Abstract
Introduction
In this study, we present the development of a chronomodulated delivery system consisting of a fast-swelling tablet core containing montelukast sodium coated with a blend of different ratios of ethyl cellulose (gastrointestinal tract (GIT)-insoluble polymer) and Eudragit L100 (enteric polymer). Montelukast sodium is a leukotriene receptor antagonist commonly prescribed for patients of asthma and allergic rhinitis. Asthma and allergic rhinitis share a common core pathophysiology and have almost similar temporal pattern in their occurrence or exacerbation of their respective symptoms, suggesting a role for chronotherapy.
Methods
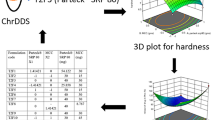
The developed formulation was optimized statistically using central composite design to achieve desired release profile. The coated tablets were studied for water uptake, bursting time, and in vitro release study.
Results
The bursting time (lag time) of coated tablet was affected by the pH of buffer, molarity of ions, and concentration of different types of surfactant in dissolution media. With increasing percentage of Eudragit L100 in coating composition, the lag time decreased and release rates significantly increased—could be attributed due to increase in water uptake and polymer leaching. As expected, with increasing coating level, lag time increased and release rate decreased due to the increased diffusion pathways. In vivo study revealed comparative pharmacokinetic profiles of core tablets and pulsatile release tablets (PRTs); however, T max of 2 h for core tablets and 6 h for PRTs were observed.
Conclusion
Thus, designed PRTs were found to be suitable in treating episodic attack of asthma in early morning and associated allergic rhinitis.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fan TY, Wei SL, Yan WW, Chen DB, Li J. An investigation of pulsatile release tablets with ethylcellulose and Eudragit L as film coating materials and cross-linked polyvinylpyrrolidone in the core tablets. J Control Release. 2001;77:245–51.
Hao J, Wang F, Wang X, Zhang D, Bi Y, Gao Y, et al. Development and optimization of baicalin-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles prepared by coacervation method using central composite design. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2012;47:497–505.
Jha N, Bapat S. Chronobiology and chronotherapeutics. Kathmandu Univ Med J. 2004;2:384–8.
Lane SJ. Leukotriene antagonism in asthma and rhinitis. Respir Med. 1998;92:795–809.
Lecomte F, Siepmann J, Walther M, MacRae RJ, Bodmeier R. Blends of enteric and GIT-insoluble polymers used for film coating: physicochemical characterization and drug release patterns. J Control Release. 2003;89:457–71.
Nayak UY, Shavi GV, Nayak Y, Averinen RK, Mutalik S, Reddy SM, et al. Chronotherapeutic drug delivery for early morning surge in blood pressure: a programmable delivery system. J Control Release. 2009;136:125–31.
Nainwal N. Chronotherapeutics—a chronopharmaceutical approach to drug delivery in the treatment of asthma. J Control Release. 2012;163(3):353–60.
Smolensky MH, Lemmer B, Reinberg AE. Chronobiology and chronotherapy of allergic rhinitis and bronchial asthma. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2007;59:852–82.
Soni ML, Namdeo KP, Jain SK, Gupta M, Dangi JS, Kumar M, et al. pH-enzyme di-dependent chronotherapeutic drug delivery system of theophylline for nocturnal asthma. Chem Pharm Bull. 2011;59:191–5.
Varshosaz J, Ghaffari S, Khoshayand MR, Atyabi F, Azarmi S, Kobarfard F. Development and optimization of solid lipid nanoparticles of amikacin by central composite design. J Liposome Res. 2010;20:97–104.
Verma S, Lan Y, Gokhale R, Burgess DJ. Quality by design approach to understand the process of nanosuspension preparation. Int J Pharm. 2009;377:185–98.
Yassin AE, Aodah AH, Al-Suwayeh S, Taha EI. Theophylline colon specific tablets for chronotherapeutic treatment of nocturnal asthma. Pharm Dev Technol. 2012;17:712–8.
Zhu Y, Zheng L. Development and mathematical simulation of theophylline pulsatile release tablets. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2005;31:1009–17.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to acknowledge Manipal College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Manipal University, Manipal for providing infrastructure facility and ICMR, New Delhi, India for financial support.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ranjan, O.P., Nayak, U.Y., Reddy, M.S. et al. Optimization of Chronomodulated Delivery System Coated with a Blend of Ethyl Cellulose and Eudragit L100 by Central Composite Design: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation. J Pharm Innov 9, 95–105 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12247-014-9176-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12247-014-9176-3