Abstract
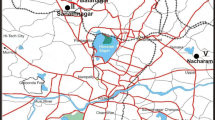
Road dust samples were collected from four different areas having different landuse patterns: industrial, heavy traffic, residential and mixed use in Delhi city of India. The samples were analyzed for Ba, Co, Cr, Cu Fe, Mn, Ni, Pb and Zn by ICP-AES. Results indicate high levels of Co, Cr, Cu, Mn and Ni in samples collected from industrial area. Ba, Pb and Zn showed higher concentration levels in heavy traffic area while Fe did not show any discernible variation between the localities. The concentrations of Fe, Mn, Ba, Zn, Cr, Cu, Pb, Ni and Co showed a decreasing trend. The content of heavy metals was comparable to those in other cities in the world. A multivariate statistical approach which includes Pearson’s correlations and principal component analysis was used to identify the possible sources of metals in the road dust. Enrichment factors were estimated for further confirming the sources of contamination. Significant positively correlations between road dust metals Cu–Mn–Co–Cr–Ni suggest that major common source of origin is industrial activities. A meaningful correlation between Ba and Zn, and a moderate positive correlation between Pb and Ba indicate the influence of traffic activities. Enrichment factors calculation indicated that Pb, Cu, Cr and Zn are moderately enriched whereas Co, Ni and Mn are less enriched while Ba exhibited very low enrichment in the dust samples. The results indicate that industrial and vehicular traffic are the two major sources. Traffic appears to be responsible for the high levels of Zn, Cu and Ba. High concentration of Co, Cr, Cu and Mn may be due to industrial sources.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adriano DC (1986) Trace element in the terrestrial environments. Springer, Heidelberg
Ahmed F, Ishiga H (2006) Trace metal concentrations in street dusts of Dhaka city, Bangladesh. Atmos Environ 40:3835–3844
Akhter MS, Madany IM (1993) Heavy metals in street and house dust in Bahrain. Water Air Soil Pollut 66:111–119
Al-Chalabi AS, Hawker D (2000) Distribution of vehicles leads in roadside soils of major roads of Brisbane, Australia. Water Air Soil Pollut 118:299–310
Al-Khashman OA (2007) Determination of metal accumulation in deposited street dusts in Amman, Jordan. Environ Geochem Health 29:1–10
Al-Khashman OA (2013) Assessment of heavy metals contamination in deposited street dusts in different urbanized areas in the city of Ma’an, Jordan. Environ Earth Sci 70:2603–2612
Alloway BJ (1990) Heavy metals in soils. Wiley, New York
Al-Momani IF (2009) Assessment of trace metal distribution and contamination in surface soils of Amman, Jordan. Jordan J Chem 4:77–87
Amato FM, Pandolfi M, Viana X, Querol A, Alastuey T, Moreno T (2009) Spatial and chemical patterns of PM 10 in road dust deposited in urban environment. Atmos Environ 43:1650–1659
Arslan H (2001) Heavy metals in street dust in Bursa, Turkey. J Trace Microprobe Tech 19:439–445
Banerjee ADK (2003) Heavy metal levels and solid phase speciation in street dusts of Delhi, India. Environ Pollut 123:95–105
Bhanarkar AD, Gajghate DG, Hassan MZ (2002) Assessment of air pollution from small scale industry. Environ Monit Asses 80:125–133
Bhanarkar AD, Gajghate DG, Rao PS, Nema P (2005) Inventory of SO2, PM and toxic metals emissions from industrial sources in greater Mumbai, India. Atmos Environ 39:3851–3864
CCME (2007) Canadian soil quality guidelines for the protection of environmental and human health. Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment, Winnipeg
Census of India (2011) Delhi population, provisional population totals
Charlesworth S, Everett M, McCarthy R, Ordonez A, De Miguel E (2003) A comparative study of heavy metal concentration and distribution in deposited street dusts in a large and a small urban area: Birmingham and Coventry, West Midlands, UK. Environ Int 29:563–573
Chatterjee A, Banerjee RN (1999) Determination of lead and other metals in a residential area of greater Calcutta. Sci Total Environ 227:175–185
Chon HT, Kim KW, Kim JY (1995) Metal contamination of soils and dusts in Seoul metropolitan city, Korea. Environ Geochem Health 17:139–146
Davydova S (2005) Heavy metals as toxicants in big cities. Microchem J 79:133–136
De Miguel E, Llamas JF, Chacón E, Berg T, Larssen S, Royset O, Vadset M (1997) Origin and patterns of distribution of trace elements in street dust: unleaded petrol and urban lead. Atmos Environ 31:2733–2740
Diana MF, Margarita DV, Maria LP (2007) Heavy metal distribution in dust from elementary schools in Hermosillo, Sonora, Mexico. Atmos Environ 41:276–288
Ferreira-Baptista L, Miguel ED (2005) Geochemistry and risk assessment of street dust in Luanda, Angola: a tropical urban environment. Atmos Environ 39:4501–4512
GOI (2002) Auto fuel policy report. Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas, New Delhi
Govt of NCT (2010) State of environment report for Delhi, 2010. Department of Environment and Forest, Government of NCT Delhi, New Delhi
Gowd S, Reddy S, Govil MRPK (2010) Assessment of heavy metal contamination in soils at Jajmau (Kanpur) and Unnao industrial areas of the Ganga Plain, Uttar Pradesh, India. J Hazard Mater 174:113–121
Gupta RK, Deepanjan Majumdar, Trivedi JV, Bhanarkar AD (2012) Particulate matter and elemental emissions from a cement kiln. Fuel Process Technol 104:343–351
Howe PD, Malcolm HM, Dobson S (2004) Manganese and its compounds: environmental aspects, Concise International Chemical Assessment Document 63, United Nations Environment Programme. World Health Organization, Geneva
Iijima A, Sato K, Yano K, Tago H, Kato M, Kimura H, Furuta N (2007) Particle size and composition distribution analysis of automotive brake abrasion dusts for the evaluation of antimony sources of airborne particulate matter. Atmos Environ 41:4908–4919
Imperato M, Adamo P, Naimo D, Arienzo M, Stanzione D, Violante P (2003) Spatial distribution of heavy metals in urban soils of Naples city (Italy). Environ Pollut 124:247–256
Jiries AG, Hussein HH, Halash Z (2001) The quality of water and sediments of street runoff in Amman, Jordan. Hydrol Process 15:815–824
Khillare PS, Hasan A, Sarkar S (2013) Accumulation and risks of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and trace metals in tropical urban soils. Environ Monit Assess. doi:10.1007/s10661-013-3589-1
Kim JH, Gibb HJ, Howe PD (2006) Cobalt and inorganic cobalt compounds, Concise International Chemical Assessment Document 69, United Nations Environment Programme. World Health Organization, Geneva
Kuhad MS, Malik RS, Singh A, Dahiya IS (1989) Background levels of heavy metals in agricultural soils of Indogangetic plains of Haryana. J Indian Soc Soil Sci 3:700–705
Lee CSL, Li XD, Zhang G, Li J, Ding AJ, Wang T (2007) Heavy metals and Pb isotopic composition of aerosols in urban and suburban areas of Hong Kong and Guangzhou, South China–evidence of the long-range transport of air contaminants. Atmos Environ 41:432–447
Lu X, Wang L, Li Y, Lei K, Huang L, Kang D (2010) Multivariate statistical analysis of heavy metal in street dust of Baoji, NW China. J Hazard Mater 173:744–749
Mason B (1952) Principles of geochemistry. Wiley, New York
NEPA (1995) Environmental quality standard for soils (GB 15618-1995). National Environmental Protection Agency of China, Beijing
Pacyna JM (1986) Atmospheric trace elements from natural and anthropogenic sources. Adv Environ Sci Technol 17:33–52
Radha R, Tripathi RM, Vinod KA, Sathe AP, Khandekar RN, Nambi KSV (1999) Assessment of Pb, Cd, Cu, and Zn exposures of 6- to 10-year-old children in Mumbai. Environ Res 80:215–221
Rawat M, Ramanathan AL, Subramanian V (2009) Quantification and distribution of heavy metals from small-scale industrial areas of Kanpur city, India. J Hazard Mater 172:1145–1149
Serife T, Senol K (2006) Multivariate analysis of the data and speciation of heavy metals in street dust samples from the organized industrial district in Kayseri (Turkey). Atmos Environ 40:2797–2805
Sezgin N, Ozcan HK, Demir G, Nemlioglu S, Bayat C (2003) Determination of heavy metal concentrations in street dusts in Istanbul E-5 highway. Environ Int 29:979–985
Shi WG (1990) Street surface sediment accumulation and pollution characteristics—For example in Chengdu. Environ Sci 3:18–23
Shi G, Chen Z, Xu S, Zhang J, Wang L, Bi C, Teng J (2008) Potentially toxic metal contamination of urban soils and roadside dust in Shanghai, China. Environ Pollut 156:251–260
Shridhar V, Khillare PS, Agarwal T, Ray S (2010) Metallic species in ambient particulate matter at rural and urban location of Delhi. J Hazard Mater 175:600–607
Swietlik R, Strzelecka M, Trojanowska M (2013) Evaluation of traffic-related heavy metals emissions using noise barrier road dust analysis. Pol J Environ Stud 22:561–567
Tanner PA, Ma HL, Yu PKN (2008) Fingerprinting metals in urban street dust of Beijing, Shanghai and Hong Kong. Environ Sci Technol 42:7111–7117
Taylor SR, McLennan SM (1995) The geochemical evolution of the continental crust. Rev Geophys 33:241–265
Tokalioglu S, Karta S (2006) Multivariate analysis of the data and speciation of heavy metals in street dust samples from the organized industrial district in Kayseri (Turkey). Atmos Environ 40:2797–2805
USEPA (1999) Compendium of methods for the determination of inorganic compounds in ambient air compendium method IO-3.1. USEPA/625/R-96/010a, June 1999
Wang CF, Chang CY, Tsai SF, Chiang HL (2005) Characteristics of road dust from different sampling sites in northen Taiwan. J Air Waste Manag Asso 55:1236–1244
Wcisło E (2012) Polish soil quality standards versus risk-based soil screening levels for metals and arsenic. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 18:569–587
Acknowledgments
The authors express their gratitude to Director, NEERI, Nagpur for encouragement and permission to publish the paper. Authors are also thankful to their colleagues who participated and provided support in the study. The authors also would like to thank all the editors and reviewers for their help in the development and improvement of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rajaram, B.S., Suryawanshi, P.V., Bhanarkar, A.D. et al. Heavy metals contamination in road dust in Delhi city, India. Environ Earth Sci 72, 3929–3938 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3281-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3281-y