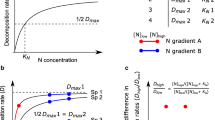
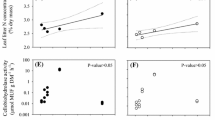
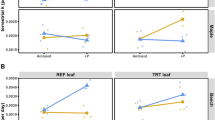
Abstract
Excess nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) inputs to streams occur globally, and affect not only stream autotrophs, but also heterotrophic microbes and detrital carbon processing. Detrital carbon, such as leaf litter, supports stream food webs and their connectivity via downstream detritus fluxes. Nutrient enrichment increases litter decomposition rates across multiple scales and trophic levels by stimulating activity of microbial decomposers and enhancing interactions among microbial decomposers, detritivores, and physical abrasion. Nutrient effects on microbial and detritivore-mediated decomposition are typically greater for recalcitrant vs. labile litter, especially when coupled to low initial nutrient concentrations. Recent studies and syntheses show that (1) dissolved N and P affect litter by stimulating fungal activity and nutrient immobilization, thus, increasing detrital nutrient content, (2) nutrient effects are greatest with N and P together (vs. individually) and when detritivores are present, and (3) ecosystem-level effects of nutrient enrichment can be predicted from small-scale measurements. Despite extensive studies of leaf litter decomposition, its application as a tool to manage nutrient enrichment issues trails comparable tools for autotrophic (i.e., algal) pathways. Thus, better understanding of the consequences of nutrient enrichment on leaf litter and other detrital carbon is important to predict how nutrients will affect stream ecosystem functioning.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abelho, M. (2001). From litterfall to breakdown in streams: A review. The Scientific World Journal, 1, 656–680. https://doi.org/10.1100/tsw.2001.103.
Ardón, M., Stallcup, L. A., & Pringle, C. M. (2006). Does leaf quality mediate the stimulation of leaf breakdown by phosphorus in Neotropical streams? Freshwater Biology, 51(4), 618–633. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.2006.01515.x.
Arroita, M., Elosegi, A., & Hall, R. O. (2019). Twenty years of daily metabolism show riverine recovery following sewage abatement. Limnology and Oceanography, 64(S1), S77–S92. https://doi.org/10.1002/lno.11053.
Azevedo-Pereira, H. V. S., Graça, M. A. S., & González, J. M. (2006). Life history of Lepidostoma hirtum in an Iberian stream and its role in organic matter processing. Hydrobiologia, 559(1), 183–192. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-005-1267-1.
Baldy, V., Gessner, M. O., & Chauvet, E. (1995). Bacteria, fungi and the breakdown of leaf litter in a large river. Oikos, 74(1), 93–102. JSTOR. https://doi.org/10.2307/3545678.
Baldy, V., Gobert, V., Guerold, F., Chauvet, E., Lambrigot, D., & Charcosset, J.-Y. (2007). Leaf litter breakdown budgets in streams of various trophic status: Effects of dissolved inorganic nutrients on microorganisms and invertebrates. Freshwater Biology, 52(7), 1322–1335. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.2007.01768.x.
Bärlocher, F. (1985). The role of fungi in the nutrition of stream invertebrates. Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society, 91(1–2), 83–94. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8339.1985.tb01137.x.
Bärlocher, F., & Sridhar, K. R. (2014). 19. Association of animals and fungi in leaf decomposition. In E. B. G. Jones, K. D. Hyde, & K.-L. Pang (Eds.), Freshwater Fungi. De Gruyter. https://doi.org/10.1515/9783110333480.413.
Benstead, J. P., Rosemond, A. D., Cross, W. F., Wallace, J. B., Eggert, S. L., Suberkropp, K., Gulis, V., Greenwood, J. L., & Tant, C. J. (2009). Nutrient enrichment alters storage and fluxes of detritus in a headwater stream ecosystem. Ecology, 90(9), 2556–2566. https://doi.org/10.1890/08-0862.1.
Bernot, M. J., Sobota, D. J., Hall, R. O., Mulholland, P. J., Dodds, W. K., Webster, J. R., Tank, J. L., Ashkenas, L. R., Cooper, L. W., Dahm, C. N., Gregory, S. V., Grimm, N. B., Hamilton, S. K., Johnson, S. L., Mcdowell, W. H., Meyer, J. L., Peterson, B., Poole, G. C., Valett, H. M., … Wilson, K. (2010). Inter-regional comparison of land-use effects on stream metabolism. Freshwater Biology, 55(9), 1874–1890. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.20.
Boyero, L., Pearson, R. G., Dudgeon, D., Graça, M. A. S., Gessner, M. O., Albariño, R. J., Ferreira, V., Yule, C. M., Boulton, A. J., Arunachalam, M., Callisto, M., Chauvet, E., Ramírez, A., Chará, J., Moretti, M. S., Gonçalves, J. F., Helson, J. E., Chará-Serna, A. M., Encalada, A. C., … Pringle, C. M. (2011). Global distribution of a key trophic guild contrasts with common latitudinal diversity patterns. Ecology, 92(9), 1839–1848. https://doi.org/10.1890/10-2244.1.
Boyero, L., Pearson, R. G., Gessner, M. O., Barmuta, L. A., Ferreira, V., Graça, M. A. S., Dudgeon, D., Boulton, A. J., Callisto, M., Chauvet, E., Helson, J. E., Bruder, A., Albariño, R. J., Yule, C. M., Arunachalam, M., Davies, J. N., Figueroa, R., Flecker, A. S., Ramírez, A., … West, D. C. (2011). A global experiment suggests climate warming will not accelerate litter decomposition in streams but might reduce carbon sequestration. Ecology Letters, 14(3), 289–294. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2010.01578.x.
Boyero, L., Pearson, R. G., Hui, C., Gessner, M. O., Pérez, J., Alexandrou, M. A., Graça, M. A. S., Cardinale, B. J., Albariño, R. J., Arunachalam, M., Barmuta, L. A., Boulton, A. J., Bruder, A., Callisto, M., Chauvet, E., Death, R. G., Dudgeon, D., Encalada, A. C., Ferreira, V., … Yule, C. M. (2016). Biotic and abiotic variables influencing plant litter breakdown in streams: A global study. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 283(1829), 20152664. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2015.2664.
Boyero, L., Pearson, R. G., Swan, C. M., Hui, C., Albariño, R. J., Arunachalam, M., Callisto, M., Chará, J., Chará-Serna, A. M., Chauvet, E., Cornejo, A., Dudgeon, D., Encalada, A. C., Ferreira, V., Gessner, M. O., Gonçalves, J., Graça, M. A. S., Helson, J. E., Mathooko, J. M., … Yule, C. M. (2015). Latitudinal gradient of nestedness and its potential drivers in stream detritivores. Ecography, 38(9), 949–955. https://doi.org/10.1111/ecog.00982.
Canhoto, C., & Graça, M. A. S. (2006). Digestive tract and leaf processing capacity of the stream invertebrate Tipula lateralis. Canadian Journal of Zoology, 84(8), 1087–1095. https://doi.org/10.1139/z06-092.
Cebrian, J., & Lartigue, J. (2004). Patterns of herbivory and decomposition in aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems. Ecological Monographs, 74(2), 237–259. https://doi.org/10.1890/03-4019.
Chadwick, M. A., & Huryn, A. D. (2003). Effect of a whole-catchment N addition on stream detritus processing. Journal of the North American Benthological Society, 22(2), 194–206. https://doi.org/10.2307/1467992.
Chauvet, E., Ferreira, V., Giller, P. S., McKie, B. G., Tiegs, S. D., Woodward, G., Elosegi, A., Dobson, M., Fleituch, T., Graça, M. A. S., Gulis, V., Hladyz, S., Lacoursière, J. O., Lecerf, A., Pozo, J., Preda, E., Riipinen, M., Rîşnoveanu, G., Vadineanu, A., … Gessner, M. O. (2016). Litter decomposition as an indicator of stream ecosystem functioning at local-to-continental scales: Insights from the European RivFunction project. In A. J. Dumbrell, R. L. Kordas, & G. Woodward (Eds.), Advances in ecological research (pp. 99–182). Academic Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.aecr.2016.08.006.
Cheever, B. M., Webster, J. R., Bilger, E. E., & Thomas, S. A. (2013). The relative importance of exogenous and substrate-derived nitrogen for microbial growth during leaf decomposition. Ecology, 94(7), 1614–1625. https://doi.org/10.1890/12-1339.1.
Chung, N., & Suberkropp, K. (2009a). Contribution of fungal biomass to the growth of the shredder, Pycnopsyche gentilis (Trichoptera: Limnephilidae). Freshwater Biology, 54(11), 2212–2224. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.2009.02260.x.
Chung, N., & Suberkropp, K. (2009b). Effects of aquatic fungi on feeding preferences and bioenergetics of Pycnopsyche gentilis (Trichoptera: Limnephilidae). Hydrobiologia, 630(1), 257–269. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-009-9820-y.
Colas, F., Woodward, G., Burdon, F. J., Guérold, F., Chauvet, E., Cornut, J., Cébron, A., Clivot, H., Danger, M., Danner, M. C., Pagnout, C., & Tiegs, S. D. (2019). Towards a simple global-standard bioassay for a key ecosystem process: Organic-matter decomposition using cotton strips. Ecological Indicators, 106, 105466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.105466.
Conley, D. J., Paerl, H. W., Howarth, R. W., Boesch, D. F., Seitzinger, S. P., Havens, K. E., Lancelot, C., & Likens, G. E. (2009). Ecology: Controlling eutrophication: Nitrogen and phosphorus. Science, 323(5917), 1014–1015. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1167755.
Connolly, N. M., & Pearson, R. G. (2013). Nutrient enrichment of a heterotrophic stream alters leaf litter nutritional quality and shredder physiological condition via the microbial pathway. Hydrobiologia, 718(1), 85–92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-013-1605-7.
Cornut, J., Elger, A., Lambrigot, D., Marmonier, P., & Chauvet, E. (2010). Early stages of leaf decomposition are mediated by aquatic fungi in the hyporheic zone of woodland streams. Freshwater Biology, 55(12), 2541–2556. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.2010.02483.x.
Cornut, J., Ferreira, V., Gonçalves, A. L., Chauvet, E., & Canhoto, C. (2015). Fungal alteration of the elemental composition of leaf litter affects shredder feeding activity. Freshwater Biology, 60(9), 1755–1771. https://doi.org/10.1111/fwb.12606.
Cross, W. F., Benstead, J. P., Frost, P. C., & Thomas, S. A. (2005). Ecological stoichiometry in freshwater benthic systems: Recent progress and perspectives. Freshwater Biology, 50(11), 1895–1912. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.2005.01458.x.
Cross, W. F., Benstead, J. P., Rosemond, A. D., & Wallace, J. B. (2003). Consumer-resource stoichiometry in detritus-based streams. Ecology Letters, 6(8), 721–732. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1461-0248.2003.00481.x.
Cross, W. F., Wallace, J. B., Rosemond, A. D., & Eggert, S. L. (2006). Whole-system nutrient enrichment increases secondary production in a detritus-based ecosystem. Ecology, 87(6), 1556–1565. https://doi.org/10.1890/0012-9658(2006)87%5b1556:wneisp%5d2.0.co;2.
Cummins, K. W., & Klug, M. J. (1979). Feeding ecology of stream invertebrates. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 10(1), 147–172. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.es.10.110179.001051.
Dang, C. K., Schindler, M., Chauvet, E., & Gessner, M. O. (2009). Temperature oscillation coupled with fungal community shifts can modulate warming effects on litter decomposition. Ecology, 90(1), 122–131. https://doi.org/10.1890/07-1974.1.
Danger, M., & Chauvet, E. (2013). Elemental composition and degree of homeostasis of fungi: Are aquatic hyphomycetes more like metazoans, bacteria or plants? Fungal Ecology, 6(5), 453–457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.funeco.2013.05.007.
Danger, M., Funck, J. A., Devin, S., Heberle, J., & Felten, V. (2013). Phosphorus content in detritus controls life-history traits of a detritivore. Functional Ecology, 27(3), 807–815. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2435.12079.
Davis, J. M., Rosemond, A. D., Eggert, S. L., Cross, W. F., & Wallace, J. B. (2010). Nutrient enrichment differentially affects body sizes of primary consumers and predators in a detritus-based stream. Limnology and Oceanography, 55(6), 2305–2316. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2010.55.6.2305.
Demi, L. M., Benstead, J. P., Rosemond, A. D., & Maerz, J. C. (2018). Litter P content drives consumer production in detritus-based streams spanning an experimental N: P gradient. Ecology, 99(2), 347–359. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecy.2118.
Demi, L. M., Benstead, J. P., Rosemond, A. D., & Maerz, J. C. (2019). Experimental N and P additions alter stream macroinvertebrate community composition via taxon-level responses to shifts in detrital resource stoichiometry. Functional Ecology, 33(5), 855–867. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2435.13289.
Dodds, W. K. (2006). Eutrophication and trophic state in rivers and streams. Limnology and Oceanography, 51, 671–680. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2006.51.1_part_2.0671.
Dodds, W. K., Clements, W. H., Gido, K., Hilderbrand, R. H., & King, R. S. (2010). Thresholds, breakpoints, and nonlinearity in freshwaters as related to management. Journal of the North American Benthological Society, 29(3), 988–997. https://doi.org/10.1899/09-148.1.
Dodds, W. K., & Cole, J. J. (2007). Expanding the concept of trophic state in aquatic ecosystems: It’s not just the autotrophs. Aquatic Sciences, 69(4), 427–439. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00027-007-0922-1.
Dodds, W., & Smith, V. (2016). Nitrogen, phosphorus, and eutrophication in streams. Inland Waters, 6(2), 155–164. https://doi.org/10.5268/IW-6.2.909.
Eggert, S. L., & Wallace, J. B. (2007). Wood biofilm as a food resource for stream detritivores. Limnology and Oceanography, 52(3), 1239–1245. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2007.52.3.1239.
Elwood, J. W., Newbold, J. D., Trimble, A. F., & Stark, R. W. (1981). The limiting role of phosphorus in a woodland stream ecosystem: Effects of P enrichment on leaf decomposition and primary producers. Ecology, 62(1), 146–158. https://doi.org/10.2307/1936678.
Enríquez, S., Duarte, C. M., & Sand-Jensen, K. (1993). Patterns in decomposition rates among photosynthetic organisms: The importance of detritus C:N: P content. Oecologia, 94(4), 457–471. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00566960.
Fernandes, I., Seena, S., Pascoal, C., & Cássio, F. (2014). Elevated temperature may intensify the positive effects of nutrients on microbial decomposition in streams. Freshwater Biology, 59(11), 2390–2399. https://doi.org/10.1111/fwb.12445.
Ferreira, V., & Canhoto, C. (2015). Future increase in temperature may stimulate litter decomposition in temperate mountain streams: Evidence from a stream manipulation experiment. Freshwater Biology, 60(5), 881–892. https://doi.org/10.1111/fwb.12539.
Ferreira, V., Castagneyrol, B., Koricheva, J., Gulis, V., Chauvet, E., & Graça, M. A. S. (2015). A meta-analysis of the effects of nutrient enrichment on litter decomposition in streams. Biological Reviews, 90(3), 669–688. https://doi.org/10.1111/brv.12125.
Ferreira, V., & Chauvet, E. (2011). Synergistic effects of water temperature and dissolved nutrients on litter decomposition and associated fungi. Global Change Biology, 17(1), 551–564. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2486.2010.02185.x.
Ferreira, V., Gulis, V., & Graça, M. A. S. (2006). Whole-stream nitrate addition affects litter decomposition and associated fungi but not invertebrates. Oecologia, 149(4), 718–729. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-006-0478-0.
Ferreira, V., Raposeiro, P. M., Pereira, A., Cruz, A. M., Costa, A. C., Graça, M. A. S., & Gonçalves, V. (2016). Leaf litter decomposition in remote oceanic island streams is driven by microbes and depends on litter quality and environmental conditions. Freshwater Biology, 61(5), 783–799. https://doi.org/10.1111/fwb.12749.
Fisher, S. G., & Likens, G. E. (1973). Energy flow in Bear Brook, New Hampshire: An integrative approach to stream ecosystem metabolism. Ecological Monographs, 43(4), 421–439. JSTOR. https://doi.org/10.2307/1942301.
Flecker, A. S., & Townsend, C. R. (1994). Community-wide consequences of trout introduction in New Zealand streams. Ecological Applications, 4(4), 798–807. https://doi.org/10.2307/1942009.
Foucreau, N., Puijalon, S., Hervant, F., & Piscart, C. (2013). Effect of leaf litter characteristics on leaf conditioning and on consumption by Gammarus pulex. Freshwater Biology, 58(8), 1672–1681. https://doi.org/10.1111/fwb.12158.
Fowler, D., O’Donoghue, M., Muller, J. B. A., Smith, R. I., Dragosits, U., Skiba, U., Sutton, M. A., & Brimblecombe, P. (2004). A chronology of nitrogen deposition in the UK between 1900 and 2000. Water, Air, & Soil Pollution: Focus, 4(6), 9–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11267-004-3009-1.
Frainer, A., Jabiol, J., Gessner, M. O., Bruder, A., Chauvet, E., & McKie, B. G. (2016). Stoichiometric imbalances between detritus and detritivores are related to shifts in ecosystem functioning. Oikos, 125(6), 861–871. https://doi.org/10.1111/oik.02687.
Gallo, M. E., Porras-Alfaro, A., Odenbach, K. J., & Sinsabaugh, R. L. (2009). Photoacceleration of plant litter decomposition in an arid environment. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 41(7), 1433–1441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2009.03.025.
Gessner, M. O., Gulis, V., Kuehn, K., Chauvet, E., & Suberkropp, K.. (Eds.). (2007). Fungal decomposers of plant litter in aquatic ecosystems. In C. P. Kubicek, & I. S. Druzhinina (eds.), Environmental and microbial relationships (pp. 301–324). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-71840-6_17.
Gessner, M. O., Swan, C. M., Dang, C. K., McKie, B. G., Bardgett, R. D., Wall, D. H., & Hättenschwiler, S. (2010). Diversity meets decomposition. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 25(6), 372–380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2010.01.010.
Gomi, T., Moore, R. D., & Dhakal, A. S. (2006). Headwater stream temperature response to clear-cut harvesting with different riparian treatments, coastal British Columbia, Canada. Water Resources Research, 42(8). https://doi.org/10.1029/2005wr004162.
Graça, M. A. S. (2001). The role of invertebrates on leaf litter decomposition in streams—A review. International Review of Hydrobiology, 86(4–5), 383–393. https://doi.org/10.1002/1522-2632(200107)86:4/5%3c383:AID-IROH383%3e3.0.CO;2-D.
Greenwood, J. L., Rosemond, A. D., Wallace, J. B., Cross, W. F., & Weyers, H. S. (2007). Nutrients stimulate leaf breakdown rates and detritivore biomass: Bottom-up effects via heterotrophic pathways. Oecologia, 151(4), 637–649. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-006-0609-7.
Grimmett, I. J., Shipp, K. N., Macneil, A., & Bärlocher, F. (2013). Does the growth rate hypothesis apply to aquatic hyphomycetes? Fungal Ecology, 6(6), 493–500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.funeco.2013.08.002.
Gulis, V., Ferreira, V., & Graça, M. A. S. (2006). Stimulation of leaf litter decomposition and associated fungi and invertebrates by moderate eutrophication: Implications for stream assessment. Freshwater Biology, 51(9), 1655–1669. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.2006.01615.x.
Gulis, V., Kuehn, K., & Suberkropp, K. (2006). The role of fungi in carbon and nitrogen cycles in freshwater ecosystems. In G. M. Gadd (Ed.), Fungi in biogeochemical cycles (pp. 404–435). Cambridge University Press. https://doi.org/10.1017/cbo9780511550522.018.
Gulis, V., Kuehn, K. A., Schoettle, L. N., Leach, D., Benstead, J. P., & Rosemond, A. D. (2017). Changes in nutrient stoichiometry, elemental homeostasis and growth rate of aquatic litter-associated fungi in response to inorganic nutrient supply. The ISME Journal, 11(12), 2729–2739. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2017.123.
Gulis, V., Rosemond, A. D., Suberkropp, K., Weyers, H. S., & Benstead, J. P. (2004). Effects of nutrient enrichment on the decomposition of wood and associated microbial activity in streams. Freshwater Biology, 49(11), 1437–1447. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.2004.01281.x.
Gulis, V., & Suberkropp, K. (2003a). Leaf litter decomposition and microbial activity in nutrient-enriched and unaltered reaches of a headwater stream. Freshwater Biology, 48(1), 123–134. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2427.2003.00985.x.
Gulis, V., & Suberkropp, K. (2003b). Effect of inorganic nutrients on relative contributions of fungi and bacteria to carbon flow from submerged decomposing leaf litter. Microbial Ecology, 45(1), 11–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-002-1032-1.
Gulis, V., & Suberkropp, K. (2003c). Interactions between stream fungi and bacteria associated with decomposing leaf litter at different levels of nutrient availability. Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 30, 149–157.
Gulis, V., Suberkropp, K., & Rosemond, A. D. (2008). Comparison of fungal activities on wood and leaf litter in unaltered and nutrient-enriched headwater streams. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 74(4), 1094–1101. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01903-07.
Güsewell, S., & Freeman, C. (2005). Nutrient limitation and enzyme activities during litter decomposition of nine wetland species in relation to litter N: P ratios. Functional Ecology, 19(4), 582–593. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2435.2005.01002.x.
Halvorson, H. M., Fuller, C. L., Entrekin, S. A., Scott, J. T., & Evans-White, M. A. (2018). Detrital nutrient content and leaf species differentially affect growth and nutritional regulation of detritivores. Oikos, 127(10), 1471–1481. https://doi.org/10.1111/oik.05201.
Halvorson, H. M., White, G., Scott, J. T., & Evans-White, M. A. (2016). Dietary and taxonomic controls on incorporation of microbial carbon and phosphorus by detritivorous caddisflies. Oecologia, 180(2), 567–579. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-015-3464-6.
Harpole, W. S., Ngai, J. T., Cleland, E. E., Seabloom, E. W., Borer, E. T., Bracken, M. E. S., Elser, J., Gruner, D. S., Hillebrand, H., Shurin, J. B., & Smith, J. E. (2011). Nutrient co-limitation of primary producer communities. Ecology Letters, 14(9), 852–862. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2011.01651.x.
Hartmann, J., Lauerwald, R., & Moosdorf, N. (2014). A brief overview of the GLObal RIver Chemistry Database, Glorich. Procedia Earth and Planetary Science, 10, 23–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeps.2014.08.005.
Hartmann, J., Lauerwald, R., & Moosdorf, N. (2019). GLORICH—Global river chemistry database [Data set]. Supplement to: Hartmann, J et al. (2014): A Brief Overview of the GLObal RIver Chemistry Database, GLORICH. Procedia Earth and Planetary Science, 10, 23–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.Proeps.2014.08.005. PANGAEA. https://doi.org/10.1594/pangaea.902360.
Hendel, B., Sinsabaugh, R. L., & Marxsen, J. (2020). Lignin-degrading enzymes: Phenoloxidase and Peroxidase. In F. Bärlocher, M. O. Gessner, & M. A. S. Graça (Eds.), Methods to study litter decomposition: A practical guide (pp. 425–431). Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-30515-4_46.
Hieber, M., & Gessner, M. O. (2002). Contribution of stream detritivores, fungi, and bacteria to leaf breakdown based on biomass estimates. Ecology, 83(4), 1026–1038. https://doi.org/10.2307/3071911.
Hill, B. H., Bolgrien, D. W., Herlihy, A. T., Jicha, T. M., & Angradi, T. R. (2011). A synoptic survey of nitrogen and phosphorus in tributary streams and Great Rivers of the upper Mississippi, Missouri, and Ohio River basins. Water, Air, and Soil pollution, 216(1), 605–619. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-010-0556-0.
Hladyz, S., Gessner, M. O., Giller, P. S., Pozo, J., & Woodward, G. (2009). Resource quality and stoichiometric constraints on stream ecosystem functioning. Freshwater Biology, 54(5), 957–970. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.2008.02138.x.
Jabiol, J., Lecerf, A., Lamothe, S., Gessner, M. O., & Chauvet, E. (2019). Litter quality modulates effects of dissolved nitrogen on leaf decomposition by stream microbial communities. Microbial Ecology, 77(4), 959–966. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-019-01353-3.
Jarvie, H. P., Sharpley, A. N., Withers, P. J. A., Scott, J. T., Haggard, B. E., & Neal, C. (2013). Phosphorus mitigation to control river eutrophication: Murky waters, inconvenient truths, and “postnormal” science. Journal of Environmental Quality, 42(2), 295–304. https://doi.org/10.2134/jeq2012.0085.
Jenkins, C. C., & Suberkropp, K. (1995). The influence of water chemistry on the enzymatic degradation of leaves in streams. Freshwater Biology, 33(2), 245–253. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.1995.tb01165.x.
Johnson, S. L., & Jones, J. A. (2000). Stream temperature responses to forest harvest and debris flows in western Cascades, Oregon. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 57(S2), 30–39. https://doi.org/10.1139/f00-109.
Kaushal, S. S., Mayer, P. M., Vidon, P. G., Smith, R. M., Pennino, M. J., Newcomer, T. A., Duan, S., Welty, C., & Belt, K. T. (2014). Land use and climate variability amplify carbon, nutrient, and contaminant pulses: A review with management implications. Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 50(3), 585–614. https://doi.org/10.1111/jawr.12204.
Kiffney, P. M., Richardson, J. S., & Bull, J. P. (2003). Responses of periphyton and insects to experimental manipulation of riparian buffer width along forest streams. Journal of Applied Ecology, 40(6), 1060–1076. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2664.2003.00855.x.
Kominoski, J. S., Rosemond, A. D., Benstead, J. P., Gulis, V., Maerz, J. C., & Manning, D. W. P. (2015). Low-to-moderate nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations accelerate microbially driven litter breakdown rates. Ecological Applications, 25(3), 856–865. https://doi.org/10.1890/14-1113.1.
Lecerf, A., Usseglio-Polatera, P., Charcosset, J.-Y., Lambrigot, D., Bracht, B., & Chauvet, E. (2006). Assessment of functional integrity of eutrophic streams using litter breakdown and benthic macroinvertebrates. Archiv Für Hydrobiologie, 165(1), 105–126. https://doi.org/10.1127/0003-9136/2006/0165-0105.
LeRoy, C. J., Hipp, A. L., Lueders, K., Shah, J. J. F., Kominoski, J. S., Ardón, M., Dodds, W. K., Gessner, M. O., Griffiths, N. A., Lecerf, A., Manning, D. W. P., Sinsabaugh, R. L., & Webster, J. R. (2020). Plant phylogenetic history explains in-stream decomposition at a global scale. Journal of Ecology, 108(1), 17–35. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2745.13262.
LeRoy, C. J., & Marks, J. C. (2006). Litter quality, stream characteristics and litter diversity influence decomposition rates and macroinvertebrates. Freshwater Biology, 51(4), 605–617. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.2006.01512.x.
Linker, L. C., Dennis, R., Shenk, G. W., Batiuk, R. A., Grimm, J., & Wang, P. (2013). Computing atmospheric nutrient loads to the Chesapeake Bay watershed and tidal waters. Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 49(5), 1025–1041. https://doi.org/10.1111/jawr.12112.
Linkins, A. E., Sinsabaugh, R. L., Mcclaugherty, C. A., & Melillo, J. M. (1990). Comparison of cellulase activity on decomposing leaves in a hardwood forest and woodland stream. Soil Biology & Biochemistry, 22(3), 423–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-0717(90)90123-H.
Manning, D. W. P., Rosemond, A. D., Benstead, J. P., Bumpers, P. M., & Kominoski, J. S. (2020). Transport of N and P in U.S. streams and rivers differs with land use and between dissolved and particulate forms. Ecological Applications. https://doi.org/10.1002/eap.2130.
Manning, D. W. P., Rosemond, A. D., Gulis, V., Benstead, J. P., & Kominoski, J. S. (2018). Nutrients and temperature additively increase stream microbial respiration. Global Change Biology, 24(1), e233–e247. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.13906.
Manning, D. W. P., Rosemond, A. D., Gulis, V., Benstead, J. P., Kominoski, J. S., & Maerz, J. C. (2016). Convergence of detrital stoichiometry predicts thresholds of nutrient-stimulated breakdown in streams. Ecological Applications, 26(6), 1745–1757. https://doi.org/10.1890/15-1217.1.
Manning, D. W. P., Rosemond, A. D., Kominoski, J. S., Gulis, V., Benstead, J. P., & Maerz, J. C. (2015). Detrital stoichiometry as a critical nexus for the effects of streamwater nutrients on leaf litter breakdown rates. Ecology, 96(8), 2214–2224. https://doi.org/10.1890/14-1582.1.
Manzoni, S., Trofymow, J. A., Jackson, R. B., & Porporato, A. (2010). Stoichiometric controls on carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus dynamics in decomposing litter. Ecological Monographs, 80(1), 89–106. https://doi.org/10.1890/09-0179.1.
Marks, J. C. (2019). Revisiting the fates of dead leaves that fall into streams. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 50(1). https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-ecolsys-110218-024755.
McDowell, R. W., Noble, A., Pletnyakov, P., Haggard, B. E., & Mosley, L. M. (2020). Global mapping of freshwater nutrient enrichment and periphyton growth potential. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 3568. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-60279-w.
Moore, J. C., Berlow, E. L., Coleman, D. C., Ruiter, P. C., de, Dong, Q., Hastings, A., Johnson, N. C., McCann, K. S., Melville, K., Morin, P. J., Nadelhoffer, K., Rosemond, A. D., Post, D. M., Sabo, J. L., Scow, K. M., Vanni, M. J., & Wall, D. H. (2004). Detritus, trophic dynamics and biodiversity. Ecology Letters, 7(7), 584–600. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2004.00606.x.
Moretti, M. S., Loyola, R. D., Becker, B., & Callisto, M. (2009). Leaf abundance and phenolic concentrations codetermine the selection of case-building materials by Phylloicus sp. (Trichoptera, Calamoceratidae). Hydrobiologia, 630(1), 199–206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-009-9792-y.
Moss, B., Kosten, S., Meerhoff, M., Battarbee, R. W., Jeppesen, E., Mazzeo, N., Havens, K., Lacerot, G., Liu, Z., de Meester, L., Paerl, H., & Scheffer, M. (2011). Allied attack: Climate change and eutrophication. Inland Waters, 1(2), 101–105. https://doi.org/10.5268/IW-1.2.359.
Mulholland, P. J., & Hill, W. R. (1997). Seasonal patterns in streamwater nutrient and dissolved organic carbon concentrations: Separating catchment flow path and in-stream effects. Water Resources Research, 33(6), 1297–1306. https://doi.org/10.1029/97WR00490.
Murdoch, P. S., Baron, J. S., & Miller, T. L. (2000). Potential effects of climate change on surface-water quality in North America. Journal of the American Water Resources Association, 36(2), 347–366. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1752-1688.2000.tb04273.x.
Newbold, J. D., Elwood, J. W., O’Neill, R. V., & Sheldon, A. L. (1983). Phosphorus dynamics in a woodland stream ecosystem: A study of nutrient spiralling. Ecology, 64(5), 1249–1265. https://doi.org/10.2307/1937833.
Newbold, J. D., Elwood, J. W., Schulze, M. S., Stark, R. W., & Barmeier, J. C. (1983). Continuous ammonium enrichment of a woodland stream: Uptake kinetics, leaf decomposition, and nitrification. Freshwater Biology, 13(2), 193–204. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.1983.tb00671.x.
Pascoal, C., & Cássio, F. (2004). Contribution of fungi and bacteria to leaf litter decomposition in a polluted river. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 70(9), 5266–5273. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.70.9.5266-5273.2004.
Pascoal, C., Cássio, F., Marcotegui, A., Sanz, B., & Gomes, P. (2005). Role of fungi, bacteria, and invertebrates in leaf litter breakdown in a polluted river. Journal of the North American Benthological Society, 24(4), 784–797. https://doi.org/10.1899/05-010.1.
Pastor, A., Compson, Z. G., Dijkstra, P., Riera, J. L., Martí, E., Sabater, F., Hungate, B. A., & Marks, J. C. (2014). Stream carbon and nitrogen supplements during leaf litter decomposition: Contrasting patterns for two foundation species. Oecologia, 176(4), 1111–1121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-014-3063-y.
Piggott, J. J., Lange, K., Townsend, C. R., & Matthaei, C. D. (2012). Multiple stressors in agricultural streams: A mesocosm study of interactions among raised water temperature, sediment addition and nutrient enrichment. PLoS ONE, 7(11), https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0049873.
Piggott, J. J., Niyogi, D. K., Townsend, C. R., & Matthaei, C. D. (2015). Multiple stressors and stream ecosystem functioning: Climate warming and agricultural stressors interact to affect processing of organic matter. Journal of Applied Ecology, 52(5), 1126–1134. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2664.12480.
Prater, C., Bumpers, P. M., Demi, L. M., Rosemond, A. D., & Jeyasingh, P. D. (2020). Differential responses of macroinvertebrate ionomes across experimental N: P gradients in detritus-based headwater streams. Oecologia. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-020-04720-x.
Prater, C., Norman, E. J., & Evans-White, M. A. (2015). Relationships among nutrient enrichment, detritus quality and quantity, and large-bodied shredding insect community structure. Hydrobiologia, 753(1), 219–232. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-015-2208-2.
Rincón, J., & Martínez, I. (2006). Food quality and feeding preferences of Phylloicus sp. (Trichoptera: Calamoceratidae). Journal of the North American Benthological Society, 25(1), 209–215. https://doi.org/10.1899/0887-3593(2006)25%5b209:fqafpo%5d2.0.co;2.
Robbins, C. J., Matthaeus, W. J., Cook, S. C., Housley, L. M., Robison, S. E., Garbarino, M. A., LeBrun, E. S., Raut, S., Tseng, C.‐Y., & King, R. S. (2019). Leaf litter identity alters the timing of lotic nutrient dynamics. Freshwater Biology. https://doi.org/10.1111/fwb.13410.
Rose, L. A., Karwan, D. L., & Godsey, S. E. (2018). Concentration–discharge relationships describe solute and sediment mobilization, reaction, and transport at event and longer timescales. Hydrological Processes, 32(18), 2829–2844. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.13235.
Rosemond, A. D., Benstead, J. P., Bumpers, P. M., Gulis, V., Kominoski, J. S., Manning, D. W. P., Suberkropp, K., & Wallace, J. B. (2015). Experimental nutrient additions accelerate terrestrial carbon loss from stream ecosystems. Science, 347(6226), 1142–1145. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaa1958.
Rosemond, A. D., Pringle, C. M., Ramírez, A., Paul, M. J., & Meyer, J. L. (2002). Landscape variation in phosphorus concentration and effects on detritus-based tropical streams. Limnology and Oceanography, 47(1), 278–289. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2002.47.1.0278.
Royer, T. V., & Minshall, G. W. (2001). Effects of nutrient enrichment and leaf quality on the breakdown of leaves in a hardwater stream. Freshwater Biology, 46(5), 603–610. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2427.2001.00694.x.
Sanpera-Calbet, I., Lecerf, A., & Chauvet, E. (2009). Leaf diversity influences in-stream litter decomposition through effects on shredders. Freshwater Biology, 54(8), 1671–1682. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.2009.02216.x.
Scott, E. E., Prater, C., Norman, E., Baker, B. C., Evans-White, M., & Scott, J. T. (2013). Leaf-litter stoichiometry is affected by streamwater phosphorus concentrations and litter type. Freshwater Science, 32(3), 753–761. https://doi.org/10.1899/12-215.1.
Seena, S., Bärlocher, F., Sobral, O., Gessner, M. O., Dudgeon, D., McKie, B. G., Chauvet, E., Boyero, L., Ferreira, V., Frainer, A., Bruder, A., Matthaei, C. D., Fenoglio, S., Sridhar, K. R., Albariño, R. J., Douglas, M. M., Encalada, A. C., Garcia, E., Ghate, S. D., … Graça, M. A. S. (2019). Biodiversity of leaf litter fungi in streams along a latitudinal gradient. Science of the Total Environment, 661, 306–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.01.122.
Smith, V. H., Joye, S. B., & Howarth, R. W. (2006). Eutrophication of freshwater and marine ecosystems. Limnology and Oceanography, 51, 351–355. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2006.51.1_part_2.0351.
Sridhar, K. R., & Bärlocher, F. (1997). Water chemistry and sporulation by aquatic hyphomycetes. Mycological Research, 101(5), 591–596. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0953756296003024.
Stelzer, R. S., Heffernan, J., & Likens, G. E. (2003). The influence of dissolved nutrients and particulate organic matter quality on microbial respiration and biomass in a forest stream. Freshwater Biology, 48(11), 1925–1937. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2427.2003.01141.x.
Stets, E. G., Sprague, L. A., Oelsner, G. P., Johnson, H. M., Murphy, J. C., Ryberg, K., Vecchia, A. V., Zuellig, R. E., Falcone, J. A., & Riskin, M. L. (2020). Landscape drivers of dynamic change in water quality of U.S. rivers. Environmental Science & Technology, 54(7), 4336–4343. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.9b05344.
Stoddard, J. L., Van Sickle, J., Herlihy, A. T., Brahney, J., Paulsen, S., Peck, D. V., Mitchell, R., & Pollard, A. I. (2016). Continental-scale increase in lake and stream phosphorus: Are oligotrophic systems disappearing in the United States? Environmental Science & Technology, 50(7), 3409–3415. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b05950.
Suberkropp, K. (1991). Relationships between growth and sporulation of aquatic hyphomycetes on decomposing leaf litter. Mycological Research, 95(7), 843–850. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0953-7562(09)80048-8.
Suberkropp, K. (1992). Interactions with invertebrates. In F. Bärlocher (Ed.), The ecology of aquatic hyphomycetes (pp. 118–134). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-76855-2_6.
Suberkropp, K. (1995). The influence of nutrients on fungal growth, productivity, and sporulation during leaf breakdown in streams. Canadian Journal of Botany, 73(S1), 1361–1369. https://doi.org/10.1139/b95-398.
Suberkropp, K. (1998). Effect of dissolved nutrients on two aquatic hyphomycetes growing on leaf litter. Mycological Research, 102(8), 998–1002. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0953756297005807.
Suberkropp, K. & Chauvet, E. (1995). Regulation of leaf breakdown by fungi in streams: Influences of water chemistry. Ecology, 76(5), 1433–1445. https://doi.org/10.2307/1938146.
Suberkropp, K., Gulis, V., Rosemond, A. D., & Benstead, J. P. (2010). Ecosystem and physiological scales of microbial responses to nutrients in a detritus-based stream: Results of a 5-year continuous enrichment. Limnology and Oceanography, 55(1), 149–160. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2010.55.1.0149.
Tank, J. L., Rosi-Marshall, E. J., Griffiths, N. A., Entrekin, S. A., & Stephen, M. L. (2010). A review of allochthonous organic matter dynamics and metabolism in streams. Journal of the North American Benthological Society, 29(1), 118–146. https://doi.org/10.1899/08-170.1.
Tant, C. J., Rosemond, A. D., & First, M. R. (2013). Stream nutrient enrichment has a greater effect on coarse than on fine benthic organic matter. Freshwater Science, 32(4), 1111–1121. https://doi.org/10.1899/12-049.1.
Tant, C. J., Rosemond, A. D., Helton, A. M., & First, M. R. (2015). Nutrient enrichment alters the magnitude and timing of fungal, bacterial, and detritivore contributions to litter breakdown. Freshwater Science, 34(4), 1259–1271. https://doi.org/10.1086/683255.
Taylor, B. R., & Chauvet, E. E. (2014). Relative influence of shredders and fungi on leaf litter decomposition along a river altitudinal gradient. Hydrobiologia, 721(1), 239–250. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-013-1666-7.
Tiegs, S. D., Costello, D. M., Isken, M. W., Woodward, G., McIntyre, P. B., Gessner, M. O., Chauvet, E., Griffiths, N. A., Flecker, A. S., Acuña, V., Albariño, R., Allen, D. C., Alonso, C., Andino, P., Arango, C., Aroviita, J., Barbosa, M. V. M., Barmuta, L. A., Baxter, C. V., … Zwart, J. A. (2019). Global patterns and drivers of ecosystem functioning in rivers and riparian zones. Science Advances, 5(1), eaav0486. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aav0486.
US Environmental Protection Agency. (2016). National rivers and streams assessment 2008–2009 report [Reports and Assessments]. https://www.epa.gov/national-aquatic-resource-surveys/national-rivers-and-streams-assessment-2008-2009-report.
Usher, R. L., Wood, J., Bumpers, P. M., Wenger, S. J., & Rosemond, A. D. (2020). Streamwater nutrients stimulate respiration and breakdown of standardized detrital substrates across a landscape gradient: Effects of nitrogen, phosphorus, and carbon quality. Freshwater Science, 39(1), 101–114. https://doi.org/10.1086/707598.
Venarsky, M. P., Benstead, J. P., Huryn, A. D., Huntsman, B. M., Edmonds, J. W., Findlay, R. H., & Bruce Wallace, J. (2018). Experimental detritus manipulations unite surface and cave stream ecosystems along a common energy gradient. Ecosystems, 21(4), 629–642. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10021-017-0174-4.
Wallace, J. B., Eggert, S. L., Meyer, J. L., & Webster, J. R. (1997). Multiple trophic levels of a forest stream linked to terrestrial litter inputs. Science, 277(5322), 102–104. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.277.5322.102.
Walther, D. A., & Whiles, M. R. (2011). Secondary production in a southern Illinois headwater stream: Relationships between organic matter standing stocks and macroinvertebrate productivity. Journal of the North American Benthological Society, 30(2), 357–373. https://doi.org/10.1899/10-006.1.
Webster, J. R. (2007). Spiraling down the river continuum: Stream ecology and the U-shaped curve. Journal of the North American Benthological Society, 26(3), 375–389. https://doi.org/10.1899/06-095.1.
Webster, J. R., & Benfield, E. F. (1986). Vascular plant breakdown in freshwater ecosystems. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics, 17(1), 567–594. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.es.17.110186.003031.
Weyers, H. S., & Suberkropp, K. (1996). Fungal and bacterial production during the breakdown of yellow poplar leaves in 2 Streams. Journal of the North American Benthological Society, 15(4), 408–420. https://doi.org/10.2307/1467795.
Woodward, G., Gessner, M. O., Giller, P. S., Gulis, V., Hladyz, S., Lecerf, A., Malmqvist, B., McKie, B. G., Tiegs, S. D., Cariss, H., Dobson, M., Elosegi, A., Ferreira, V., Graça, M. A. S., Fleituch, T., Lacoursière, J. O., Nistorescu, M., Pozo, J., Risnoveanu, G., … Chauvet, E. (2012). Continental-scale effects of nutrient pollution on stream ecosystem functioning. Science, 336(6087), 1438–1440. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1219534.
Wurtsbaugh, W. A., Paerl, H. W., & Dodds, W. K. (2019). Nutrients, eutrophication and harmful algal blooms along the freshwater to marine continuum. WIREs Water, 6(5), https://doi.org/10.1002/wat2.1373.
Yule, C. M., Boyero, L., & Marchant, R. (2010). Effects of sediment pollution on food webs in a tropical river (Borneo, Indonesia). Marine & Freshwater Research, 61(2), 204. https://doi.org/10.1071/MF09065.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Manning, D.W.P., Ferreira, V., Gulis, V., Rosemond, A.D. (2021). Pathways, Mechanisms, and Consequences of Nutrient-Stimulated Plant Litter Decomposition in Streams. In: Swan, C.M., Boyero, L., Canhoto, C. (eds) The Ecology of Plant Litter Decomposition in Stream Ecosystems. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-72854-0_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-72854-0_16
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-72853-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-72854-0
eBook Packages: Biomedical and Life SciencesBiomedical and Life Sciences (R0)