Abstract
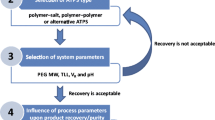
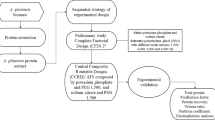
The aqueous two-phase system (ATPS), formed when two polymers or one polymer and one salt are mixed together at appropriate concentrations, is a clean technique to separate and purify biomolecules. ATPS has many advantages over traditional downstream process, especially on the integration of concentration, extraction, and partial purification if properly optimized, which reduce multiple processing steps involved hence in improving the yields and costs of the recovery process. Here, we describe an integrated purification process of glutamate decarboxylase (GAD) from E. coli cell extract using the established ATPS that consists of polyethylene glycol (PEG) and sodium sulfate.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saravanan S, Rao JR, Murugesan T et al (2007) Partition of tannery wastewater proteins in aqueous two-phase poly (ethylene glycol)-magnesium sulfate systems: effects of molecular weights and pH. Chem Eng Sci 62:969–978
Balasubramaniam D, Wilkinson C, Van Cott K et al (2003) Tobacco protein separation by aqueous two-phase extraction. J Chromatogr A 989:119–129
da Silva CAS, Coimbra JSR, Rojas EEG et al (2009) Partitioning of glycomacropeptide in aqueous two-phase systems. Process Biochem 44:1213–1216
Mahadevan H, Hall CK (1992) Theory of precipitation of protein mixtures by nonionic polymer. AIChE J 38:573–591
Naganagouda K, Mulimani VH (2008) Aqueous two-phase extraction (ATPE): an attractive and economically viable technology for downstream processing of aspergillus oryzae alpha-galactosidase. Process Biochem 43:1293–1299
Albertsson PA (1990) Separation of cell particles and molecules - a citation-classic commentary on partition of cell particles and macromolecules by Albertsson, P.A. Current Contents/Life Sciences. Wiley, New York, p 22
Carvalho CP, Coimbra JSR, Costa IAF et al (2007) Equilibrium data for Peg 4000 plus salt plus water systems from (278.15 to 318.15) K. J Chem Eng Data 52:351–356
Costa MJL, Cunha MT, Cabral JMS et al (2000) Scale-up of recombinant cutinase recovery by whole broth extraction with Peg-phosphate aqueous two-phase. Bioseparation 9:231–238
Yao W, Wu X, Zhu J et al (2011) System establishment of ATPS for one-step purification of glutamate decarboxylase from E. coli after cell disruption. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 164:1339–1349
Capezio L, Romanini D, Pico GA et al (2005) Partition of whey milk proteins in aqueous two-phase systems of polyethylene glycol-phosphate as a starting point to isolate proteins expressed in transgenic milk. J Chromatogr B 819:25–31
de Sousa Rde C, Coimbra JS, da Silva LH et al (2009) Thermodynamic studies of partitioning behavior of lysozyme and conalbumin in aqueous two-phase systems. J Chromatogr B 877:2579–2584
Romero R, Bagur MG, Sanchez-Vinas M et al (2000) Optimization of experimental variables in the dabsyl chloride derivatization of biogenic amines for their determination by RP-HPLC. Chromatographia 51:404–410
Syu KY, Lin CL, Huang HC et al (2008) Determination of theanine, GABA, and other amino acids in green, oolong, black, and Pu-Erh teas with dabsylation and high-performance liquid chromatography. J Agric Food Chem 56:7637–7643
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Yao, W., Zhu, J., Sun, B. (2014). One-Step Purification of Glutamate Decarboxylase from E. coli Using Aqueous Two-Phase System. In: Labrou, N. (eds) Protein Downstream Processing. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 1129. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-62703-977-2_38
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-62703-977-2_38
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana Press, Totowa, NJ
Print ISBN: 978-1-62703-976-5
Online ISBN: 978-1-62703-977-2
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols