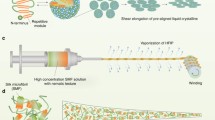
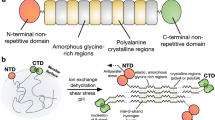
Abstract
Natural silk protein fibers have shown a great attraction to the researchers due to the extraordinary mechanical property, biocompatibility, and functional diversity. Unfortunately, the low yield and unevenness have hampered the scale use of the natural silk fibers. Herein, the appearance of the bioinspired artificial spinning strategy offers an effective way to fabricate silk fibers with controllable structures and functionality. This chapter describes an experimental method to prepare silk protein fibers on a large scale and summarizes the method to investigate the effects of the structure–property relationship of the recombinant protein fibers.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yoshioka T, Tsubota T, Tashiro K, Jouraku A, Kameda T (2019) A study of the extraordinarily strong and tough silk produced by bagworms. Nat Commun 10:1469
Porter D, Guan J, Vollrath F (2013) Spider silk: super material or thin fibre? Adv Mater 25:1275–1279
Hu F, Lin N, Liu XY (2020) Interplay between Light and Functionalized Silk Fibroin and Applications. iScience 23:101035
Wang C, Xia K, Zhang Y, Kaplan DL (2019) Silk-based advanced materials for soft electronics. Acc Chem Res 52:2916–2927
Vepari C, Kaplan DL (2007) Silk as a biomaterial. Prog Polym Sci 32:991–1007
Huang W, Ling S, Li C, Omenetto FG, Kaplan DL (2018) Silkworm silk-based materials and devices generated using bio-nanotechnology. Chem Soc Rev 47:6486–6504
Yang N, Zhang W, Ye C, Chen X, Ling S (2019) Nanobiopolymers fabrication and their life cycle assessments. Biotechnol J 14:e1700754
Zheng K, Ling S (2019) De novo Design of Recombinant Spider Silk Proteins for material applications. Biotechnol J 14:e1700753
Zhang W, Ye C, Zheng K, Zhong J, Tang Y, Fan Y, Buehler MJ, Ling S, Kaplan DL (2018) Tensan silk-inspired hierarchical fibers for smart textile applications. ACS Nano 12:6968–6977
Zhang C, Xia L, Deng B, Li C, Wang Y, Li R, Dai F, Liu X, Xu W (2020) Fabrication of a high-toughness polyurethane/fibroin composite without interfacial treatment and its toughening mechanism. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:25409–25418
Ling S, Chen W, Fan Y, Zheng K, Jin K, Yu H, Buehler MJ, Kaplan DL (2018) Biopolymer nanofibrils: structure, modeling, preparation, and applications. Prog Polym Sci 85:1–56
Andersson M, Jia Q, Abella A, Lee XY, Landreh M, Purhonen P, Hebert H, Tenje M, Robinson CV, Meng Q, Plaza GR, Johansson J, Rising A (2017) Biomimetic spinning of artificial spider silk from a chimeric minispidroin. Nat Chem Biol 13:262–264
Madurga R, Ganan-Calvo AM, Plaza GR, Guinea GV, Elices M, Perez-Rigueiro J (2017) Production of high performance bioinspired silk fibers by straining flow spinning. Biomacromolecules 18:1127–1133
Li S, Hang Y, Ding Z, Lu Q, Lu G, Chen H, Kaplan DL (2020) Microfluidic silk fibers with aligned hierarchical microstructures. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 6:2847–2854
Heim M, Keerl D, Scheibel T (2009) Spider silk: from soluble protein to extraordinary fiber. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 48:3584–3596
Zhou G, Shao Z, Knight DP, Yan J, Chen X (2009) Silk fibers extruded artificially from aqueous solutions of RegeneratedBombyx moriSilk fibroin are tougher than their natural counterparts. Adv Mater 21:366–370
Ren J, Wang Y, Yao Y, Wang Y, Fei X, Qi P, Lin S, Kaplan DL, Buehler MJ, Ling S (2019) Biological material interfaces as inspiration for mechanical and optical material designs. Chem Rev 119:12279–12336
Wei W, Zhang Y, Zhao Y, Luo J, Shao H, Hu X (2011) Bio-inspired capillary dry spinning of regenerated silk fibroin aqueous solution. Mater Sci Eng C 31:1602–1608
Peng Q, Shao H, Hu X, Zhang Y (2015) Role of humidity on the structures and properties of regenerated silk fibers. Prog Nat Sci Mater Int 25:430–436
Yue X, Zhang F, Wu H, Ming J, Fan Z, Zuo B (2014) A novel route to prepare dry-spun silk fibers from CaCl2–formic acid solution. Mater Lett 128:175–178
Luo J, Zhang L, Peng Q, Sun M, Zhang Y, Shao H, Hu X (2014) Tough silk fibers prepared in air using a biomimetic microfluidic chip. Int J Biol Macromol 66:319–324
Ling S, Qin Z, Li C, Huang W, Kaplan DL, Buehler MJ (2017) Polymorphic regenerated silk fibers assembled through bioinspired spinning. Nat Commun 8:1387
Gu L, Jiang Y, Hu J (2019) Scalable spider-silk-like Supertough fibers using a Pseudoprotein polymer. Adv Mater 31:e1904311
Wang X, Ding B, Yu J, Wang M (2011) Engineering biomimetic superhydrophobic surfaces of electrospun nanomaterials. Nano Today 6:510–530
Wang X, Ding B, Sun G, Wang M, Yu J (2013) Electro-spinning/netting: a strategy for the fabrication of three-dimensional polymer nano-fiber/nets. Prog Mater Sci 58:1173–1243
Zhang CL, Yu SH (2014) Nanoparticles meet electrospinning: recent advances and future prospects. Chem Soc Rev 43:4423–4448
Wang X-X, Yu G-F, Zhang J, Yu M, Ramakrishna S, Long Y-Z (2021) Conductive polymer ultrafine fibers via electrospinning: preparation, physical properties and applications. Prog Mater Sci 115:100704
Mishra RK, Mishra P, Verma K, Mondal A, Chaudhary RG, Abolhasani MM, Loganathan S (2018) Electrospinning production of nanofibrous membranes. Environ Chem Lett 17:767–800
Xue J, Wu T, Dai Y, Xia Y (2019) Electrospinning and electrospun nanofibers: methods, materials, and applications. Chem Rev 119:5298–5415
Jiang SH, Chen YM, Duan GG, Mei CT, Greiner A, Agarwal S (2018) Electrospun nanofiber reinforced composites: a review. Polym Chem 9:2685–2720
Qian CY, Xin TW, Xiao WS, Zhu HJ, Zhang Q, Liu LL, Cheng RY, Wang Z, Cui WG, Ge ZL (2020) Vascularized silk electrospun fiber for promoting oral mucosa regeneration. NPG Asia Mater 12:39
Chen D, Narayanan N, Federici E, Yang Z, Zuo X, Gao J, Fang F, Deng M, Campanella OH, Jones OG (2020) Electrospinning induced orientation of protein fibrils. Biomacromolecules 21:2772–2785
Zhu M, Gu J, He L, Mahar FK, Kim I, Wei K (2019) Fabrication and osteoblastic adhesion behavior of regenerated silk fibroin/PLLA Nanofibrous scaffold by double syringe electrospinning. Fibers Polym 20:1850–1856
Zhou CJ, Li Y, Yao SW, He JH (2019) Silkworm-based silk fibers by electrospinning. Results Phys 15:102646
Kong N, Wan F, Dai W, Lu Y, Cheng P, Dai J, Li Y-Y, Gong J, Ling S, Yao Y (2020) Bioinspired polypeptide as building blocks for multifunctional material design. Appl Mater Today 20:100683
Dai J, Wang YQ, Wu DH, Wan FJ, Lu Y, Kong N, Li XC, Gong JK, Ling SJ, Yao Y (2020) Biointerface mediates cytoskeletal rearrangement of pancreatic cancer cell and modulates its drug sensitivity. Colloid Interface Sci Commun 35:100250
Acknowledgments
Project funded by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2020M681344).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature
About this protocol
Cite this protocol
Cao, L. (2021). Spinning Methods Used for Construction of One- and Two-Dimensional Fibrous Protein Materials. In: Ling, S. (eds) Fibrous Proteins. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2347. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1574-4_15
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1574-4_15
Published:
Publisher Name: Humana, New York, NY
Print ISBN: 978-1-0716-1573-7
Online ISBN: 978-1-0716-1574-4
eBook Packages: Springer Protocols