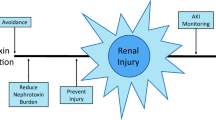
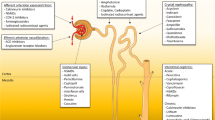
Abstract
The excretion of endogenous and exogenous compounds is a fundamental aspect of renal function, which, by necessity, exposes the kidney to high concentrations of these substances and their metabolites. Some of these compounds are “toxic” to the kidney and substances capable of causing renal damage or injury are termed “nephrotoxins.” While naturally occurring nephrotoxins exist and environmental exposures can cause injury, the focus of this chapter is on the pharmaceutical agents used to treat medical disease and its sequelae. While specific, ubiquitously prescribed agents are discussed in detail, equal weight is placed on highlighting core nephrotoxin concepts, illustrating the most commonly seen nephrotoxicity phenotypes, and describing the mechanisms by which these compounds cause injury. This foundation creates the context for discussing approaches to avoid, minimize, and manage the impact of nephrotoxin exposure. Although targeted treatments for nephrotoxic acute kidney injury do not yet exist, broad multidisciplinary strategies are capable of predicting, preventing, and mitigating the impact of these medications. Furthermore, a thorough understanding of the core concepts underpinning nephrotoxicity will allow future development of disease-specific interventions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avner ED, Harmon WE, Niaudet P, Yoshikawa N, Goldstein SL, editors. Pediatric nephrology. Berlin/Heidelberg: Springer; 2016.
Pritchard JB, Miller DS. Mechanisms mediating renal secretion of organic anions and cations. Physiol Rev. 1993;73(4):765–96.
Sekine T, Miyazaki H, Endou H. Molecular physiology of renal organic anion transporters. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2006;290(2):F251–61.
Ullrich KJ. Renal transporters for organic anions and organic cations. Structural requirements for substrates. J Membr Biol. 1997;158(2):95–107.
Schreiner GE. Toxic nephropathy: adverse renal effects caused by drugs and chemicals. JAMA. 1965;191:849–50.
Uber AM, Sutherland SM. Nephrotoxins and nephrotoxic acute kidney injury. Pediatr Nephrol (Berlin, Germany). 2020;35(10):1825–33.
Kleinknecht D, Landais P, Goldfarb B. Drug-associated acute renal failure. A prospective collaborative study of 81 biopsied patients. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1987;212:125–8.
Schetz M, Dasta J, Goldstein S, Golper T. Drug-induced acute kidney injury. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2005;11(6):555–65.
Mehta RL, Awdishu L, Davenport A, Murray PT, Macedo E, Cerda J, et al. Phenotype standardization for drug-induced kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2015;88(2):226–34.
Hogan JJ, Markowitz GS, Radhakrishnan J. Drug-induced glomerular disease: immune-mediated injury. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015;10(7):1300–10.
McWilliam SJ, Antoine DJ, Smyth RL, Pirmohamed M. Aminoglycoside-induced nephrotoxicity in children. Pediatr Nephrol (Berlin, Germany). 2017;32(11):2015–25.
Blossom AP, Cleary JD, Daley WP. Acyclovir-induced crystalluria. Ann Pharmacother. 2002;36(3):526.
Roberts DM, Smith MW, McMullan BJ, Sevastos J, Day RO. Acute kidney injury due to crystalluria following acute valacyclovir overdose. Kidney Int. 2011;79(5):574.
Kashoor I, Batlle D. Proximal renal tubular acidosis with and without Fanconi syndrome. Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2019;38(3):267–81.
Kitterer D, Schwab M, Alscher MD, Braun N, Latus J. Drug-induced acid-base disorders. Pediatr Nephrol (Berlin, Germany). 2015;30(9):1407–23.
Fayolle M, Souweine JS, Mathieu O, Bargnoux AS, Cristol JP, Badiou S. Water, lithium and sodium: watch out for dangerous injuries. Ann Biol Clin. 2020;78(4):449–53.
Bockenhauer D, Bichet DG. Pathophysiology, diagnosis and management of nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2015;11(10):576–88.
Izzedine H, Launay-Vacher V, Bourry E, Brocheriou I, Karie S, Deray G. Drug-induced glomerulopathies. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2006;5(1):95–106.
Pape L, Ahlenstiel T. mTOR inhibitors in pediatric kidney transplantation. Pediatr Nephrol (Berlin, Germany). 2014;29(7):1119–29.
Lee Y, Lee ST, Cho H. D-penicillamine-induced ANA (+) ANCA (+) vasculitis in pediatric patients with Wilson’s disease. Clin Nephrol. 2016;85(5):296–300.
Goldman RD, Koren G. Amphotericin B nephrotoxicity in children. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2004;26(7):421–6.
Clavé S, Rousset-Rouvière C, Daniel L, Tsimaratos M. The invisible threat of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for kidneys. Front Pediatr. 2019;7:520.
Sriperumbuduri S, Hiremath S. The case for cautious consumption: NSAIDs in chronic kidney disease. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2019;28(2):163–70.
Lacquaniti A, Campo S, Casuscelli Di Tocco T, Rovito S, Bucca M, Ragusa A, et al. Acute and chronic kidney disease after pediatric liver transplantation: an underestimated problem. Clin Transpl. 2020;34:e14082.
Downes KJ, Hayes M, Fitzgerald JC, Pais GM, Liu J, Zane NR, et al. Mechanisms of antimicrobial-induced nephrotoxicity in children. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2020;75(1):1–13.
Hanna MH, Askenazi DJ, Selewski DT. Drug-induced acute kidney injury in neonates. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2016;28(2):180–7.
Ligi I, Boubred F, Grandvuillemin I, Simeoni U. The neonatal kidney: implications for drug metabolism and elimination. Curr Drug Metab. 2013;14(2):174–7.
Girardi A, Raschi E, Galletti S, Allegaert K, Poluzzi E, De Ponti F. Drug-induced renal injury in neonates: challenges in clinical practice and perspectives in drug development. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2017;13(5):555–65.
Nada A, Bonachea EM, Askenazi DJ. Acute kidney injury in the fetus and neonate. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2017;22(2):90–7.
Pandey R, Koshy RG, Dako J. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors induced acute kidney injury in newborn. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2017;30(6):748–50.
Bartelink IH, Rademaker CM, Schobben AF, van den Anker JN. Guidelines on paediatric dosing on the basis of developmental physiology and pharmacokinetic considerations. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2006;45(11):1077–97.
Saint-Faust M, Boubred F, Simeoni U. Renal development and neonatal adaptation. Am J Perinatol. 2014;31(9):773–80.
McMahon KR, Rassekh SR, Schultz KR, Blydt-Hansen T, Cuvelier GDE, Mammen C, et al. Epidemiologic characteristics of acute kidney injury during cisplatin infusions in children treated for cancer. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3(5):e203639.
Bhatt J, Jahnke N, Smyth AR. Once-daily versus multiple-daily dosing with intravenous aminoglycosides for cystic fibrosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019;9(9):Cd002009.
Thomas MC. Diuretics, ACE inhibitors and NSAIDs—the triple whammy. Med J Aust. 2000;172(4):184–5.
Goldstein SL, Dahale D, Kirkendall ES, Mottes T, Kaplan H, Muething S, et al. A prospective multi-center quality improvement initiative (NINJA) indicates a reduction in nephrotoxic acute kidney injury in hospitalized children. Kidney Int. 2020;97(3):580–8.
Goldstein SL, Kirkendall E, Nguyen H, Schaffzin JK, Bucuvalas J, Bracke T, et al. Electronic health record identification of nephrotoxin exposure and associated acute kidney injury. Pediatrics. 2013;132(3):e756–67.
Goldstein SL, Mottes T, Simpson K, Barclay C, Muething S, Haslam DB, et al. A sustained quality improvement program reduces nephrotoxic medication-associated acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2016;90(1):212–21.
Goswami E, Ogden RK, Bennett WE, Goldstein SL, Hackbarth R, Somers MJG, et al. Evidence-based development of a nephrotoxic medication list to screen for acute kidney injury risk in hospitalized children. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2019;76(22):1869–74.
Xu X, Nie S, Zhang A, Mao J, Liu HP, Xia H, et al. Acute kidney injury among hospitalized children in China. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018;13(12):1791–800.
Toth-Manikowski S, Grams ME. Proton pump inhibitors and kidney disease – GI upset for the nephrologist? Kidney Int Rep. 2017;2(3):297–301.
Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Acute Kidney Injury Work Group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2012;2:1–138.
Estrada CC, Maldonado A, Mallipattu SK. Therapeutic inhibition of VEGF signaling and associated nephrotoxicities. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019;30(2):187–200.
Perazella MA. Pharmacology behind common drug nephrotoxicities. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018;13(12):1897–908.
Loden JK, Seger DL, Spiller HA, Wang L, Byrne DW. Cutaneous-hemolytic loxoscelism following brown recluse spider envenomation: new understandings. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2020:58(12):1297–1305. https://doi.org/10.1080/15563650.2020.1739701. Epub 2020 Mar 18.
Isbister GK, Fan HW. Spider bite. Lancet (London, England). 2011;378(9808):2039–47.
Vikrant S, Jaryal A, Gupta D, Parashar A. Epidemiology and outcome of acute kidney injury due to venomous animals from a subtropical region of India. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2019;57(4):240–5.
Furtado AA, Daniele-Silva A, Silva-Júnior AAD, Fernandes-Pedrosa MF. Biology, venom composition, and scorpionism induced by brazilian scorpion Tityus stigmurus (Thorell, 1876) (Scorpiones: Buthidae): a mini-review. Off J Int Soc Toxinol. 2020;185:36–45.
Berger M, Santi L, Beys-da-Silva WO, Oliveira FM, Caliari MV, Yates JR 3rd, et al. Mechanisms of acute kidney injury induced by experimental lonomia obliqua envenomation. Arch Toxicol. 2015;89(3):459–83.
Schmidt JO. Clinical consequences of toxic envenomations by Hymenoptera. Off J Int Soc Toxinol. 2018;150:96–104.
Wijayaratne DR, Bavanthan V, de Silva MVC, Nazar ALM, Wijewickrama ES. Star fruit nephrotoxicity: a case series and literature review. BMC Nephrol. 2018;19(1):288.
Albersmeyer M, Hilge R, Schröttle A, Weiss M, Sitter T, Vielhauer V. Acute kidney injury after ingestion of rhubarb: secondary oxalate nephropathy in a patient with type 1 diabetes. BMC Nephrol. 2012;13:141.
Moyses-Neto M, Brito BRS, de Araújo Brito DJ, Barros NDC, Dantas M, Salgado-Filho N, et al. Vitamin C-induced oxalate nephropathy in a renal transplant patient related to excessive ingestion of cashew pseudofruit (Anacardium occidentale L.): a case report. BMC Nephrol. 2018;19(1):265.
Bunawan NC, Rastegar A, White KP, Wang NE. Djenkolism: case report and literature review. Int Med Case Rep J. 2014;7:79–84.
Yang B, Xie Y, Guo M, Rosner MH, Yang H, Ronco C. Nephrotoxicity and Chinese herbal medicine. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018;13(10):1605–11.
Anger EE, Yu F, Li J. Aristolochic acid-induced nephrotoxicity: molecular mechanisms and potential protective approaches. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(3):1157.
Scarpa A, Guerci A. Various uses of the castor oil plant (Ricinus communis L.). a review. J Ethnopharmacol. 1982;5(2):117–37.
Brandenburg WE, Ward KJ. Mushroom poisoning epidemiology in the United States. Mycologia. 2018;110(4):637–41.
Audi J, Belson M, Patel M, Schier J, Osterloh J. Ricin poisoning: a comprehensive review. JAMA. 2005;294(18):2342–51.
Garcia J, Costa VM, Carvalho A, Baptista P, de Pinho PG, de Lourdes BM, et al. Amanita phalloides poisoning: mechanisms of toxicity and treatment. Food Chem Toxicol. 2015;86:41–55.
Scammell MK, Sennett CM, Petropoulos ZE, Kamal J, Kaufman JS. Environmental and occupational exposures in kidney disease. Semin Nephrol. 2019;39(3):230–43.
Jacobsen D, Hewlett TP, Webb R, Brown ST, Ordinario AT, McMartin KE. Ethylene glycol intoxication: evaluation of kinetics and crystalluria. Am J Med. 1988;84(1):145–52.
Gómez HF, Borgialli DA, Sharman M, Shah KK, Scolpino AJ, Oleske JM, et al. Blood Lead levels of children in Flint, Michigan: 2006–2016. J Pediatr. 2018;197:158–64.
Johnson RJ, Wesseling C, Newman LS. Chronic kidney disease of unknown cause in agricultural communities. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(19):1843–52.
Hassanin NM, Awad OM, El-Fiki S, Abou-Shanab RAI, Abou-Shanab ARA, Amer RA. Association between exposure to pesticides and disorder on hematological parameters and kidney function in male agricultural workers. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018;25(31):30802–7.
Tait RJ, Caldicott D, Mountain D, Hill SL, Lenton S. A systematic review of adverse events arising from the use of synthetic cannabinoids and their associated treatment. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2016;54(1):1–13.
Nanavati A, Herlitz LC. Tubulointerstitial injury and drugs of abuse. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2017;24(2):80–5.
Pendergraft WF 3rd, Herlitz LC, Thornley-Brown D, Rosner M, Niles JL. Nephrotoxic effects of common and emerging drugs of abuse. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014;9(11):1996–2005.
Rivosecchi RM, Kellum JA, Dasta JF, Armahizer MJ, Bolesta S, Buckley MS, et al. Drug class combination-associated acute kidney injury. Ann Pharmacother. 2016;50(11):953–72.
Jeffres MN. The whole price of vancomycin: toxicities, troughs, and time. Drugs. 2017;77(11):1143–54.
Perazella MA. Drug-induced acute kidney injury: diverse mechanisms of tubular injury. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2019;25(6):550–7.
Luque Y, Louis K, Jouanneau C, Placier S, Esteve E, Bazin D, et al. Vancomycin-associated cast nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017;28(6):1723–8.
Wang K, Kestenbaum B. Proximal tubular secretory clearance: a neglected partner of kidney function. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018;13(8):1291–6.
Miners JO, Yang X, Knights KM, Zhang L. The role of the kidney in drug elimination: transport, metabolism, and the impact of kidney disease on drug clearance. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2017;102(3):436–49.
Patzer L. Nephrotoxicity as a cause of acute kidney injury in children. Pediatr Nephrol (Berlin, Germany). 2008;23(12):2159–73.
Bosch X, Poch E, Grau JM. Rhabdomyolysis and acute kidney injury. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(1):62–72.
Patel AM, Shariff S, Bailey DG, Juurlink DN, Gandhi S, Mamdani M, et al. Statin toxicity from macrolide antibiotic coprescription: a population-based cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 2013;158(12):869–76.
Desai CS, Martin SS, Blumenthal RS. Non-cardiovascular effects associated with statins. BMJ (Clinical Research Ed). 2014;349:g3743.
O’Connor ME, Prowle JR. Fluid Overload. Crit Care Clin. 2015;31(4):803–21.
Alobaidi R, Basu RK, DeCaen A, Joffe AR, Lequier L, Pannu N, et al. Fluid accumulation in critically ill children. Crit Care Med. 2020;48(7):1034–41.
Sutherland SM, Goldstein SL, Alexander SR. The prospective pediatric continuous renal replacement therapy (ppCRRT) registry: a critical appraisal. Pediatr Nephrol (Berlin, Germany). 2014;29(11):2069–76.
Gordon AC, Mason AJ, Thirunavukkarasu N, Perkins GD, Cecconi M, Cepkova M, et al. Effect of early vasopressin vs norepinephrine on kidney failure in patients with septic shock: the VANISH randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2016;316(5):509–18.
Wu Q, Kuca K. Metabolic pathway of cyclosporine a and its correlation with nephrotoxicity. Curr Drug Metab. 2019;20(2):84–90.
Wu H, Huang J. Drug-induced nephrotoxicity: pathogenic mechanisms, biomarkers and prevention strategies. Curr Drug Metab. 2018;19(7):559–67.
Toriu N, Sekine A, Mizuno H, Hasegawa E, Yamanouchi M, Hiramatsu R, et al. Renal-limited thrombotic microangiopathy due to bevacizumab therapy for metastatic colorectal cancer: a case report. Case Rep Oncol. 2019;12(2):391–400.
Daviet F, Rouby F, Poullin P, Moussi-Francès J, Sallée M, Burtey S, et al. Thrombotic microangiopathy associated with gemcitabine use: presentation and outcome in a national French retrospective cohort. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2019;85(2):403–12.
Al-Nouri ZL, Reese JA, Terrell DR, Vesely SK, George JN. Drug-induced thrombotic microangiopathy: a systematic review of published reports. Blood. 2015;125(4):616–8.
Kundra A, Wang JC. Interferon induced thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA): analysis and concise review. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2017;112:103–12.
Tada K, Ito K, Hamauchi A, Takahashi K, Watanabe R, Uchida A, et al. Clopidogrel-induced thrombotic microangiopathy in a patient with hypocomplementemia. Int Med (Tokyo, Japan). 2016;55(8):969–73.
Paueksakon P, Fogo AB. Drug-induced nephropathies. Histopathology. 2017;70(1):94–108.
Markowitz GS, Bomback AS, Perazella MA. Drug-induced glomerular disease: direct cellular injury. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015;10(7):1291–9.
Matthai SM, Basu G, Varughese S, Pulimood AB, Veerasamy T, Korula A. Collapsing glomerulopathy following anabolic steroid use in a 16-year-old boy with IgA nephropathy. Indian J Nephrol. 2015;25(2):99–102.
Pabla N, Dong Z. Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: mechanisms and renoprotective strategies. Kidney Int. 2008;73(9):994–1007.
Perazella MA, Markowitz GS. Drug-induced acute interstitial nephritis. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2010;6(8):461–70.
Barreto EF, Rule AD. Management of Drug-Associated Acute Interstitial Nephritis. Kidney360. 2020;1(1):62–4.
Rossert J. Drug-induced acute interstitial nephritis. Kidney Int. 2001;60(2):804–17.
Shimada M, Johnson RJ, May WS Jr, Lingegowda V, Sood P, Nakagawa T, et al. A novel role for uric acid in acute kidney injury associated with tumour lysis syndrome. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2009;24(10):2960–4.
Shepshelovich D, Schechter A, Calvarysky B, Diker-Cohen T, Rozen-Zvi B, Gafter-Gvili A. Medication-induced SIADH: distribution and characterization according to medication class. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2017;83(8):1801–7.
Kovnat P, Labovitz E, Levison SP. Antibiotics and the kidney. Med Clin North Am. 1973;57(4):1045–63.
Filippone EJ, Kraft WK, Farber JL. The nephrotoxicity of vancomycin. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2017;102(3):459–69.
Cook FV, Farrar WE Jr. Vancomycin revisited. Ann Intern Med. 1978;88(6):813–8.
Hashisaki PA, Jacobson JA. Characteristics, control, and treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections. Clin Pharm. 1982;1(4):343–8.
Sharma R, Hammerschlag MR. Treatment of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infections in children: a reappraisal of vancomycin. Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2019;21(10):37.
Pais GM, Liu J, Zepcan S, Avedissian SN, Rhodes NJ, Downes KJ, et al. Vancomycin-induced kidney injury: animal models of toxicodynamics, mechanisms of injury, human translation, and potential strategies for prevention. Pharmacotherapy. 2020;40(5):438–54.
Sinha Ray A, Haikal A, Hammoud KA, Yu AS. Vancomycin and the risk of AKI: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016;11(12):2132–40.
van Hal SJ, Paterson DL, Lodise TP. Systematic review and meta-analysis of vancomycin-induced nephrotoxicity associated with dosing schedules that maintain troughs between 15 and 20 milligrams per liter. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013;57(2):734–44.
Rutter WC, Hall RG, Burgess DS. Impact of total body weight on rate of acute kidney injury in patients treated with piperacillin-tazobactam and vancomycin. Am J Health Syst pharm. 2019;76(16):1211–7.
Covvey JR, Erickson O, Fiumara D, Mazzei K, Moszczenski Z, Slipak K, et al. Comparison of vancomycin area-under-the-curve dosing versus trough target-based dosing in obese and nonobese patients with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. Ann Pharmacother. 2020;54(7):644–51.
Panwar B, Johnson VA, Patel M, Balkovetz DF. Risk of vancomycin-induced nephrotoxicity in the population with chronic kidney disease. Am J Med Sci. 2013;345(5):396–9.
Sridharan K, Al Daylami A, Ajjawi R, Al-Ajooz H, Veeramuthu S. Clinical pharmacokinetics of vancomycin in critically ill children. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2019;44(6):807–16.
Robertson AD, Li C, Hammond DA, Dickey TA. Incidence of acute kidney injury among patients receiving the combination of vancomycin with piperacillin-tazobactam or meropenem. Pharmacotherapy. 2018;38(12):1184–93.
Ciarambino T, Giannico OV, Campanile A, Tirelli P, Para O, Signoriello G, et al. Acute kidney injury and vancomycin/piperacillin/tazobactam in adult patients: a systematic review. Intern Emerg Med. 2020;15(2):327–31.
Covert KL, Knoetze D, Cole M, Lewis P. Vancomycin plus piperacillin/tazobactam and acute kidney injury risk: a review of the literature. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2020;45:1253–63.
Kalligeros M, Karageorgos SA, Shehadeh F, Zacharioudakis IM, Mylonakis E. The association of acute kidney injury with the concomitant use of vancomycin and piperacillin/tazobactam in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019;63(12):e01572.
Girand HL. Continuous infusion vancomycin in pediatric patients: a critical review of the evidence. J Pediatr Pharmacol Ther. 2020;25(3):198–214.
Rybak MJ, Le J, Lodise TP, Levine DP, Bradley JS, Liu C, et al. Therapeutic monitoring of vancomycin for serious methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections: A revised consensus guideline and review by the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, the Infectious Diseases Society of America, the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society, and the Society of Infectious Diseases Pharmacists. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2020;77(11):835–64.
Zappitelli M, Moffett BS, Hyder A, Goldstein SL. Acute kidney injury in non-critically ill children treated with aminoglycoside antibiotics in a tertiary healthcare centre: a retrospective cohort study. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011;26(1):144–50.
Saad A, Young MR, Studtmann AE, Autry EB, Schadler A, Beckman EJ, et al. Incidence of nephrotoxicity with prolonged aminoglycoside exposure in patients with cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2020;55(12):3384–90.
Huang H, Jin WW, Huang M, Ji H, Capen DE, Xia Y, et al. Gentamicin-induced acute kidney injury in an animal model involves programmed necrosis of the collecting duct. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020;31(9):2097–115.
Le Moyec L, Racine S, Le Toumelin P, Adnet F, Larue V, Cohen Y, et al. Aminoglycoside and glycopeptide renal toxicity in intensive care patients studied by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of urine. Crit Care Med. 2002;30(6):1242–5.
Humes HD. Aminoglycoside nephrotoxicity. Kidney Int. 1988;33(4):900–11.
Smith CR, Moore RD, Lietman PS. Studies of risk factors for aminoglycoside nephrotoxicity. Am J Kidney Dis. 1986;8(5):308–13.
Zager RA. Endotoxemia, renal hypoperfusion, and fever: interactive risk factors for aminoglycoside and sepsis-associated acute renal failure. Am J Kidney Dis. 1992;20(3):223–30.
Bertino JS Jr, Booker LA, Franck PA, Jenkins PL, Franck KR, Nafziger AN. Incidence of and significant risk factors for aminoglycoside-associated nephrotoxicity in patients dosed by using individualized pharmacokinetic monitoring. J Infect Dis. 1993;167(1):173–9.
Gonzalez LS 3rd, Spencer JP. Aminoglycosides: a practical review. Am Fam Physician. 1998;58(8):1811–20.
Wargo KA, Edwards JD. Aminoglycoside-induced nephrotoxicity. J Pharm Pract. 2014;27(6):573–7.
Rybak MJ, Albrecht LM, Boike SC, Chandrasekar PH. Nephrotoxicity of vancomycin, alone and with an aminoglycoside. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1990;25(4):679–87.
Moore RD, Smith CR, Lipsky JJ, Mellits ED, Lietman PS. Risk factors for nephrotoxicity in patients treated with aminoglycosides. Ann Intern Med. 1984;100(3):352–7.
Miron D. Once daily dosing of gentamicin in infants and children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2001;20(12):1169–73.
Contopoulos-Ioannidis DG, Giotis ND, Baliatsa DV, Ioannidis JP. Extended-interval aminoglycoside administration for children: a meta-analysis. Pediatrics. 2004;114(1):e111–8.
Cannella CA, Wilkinson ST. Acute renal failure associated with inhaled tobramycin. American journal of health-system pharmacy: AJHP: official journal of the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. 2006;63(19):1858–61.
Pai VB, Nahata MC. Efficacy and safety of aerosolized tobramycin in cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2001;32(4):314–27.
Chandiramani R, Cao D, Nicolas J, Mehran R. Contrast-induced acute kidney injury. Cardiovasc Interv Ther. 2020;35(3):209–17.
Azzalini L, Spagnoli V, Ly HQ. Contrast-induced nephropathy: from pathophysiology to preventive strategies. Can J Cardiol. 2016;32(2):247–55.
Murphy SW, Barrett BJ, Parfrey PS. Contrast nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2000;11(1):177–82.
Fang LS, Sirota RA, Ebert TH, Lichtenstein NS. Low fractional excretion of sodium with contrast media-induced acute renal failure. Arch Intern Med. 1980;140(4):531–3.
Wang Y, Liu K, Xie X, Song B. Contrast-associated acute kidney injury: an update of risk factors, risk factor scores, and preventive measures. Clin Imaging. 2020;69:354–62.
Davenport MS, Perazella MA, Yee J, Dillman JR, Fine D, McDonald RJ, et al. Use of intravenous iodinated contrast media in patients with kidney disease: consensus statements from the American College of Radiology and the National Kidney Foundation. Kidney Med. 2020;2(1):85–93.
Lautin EM, Freeman NJ, Schoenfeld AH, Bakal CW, Haramati N, Friedman AC, et al. Radiocontrast-associated renal dysfunction: a comparison of lower-osmolality and conventional high-osmolality contrast media. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1991;157(1):59–65.
Tumlin J, Stacul F, Adam A, Becker CR, Davidson C, Lameire N, et al. Pathophysiology of contrast-induced nephropathy. Am J Cardiol. 2006;98(6a):14k–20k.
Aoun J, Nicolas D, Brown JR, Jaber BL. Maximum allowable contrast dose and prevention of acute kidney injury following cardiovascular procedures. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2018;27(2):121–9.
Davenport MS, Khalatbari S, Cohan RH, Dillman JR, Myles JD, Ellis JH. Contrast material-induced nephrotoxicity and intravenous low-osmolality iodinated contrast material: risk stratification by using estimated glomerular filtration rate. Radiology. 2013;268(3):719–28.
McDonald JS, McDonald RJ, Carter RE, Katzberg RW, Kallmes DF, Williamson EE. Risk of intravenous contrast material-mediated acute kidney injury: a propensity score-matched study stratified by baseline-estimated glomerular filtration rate. Radiology. 2014;271(1):65–73.
Gilligan LA, Davenport MS, Trout AT, Su W, Zhang B, Goldstein SL, et al. Risk of acute kidney injury following contrast-enhanced CT in hospitalized pediatric patients: a propensity score analysis. Radiology. 2020;294(3):548–56.
McDonald JS, McDonald RJ, Tran CL, Kolbe AB, Williamson EE, Kallmes DF. Postcontrast acute kidney injury in pediatric patients: a cohort study. Am J Kidney Dis. 2018;72(6):811–8.
Jack DB. One hundred years of aspirin. Lancet (London, England). 1997;350(9075):437–9.
Montinari MR, Minelli S, De Caterina R. The first 3500 years of aspirin history from its roots - a concise summary. Vasc Pharmacol. 2019;113:1–8.
Paulose-Ram R, Hirsch R, Dillon C, Losonczy K, Cooper M, Ostchega Y. Prescription and non-prescription analgesic use among the US adult population: results from the third national health and nutrition examination survey (NHANES III). Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf. 2003;12(4):315–26.
Zidar N, Odar K, Glavac D, Jerse M, Zupanc T, Stajer D. Cyclooxygenase in normal human tissues – is COX-1 really a constitutive isoform, and COX-2 an inducible isoform? J Cell Mol Med. 2009;13(9b):3753–63.
Bakhriansyah M, Souverein PC, van den Hoogen MWF, de Boer A, Klungel OH. Risk of nephrotic syndrome for non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug users. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019;14(9):1355–62.
Whelton A. Nephrotoxicity of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: physiologic foundations and clinical implications. Am J Med. 1999;106(5b):13s–24s.
Turini ME, DuBois RN. Cyclooxygenase-2: a therapeutic target. Annu Rev Med. 2002;53:35–57.
Schlondorff D. Renal prostaglandin synthesis. Sites of production and specific actions of prostaglandins. Am J Med. 1986;81(2b):1–11.
Gambaro G, Perazella MA. Adverse renal effects of anti-inflammatory agents: evaluation of selective and nonselective cyclooxygenase inhibitors. J Intern Med. 2003;253(6):643–52.
Schlondorff D. Renal complications of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Kidney Int. 1993;44(3):643–53.
Wharam PC, Speedy DB, Noakes TD, Thompson JM, Reid SA, Holtzhausen LM. NSAID use increases the risk of developing hyponatremia during an ironman triathlon. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2006;38(4):618–22.
González E, Gutiérrez E, Galeano C, Chevia C, de Sequera P, Bernis C, et al. Early steroid treatment improves the recovery of renal function in patients with drug-induced acute interstitial nephritis. Kidney Int. 2008;73(8):940–6.
Jones M, Tomson C. Acute kidney injury and ‘nephrotoxins’: mind your language. Clin Med (Lond). 2018;18(5):384–6.
Perazella MA, Coca SG. Three feasible strategies to minimize kidney injury in ‘incipient AKI’. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2013;9(8):484–90.
Abuelo JG. Normotensive ischemic acute renal failure. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(8):797–805.
Yusuf S, Teo KK, Pogue J, Dyal L, Copland I, Schumacher H, et al. Telmisartan, ramipril, or both in patients at high risk for vascular events. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(15):1547–59.
Yacoub R, Patel N, Lohr JW, Rajagopalan S, Nader N, Arora P. Acute kidney injury and death associated with renin angiotensin system blockade in cardiothoracic surgery: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Am J Kidney Dis. 2013;62(6):1077–86.
Ghazi P, Moffett BS, Cabrera AG. Hypotension as the etiology for angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor-associated acute kidney injury in pediatric patients. Pediatr Cardiol. 2014;35(5):767–70.
Moffett BS, Goldstein SL, Adusei M, Kuzin J, Mohan P, Mott AR. Risk factors for postoperative acute kidney injury in pediatric cardiac surgery patients receiving angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2011;12(5):555–9.
Holtkamp FA, de Zeeuw D, Thomas MC, Cooper ME, de Graeff PA, Hillege HJ, et al. An acute fall in estimated glomerular filtration rate during treatment with losartan predicts a slower decrease in long-term renal function. Kidney Int. 2011;80(3):282–7.
Raza MN, Hadid M, Keen CE, Bingham C, Salmon AH. Acute tubulointerstitial nephritis, treatment with steroid and impact on renal outcomes. Nephrology (Carlton). 2012;17(8):748–53.
Valluri A, Hetherington L, McQuarrie E, Fleming S, Kipgen D, Geddes CC, et al. Acute tubulointerstitial nephritis in Scotland. QJM. 2015;108(7):527–32.
Moledina DG, Perazella MA. Drug-induced acute interstitial nephritis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017;12(12):2046–9.
Izzedine H, Launay-Vacher V, Deray G. Antiviral drug-induced nephrotoxicity. Am J Kidney Dis. 2005;45(5):804–17.
Howard SC, McCormick J, Pui CH, Buddington RK, Harvey RD. Preventing and managing toxicities of high-dose methotrexate. Oncologist. 2016;21(12):1471–82.
Arbel Y, Ben-Assa E, Puzhevsky D, Litmanowicz B, Galli N, Chorin E, et al. Forced diuresis with matched hydration during transcatheter aortic valve implantation for reducing acute kidney injury: a randomized, sham-controlled study (REDUCE-AKI). Eur Heart J. 2019;40(38):3169–78.
Weisbord SD, Gallagher M, Jneid H, Garcia S, Cass A, Thwin SS, et al. Outcomes after angiography with sodium bicarbonate and acetylcysteine. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(7):603–14.
McLaughlin GE, Abitbol CL. Reversal of oliguric tacrolimus nephrotoxicity in children. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2005;20(7):1471–5.
Axelrod DM, Sutherland SM, Anglemyer A, Grimm PC, Roth SJ. A double-blinded, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial of aminophylline to prevent acute kidney injury in children following congenital heart surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2016;17(2):135–43.
Bhatt GC, Gogia P, Bitzan M, Das RR. Theophylline and aminophylline for prevention of acute kidney injury in neonates and children: a systematic review. Arch Dis Child. 2019;104(7):670–9.
Sutherland SM. Big data and pediatric acute kidney injury: the promise of electronic health record systems. Front Pediatr. 2019;7:536.
Menon S, Tarrago R, Carlin K, Wu H, Yonekawa K. Impact of integrated clinical decision support systems in the management of pediatric acute kidney injury: a pilot study. Pediatr Res. 2020; https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-020-1046-8. Online ahead of print.
McCoy AB, Waitman LR, Gadd CS, Danciu I, Smith JP, Lewis JB, et al. A computerized provider order entry intervention for medication safety during acute kidney injury: a quality improvement report. Am J Kidney Dis. 2010;56(5):832–41.
Lachance P, Villeneuve PM, Rewa OG, Wilson FP, Selby NM, Featherstone RM, et al. Association between e-alert implementation for detection of acute kidney injury and outcomes: a systematic review. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2017;32(2):265–72.
Al-Jaghbeer M, Dealmeida D, Bilderback A, Ambrosino R, Kellum JA. Clinical decision support for in-hospital AKI. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018;29(2):654–60.
Park S, Baek SH, Ahn S, Lee KH, Hwang H, Ryu J, et al. Impact of electronic acute kidney injury (AKI) alerts with automated nephrologist consultation on detection and severity of AKI: a quality improvement study. Am J Kidney Dis. 2018;71(1):9–19.
Roshanov PS, Fernandes N, Wilczynski JM, Hemens BJ, You JJ, Handler SM, et al. Features of effective computerised clinical decision support systems: meta-regression of 162 randomised trials. BMJ (Clinical Research Ed). 2013;346:f657.
Allen DW, Ma B, Leung KC, Graham MM, Pannu N, Traboulsi M, et al. Risk prediction models for contrast-induced acute kidney injury accompanying cardiac catheterization: systematic review and meta-analysis. Can J Cardiol. 2017;33(6):724–36.
Hodgson LE, Sarnowski A, Roderick PJ, Dimitrov BD, Venn RM, Forni LG. Systematic review of prognostic prediction models for acute kidney injury (AKI) in general hospital populations. BMJ Open. 2017;7(9):e016591.
Park S, Cho H, Park S, Lee S, Kim K, Yoon HJ, et al. Simple postoperative AKI risk (SPARK) classification before noncardiac surgery: a prediction index development study with external validation. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019;30(1):170–81.
Moffett BS, Goldstein SL. Acute kidney injury and increasing nephrotoxic-medication exposure in noncritically-ill children. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011;6(4):856–63.
Stoops C, Stone S, Evans E, Dill L, Henderson T, Griffin R, et al. Baby NINJA (Nephrotoxic injury negated by just-in-time action): reduction of nephrotoxic medication-associated acute kidney injury in the neonatal intensive care unit. J Pediatr. 2019;215:223–8.e6.
Kane-Gill SL, Smithburger PL, Kashani K, Kellum JA, Frazee E. Clinical relevance and predictive value of damage biomarkers of drug-induced kidney injury. Drug Saf. 2017;40(11):1049–74.
Tajima S, Yamamoto N, Masuda S. Clinical prospects of biomarkers for the early detection and/or prediction of organ injury associated with pharmacotherapy. Biochem Pharmacol. 2019;170:113664.
Menon S, Goldstein SL, Mottes T, Fei L, Kaddourah A, Terrell T, et al. Urinary biomarker incorporation into the renal angina index early in intensive care unit admission optimizes acute kidney injury prediction in critically ill children: a prospective cohort study. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2016;31(4):586–94.
Barreto EF, Rule AD, Voils SA, Kane-Gill SL. Innovative use of novel biomarkers to improve the safety of renally eliminated and nephrotoxic medications. Pharmacotherapy. 2018;38(8):794–803.
Srisawat N, Kellum JA. The role of biomarkers in acute kidney injury. Crit Care Clin. 2020;36(1):125–40.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry
Yonekawa, K.E., Barreto, E.F., Sutherland, S.M. (2022). Nephrotoxins. In: Emma, F., Goldstein, S.L., Bagga, A., Bates, C.M., Shroff, R. (eds) Pediatric Nephrology. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-52719-8_126
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-52719-8_126
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-52718-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-52719-8
eBook Packages: MedicineReference Module Medicine