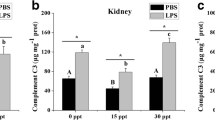
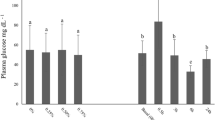
Abstract
Emerging evidence from North Sea investigations indicates that the discharge of produced water (PW) may impact biota over greater distances from operational offshore platforms than originally predicted. We have investigated the effects of PW on cod immunity, feeding and general metabolism by exposing fish to diluted PW at concentrations of 0, 100 and 200 ppm for 76 days. No significant differences were observed in weight gain or food intake. Similarly, serum metabolites, whole blood fatty acid percentages and mRNA expression of a brain appetite-regulating factor (cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript) remained unchanged between groups. Other than an irritant-induced alteration in gill cells found in treated cod, resting immunity and stress response were not affected by PW. Catalase and lactate dehydrogenase changes in activities were recorded in livers but not in gills, suggesting an effect on oxidative metabolism subsequent to hepatic detoxification processes. At the end of the exposure, fish from the three groups were challenged by injection of Aeromonas salmonicida lipopolysaccharides (LPS). LPS injection affected respiratory burst activity of head-kidney cells, and circulating white blood cells ratios, and increased serum cortisol in all groups. The most pronounced changes were seen in the group exposed to the highest PW dose (200 ppm). Our results indicate an effect of PW on cod immunity after immune challenge with LPS as well as an impact on the liver oxidative metabolism.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aas E, Klungsoyr J (1998) PAH metabolites in bile and EROD activity in North Sea fish. Mar Environ Res 46:229–232
Abrahamson A, Brandt I, Brunstorm B et al (2008) Monitoring contaminants from oil production at sea by measuring gill EROD activity in Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua). Environ Poll 153: 169–175
Alkanani T, Parrish CC, Rodnick KJ et al (2005) Lipid classes and nonesterified fatty acid profiles in plasma of North Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua). Can J Fish Aquat Sci 52:2509–2518
Banoub J, Cohen A, El Aneed A et al (2004) Structural reinvestigation of the core oligosaccharide of a mutant form of Aeromonas salmonicida lipopolysaccharide containing an O-4 phosphorylated and O-5 substituted Kdo reducing end group using electrospray QqTOF-MS/MS”. Eur J Mass Spectrom 10:541–554
Bass DA, Parce WJ, Dechatelet LR et al (1983) Flow cytometric studies of oxidative product formation by neutrophils: A graded response to membrane stimulation. J Immunol 130(4):1910–1917
Bjornsson B, Steinarsson A, Arnason T (2007) Growth model for Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua): Effects of temperature and body weight on growth rate. Aquaculture 271:216–226
Bohne-Kjersem A, Skadsheim A, Goksoyr A, Grosvik BE (2009) Candidate biomarker discovery in plasma of juvenile cod (Gadus morhua) exposed to crude North Sea oil, alkyl phenols and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Mar Envir Res 68(5):268–277
Chance B, Herbert D (1950) The enzyme-substrate compounds of bacterial catalase and peroxide. Biochem J 46:402–414
Crippen TL, Bootland LM, Leong JA et al (2001) Analysis of salmonid leucocytes by hypotonic lysis of erythrocytes. J Aquat Anim Health 13:234–245
Demers NE, Bayne CJ (1997) The immediate effects of stress on hormones and plasma lysosyme in rainbow trout. Dev Comp Immunol 21:363–373
Dunier M, Siwicki AK (1993) Effects of pesticides and other organic pollutants in the aquatic environment on immunity of fish: a review. Fish Shellfish Immunol 3:423–438
Espelid S, Rodseth OM, Jorgensen TO (1991) Vaccination experiments and studies of the humoral immune response in cod, Gadus morhua L., to four strains of monoclonal-defined Vibrio anguillarum. J Fish Dis 14:185–197
Gulland FM (1995) The impact of infectious diseases on wild animal populations- a review. In: Grenfell BT, Dobson AP (eds) Ecology of infectious diseases in natural populations. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 20–51
Hasselberg L, Meier S, Svardal A (2004) Effects of alkylphenols on redox status in first spawning Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua). Aquat Toxicol 69:95–105
Hoeger B, Van Den Heuvel MR, Hitzfeld BC et al (2004) Effects of treated sewage effluent on immune function in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquat Toxicol 70: 345–355
Hontela A, Daniel C, Ricard AC (1996) Effects of acute and subacute exposures to cadmium on the interregnal and thyroid function in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Aquat Toxicol 35:171–182
Kehoe A, Volkoff H (2007) Cloning and characterization of neuropeptide Y (NPY) and cocaine and amphetamine regulated transcript (CART) in Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua). Comp Biochem Physiol A 146(3):451–461
Khan RA, Kiceniuk J (1984) Histopathological effects of crude oil on Atlantic cod following chronic exposure. Can J Zool 62:2038–2043
Kiceniuk JW, Khan RA (1987) Effect of petroleum hydrocarbons on Atlantic cod, Gadus morhua, following chronic exposure. Can J Zool 65(3):490–494
Livingstone DR (2001) Contaminant-stimulated reactive oxygen species production and oxidative damage in aquatic organisms. Mar Poll Bull 42:656–666
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Lewis Farr A et al (1951) Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Luna LG (1968) Manual of Histological Staining Methods of the Armed Forces Institute of Pathology. McGraw-Hill, New York, NY
Lynch M, Raphael S, Mellor L et al (1969) Medical laboratory technology and clinical pathology. Saunders Company, Newberg, OR
Magnadottir B, Jonsdottir H, Helgason S et al (1999) Humoral immune parameters in Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.) II. The effects of size and gender under different environmental conditions. Comp Biochem Physiol B 122:181–188
McKeown BA (1984) Fish migration. Croom Helm, London and Sydney, 224 pp
Mitchell DB, Santone KS, Acosta D (1980) Evaluation of cytotoxicity in cultured cells by enzyme leakage. J Tissue Culture Methods 6:113–16
Murray-Smith R, Gore D, Flynn SA et al (1996) Development and appraisal of a particle tracking model for the dispersion of produced water discharged from an oil production platform in the North Sea. In: Reed M, Johnsen S (eds) Environmental science research 52: produced water2. Environmental issues and mitigation technologies. Plenum Press, New York, NY, pp 225–245
Myers MS, Fournie JW (2002) Histopathological biomarkers as integrators of anthropogenic and environmental stressors. In: Adams M (ed) Biological indicators of aquatic ecosystem stress. American Fisheries Society Publication, Bethesda, MD, pp 221–287
Pacheco M, Santos MA (2001) Biotransformation, endocrine, and genetic responses of Anguilla anguilla L. to petroleum distillate products and environmentally contaminated waters. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 49:64–75
Parrish CC (1987) Separation of aquatic lipid classes by Chromarod thin-layer chromatography with measurement by Iatroscan flame ionization detection. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 44(4):722–731
Phillips MCL, Moyes CD, Tufts BL (2000) The effects of cell ageing on metabolism in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) red blood cells. J Exp Biology 203:1039–1045
Pipe R, Coles JA, Carissan FMM et al (1999) Copper induced immunomodulation in the marine mussel M. edulis. Aquat Toxicol 46:43–54
Roe TI (1998) Produced water discharges to the North Sea: a study of bioavailability of organic produced water compounds to marine organisms. PhD thesis, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim, Norway
Schreck CB (1996) Immunomodulation: endogenous factors. In: Iwana G, Nakanishi T (eds) The fish immune system, organism, pathogen, and environment, Academic, New York, NY, pp 339–366
Seternes T, Dalmo RA, Hoffman J et al (2001) Scavenger-receptor-mediated endocytosis of lipopolysaccharide in Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.). The J Exp Biol 204:4055–4064
Somerville HJ, Bennett D, Davenport JN et al (1987) Environmental effects of produced water from North Sea oil operations. Mar Poll Bull 18:549–553
Sorensen KK, Sveinbjornsson B, Dalmo RA et al (1997) Isolation, cultivation and characterization of head kidney macrophages from Atlantic cod, Gadus morhua L. J Fish Dis 20:93–107
Stenvik J, Solstad T, Strand C et al (2004) Cloning and analyses of a BPI/LBP cDNA of the Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua L.). Dev Comp Immunol 28:307–323
Stephens SM, Frankling SC, Stagg RM et al (2000) Sub-lethal effects of exposure of juvenile turbot to oil produced water. Mar Poll Bull 40(11):928–937
Sturve J, Hasselber L, Falth H et al (2006) Effects of North Sea oil and alkylphenols on biomarker responses in juvenile Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua). Aquat Toxicol 78S:73–78
Sundt RC, Meier S, Jonsson G et al (2009) Development of a laboratory exposure system using marine fish to carry out realistic effect studies with produced water discharged from offshore oil production. Mar Poll Bull 58:1382–1388
Tintos A, Gesto M, Miguez JM et al (2008) ß-Naphthoflavone and benzo(a)pyrene treatment affect liver intermediary metabolism and plasma cortisol levels in rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 69:180–186
Turner K, Righton D, Metcalfe JD (2002) The dispersal patterns and behaviour of North Sea cod (Gadus morhua) studied using electronic data storage tags. Hydrobiol 483:201–208
Van Den Heuvel MR, O’Halloran K, Ellis RJ et al (2005) Measures of resting immune function and related physiology in juvenile rainbow trout exposed to a pulp mill effluent. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 48:520–529
Volkoff H, Peter RE (2004) Effects of lipopolysaccharide treatment on feeding of goldfish: role of appetite-regulating peptides. Brain Res 998(2):139–147
Volkoff H, Canosa LF, Unniappan S et al (2005) Neuropeptides and the control of food intake in fish. Gen Comp Endocrinol 142(1-2):3–19
Weeks BA, Warinner JE (1984) Effects of toxic chemicals on macrophage phagocytosis in two estuarine fishes. Mar Environ Res 14:327–335
Weyts FAA, Flik G, Rombout JHWM et al (1998) Cortisol induces apoptosis in activated B cells, not in other lymphoid cells of the common carp. Dev Comp Endocrinol 22:551–562
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2011 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Hamoutene, D. et al. (2011). Effect of Produced Water on Innate Immunity, Feeding and Antioxidant Metabolism in Atlantic Cod (Gadus morhua). In: Lee, K., Neff, J. (eds) Produced Water. Springer, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-0046-2_16
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-0046-2_16
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-4614-0045-5
Online ISBN: 978-1-4614-0046-2
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)