Abstract
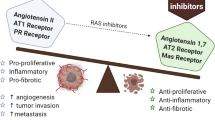
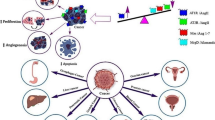
Renin-Angiotensin System (RAS) is a vital system regulating blood pressure and maintaining sodium homeostasis in the human body. It consists of Angiotensin I (Ang I), Angiotensin II (Ang II), Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE), Angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1R), and angiotensin II type 2 receptor (AT2R), which functions in both normal and pathological conditions including cancer. Besides, the effectors of RAS are also included, such as Angiotensin-(1-7). This review focuses on the pre-clinical studies and clinical trials assessing the roles of RAS in regulating tumor progression as well as the underlying mechanisms.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACE:
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme
- Ang II:
-
Angiotensin II
- AT1R:
-
Angiotensin II type 1 receptor
- AT2R:
-
Angiotensin II type 2 receptor
- Ang (1-7):
-
Angiotensin 1-7
- MASR:
-
MAS Receptor
- ACE-2:
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
- EMT:
-
Epithelial mesenchymal transition
- MMPs:
-
Matrix metalloproteinases
- ECM:
-
Extracellular matrix
- ACE-Is:
-
ACE inhibitors
- ARBs:
-
AT1R blockers
- EC:
-
Endometrial cancer
- PC:
-
Prostate cancer
- PTK:
-
Protein tyrosine kinase
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- AMPK:
-
AMP-activated protein kinase
- mTOR:
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin
- EGFR:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor
- MAPK/STAT:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription
- PI3K/AKT:
-
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt
- RCC:
-
Renal cell carcinoma
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- CRC:
-
Colorectal cancer
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small cell lung cancer
References
Patel S, Rauf A, Khan H, Abu-Izneid T (2017) Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone (RAAS): the ubiquitous system for homeostasis and pathologies. Biomed Pharmacother 94:317–325
Takimoto-Ohnishi E, Murakami K (2019) Renin-angiotensin system research: from molecules to the whole body. J Physiol Sci 69:581–587
Juillerat-Jeanneret L, Celerier J, Chapuis Bernasconi C et al (2004) Renin and angiotensinogen expression and functions in growth and apoptosis of human glioblastoma. Br J Cancer 90:1059–1068
Medina D, Arnold AC (2019) Angiotensin-(1-7): translational avenues in cardiovascular control. Am J Hypertens 32:1133–1142
Hsueh WA, Wyne K (2011) Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in diabetes and hypertension. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich) 13:224–237
Marcheselli S, Micieli G (2008) Renin-angiotensin system and stroke. Neurol Sci 29(Suppl 2):S277–S278
Shrikrishna D, Astin R, Kemp PR, Hopkinson NS (2012) Renin-angiotensin system blockade: a novel therapeutic approach in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Clin Sci (Lond) 123:487–498
Afsar B, Afsar RE, Ertuglu LA et al (2021) Renin-angiotensin system and cancer: epidemiology, cell signaling, genetics and epigenetics. Clin Transl Oncol 23:682–696
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2000) The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 100:57–70
Beitia M, Solano-Iturri JD, Errarte P et al (2019) Altered expression of renin-angiotensin system receptors throughout colorectal adenoma-adenocarcinoma sequence. Int J Med Sci 16:813–821
Uemura H, Hoshino K, Kubota Y (2011) Engagement of renin-angiotensin system in prostate cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 11:442–450
Siljee S, Milne B, Brasch HD et al (2021) Expression of components of the renin-angiotensin system by cancer stem cells in renal clear cell carcinoma. Biomolecules 11
Perdomo-Pantoja A, Mejía-Pérez SI, Gómez-Flores-Ramos L et al (2018) Renin angiotensin system and its role in biomarkers and treatment in gliomas. J Neurooncol 138:1–15
Siddique A, Kowdley KV (2011) Insulin resistance and other metabolic risk factors in the pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Liver Dis 15:281–296, vii–x
Price JA, Kovach SJ, Johnson T et al (2002) Insulin-like growth factor I is a comitogen for hepatocyte growth factor in a rat model of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 36:1089–1097
Boissan M, Beurel E, Wendum D et al (2005) Overexpression of insulin receptor substrate-2 in human and murine hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Pathol 167:869–877
Zhang HF, Gao X, Wang X et al (2021) The mechanisms of renin-angiotensin system in hepatocellular carcinoma: from the perspective of liver fibrosis, HCC cell proliferation, metastasis and angiogenesis, and corresponding protection measures. Biomed Pharmacother 141:111868
Zhao Y, Chen X, Cai L et al (2010) Angiotensin II/angiotensin II type I receptor (AT1R) signaling promotes MCF-7 breast cancer cells survival via PI3-kinase/Akt pathway. J Cell Physiol 225:168–173
Du N, Feng J, Hu LJ et al (2012) Angiotensin II receptor type 1 blockers suppress the cell proliferation effects of angiotensin II in breast cancer cells by inhibiting AT1R signaling. Oncol Rep 27:1893–1903
Ino K, Uehara C, Kikkawa F et al (2003) Enhancement of aminopeptidase A expression during angiotensin II-induced choriocarcinoma cell proliferation through AT1 receptor involving protein kinase C- and mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent signaling pathway. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88:3973–3982
Kohlstedt K, Brandes RP, Müller-Esterl W et al (2004) Angiotensin-converting enzyme is involved in outside-in signaling in endothelial cells. Circ Res 94:60–67
Alvarenga EC, Fonseca MC, Carvalho CC et al (2016) Angiotensin converting enzyme regulates cell proliferation and migration. PLoS One 11:e0165371
Guimarães PB, Alvarenga ÉC, Siqueira PD et al (2011) Angiotensin II binding to angiotensin I-converting enzyme triggers calcium signaling. Hypertension 57:965–972
Rodrigues MA, Gomes DA, Nathanson MH, Leite MF (2009) Nuclear calcium signaling: a cell within a cell. Braz J Med Biol Res 42:17–20
Suganuma T, Ino K, Shibata K et al (2005) Functional expression of the angiotensin II type 1 receptor in human ovarian carcinoma cells and its blockade therapy resulting in suppression of tumor invasion, angiogenesis, and peritoneal dissemination. Clin Cancer Res 11:2686–2694
Humpel C, Lippoldt A, Strömberg I et al (1994) Human angiotensinogen is highly expressed in astrocytes in human cortical grafts. Glia 10:186–192
Ariza A, Fernandez LA, Inagami T et al (1988) Renin in glioblastoma multiforme and its role in neovascularization. Am J Clin Pathol 90:437–441
Juillerat-Jeanneret L, Lohm S, Hamou MF, Pinet F (2000) Regulation of aminopeptidase A in human brain tumor vasculature: evidence for a role of transforming growth factor-beta. Lab Invest 80:973–980
Célérier J, Cruz A, Lamandé N et al (2002) Angiotensinogen and its cleaved derivatives inhibit angiogenesis. Hypertension 39:224–228
Ferrara N (1999) Vascular endothelial growth factor: molecular and biological aspects. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 237:1–30
Zhang Q, Lu S, Li T et al (2019) ACE2 inhibits breast cancer angiogenesis via suppressing the VEGFa/VEGFR2/ERK pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 38:173
Zhong H, Chiles K, Feldser D et al (2000) Modulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha expression by the epidermal growth factor/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/PTEN/AKT/FRAP pathway in human prostate cancer cells: implications for tumor angiogenesis and therapeutics. Cancer Res 60:1541–1545
Maity A, Pore N, Lee J et al (2000) Epidermal growth factor receptor transcriptionally up-regulates vascular endothelial growth factor expression in human glioblastoma cells via a pathway involving phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase and distinct from that induced by hypoxia. Cancer Res 60:5879–5886
Fukumura D, Gohongi T, Kadambi A et al (2001) Predominant role of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in vascular endothelial growth factor-induced angiogenesis and vascular permeability. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:2604-2609
Kim I, Kim HG, So JN et al (2000) Angiopoietin-1 regulates endothelial cell survival through the phosphatidylinositol 3′-Kinase/Akt signal transduction pathway. Circ Res 86:24–29
Kim I, Kim JH, Moon SO et al (2000) Angiopoietin-2 at high concentration can enhance endothelial cell survival through the phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase/Akt signal transduction pathway. Oncogene 19:4549–4552
Ando H, Nagasaka T, Nomura M et al (2002) Premenstrual disappearance of aminopeptidase A in endometrial stromal cells around endometrial spiral arteries/arterioles during the decidual change. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87:2303–2309
Ito M, Itakura A, Ohno Y et al (2002) Possible activation of the renin-angiotensin system in the feto-placental unit in preeclampsia. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87:1871–1878
Ando H, Furugori K, Shibata D et al (2003) Dual renin-angiotensin blockade therapy in patients at high risk of early ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome receiving IVF and elective embryo cryopreservation: a case series. Hum Reprod 18:1219–1222
Yamamoto S, Konishi I, Mandai M et al (1997) Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in epithelial ovarian neoplasms: correlation with clinicopathology and patient survival, and analysis of serum VEGF levels. Br J Cancer 76:1221–1227
Kikkawa F, Mizuno M, Shibata K et al (2004) Activation of invasiveness of cervical carcinoma cells by angiotensin II. Am J Obstet Gynecol 190:1258–1263
Suganuma T, Ino K, Shibata K et al (2004) Regulation of aminopeptidase A expression in cervical carcinoma: role of tumor-stromal interaction and vascular endothelial growth factor. Lab Invest 84:639–648
Watanabe Y, Shibata K, Kikkawa F et al (2003) Adipocyte-derived leucine aminopeptidase suppresses angiogenesis in human endometrial carcinoma via renin-angiotensin system. Clin Cancer Res 9:6497–6503
Ino K, Shibata K, Kajiyama H et al (2006) Angiotensin II type 1 receptor expression in ovarian cancer and its correlation with tumour angiogenesis and patient survival. Br J Cancer 94:552–560
Egami K, Murohara T, Shimada T et al (2003) Role of host angiotensin II type 1 receptor in tumor angiogenesis and growth. J Clin Invest 112:67–75
Yang S, Yang C, Yu F et al (2018) Endoplasmic reticulum resident oxidase ERO1-Lalpha promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis and angiogenesis through the S1PR1/STAT3/VEGF-A pathway. Cell Death Dis 9:1105
Wang J, Liu Q, Xiao H et al (2019) Suppressive effects of Momordin Ic on HepG2 cell migration and invasion by regulating MMP-9 and adhesion molecules: involvement of p38 and JNK pathways. Toxicol In Vitro 56:75–83
Fan F, Tian C, Tao L et al (2016) Candesartan attenuates angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma via downregulating AT1R/VEGF pathway. Biomed Pharmacother 83:704–711
Cao H, Xu E, Liu H et al (2015) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer metastasis: a system review. Pathol Res Pract 211:557–569
Pinter M, Jain RK (2017) Targeting the renin-angiotensin system to improve cancer treatment: implications for immunotherapy. Sci Transl Med 9
Yoshida T, Kinoshita H, Fukui K et al (2017) Prognostic impact of renin-angiotensin inhibitors in patients with bladder cancer undergoing radical cystectomy. Ann Surg Oncol 24:823–831
Araújo WF, Naves MA, Ravanini JN et al (2015) Renin-angiotensin system (RAS) blockade attenuates growth and metastatic potential of renal cell carcinoma in mice. Urol Oncol 33:389.e1–389.e7
Feng Y, Zu LL, Zhang L (2018) MicroRNA-26b inhibits the tumor growth of human liver cancer through the PI3K/Akt and NF-κB/MMP-9/VEGF pathways. Oncol Rep 39:2288–2296
Saber S, Mahmoud AAA, Goda R et al (2018) Perindopril, fosinopril and losartan inhibited the progression of diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocellular carcinoma in mice via the inactivation of nuclear transcription factor kappa-B. Toxicol Lett 295:32–40
Yu C, Tang W, Wang Y et al (2016) Downregulation of ACE2/Ang-(1-7)/Mas axis promotes breast cancer metastasis by enhancing store-operated calcium entry. Cancer Lett 376:268–277
Qian YR, Guo Y, Wan HY et al (2013) Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 attenuates the metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer through inhibition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncol Rep 29:2408–2414
Sankpal UT, Maliakal P, Bose D et al (2012) Expression of specificity protein transcription factors in pancreatic cancer and their association in prognosis and therapy. Curr Med Chem 19:3779–3786
Ishikane S, Hosoda H, Nojiri T et al (2018) Angiotensin II promotes pulmonary metastasis of melanoma through the activation of adhesion molecules in vascular endothelial cells. Biochem Pharmacol 154:136–147
Wang Y, Xu H, Fu W et al (2019) 20(S)-Protopanaxadiol inhibits angiotensin II-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition by downregulating SIRT1. Front Pharmacol 10:475
Neo JH, Ager EI, Angus PW et al (2010) Changes in the renin angiotensin system during the development of colorectal cancer liver metastases. BMC Cancer 10:134
Childers WK (2015) Interactions of the renin-angiotensin system in colorectal cancer and metastasis. Int J Colorectal Dis 30:749–752
Qi Y, Li H, Shenoy V et al (2012) Moderate cardiac-selective overexpression of angiotensin II type 2 receptor protects cardiac functions from ischaemic injury. Exp Physiol 97:89–101
Sun L, Wang W, Xiao W et al (2012) Angiotensin II induces apoptosis in intestinal epithelial cells through the AT2 receptor, GATA-6 and the Bax pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 424:663–668
Wang X, Lu J, Khaidakov M et al (2012) Delineation of the effects of angiotensin type 1 and 2 receptors on HL-1 cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Apoptosis 17:908–915
Li H, Qi Y, Li C et al (2009) Angiotensin type 2 receptor-mediated apoptosis of human prostate cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther 8:3255–3265
Du H, Liang Z, Zhang Y et al (2013) Effects of angiotensin II type 2 receptor overexpression on the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One 8:e83754
Kawabata A, Baoum A, Ohta N et al (2012) Intratracheal administration of a nanoparticle-based therapy with the angiotensin II type 2 receptor gene attenuates lung cancer growth. Cancer Res 72:2057–2067
Arrieta O, Guevara P, Escobar E et al (2005) Blockage of angiotensin II type I receptor decreases the synthesis of growth factors and induces apoptosis in C6 cultured cells and C6 rat glioma. Br J Cancer 92:1247–1252
Tejera N, Gómez-Garre D, Lázaro A et al (2004) Persistent proteinuria up-regulates angiotensin II type 2 receptor and induces apoptosis in proximal tubular cells. Am J Pathol 164:1817–1826
Pei N, Jie F, Luo J et al (2014) Gene expression profiling associated with angiotensin II type 2 receptor-induced apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells. PLoS One 9:e92253
Pei N, Mao Y, Wan P et al (2017) Angiotensin II type 2 receptor promotes apoptosis and inhibits angiogenesis in bladder cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 36:77
Cambados N, Walther T, Nahmod K et al (2017) Angiotensin-(1-7) counteracts the transforming effects triggered by angiotensin II in breast cancer cells. Oncotarget 8:88475–88487
Ateeq B, Tomlins SA, Chinnaiyan AM (2009) AGTR1 as a therapeutic target in ER-positive and ERBB2-negative breast cancer cases. Cell Cycle 8:3794–3795
Rhodes DR, Ateeq B, Cao Q et al (2009) AGTR1 overexpression defines a subset of breast cancer and confers sensitivity to losartan, an AGTR1 antagonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:10284–10289
Oh E, Kim JY, Cho Y et al (2016) Overexpression of angiotensin II type 1 receptor in breast cancer cells induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and promotes tumor growth and angiogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1863:1071–1081
Yang F, Huang XR, Chung AC et al (2010) Essential role for Smad3 in angiotensin II-induced tubular epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Pathol 221:390–401
Carvajal G, Rodríguez-Vita J, Rodrigues-Díez R et al (2008) Angiotensin II activates the Smad pathway during epithelial mesenchymal transdifferentiation. Kidney Int 74:585–595
Miyajima A, Kosaka T, Asano T et al (2002) Angiotensin II type I antagonist prevents pulmonary metastasis of murine renal cancer by inhibiting tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Res 62:4176–4179
Ni L, Feng Y, Wan H et al (2012) Angiotensin-(1-7) inhibits the migration and invasion of A549 human lung adenocarcinoma cells through inactivation of the PI3K/Akt and MAPK signaling pathways. Oncol Rep 27:783–790
Zhao Y, Wang H, Li X et al (2014) Ang II-AT1R increases cell migration through PI3K/AKT and NF-κB pathways in breast cancer. J Cell Physiol 229:1855–1862
Rodrigues-Ferreira S, Abdelkarim M, Dillenburg-Pilla P et al (2012) Angiotensin II facilitates breast cancer cell migration and metastasis. PLoS One 7:e35667
Pei N, Wan R, Chen X et al (2016) Angiotensin-(1-7) decreases cell growth and angiogenesis of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma xenografts. Mol Cancer Ther 15:37–47
Fogarty DJ, Sánchez-Gómez MV, Matute C (2002) Multiple angiotensin receptor subtypes in normal and tumor astrocytes in vitro. Glia 39:304–313
Burns WC, Velkoska E, Dean R et al (2010) Angiotensin II mediates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transformation in tubular cells by ANG 1-7/MAS-1-dependent pathways. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 299:F585–F593
Khanna P, Soh HJ, Chen CH et al (2021) ACE2 abrogates tumor resistance to VEGFR inhibitors suggesting angiotensin-(1-7) as a therapy for clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Sci Transl Med 13
Attoub S, Gaben AM, Al-Salam S et al (2008) Captopril as a potential inhibitor of lung tumor growth and metastasis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1138:65–72
Hii SI, Nicol DL, Gotley DC et al (1998) Captopril inhibits tumour growth in a xenograft model of human renal cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer 77:880–883
Wysocki PJ, Kwiatkowska EP, Kazimierczak U et al (2006) Captopril, an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, promotes growth of immunogenic tumors in mice. Clin Cancer Res 12:4095–4102
Silvestre JS, Bergaya S, Tamarat R et al (2001) Proangiogenic effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition is mediated by the bradykinin B(2) receptor pathway. Circ Res 89:678–683
Ebrahimian TG, Tamarat R, Clergue M et al (2005) Dual effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition on angiogenesis in type 1 diabetic mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 25:65–70
Rasha F, Ramalingam L, Gollahon L et al (2019) Mechanisms linking the renin-angiotensin system, obesity, and breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer 26:R653–R672
Yoshiji H, Kuriyama S, Kawata M et al (2001) The angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitor perindopril suppresses tumor growth and angiogenesis: possible role of the vascular endothelial growth factor. Clin Cancer Res 7:1073–1078
Sipahi I, Debanne SM, Rowland DY et al (2010) Angiotensin-receptor blockade and risk of cancer: meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Lancet Oncol 11:627–636
Xie Y, Xu P, Wang M et al (2020) Antihypertensive medications are associated with the risk of kidney and bladder cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Aging (Albany NY) 12:1545–1562
Renziehausen A, Wang H, Rao B et al (2019) The renin angiotensin system (RAS) mediates bifunctional growth regulation in melanoma and is a novel target for therapeutic intervention. Oncogene 38:2320–2336
Arnold SA, Rivera LB, Carbon JG et al (2012) Losartan slows pancreatic tumor progression and extends survival of SPARC-null mice by abrogating aberrant TGFβ activation. PLoS One 7:e31384
Friis S, Sørensen HT, Mellemkjaer L et al (2001) Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and the risk of cancer: a population-based cohort study in Denmark. Cancer 92:2462–2470
Htoo PT, Stürmer T, Jonsson-Funk M et al (2019) Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system-based antihypertensive agents and the risk of colorectal cancer among Medicare beneficiaries. Epidemiology 30:867–875
Mandilaras V, Bouganim N, Yin H et al (2017) The use of drugs acting on the renin-angiotensin system and the incidence of pancreatic cancer. Br J Cancer 116:103–108
Liu H, Naxerova K, Pinter M et al (2017) Use of Angiotensin system inhibitors is associated with immune activation and longer survival in nonmetastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 23:5959–5969
Sun H, Li T, Zhuang R et al (2017) Do renin-angiotensin system inhibitors influence the recurrence, metastasis, and survival in cancer patients? Evidence from a meta-analysis including 55 studies. Medicine (Baltimore) 96:e6394
Nakai Y, Isayama H, Ijichi H et al (2010) Inhibition of renin-angiotensin system affects prognosis of advanced pancreatic cancer receiving gemcitabine. Br J Cancer 103:1644–1648
Aydiner A, Ciftci R, Sen F (2015) Renin-Angiotensin system blockers may prolong survival of metastatic non-small cell lung cancer patients receiving erlotinib. Medicine (Baltimore) 94:e887
Röcken C, Röhl FW, Diebler E et al (2007) The angiotensin II/angiotensin II receptor system correlates with nodal spread in intestinal type gastric cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 16:1206–1212
Keizman D, Huang P, Eisenberger MA et al (2011) Angiotensin system inhibitors and outcome of sunitinib treatment in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a retrospective examination. Eur J Cancer 47:1955–1961
McKay RR, Rodriguez GE, Lin X et al (2015) Angiotensin system inhibitors and survival outcomes in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 21:2471–2479
Izzedine H, Derosa L, Le Teuff G et al (2015) Hypertension and angiotensin system inhibitors: impact on outcome in sunitinib-treated patients for metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Ann Oncol 26:1128–1133
Wilop S, von Hobe S, Crysandt M et al (2009) Impact of angiotensin I converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockers on survival in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer undergoing first-line platinum-based chemotherapy. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 135:1429–1435
Miao L, Chen W, Zhou L et al (2016) Impact of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II Type-1 receptor blockers on survival of patients with NSCLC. Sci Rep 6:21359
Menter AR, Carroll NM, Sakoda LC et al (2017) Effect of angiotensin system inhibitors on survival in patients receiving chemotherapy for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer 18:189–197.e3
Wei J, Zhou Z, Xu Z et al (2019) Retrospective clinical study of renin-angiotensin system blockers in lung cancer patients with hypertension. PeerJ 7:e8188
O'Rawe M, Wickremesekera AC, Pandey R et al (2022) Treatment of glioblastoma with re-purposed renin-angiotensin system modulators: results of a phase I clinical trial. J Clin Neurosci 95:48–54
Zaher H, Rasheed H, El-Komy MM et al (2016) Propranolol versus captopril in the treatment of infantile hemangioma (IH): a randomized controlled trial. J Am Acad Dermatol 74:499–505
Makar GA, Holmes JH, Yang YX (2014) Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor therapy and colorectal cancer risk. J Natl Cancer Inst 106:djt374
Acknowledgement
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81973341 to Q.Q.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Su, J., Zou, Q., Li, S., Qi, Q. (2023). Renin-Angiotensin System and Cancer: From Laboratory to Clinics. In: Bhullar, S.K., Tappia, P.S., Dhalla, N.S. (eds) The Renin Angiotensin System in Cancer, Lung, Liver and Infectious Diseases. Advances in Biochemistry in Health and Disease, vol 25. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-23621-1_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-23621-1_16
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-23620-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-23621-1
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)