188
Li H, Yang Y, Zhang H et al (2016) A genetic relationship between phosphorus efficiency and photosynthetic traits in soybean as revealed by QTL analysis using a high-density genetic map. Front Plant Sci 7:924
Liang Q, Cheng X, Mei M et al (2010) QTL analysis of root traits as related to phosphorus efficiency in soybean. Ann Bot 106(1):223–234
Liang CY, Chen ZJ, Yao ZF et al (2012) Characterization of two putative protein phosphatase genes and their involvement in phosphorus efficiency in Phaseolus vulgaris. J Integr Plant Biol 54(6):400–411
Liang H, Yu Y, Yang H et al (2014) Inheritance and QTL mapping of related root traits in soybean at the seedling stage. Theor Appl Genet 127(10):2127–2137
Liao H, Yan X, Rubio G et al (2004) Genetic mapping of basal root gravitropism and phosphorus acquisition efficiency in common bean. Funct Plant Biol 31(10):959–970
Liu JQ, Allan DL, Vance CP (2010) Systemic signaling and local sensing of phosphate in common bean: cross-talk between photosynthate and microRNA399. Mol Plant 3(2):428–437
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25(4):402–408
Lü J, Suo H, Yi R et al (2015) Glyma11g13220, a homolog of the vernalization pathway gene VERNALIZATION 1 from soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr.], promotes flowering in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol 15(1):232
Lynch JP, Brown KM (2008) Root strategies for phosphorus acquisition. In: White PJ, Hammond JP (eds) The ecophysiology of plant-phosphorus interactions. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 83–116
Manavalan LP, Guttikonda SK, Nguyen VT et al (2010) Evaluation of diverse soybean germplasm for root growth and architecture. Plant Soil 330(1–2):503–514
May A, Berger S, Hertel T et al (2011) The Arabidopsis thaliana phosphate starvation responsive gene AtPPsPase1 encodes a novel type of inorganic pyrophosphatase. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) Gen Subj 1810(2):178–185
May A, Spinka M, Köck M (2012) Arabidopsis thaliana PECP1—enzymatic characterization and structural organization of the first plant phosphoethanolamine/phosphocholine phosphatase. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) Proteins Proteomics 1824(2):319–325
Miguel MA, Widrig A, Vieira RF et al (2013) Basal root whorl number: a modulator of phosphorus acquisition in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris). Ann Bot 112(6):973–982
Niu J, Guo N, Sun J et al (2017) Fine mapping of a resistance gene RpsHN that controls Phytophthora sojae using recombinant inbred lines and secondary populations. Front Plant Sci 8:538
Nurlaeny N, Marschner H, George E (1996) Effects of liming and mycorrhizal colonization on soil phosphate depletion and phosphate uptake by maize (Zea mays L.) and soybean (Glycine max L.) grown in two tropical acid soils. Plant Soil 181(2):275–285
Peng Y, Hu Y, Mao B et al (2016) Genetic analysis for rice grain quality traits in the YVB stable variant line using RAD-seq. Mol Genet Genom 291(1):297–307
Prince SJ, Song L, Qiu D et al (2015) Genetic variants in root architecture-related genes in a Glycine soja accession, a potential resource to improve cultivated soybean. BMC Genom 16(1):132
Qu T, Liu R, Wang W et al (2011) Brassinosteroids regulate pectin methylesterase activity and AtPME41 expression in Arabidopsis under chilling stress. Cryobiology 63(2):111–117
Rao IM, Miles JW, Beebe SE et al (2016) Root adaptations to soils with low fertility and aluminium toxicity. Ann Bot 118(4):593–605
Richardson AE, Hocking PJ, Simpson RJ et al (2009) Plant mechanisms to optimise access to soil phosphorus. Crop Pasture Sci 60(2):124–143
Saengwilai P, Tian X, Lynch JP (2014) Low crown root number enhances nitrogen acquisition from low-nitrogen soils in maize. Plant Physiol 166(2):581–589
Sheshukova EV, Komarova TV, Pozdyshev DV et al (2017) The intergenic interplay between aldose 1-epimerase-like protein and pectin methylesterase in abiotic and biotic stress control. Front Plant Sci 8:1646
Song W, Wang B, Hauck AL et al (2016) Genetic dissection of maize seedling root system architecture traits using an ultrahigh density binmap and a recombinant inbred line population. J Integr Plant Biol 58(3):266–279
Steele KA, Price AH, Shashidhar HE et al (2006) Marker-assisted selection to introgress rice QTLs controlling root traits into an Indian upland rice variety. Theor Appl Genet 112(2):208–221
Tian J, Venkatachalam P, Liao H et al (2007) Molecular cloning and characterization of phosphorus starvation responsive genes in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Planta 227(1):151–165
Tribble GD, Mao S, James CE et al (2006) A porphyromonas gingivalis haloacid dehalogenase family phosphatase interacts with human phosphoproteins and is important for invasion. Proc Natl Acad Sci 103(29):11027–11032
Tuberosa R, Salvi S, Sanguineti MC et al (2003) Searching for quantitative trait loci controlling root traits in maize: a critical appraisal[M]//roots: the dynamic interface between plants and the earth. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 35–54
Uzokwe VNE, Asafo-Adjei B, Fawole I et al (2017) Generation mean analysis of phosphorus-use efficiency in freely nodulating soybean crosses grown in low-phosphorus soil. Plant Breed 136(2):139–146
Van Nguyen L, Takahashi R, Githiri SM et al (2017) Mapping quantitative trait loci for root development under hypoxia conditions in soybean (Glycine max L. Merr.). Theor Appl Genet 130(4):743–755
Vejchasarn P, Lynch JP, Brown KM (2016) Genetic variability in phosphorus responses of rice root phenotypes. Rice 9(1):1–16
Vieira AJD, Oliveira DA, Soares TCB et al (2006) Use of the QTL approach to the study of soybean trait relationships in two populations of recombinant inbred lines at the F7 and F8 generations. Braz J Plant Physiol 18(2):281–290
Walia H, Wilson C, Condamine P et al (2005) Comparative transcriptional profiling of two contrasting rice genotypes under salinity stress during the vegetative growth stage. Plant Physiol 139(2):822–835
Wang X, Yan X, Liao H (2010) Genetic improvement for phosphorus efficiency in soybean: a radical approach. Ann Bot 106(1):215–222
Wang X, Pan Q, Chen F et al (2011) Effects of co-inoculation with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and rhizobia on soybean growth as related to root architecture and availability of N and P. Mycorrhiza 21(3):173–181
Wang Y, Yu K, Poysa V et al (2012) Selection of reference genes for normalization of qRT-PCR analysis of differentially expressed genes in soybean exposed to cadmium. Mol Biol Rep 39(2):1585–1594
Wang Q, Wang J, Yang Y et al (2016) A genome-wide expression profile analysis reveals active genes and pathways coping with phosphate starvation in soybean. BMC Genom 17(1):192
Wang J, Wang Z, Du X et al (2017) A high-density genetic map and QTL analysis of agronomic traits in foxtail millet [Setaria italica (L.) P. Beauv.] using RAD-seq. PLoS ONE 12(6):e0179717
White PJ, Hammond JP (2008) Phosphorus nutrition of terrestrial plants. In: White PJ, Hammond JP (eds) The ecophysiology of plant-phosphorus interactions. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 51–81
White PJ, George TS, Gregory PJ et al (2013) Matching roots to their environment. Ann Bot 112(2):207–222
Woodend JJ, Glass ADM (1993) Inheritance of potassium uptake and utilization in wheat (T. aestivum L.) grown under potassium stress. J Genet Breed 47:95
Wu K, Liu H, Yang M et al (2014) High-density genetic map construction and QTLs analysis of grain yield-related traits in Sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) based on RAD-Seq technology. BMC Plant Biol 14(1):274
Wu HC, Huang YC, Stracovsky L et al (2017) Pectin methylesterase is required for guard cell function in response to heat. Plant Signal Behav 12(6):e1338227
Yan X, Lynch JP, Beebe SE (1995) Genetic variation for phosphorus efficiency of common bean in contrasting soil types: I. Vegetative response. Crop Sci 35(4):1086–1093
Yan X, Liao H, Beebe SE et al (2004) QTL mapping of root hair and acid exudation traits and their relationship to phosphorus uptake in common bean. Plant Soil 265(1–2):17–29
Yang K, Moon JK, Jeong N et al (2011a) Novel major quantitative trait loci regulating the content of isoflavone in soybean seeds. Genes Genom 33(6):685–692
Yang M, Ding G, Shi L et al (2011b) Detection of QTL for phosphorus efficiency at vegetative stage in Brassica napus. Plant Soil 339(1–2):97–111
Yu H, Xie W, Wang J et al (2011) Gains in QTL detection using an ultra-high density SNP map based on population sequencing relative to traditional RFLP/SSR markers. PLoS ONE 6(3):e17595
Zeng W, Sun Z, Cai Z et al (2015) The identification and selection of different new soybean varieties with high phosphorus efficiency in seedling stage. J Guangxi Agric 2015(01):14–17
Zeng H, Wang G, Zhang Y et al (2016) Genome-wide identification of phosphate-deficiency-responsive genes in soybean roots by high-throughput sequencing. Plant Soil 398(1–2):207–227
Zhang D, Cheng H, Geng L et al (2009) Detection of quantitative trait loci for phosphorus deficiency tolerance at soybean seedling stage. Euphytica 167(3):313–322
Zhang D, Liu C, Cheng H et al (2010) Quantitative trait loci associated with soybean tolerance to low phosphorus stress based on flower and pod abscission. Plant Breed 129(3):243–249
Zhang D, Song H, Cheng H et al (2014) The acid phosphatase-encoding gene GmACP1 contributes to soybean tolerance to low-phosphorus stress. PLoS Genet 10(1):e1004061
Zhang Y, Thomas CL, Xiang J et al (2016) QTL meta-analysis of root traits in Brassica napus under contrasting phosphorus supply in two growth systems. Sci Rep 6:33113
Zhang D, Zhang H, Chu S et al (2017) Integrating QTL mapping and transcriptomics identifies candidate genes underlying QTLs associated with soybean tolerance to low-phosphorus stress. Plant Mol Biol 93(1–2):137–150
Zhu J, Kaeppler SM, Lynch JP (2005) Mapping of QTL controlling root hair length in maize (Zea mays L.) under phosphorus deficiency. Plant Soil 270(1):299–310
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Key R&D Program of China (2017YFD0101500), the China Agricultural Research System (CARS-04-PS09) and the Research Project of the State Key Laboratory of Agricultural and Biological Resources Protection and Utilization in Subtropics.
Author contribution statement
Y.C., Q.M. and H.N. provided the soybean materials used in this study. Y.C., P.X., K.W. and Z.C. performed the experiments and date analyses. Q.X. and G.Z. performed QTL mapping. Z.C. and H.N. prepared the manuscript. H.N. planned, supervised and financed this work, as well as edited the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final version of the manuscript to be published.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Henry T. Nguyen.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, Z., Cheng, Y., Xian, P. et al. Acid phosphatase gene GmHAD1 linked to low phosphorus tolerance in soybean, through fine mapping. Theor Appl Genet 131, 1715–1728 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-018-3109-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-018-3109-3