Abstract
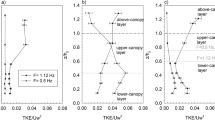
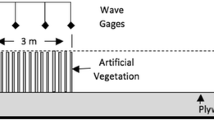
Surface wave interaction with aquatic vegetation appears to play a key role in coastal hydro-morpho-dynamics. As an example, the presence of a dense meadow at intermediate water depth is usually associated with a stable and resilient shore. Wave-meadow interactions are investigated here by means of physical modelling, with a focus on wave height distribution and hydrodynamics. The central part of a wave flume is covered by flexible artificial seagrass, composed of polyethylene leaves. This vegetation is tested in both near emergent and submerged conditions. The wave height reduction is evaluated by means of a drag coefficient defined from linear wave theory, which contains all the unknowns of the adopted methodology. The behaviour of such a coefficient is investigated as a function of a wave related Reynolds number. The influence of the flexibility of the leaves is also considered, together with a wave frequency parameter. The results show a complex behaviour with three different trends for near rigid, intermediate or highly flexible leaves. Amplitudes of the orbital velocities are investigated and show a fairly good match with the linear wave theory. On the contrary, the mean velocity along the water column appears to be modified by the seagrass for submerged leaves.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asano T, Tsutsui S, Sakai T (1988) Wave damping characteristics due to seaweed. In: Proceedings of 35th coastal engineering conference in Japan, Japan Society of Civil Engineers (JSCE), pp 138–142 (in Japanese)
Bouma TJ, De Vries MB, Low E, Peralta G, Tnczos IC, van de Koppel J, Herman PMJ (2005) Trade-offs related to ecosystem engineering: a case study on stiffness of emerging macrophytes. Ecology 86(8):2187–2199. doi:10.1890/04-1588
Bradley K, Houser C (2009) Relative velocity of seagrass blades: implications for wave attenuation in low-energy environments. J Geophys Res-Earth 114(F1). doi:10.1029/2007JF000951
Carpenter SR, Lodge DM (1986) Effects of submersed macrophytes on ecosystem processes. Aquat Bot 26:341–370. doi:10.1016/0304-3770(86)90031-8
Cavallaro L, Lo Re C, Paratore G, Viviano A, Foti E (2010) Response of Posidonia Oceanica to wave motion in shallow-waters-preliminary experimental results. In: Proceedings of 32nd Conference on Coastal Engineering (Shanghai, China), pp 49–59
Cavallaro L, Scandura P, Foti E (2011) Turbulence-induced steady streaming in an oscillating boundary layer: on the reliability of turbulence closure models. Coast Eng 58(4):290–304
Dalrymple RA, Kirby JT, Hwang PA (1984) Wave diffraction due to areas of energy dissipation. J Waterw Port Coast 110(1):67–79. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-950X(1984)110:1(67)
Dean RG, Dalrymple RA (1991) Water wave mechanics for engineers and scientists. World Scientific, Singapore, 368 p
Dingemans M (1997) Wave propagation over uneven bottoms. Advanced Series on Ocean Engineering 13, World Scientific, Singapore, 700 p
Goda Y, Suzuki T (1976) Estimation of incident and reflected waves in random wave experiments. In: Proceedings of 15th Conference on Coastal Engineering, Honolulu, Hawaii, pp 828–845
Houser C, Trimble S, Morales B (2015) Influence of blade flexibility on the drag coefficient of aquatic vegetation. Estuar Coast 38(2):569–577
John BM, Shirlal KG, Rao S, Rajasekaran C (2016) Effect of artificial seagrass on wave attenuation and wave run-up. Int J Ocean Clim Sys 7(1):14–19. doi:10.1177/1759313115623163
Kobayashi N, Raichle AW, Asano T (1993) Wave attenuation by vegetation. J Waterw Port C 119(1):30–48. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)0733-950X(1993)119:1(30)
Koch EW, Sanford LP, Chen SN, Shafer DJ, Mckee SJ (2006) Waves in seagrass systems: review and technical recommendations. US Army Corps of Engineers, ERDC TR-06-15, 92 p
Koftis T, Prinos P, Stratigaki V (2013) Wave damping over artificial posidonia oceanica meadow: a large-scale experimental study. Coast Eng 73:71–83. doi:10.1016/j.coastaleng.2012.10.007
Lakshmanan N, Kantharaj M, Sundar V (2012) The effects of flexible vegetation on forces with a keulegan-carpenter number in relation to structures due to long waves. J Mar Sci App 11(1):24–33. doi:10.1007/s11804-012-1102-9
Longuet-Higgins MS (1953) Mass transport in water waves. Philos T R Soc A 245(903):535–581. doi:10.1098/rsta.1953.0006
Lowe RJ, Koseff JR, Monismith SG (2005) Oscillatory flow through submerged canopies: 1. velocity structure. J Geophys Res-Oceans 110(10):1–17
Luhar M, Nepf H (2016) Wave-induced dynamics of flexible blades. J Fluid Struct 61:20–41. doi:10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2015.11.007
Luhar M, Nepf HM (2011) Flow-induced reconfiguration of buoyant and flexible aquatic vegetation. Limnol Oceanogr 56(6):2003–2017. doi:10.4319/lo.2011.56.6.2003
Luhar M, Coutu S, Infantes E, Fox S, Nepf H (2010) Waveinduced velocities inside a model seagrass bed. J Geophys Res-Oceans 115(C12):C12005. doi:10.1029/2010JC006345
Luhar M, Infantes E, Orfila A, Terrados J, Nepf HM (2013) Field observations of wave-induced streaming through a submerged seagrass (posidonia oceanica) meadow. J Geophys Res-Oceans 118(4):1955–1968
Mendez FJ, Losada IJ (2004) An empirical model to estimate the propagation of random breaking and nonbreaking waves over vegetation fields. Coast Eng 51(2):103–118. doi:10.1016/j.coastaleng.2003.11.003
Mendez FJ, Losada IJ, Losada MA (1999) Hydrodynamics induced by wind waves in a vegetation field. J Geophys Res-Oceans 104(C8):18383–18396. doi:10.1029/1999JC900119
Miche R (1944) Mouvements ondulatoires de la mer en profondeur constante ou decroissante. Annales des Ponts et Chaussees 114:25–78, 131–164, 270–292, 369–406 (in French)
Peralta G, Brun FG, Prez-Llorns JL, Bouma TJ (2006) Direct effects of current velocity on the growth, morphometry and architecture of seagrasses: a case study on zostera noltii. Mar Ecol-Prog Ser 327:135–142
Sanchez-Gonzalez JF, Sanchez-Rojas V, Memos CD (2011) Wave attenuation due to posidonia oceanica meadows. J Hydraul Res 49(4):503–514. doi:10.1080/00221686.2011.552464
Scandura P (2007) Steady streaming in a turbulent oscillating boundary layer. J Fluid Mech 571:265–280
Scandura P, Armenio V, Foti E (2009) Numerical investigation of the oscillatory flow around a circular cylinder close to a wall at moderate Keulegan-Carpenter and low Reynolds numbers. J Fluid Mech 627:259–290. doi:10.1017/S0022112009006016
Starr VP (1947) A momentum integral for surface waves in deep water. J Mar Res 6(2):126–135
Sumer B, Fredsoe J (1997) Hydrodynamics around cylindrical structures. World Scientific, Singapore, 530 p
Wang X, Xie W, Zhang D, He Q (2016) Wave and vegetation effects on flow and suspended sediment characteristics: a flume study. Estuar Coast Shelf S 182:1–11. doi:10.1016/j.ecss.2016.09.009
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cavallaro, L., Viviano, A., Paratore, G. et al. Experiments on Surface Waves Interacting with Flexible Aquatic Vegetation. Ocean Sci. J. 53, 461–474 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12601-018-0037-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12601-018-0037-8